gamma-ray telescope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

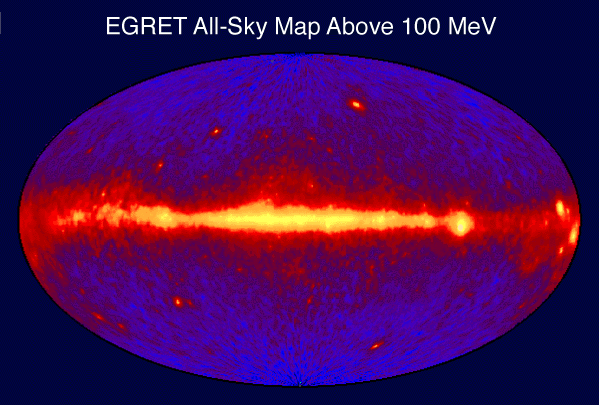
 Gamma-ray astronomy is the
Gamma-ray astronomy is the
 On June 19, 1988, from
On June 19, 1988, from
 In November 2010, using the
In November 2010, using the
/ref>
Astronomers spotted the most powerful flash of light
/ref>
A History of Gamma-Ray Astronomy Including Related DiscoveriesThe High-Altitude Water Cherenkov ObservatoryThe MAGIC Telescope ProjectThe VERITAS Ground Based Gamma-Ray ExperimentNASA's Swift gamma-ray burst missionTeVCat
a TeV gamma-ray sources catalog.
GammaLib
, a versatile toolbox for high-level analysis of astronomical gamma-ray data.
TACTIC
1-10TeV gamma-ray astronomy in India. {{DEFAULTSORT:Gamma-Ray Astronomy Astronomical sub-disciplines Gamma rays Observational astronomy


 Gamma-ray astronomy is the
Gamma-ray astronomy is the astronomical observation
Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical m ...
of gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s,Astronomical literature generally hyphenates "gamma-ray" when used as an adjective, but uses "gamma ray" without a hyphen for the noun. the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) li ...
, with photon energies above 100 keV Kev can refer to:
Given name
* Kev Adams, French comedian, actor, screenwriter and film producer born Kevin Smadja in 1991
* Kevin Kev Carmody (born 1946), Indigenous Australian singer-songwriter
* Kev Coghlan (born 1988), Scottish Grand Prix moto ...
. Radiation below 100 keV is classified as X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s and is the subject of X-ray astronomy.
In most known cases, gamma rays from solar flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other sol ...
s and Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
are generated in the MeV range, but it is now known that gamma rays in the GeV range can also be generated by solar flares. It had been believed that gamma rays in the GeV range do not originate in the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
. As GeV gamma rays are important in the study of extra-solar, and especially extra-galactic, astronomy, new observations may complicate some prior models and findings.
The mechanisms emitting gamma rays are diverse, mostly identical with those emitting X-rays but at higher energies, including electron–positron annihilation
Electron–positron annihilation occurs when an electron () and a positron (, the electron's antiparticle) collide. At low energies, the result of the collision is the annihilation of the electron and positron, and the creation of energetic photo ...
, the inverse Compton effect, and in some cases also the decay of radioactive material (gamma decay) in space reflecting extreme events such as supernovae and hypernova
A hypernova (sometimes called a collapsar) is a very energetic supernova thought to result from an extreme core-collapse scenario. In this case, a massive star (>30 solar masses) collapses to form a rotating black hole emitting twin energetic je ...
e, and the behaviour of matter under extreme conditions, as in pulsars and blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
s.
In a 18 May 2021 press release, China's Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) reported the detection of a dozen ultra-high-energy gamma rays with energies exceeding 1 peta-electron-volt (quadrillion electron-volts or PeV), including one at 1.4 PeV, the highest energy photon ever observed. The authors of the report have named the sources of these PeV gamma rays PeVatrons.
Early history
Long before experiments could detect gamma rays emitted by cosmic sources, scientists had known that the universe should be producing them. Work byEugene Feenberg
Eugene Feenberg (October 6, 1906 in Fort Smith, Arkansas – November 7, 1977) was an American physicist who made contributions to quantum mechanics and nuclear physics.
