G-proteins on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
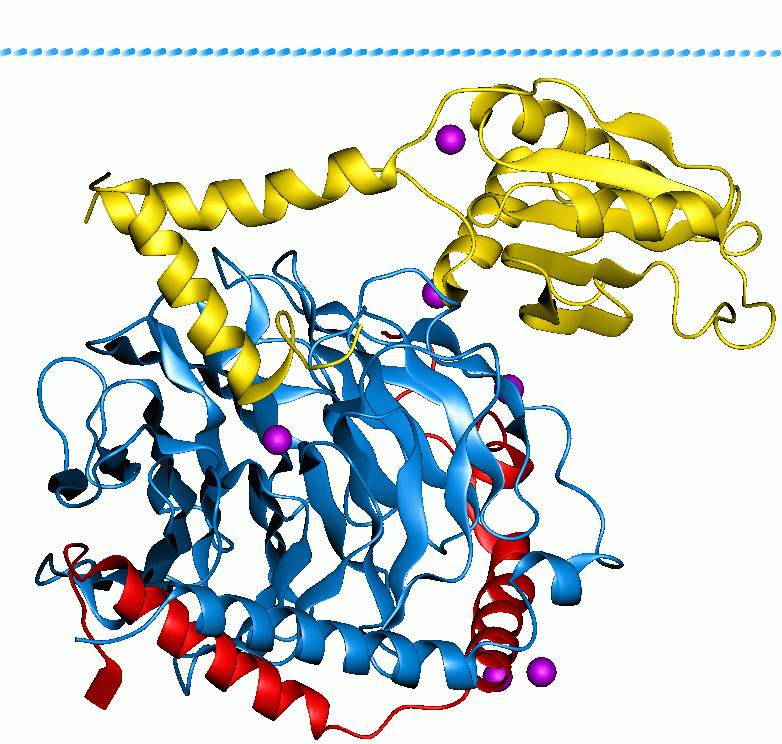

 G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a
Illustrated Lecture. For this discovery, they won the 1994
 All eukaryotes use G proteins for signaling and have evolved a large diversity of G proteins. For instance, humans encode 18 different Gα proteins, 5 Gβ proteins, and 12 Gγ proteins.
All eukaryotes use G proteins for signaling and have evolved a large diversity of G proteins. For instance, humans encode 18 different Gα proteins, 5 Gβ proteins, and 12 Gγ proteins.
 Receptor-activated G proteins are bound to the inner surface of the cell membrane. They consist of the Gα and the tightly associated Gβγ subunits. There are many classes of Gα subunits: Gsα (G stimulatory), Giα (G inhibitory), Goα (G other), Gq/11α, and G12/13α are some examples. They behave differently in the recognition of the effector molecule, but share a similar mechanism of activation.
Receptor-activated G proteins are bound to the inner surface of the cell membrane. They consist of the Gα and the tightly associated Gβγ subunits. There are many classes of Gα subunits: Gsα (G stimulatory), Giα (G inhibitory), Goα (G other), Gq/11α, and G12/13α are some examples. They behave differently in the recognition of the effector molecule, but share a similar mechanism of activation.

family of proteins
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be ...
that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only diffe ...
(GTP) to guanosine diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine.
GDP is the p ...
(GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a ...
s.
There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + ''-mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
small GTPase
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotri ...
s (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whic ...
'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex
The G beta-gamma complex (Gβγ) is a tightly bound dimeric protein complex, composed of one Gβ and one Gγ subunit, and is a component of heterotrimeric G proteins. Heterotrimeric G proteins, also called guanosine nucleotide-binding proteins, ...
.
Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell are activated by G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
s (GPCRs) that span the cell membrane. Signaling molecules bind to a domain of the GPCR located outside the cell, and an intracellular GPCR domain then in turn activates a particular G protein. Some active-state GPCRs have also been shown to be "pre-coupled" with G proteins, whereas in other cases a collision coupling mechanism is thought to occur. The G protein activates a cascade of further signaling events that finally results in a change in cell function. G protein-coupled receptor and G proteins working together transmit signals from many hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required fo ...
s, neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotr ...
s, and other signaling factors. G proteins regulate metabolic enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. ...
s, ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
s, transporter proteins, and other parts of the cell machinery, controlling transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
, motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
, contractility
Contractility refers to the ability for self- contraction, especially of the muscles or similar active biological tissue
*Contractile ring in cytokinesis
*Contractile vacuole
*Muscle contraction
** Myocardial contractility
*See contractile cell f ...