Education
In 1929, Feenberg graduated from the University of Texas at Au ...
and Henry Primakoff
Henry Primakoff (* February 12, 1914 in Odessa, Russian Empire, now Ukraine; † July 25, 1983 in Philadelphia, United States) was a theoretical physicist who is famous for his discovery of the Primakoff effect.
Primakoff contributed to the und ...
in 1948, Sachio Hayakawa and I.B. Hutchinson in 1952, and, especially, Philip Morrison
Philip Morrison (November 7, 1915 – April 22, 2005) was a professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). He is known for his work on the Manhattan Project during World War II, and for his later work in quantum physi ...
in 1958 had led scientists to believe that a number of different processes which were occurring in the universe would result in gamma-ray emission. These processes included cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
interactions with interstellar gas
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
, supernova explosions, and interactions of energetic electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s with magnetic fields.
However, it was not until the 1960s that our ability to actually detect these emissions came to pass.
Most gamma rays coming from space are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so gamma-ray astronomy could not develop until it was possible to get detectors above all or most of the atmosphere using balloon
A balloon is a flexible bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, and air. For special tasks, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), or light so ...
s and spacecraft. The first gamma-ray telescope carried into orbit, on the Explorer 11
Explorer 11 (also known as S-15) was a NASA satellite that carried the first space-borne gamma-ray telescope. This marked the beginning of space gamma-ray astronomy. Launched on 27 April 1961 by a Juno II, the satellite returned data until 17 ...
satellite in 1961, picked up fewer than 100 cosmic gamma-ray photons. They appeared to come from all directions in the Universe, implying some sort of uniform "gamma-ray background". Such a background would be expected from the interaction of cosmic rays (very energetic charged particles in space) with interstellar gas.
The first true astrophysical gamma-ray sources were solar flares, which revealed the strong 2.223 MeV line predicted by Morrison. This line results from the formation of deuterium via the union of a neutron and proton; in a solar flare the neutrons appear as secondaries from interactions of high-energy ions accelerated in the flare process. These first gamma-ray line observations were from OSO 3, OSO 7, and the Solar Maximum Mission
The Solar Maximum Mission satellite (or SolarMax) was designed to investigate Solar phenomena, particularly solar flares. It was launched on February 14, 1980. The SMM was the first satellite based on the Multimission Modular Spacecraft bus man ...
, the latter spacecraft launched in 1980. The solar observations inspired theoretical work by Reuven Ramaty and others.
Significant gamma-ray emission from our galaxy was first detected in 1967 by the detector aboard the OSO 3 satellite. It detected 621 events attributable to cosmic gamma rays. However, the field of gamma-ray astronomy took great leaps forward with the SAS-2
The Small Astronomy Satellite 2, also known also as SAS-2, SAS B or Explorer 48, was a NASA gamma ray telescope. It was launched on 15 November 1972 into the low Earth orbit with a periapsis of 443 km and an apoapsis of 632 km. It compl ...
(1972) and the Cos-B (1975–1982) satellites. These two satellites provided an exciting view into the high-energy universe (sometimes called the 'violent' universe, because the kinds of events in space that produce gamma rays tend to be high-speed collisions and similar processes). They confirmed the earlier findings of the gamma-ray background, produced the first detailed map of the sky at gamma-ray wavelengths, and detected a number of point sources. However the resolution of the instruments was insufficient to identify most of these point sources with specific visible stars or stellar systems.
A discovery in gamma-ray astronomy came in the late 1960s and early 1970s from a constellation of military defense satellites. Detectors on board the Vela satellite series, designed to detect flashes of gamma rays from nuclear bomb blasts, began to record bursts of gamma rays from deep space rather than the vicinity of the Earth. Later detectors determined that these gamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten millise ...
s are seen to last for fractions of a second to minutes, appearing suddenly from unexpected directions, flickering, and then fading after briefly dominating the gamma-ray sky. Studied since the mid-1980s with instruments on board a variety of satellites and space probes, including Soviet Venera
The Venera (, , which means "Venus" in Russian) program was the name given to a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Ten probes successfully landed on the s ...
spacecraft and the Pioneer Venus Orbiter
The Pioneer Venus Orbiter, also known as Pioneer Venus 1 or Pioneer 12, was a mission to Venus conducted by the United States as part of the Pioneer Venus project. Launched in May 1978 atop an Atlas-Centaur rocket, the spacecraft was inserted into ...