, and secretion 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical ...
, which in turn regulate diverse systemic functions such as embryonic development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm c ...
, learning and memory, and homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and i ...
.
History
G proteins were discovered in 1980 whenAlfred G. Gilman
Alfred Goodman Gilman (July 1, 1941 – December 23, 2015) was an American pharmacologist and biochemist. He and Martin Rodbell shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discovery of G-proteins and the role of these prote ...
and Martin Rodbell
Martin Rodbell (December 1, 1925 – December 7, 1998) was an American biochemist and molecular endocrinologist who is best known for his discovery of G-proteins. He shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Alfred G. Gilman for ...
investigated stimulation of cells by adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands an ...
. They found that when adrenaline binds to a receptor, the receptor does not stimulate enzymes (inside the cell) directly. Instead, the receptor stimulates a G protein, which then stimulates an enzyme. An example is adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
, which produces the second messenger cyclic AMP.The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1994Illustrated Lecture. For this discovery, they won the 1994
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
.
Nobel prizes have been awarded for many aspects of signaling by G proteins and GPCRs. These include receptor antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of rec ...
s, neurotransmitters
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotr ...
, neurotransmitter reuptake
Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal (i.e., the pre-synaptic neuron at a synapse) or glial cell after it has performed its function of transmit ...
, G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
s, G proteins, second messengers, the enzymes that trigger protein phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
in response to cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
, and consequent metabolic processes such as glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanism
The ...
.
Prominent examples include (in chronological order of awarding):
* The 1947 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to Carl Cori
Carl Ferdinand Cori, ForMemRS (December 5, 1896 – October 20, 1984) was an Austrian-American biochemist and pharmacologist born in Prague (then in Austria-Hungary, now Czech Republic) who, together with his wife Gerty Cori and Argentine phys ...
, Gerty Cori
Gerty Theresa Cori (; August 15, 1896 – October 26, 1957) was an Austro-Hungarian and American biochemist who in 1947 was the third woman to win a Nobel Prize in science, and the first woman to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Me ...
and Bernardo Houssay
Bernardo Alberto Houssay (April 10, 1887 – September 21, 1971) was an Argentine physiologist. Houssay was a co-recipient of the 1947 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for discovering the role played by pituitary hormones in regulating the ...
, for their discovery of how glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one of ...
is broken down to glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
and resynthesized in the body, for use as a store and source of energy. Glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanism
The ...
is stimulated by numerous hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required fo ...
s and neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotr ...
s including adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands an ...
.
* The 1970 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to Julius Axelrod
Julius Axelrod (May 30, 1912 – December 29, 2004) was an American biochemist. He won a share of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1970 along with Bernard Katz and Ulf von Euler. The Nobel Committee honored him for his work on the re ...
, Bernard Katz
Sir Bernard Katz, FRS (; 26 March 1911 – 20 April 2003) was a German-born British physician and biophysicist, noted for his work on nerve physiology. He shared the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine in 1970 with Julius Axelrod and Ulf von ...
and Ulf von Euler
Ulf Svante von Euler (7 February 1905 – 9 March 1983) was a Swedish physiologist and pharmacologist. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1970 for his work on neurotransmitters.
Life
Ulf Svante von Euler-Chelpin was born in S ...
for their work on the release and reuptake
Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal (i.e., the pre-synaptic neuron at a synapse) or glial cell after it has performed its function of transmit ...
of neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotr ...
s.
* The 1971 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to Earl Sutherland
Earl Wilbur Sutherland Jr. (November 19, 1915 – March 9, 1974) was an American pharmacologist and biochemist born in Burlingame, Kansas. Sutherland won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanis ...
for discovering the key role of adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
, which produces the second messenger cyclic AMP.