, the sources of these enigmatic high-energy flashes remain a mystery. They appear to come from far away in the Universe, and currently the most likely theory seems to be that at least some of them come from so-called ''hypernova
A hypernova (sometimes called a collapsar) is a very energetic supernova thought to result from an extreme core-collapse scenario. In this case, a massive star (>30 solar masses) collapses to form a rotating black hole emitting twin energetic je ...
'' explosions—supernovas creating black holes rather than neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
s.
Nuclear gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s were observed from the solar flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other sol ...
s of August 4 and 7, 1972, and November 22, 1977.
A solar flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other sol ...
is an explosion in a solar atmosphere and was originally detected visually in the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. Solar flares create massive amounts of radiation across the full electromagnetic spectrum from the longest wavelength, radio waves, to high energy gamma rays. The correlations of the high energy electrons energized during the flare and the gamma rays are mostly caused by nuclear combinations of high energy protons and other heavier ions. These gamma rays can be observed and allow scientists to determine the major results of the energy released, which is not provided by the emissions from other wavelengths.
See also Magnetar#1979 discovery detection of a soft gamma repeater
A soft gamma repeater (SGR) is an astronomical object which emits large bursts of gamma-rays and X-rays at irregular intervals. It is conjectured that they are a type of magnetar or, alternatively, neutron stars with fossil disks around them.
Hi ...
.
Detector technology
Observation of gamma rays first became possible in the 1960s. Their observation is much more problematic than that of X-rays or of visible light, because gamma-rays are comparatively rare, even a "bright" source needing an observation time of several minutes before it is even detected, and because gamma rays are difficult to focus, resulting in a very low resolution. The most recent generation of gamma-ray telescopes (2000s) have a resolution of the order of 6 arc minutes in the GeV range (seeing the Crab Nebula as a single "pixel"), compared to 0.5 arc seconds seen in the low energy X-ray (1 keV) range by theChandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 1 ...
(1999), and about 1.5 arc minutes in the high energy X-ray (100 keV) range seen by High-Energy Focusing Telescope (2005).
Very energetic gamma rays, with photon energies over ~30 GeV, can also be detected by ground-based experiments. The extremely low photon fluxes at such high energies require detector effective areas that are impractically large for current space-based instruments. Such high-energy photons produce extensive showers of secondary particles in the atmosphere that can be observed on the ground, both directly by radiation counters and optically via the Cherenkov light which the ultra-relativistic shower particles emit. The Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope technique currently achieves the highest sensitivity.
Gamma radiation in the TeV range emanating from the Crab Nebula was first detected in 1989 by the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory
The Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory is an American astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO); it is their largest field installation outside of their main site in Cambridge, Massachusetts ...
at Mt. Hopkins, in Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
in the USA. Modern Cherenkov telescope experiments like H.E.S.S., VERITAS
Veritas is the name given to the Roman virtue of truthfulness, which was considered one of the main virtues any good Roman should possess. The Greek goddess of truth is Aletheia (Ancient Greek: ). The German philosopher Martin Heidegger argues ...
, MAGIC
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
, and CANGAROO III can detect the Crab Nebula in a few minutes. The most energetic photons (up to 16 TeV) observed from an extragalactic object originate from the blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
, Markarian 501
Markarian 501 (or Mrk 501) is a galaxy with a spectrum extending to the highest energy gamma rays. It is a blazar or BL Lac object, which is an active galactic nucleus with a jet that is shooting towards the Earth.
In the very-high-energy gamma ...
(Mrk 501). These measurements were done by the High-Energy-Gamma-Ray Astronomy ( HEGRA) air Cherenkov telescopes.
Gamma-ray astronomy observations are still limited by non-gamma-ray backgrounds at lower energies, and, at higher energy, by the number of photons that can be detected. Larger area detectors and better background suppression are essential for progress in the field. A discovery in 2012 may allow focusing gamma-ray telescopes. At photon energies greater than 700 keV, the index of refraction starts to increase again.