* The 1988 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to George H. Hitchings
George Herbert Hitchings (April 18, 1905 – February 27, 1998) was an American medical doctor who shared the 1988 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Sir James Black and Gertrude Elion "for their discoveries of important principles for dr ...
, Sir James Black and Gertrude Elion
Gertrude "Trudy" Belle Elion (January 23, 1918 – February 21, 1999) was an American biochemist and pharmacologist, who shared the 1988 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with George H. Hitchings and Sir James Black for their use of innovat ...
"for their discoveries of important principles for drug treatment" targeting GPCRs.
* The 1992 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to Edwin G. Krebs
Edwin Gerhard Krebs (June 6, 1918 – December 21, 2009) was an American biochemist. He received the Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research and the Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize of Columbia University in 1989 together with Alfred Gilman and ...
and Edmond H. Fischer
Edmond Henri Fischer (April 6, 1920 – August 27, 2021) was a Swiss-American biochemist. He and his collaborator Edwin G. Krebs were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1992 for describing how reversible phosphorylation works ...
for describing how reversible phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
works as a switch to activate proteins, and to regulate various cellular processes including glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanism
The ...
.
* The 1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to Alfred G. Gilman
Alfred Goodman Gilman (July 1, 1941 – December 23, 2015) was an American pharmacologist and biochemist. He and Martin Rodbell shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discovery of G-proteins and the role of these prote ...
and Martin Rodbell
Martin Rodbell (December 1, 1925 – December 7, 1998) was an American biochemist and molecular endocrinologist who is best known for his discovery of G-proteins. He shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Alfred G. Gilman for ...
for their discovery of "G-proteins and the role of these proteins in signal transduction in cells".
* The 2000 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to Eric Kandel
Eric Richard Kandel (; born Erich Richard Kandel, November 7, 1929) is an Austrian-born American medical doctor who specialized in psychiatry, a neuroscientist and a professor of biochemistry and biophysics at the College of Physicians and Surge ...
, Arvid Carlsson
Arvid Carlsson (25 January 1923 – 29 June 2018) was a Swedish neuropharmacologist who is best known for his work with the neurotransmitter dopamine and its effects in Parkinson's disease. For his work on dopamine, Carlsson was awarded the ...
and Paul Greengard
Paul Greengard (December 11, 1925 – April 13, 2019) was an American neuroscientist best known for his work on the molecular and cellular function of neurons. In 2000, Greengard, Arvid Carlsson and Eric Kandel were awarded the Nobel Prize for ...
, for research on neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotr ...
s such as dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% o ...
, which act via GPCRs.
* The 2004 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordin ...
to Richard Axel
Richard Axel (born July 2, 1946) is an American molecular biologist and university professor in the Department of Neuroscience at Columbia University and investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. His work on the olfactory system won him ...
and Linda B. Buck
Linda Brown Buck (born January 29, 1947) is an American biologist best known for her work on the olfactory system. She was awarded the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Richard Axel, for their work on olfactory receptors. She ...
for their work on G protein-coupled olfactory receptor
Olfactory receptors (ORs), also known as odorant receptors, are chemoreceptors expressed in the cell membranes of olfactory receptor neurons and are responsible for the detection of odorants (for example, compounds that have an odor) which give r ...
s.
* The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
to Brian Kobilka
Brian Kent Kobilka (born May 30, 1955) is an American physiologist and a recipient of the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Robert Lefkowitz for discoveries that reveal the workings of G protein-coupled receptors. He is currently a professor i ...
and Robert Lefkowitz
Robert Joseph Lefkowitz (born April 15, 1943) is an American physician (internist and cardiologist) and biochemist. He is best known for his groundbreaking discoveries that reveal the inner workings of an important family G protein-coupled recep ...
for their work on GPCR function.
Function
G proteins are important signal transducing molecules in cells. "Malfunction of GPCR Protein-Coupled Receptorsignaling pathways are involved in many diseases, such asdiabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, blindness, allergies, depression, cardiovascular defects, and certain forms of cancer. It is estimated that about 30% of the modern drugs' cellular targets are GPCRs." The human genome encodes roughly 800 G protein-coupled receptors, which detect photons of light, hormones, growth factors, drugs, and other endogenous ligands. Approximately 150 of the GPCRs found in the human genome still have unknown functions.