1980s to 1990s
 On June 19, 1988, from
On June 19, 1988, from Birigüi
Birigui is a city in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The city is located on the northwest of the state and has 124,883 inhabitants (IBGE/2020) and 530.9 km2 of area.
The name ''Birigui'' comes from the Tupi–Guarani language and means "l ...
(50° 20' W, 21° 20' S) at 10:15 UTC a balloon launch occurred which carried two NaI(Tl) detectors ( total area) to an air pressure altitude of 5.5 mb for a total observation time of 6 hours. The supernova SN1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) was discovered on February 23, 1987, and its progenitor, Sanduleak -69 202, was a blue supergiant
A blue supergiant (BSG) is a hot, luminous star, often referred to as an OB supergiant. They have luminosity class I and spectral class B9 or earlier.
Blue supergiants are found towards the top left of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, above ...
with luminosity of 2-5 erg/s. The 847 keV and 1238 keV gamma-ray lines from 56Co decay have been detected.
During its High Energy Astronomy Observatory program in 1977, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
announced plans to build a "great observatory" for gamma-ray astronomy. The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory
The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was a space observatory detecting photons with photon energy, energies from 20 kElectronvolt#Properties, eV to 30 GeV, in Earth orbit from 1991 to 2000. The observatory featured four main tele ...
(CGRO) was designed to take advantage of the major advances in detector technology during the 1980s, and was launched in 1991. The satellite carried four major instruments which have greatly improved the spatial and temporal resolution of gamma-ray observations. The CGRO provided large amounts of data which are being used to improve our understanding of the high-energy processes in our Universe. CGRO was de-orbited in June 2000 as a result of the failure of one of its stabilizing gyroscopes.
BeppoSAX
BeppoSAX was an Italian–Dutch satellite for X-ray astronomy which played a crucial role in resolving the origin of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), the most energetic events known in the universe. It was the first X-ray mission capable of simultaneous ...
was launched in 1996 and deorbited in 2003. It predominantly studied X-rays, but also observed gamma-ray bursts. By identifying the first non-gamma ray counterparts to gamma-ray bursts, it opened the way for their precise position determination and optical observation of their fading remnants in distant galaxies.
The High Energy Transient Explorer 2 (HETE-2) was launched in October 2000 (on a nominally 2-year mission) and was still operational (but fading) in March 2007. The HETE-2 mission ended in March 2008.
2000s and 2010s
Swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT, ...
, a NASA spacecraft, was launched in 2004 and carries the BAT instrument for gamma-ray burst observations. Following BeppoSAX and HETE-2, it has observed numerous X-ray and optical counterparts to bursts, leading to distance determinations and detailed optical follow-up. These have established that most bursts originate in the explosions of massive stars ( supernovas and hypernova
A hypernova (sometimes called a collapsar) is a very energetic supernova thought to result from an extreme core-collapse scenario. In this case, a massive star (>30 solar masses) collapses to form a rotating black hole emitting twin energetic je ...
s) in distant galaxies. As of 2021, Swift remains operational.
Currently the (other) main space-based gamma-ray observatories are INTEGRAL
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along wit ...
(International Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory), Fermi, and AGILE (Astro-rivelatore Gamma a Immagini Leggero).
*INTEGRAL
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along wit ...
(launched on October 17, 2002) is an ESA mission with additional contributions from the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
, Poland, US, and Russia.
* AGILE is an all-Italian small mission by ASI, INAF
The National Institute for Astrophysics ( it, Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, or INAF) is an Italian research institute in astronomy and astrophysics, founded in 1999. INAF funds and operates twenty separate research facilities, which in turn ...
and INFN
The Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN; "National Institute for Nuclear Physics") is the coordinating institution for nuclear, particle, theoretical and astroparticle physics in Italy.
History
INFN was founded on 8 August 1951, to furt ...
collaboration. It was successfully launched by the Indian PSLV-C8 rocket from the Sriharikota ISRO base on April 23, 2007.
* Fermi was launched by NASA on June 11, 2008. It includes LAT, the Large Area Telescope, and GBM, the Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor, for studying gamma-ray bursts.