Whereas G proteins are activated by G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
s, they are inactivated by RGS proteins (for "Regulator of G protein signalling"). Receptors stimulate GTP binding (turning the G protein on). RGS proteins stimulate GTP hydrolysis (creating GDP, thus turning the G protein off).
Diversity
 All eukaryotes use G proteins for signaling and have evolved a large diversity of G proteins. For instance, humans encode 18 different Gα proteins, 5 Gβ proteins, and 12 Gγ proteins.
All eukaryotes use G proteins for signaling and have evolved a large diversity of G proteins. For instance, humans encode 18 different Gα proteins, 5 Gβ proteins, and 12 Gγ proteins.
Signaling
G protein can refer to two distinct families of proteins. Heterotrimeric G proteins, sometimes referred to as the "large" G proteins, are activated byG protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
s and are made up of alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) subunits. ''"Small" G proteins'' (20-25kDa) belong to the Ras
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio sta ...
superfamily of small GTPase
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotri ...
s. These proteins are homologous to the alpha (α) subunit found in heterotrimers, but are in fact monomeric, consisting of only a single unit. However, like their larger relatives, they also bind GTP and GDP and are involved in signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular ...
.
Heterotrimeric
Different types of heterotrimeric G proteins share a common mechanism. They are activated in response to aconformational change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors.
A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or othe ...
in the GPCR, exchanging GDP for GTP, and dissociating in order to activate other proteins in a particular signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular ...
pathway. The specific mechanisms, however, differ between protein types.
Mechanism
 Receptor-activated G proteins are bound to the inner surface of the cell membrane. They consist of the Gα and the tightly associated Gβγ subunits. There are many classes of Gα subunits: Gsα (G stimulatory), Giα (G inhibitory), Goα (G other), Gq/11α, and G12/13α are some examples. They behave differently in the recognition of the effector molecule, but share a similar mechanism of activation.
Receptor-activated G proteins are bound to the inner surface of the cell membrane. They consist of the Gα and the tightly associated Gβγ subunits. There are many classes of Gα subunits: Gsα (G stimulatory), Giα (G inhibitory), Goα (G other), Gq/11α, and G12/13α are some examples. They behave differently in the recognition of the effector molecule, but share a similar mechanism of activation.
Activation
When aligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electro ...
activates the G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
, it induces a conformational change in the receptor that allows the receptor to function as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated struct ...
(GEF) that exchanges GDP for GTP. The GTP (or GDP) is bound to the Gα subunit in the traditional view of heterotrimeric GPCR activation. This exchange triggers the dissociation of the Gα subunit (which is bound to GTP) from the Gβγ dimer and the receptor as a whole. However, models which suggest molecular rearrangement, reorganization, and pre-complexing of effector molecules are beginning to be accepted. Both Gα-GTP and Gβγ can then activate different ''signaling cascades'' (or '' second messenger pathways'') and effector proteins, while the receptor is able to activate the next G protein.
Termination
The Gα subunit will eventuallyhydrolyze
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
the attached GTP to GDP by its inherent enzymatic
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. ...
activity, allowing it to re-associate with Gβγ and starting a new cycle. A group of proteins called Regulator of G protein signalling
Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) are protein structural domains or the proteins that contain these domains, that function to activate the GTPase activity of heterotrimeric G-protein α-subunits.
RGS proteins are multi-functional, GTPase-a ...
(RGSs), act as GTPase-activating proteins GTPase-activating proteins or GTPase-accelerating proteins (GAPs) are a family of regulatory proteins whose members can bind to activated G proteins and stimulate their GTPase activity, with the result of terminating the signaling event. GAPs are a ...
(GAPs), are specific for Gα subunits. These proteins accelerate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP, thus terminating the transduced signal. In some cases, the effector ''itself'' may possess intrinsic GAP activity, which then can help deactivate the pathway. This is true in the case of phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role i ...
-beta, which possesses GAP activity within its C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain ( protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
region. This is an alternate form of regulation for the Gα subunit. Such Gα GAPs do not have catalytic residues (specific amino acid sequences) to activate the Gα protein. They work instead by lowering the required activation energy
In chemistry and physics, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be provided for compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules pe ...
for the reaction to take place.
Specific mechanisms
=Gαs
= Gαs activates thecAMP-dependent pathway
In the field of molecular biology, the cAMP-dependent pathway, also known as the adenylyl cyclase pathway, is a G protein-coupled receptor-triggered signaling cascade used in cell communication.
Discovery
cAMP was discovered by Earl Sutherlan ...
by stimulating the production of cyclic AMP (cAMP) from ATP. This is accomplished by direct stimulation of the membrane-associated enzyme adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
. cAMP can then act as a second messenger that goes on to interact with and activate protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
(PKA). PKA can phosphorylate a myriad downstream targets.
The cAMP-dependent pathway
In the field of molecular biology, the cAMP-dependent pathway, also known as the adenylyl cyclase pathway, is a G protein-coupled receptor-triggered signaling cascade used in cell communication.
Discovery
cAMP was discovered by Earl Sutherlan ...
is used as a signal transduction pathway for many hormones including:
* ADH – Promotes water retention by the kidneys
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
(created by the magnocellular neurosecretory cell
Magnocellular neurosecretory cells are large neuroendocrine cells within the supraoptic nucleus and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. They are also found in smaller numbers in accessory cell groups between these two nuclei, the large ...
s of the posterior pituitary
The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland which is part of the endocrine system. The posterior pituitary is not glandular as is the anterior pituitary. Instead, it is largely a collection of axonal ...
)
* GHRH – Stimulates the synthesis and release of GH (somatotropic cell
Somatotropes (from the Greek ''sōmat'' meaning "body" and ''tropikós'' meaning "of or pertaining to a turn or change") are cells in the anterior pituitary that produce growth hormone.
Structure
Somatotropic cells constitute about 30−40% of ant ...
s of the anterior pituitary
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pi ...
)
* GHIH
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-couple ...
– Inhibits the synthesis and release of GH (somatotropic cells of anterior pituitary)
* CRH CRH may refer to:
* Calibre radius head, a traditional British ordnance term for a concept in ballistic projectile design
* Celtic Resources Holdings, an Irish mining company
* China Railway High-speed, a high-speed railway service operated by China ...
– Stimulates the synthesis and release of ACTH (anterior pituitary)
* ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important co ...
– Stimulates the synthesis and release of cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland ...
(zona fasciculata
The ''zona fasciculata'' (sometimes, fascicular or fasciculate zone) constitutes the middle and also the widest zone of the adrenal cortex, sitting directly beneath the ''zona glomerulosa''. Constituent cells are organized into bundles or "fascicl ...
of the adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. It is ...
in the adrenal glands)
* TSH – Stimulates the synthesis and release of a majority of T4 (thyroid gland)
* LH – Stimulates follicular maturation and ovulation in women; or testosterone production and spermatogenesis in men
* FSH – Stimulates follicular development in women; or spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules ...
in men
* PTH – Increases blood calcium
Calcium ions (Ca2+) contribute to the physiology and biochemistry of organisms' cells. They play an important role in signal transduction pathways, where they act as a second messenger, in neurotransmitter release from neurons, in contraction of ...
levels. This is accomplished via the parathyroid hormone 1 receptor
Parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor, also known as parathyroid hormone 1 receptor (PTH1R), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PTH1R'' gene. PTH1R functions as a receptor for parathyroid hormone ( PTH) and ...
(PTH1) in the kidneys and bones, or via the parathyroid hormone 2 receptor
Parathyroid hormone 2 receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PTH2R'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family 2. This protein is a receptor for parathyroid hormone ( ...
(PTH2) in the central nervous system and brain, as well as the bones and kidneys.
* Calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing th ...
– Decreases blood calcium levels (via the calcitonin receptor
The calcitonin receptor (CT) is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds the peptide hormone calcitonin and is involved in maintenance of calcium homeostasis, particularly with respect to bone formation and metabolism.