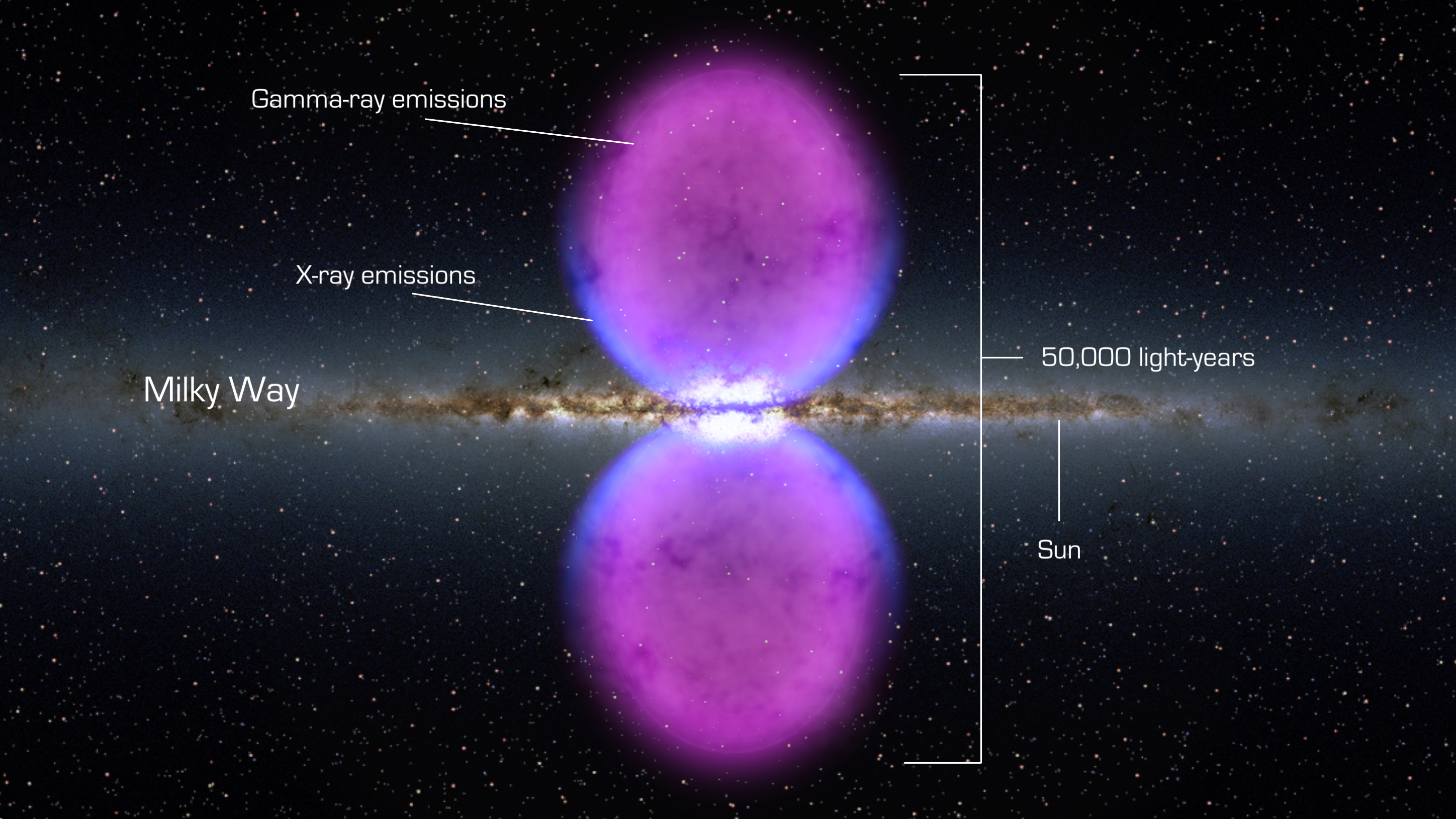
 In November 2010, using the
In November 2010, using the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope (FGST, also FGRST), formerly called the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST), is a space observatory being used to perform gamma-ray astronomy observations from low Earth orbit. Its main instrument is ...
, two gigantic gamma-ray bubbles, spanning about 25,000 light-years across, were detected at the heart of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
. These bubbles of high-energy radiation are suspected as erupting from a massive black hole or evidence of a burst of star formations from millions of years ago. They were discovered after scientists filtered out the "fog of background gamma-rays suffusing the sky". This discovery confirmed previous clues that a large unknown "structure" was in the center of the Milky Way.
In 2011 the Fermi team released its second catalog of gamma-ray sources detected by the satellite's Large Area Telescope (LAT), which produced an inventory of 1,873 objects shining with the highest-energy form of light. 57% of the sources are blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
s. Over half of the sources are active galaxies
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not pr ...
, their central black holes created gamma-ray emissions detected by the LAT. One third of the sources have not been detected in other wavelengths.
Ground-based gamma-ray observatories include HAWC, MAGIC
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
, HESS Hess or Heß may refer to:
* Hess (surname), also ''Heß'' in German, people with the surname Hess
* Hess, Oklahoma, a community in the United States
* Hess Educational Organization, the largest private provider of English instruction in the Rep ...
, and VERITAS
Veritas is the name given to the Roman virtue of truthfulness, which was considered one of the main virtues any good Roman should possess. The Greek goddess of truth is Aletheia (Ancient Greek: ). The German philosopher Martin Heidegger argues ...
. Ground-based observatories probe a higher energy range than space-based observatories, since their effective areas can be many orders of magnitude larger than a satellite.
Recent observations
In April 2018, the largest catalog yet of high-energy gamma-ray sources in space was published. In 2020 some stellar diameters were measured using gamma-rayintensity interferometry
An intensity interferometer is the name given to devices that use the Hanbury Brown and Twiss effect. In astronomy, the most common use of such an astronomical interferometer is to determine the apparent angular diameter of a radio source or star. ...
.''Gamma-ray Scientists "Dust Off" Intensity Interferometry, Upgrade Technology with Digital Electronics, Larger Telescopes, and Improved Sensitivity''/ref>
Gamma-Ray Burst GRB221009A 2022
Astronomers using the Gemini South telescope located in Chile observed flash from a Gamma-Ray Burst identified as GRB221009A, on 14 October 2022. Gamma-ray bursts are the most energetic flashes of light known to occur in the universe. Scientists of NASA estimated that the burst occurred at a point 2.4 billion light-years from earth. The Gamma-Ray Burst occurred as some giant stars exploded at the ends of their lives before collapsing into black holes, in the direction of the constellationSagitta
Sagitta is a dim but distinctive constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'arrow', not to be confused with the significantly larger constellation Sagittarius 'the archer'. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by t ...
. It has been estimated that the burst released 18 teraelectronvolts of energy. It seemed that GRB221009A was a long gamma-ray burst, possibly triggered by a supernova explosion. /ref>
See also
*Cosmic-ray observatory
A cosmic-ray observatory is a scientific installation built to detect high-energy-particles coming from space called cosmic rays. This typically includes photons (high-energy light), electrons, protons, and some heavier nuclei, as well as antimatt ...
* Galactic Center GeV excess
* Gamma-ray Burst Coordinates Network
The gamma-ray burst coordinates network (GCN) is a system that distributes information about the location of a gamma-ray burst (GRB), called ''notices'', when a burst is detected by various spacecraft. The GCN also automatically receives and dist ...
* History of gamma-ray burst research
* Steven Boggs, American astrophysicist, develops and flies gamma-ray telescopes
* Ultra-high-energy cosmic ray
In astroparticle physics, an ultra-high-energy cosmic ray (UHECR) is a cosmic ray with an energy greater than 1 EeV (1018 electronvolts, approximately 0.16 joules), far beyond both the rest mass and energies typical of other cosmic ray parti ...
References
Notes
Citations
External links
A History of Gamma-Ray Astronomy Including Related Discoveries
a TeV gamma-ray sources catalog.
GammaLib
, a versatile toolbox for high-level analysis of astronomical gamma-ray data.
TACTIC
1-10TeV gamma-ray astronomy in India. {{DEFAULTSORT:Gamma-Ray Astronomy Astronomical sub-disciplines Gamma rays Observational astronomy