CT works by activating the G ...
in the intestines, bones, kidneys, and brain)
* Glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to tre ...
– Stimulates glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one of ...
breakdown in the liver
* hCG – Promotes cellular differentiation, and is potentially involved in apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes includ ...
.
* Epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
– released by the ''adrenal medulla
The adrenal medulla ( la, medulla glandulae suprarenalis) is part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cel ...
'' during the fasting state, when body is under metabolic duress. It stimulates glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanism
The ...
, in addition to the actions of glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to tre ...
.
=Gαi
= Gαi inhibits the production of cAMP from ATP. e.g. somatostatin, prostaglandins=Gαq/11
= Gαq/11 stimulates the membrane-boundphospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role i ...
beta, which then cleaves PIP2 (a minor membrane phosphoinositol
Inositol phosphates are a group of mono- to hexaphosphorylated inositols. They play crucial roles in diverse cellular functions, such as cell growth, apoptosis, cell migration, endocytosis, and cell differentiation.
The group comprises:
* inositol ...
) into two second messengers, IP3 and diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as sur ...
(DAG).
The Inositol Phospholipid Dependent Pathway is used as a signal transduction pathway for many hormones including:
* ADH (Vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travel ...
/AVP) – Induces the synthesis and release of glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
s (Zona fasciculata
The ''zona fasciculata'' (sometimes, fascicular or fasciculate zone) constitutes the middle and also the widest zone of the adrenal cortex, sitting directly beneath the ''zona glomerulosa''. Constituent cells are organized into bundles or "fascicl ...
of adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. It is ...
); Induces vasoconstriction (V1 Cells of Posterior pituitary
The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland which is part of the endocrine system. The posterior pituitary is not glandular as is the anterior pituitary. Instead, it is largely a collection of axonal ...
)
* TRH – Induces the synthesis and release of TSH (Anterior pituitary gland
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pi ...
)
* TSH – Induces the synthesis and release of a small amount of T4 (Thyroid Gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyr ...
)
* Angiotensin II – Induces Aldosterone synthesis and release (zona glomerulosa
The ''zona glomerulosa'' (sometimes, glomerular zone) of the adrenal gland is the most superficial layer of the adrenal cortex, lying directly beneath the renal capsule. Its cells are ovoid and arranged in clusters or arches (''glomus'' is Latin ...
of adrenal cortex in kidney)
* GnRH – Induces the synthesis and release of FSH and LH (Anterior Pituitary)
=Gα12/13
= * Gα12/13 are involved in Rho family GTPase signaling (see Rho family of GTPases). This is through the RhoGEF superfamily involving theRhoGEF domain
RhoGEF domain describes two distinct structural domains with guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity to regulate small GTPases in the Rho family. Rho small GTPases are inactive when bound to GDP but active when bound to GTP; RhoGEF ...
of the proteins' structures). These are involved in control of cell cytoskeleton remodeling, and thus in regulating cell migration.
=Gβ
= *The Gβγ complexes sometimes also have active functions. Examples include coupling to and activatingG protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel
The G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs) are a family of lipid-gated inward-rectifier potassium ion channels which are activated (opened) by the signaling lipid PIP2 and a signal transduction cascade starting with ...
s.
Small GTPases
Small GTPases, also known as small G-proteins, bind GTP and GDP likewise, and are involved insignal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular ...
. These proteins are homologous to the alpha (α) subunit found in heterotrimers, but exist as monomers. They are small (20-kDa to 25-kDa) proteins that bind to guanosine triphosphate ( GTP). This family of proteins is homologous to the Ras GTPases and is also called the Ras superfamily GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a ...
s.
Lipidation
In order to associate with the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane, many G proteins and small GTPases are lipidated, that is, covalently modified with lipid extensions. They may be myristoylated, palmitoylated orprenylated
Prenylation (also known as isoprenylation or lipidation) is the addition of hydrophobic molecules to a protein or a biomolecule. It is usually assumed that prenyl groups (3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl) facilitate attachment to cell membranes, similar to ...
.
References
External links
* {{Subject bar, portal=Biology, auto=1 Peripheral membrane proteins Cell signaling Signal transduction EC 3.6