Fur People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Fur ( Fur: ''fòòrà'',
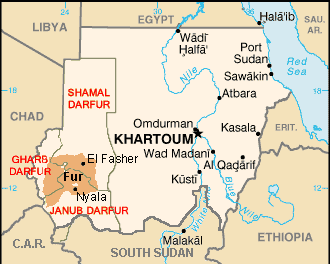
 The Fur are the largest ethnic group in the Darfur region of western
The Fur are the largest ethnic group in the Darfur region of western
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
: فور ''Fūr'') are an ethnic group predominantly inhabiting western Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
. They are concentrated in the Darfur
Darfur ( ; ar, دار فور, Dār Fūr, lit=Realm of the Fur) is a region of western Sudan. ''Dār'' is an Arabic word meaning "home f – the region was named Dardaju ( ar, دار داجو, Dār Dājū, links=no) while ruled by the Daju ...
region, where they are the largest ethnic group.Gettleman, Jeffrey, "Chaos in Darfur on rise as Arabs fight with Arabs", news article, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'', September 3, 2007, pp 1, A7 They speak the Fur language
The Fur language (or For; Fur: ''bèle fòòr'' or ''fòòraŋ bèle''; ar, فوراوي, ''Fûrâwî''; sometimes called Konjara by linguists, after a former ruling clan) is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken by the Fur of Darfur in Western Sudan. ...
, which belongs to the Nilo-Saharan family.
Overview

Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
. They are also sometimes referred to by the names Fora, Fordunga, Furawi, Konjara, or Kungara. They are an active agricultural people and may also herd cattle. Some Fur families who have accumulated a substantial cattle herd developed a more nomadic lifestyle like that of their herding neighbors, the Baqqara (Baggara) Arabs. Culturally, those cattle-herding Fur are now considered to be Baqqara. The Fur are nominally Sunni Muslims
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
following the Maliki school of Islamic law.
They are a Western Sudanese people who practice sedentary herding and agriculture, mainly the cultivation of millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets a ...
. Their society is a traditional one governed by village elders. They speak Fur, a Nilo-Saharan language, and are Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s, having adopted the religion following the region's conquest by the Kanem-Bornu Empire during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. Some of them have come to speak Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
in recent years.
The name of Darfur comes from the name of this ethnic group and means "the home of the Fur". Most of the well known governors of Darfur such as Deriage and Tegani Seisei are members of the Fur. The Fur established the historical Sultanate of Darfur which governed Darfur until 1916 (see History of Darfur).
Abdul Wahid al Nur
Abdul Wahid Mohamed al Nur (also Abdel Wahid el-Nur or Abdulwahid Mohammed Nour; ar, عبد الواحد محمد نور, ''ʿAbd al-Wāḥid Muḥammad Nūr''; born in 1968) is the leader of the rebel Sudan Liberation Movement (al Nur) faction ...
, a leader among the Fur, established the Sudan Liberation Movement and Army. Another leader of the Fur, , is Ahmed Abdelshafi (Toba).
The traditional heartland of the Fur is the mountainous region around Jebel Sî and Jebel Marra Wadi Salih and Zaligi; today, however, most of them live in the lower country west and southwest of that area, between 11–14 N and 23–26 E. Some Fur live across the border in Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
, many of them refugees
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
.
The Furs' lifestyle has led to conflict with the nomadic Baggara, cattle-herders of the region, concerning access to water and grazing land, particularly in Darfur's central Jebel Marra mountains where the best agricultural land is to be found. This has been the source of ethnic tensions for many years, culminating in the Darfur conflict which began in 2003.
Many Fur villagers were massacred in the ethnic fighting as Mahria and Terjem tribes divided up land they conquered from the Fur, according to a September 3, 2007 ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' account citing United Nations officials and Fur survivors.
Language
The Fur speak theFur language
The Fur language (or For; Fur: ''bèle fòòr'' or ''fòòraŋ bèle''; ar, فوراوي, ''Fûrâwî''; sometimes called Konjara by linguists, after a former ruling clan) is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken by the Fur of Darfur in Western Sudan. ...
, which belongs to the Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. ...
family. They also speak Arabic as a lingua franca.
There is no written or symbolic script for the Fur language. They recently have been using Arabic or Latin characters to put the language in written form. Most Fur people speak Fur fluently as their mother tongue.
Common greetings include:
*''Avilakoa'': Good Morning
*''Avilakonu'': Good Evening
Heavy drums are often used while making speeches and other public addresses.
Art
Handmade art
The Fur people make their own handmade art and utensils. These include ''talak'', which is used for cleaning pots (''talak'' looks like a sponge); ''birish'', which is a carpet for sitting; and ''gada'', which is a wood plate or bowl used for important occasions.Music, stories and entertainment
Among the Fur people, stories are told to keep children safe from the outside world. These stories are designed to keep children close to home. In some stories children are told that if they go out in the morning they will die from the heat of the sun, and in the night they are told if they go out an animal called ''nyama'' will eat them. Fur music is very popular in their culture. The main instruments are drums. The music is played with a heavy drumbeat that accompanies their celebrations. Some popular Fur musicians are; Abdalla Kioka, Marium Amo and Tour Baréé'ng Kwee.Architecture
A common type of architecture in homes and buildings is called mud architecture. They dig the clay from the ground, break it up, mix it with water, work thoroughly, and also mix other substances like straw. The clay will then pile up while still wet, pressed on to the scaffolds made out of wood , or cast in molds of various sizes into bricks. When the mud dries up in the molded shape, the process is complete. This technique is applied to most architecture in Western Sudan such as farmhouses, barns, outer walls, palaces, and even mosques. Mud is good at absorbing heat, which is advantageous for cold nights. However, because of its low resistance to wind and rain, there is a constant need to repair buildings. Therefore, the mud architecture is no longer practical because of its fragility, as well as cultural changes and foreign influences.Attire and body art
Clothes among the Fur people are similar to what is worn in Sudan. They wear casual Sudanese clothes like a jalabiya. The jalabiya is a white garment that covers the wearer from head to toe. A long time ago, when the Fur tribe was Arabised, Fur women used to poke their lower lip many times until the lip starts to swell. These dents were considered a sign of beauty.Social structure
In thesocial structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally rel ...
of the Fur people, they do not have so much regard for their wealth. A poor leader and a rich leader can become a chief. The experience of a man is based primarily on his knowledge of the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
. A man cannot even get married if he does not know a couple pages of this text.
The Quran is studied with the help of a hand-held board shaped object known as the lohh and a wooden stylus called a kalam. The Fur tribesman’s knowledge of the Quran determines their position on the tribe’s hierarchy ladder. For example, a tribesman must know almost the whole book to attain position as chieftain.
The Fur people also have their own crafts for entertainment. These include dance-games like “ALLE” (all-eh) and toys like Burajei. Burajei is a small doll-like toy made from a camel’s back. It is bound by rope and sewn by thorns.
Social behavior
When greeting each other, a woman and a man have different forms of respect. The woman must kneel down before the man and the man must slow his pace. Different sexes can also dance together but are forbidden to touch or live with each other unless they are family. Men and women usually get married in their late teens to their early twenties. The groom and wife will meet each other and get to know about them, their accomplishments and other important attributes. If everything goes well they will proceed to wed.Roles of men and women
The men bear the family name. They work to bring money to the family and are responsible for all important decisions related to the family, such as finances and marriages. The women get water, prepare the food and ensure the cleanliness of the home. Daughters normally help their mothers, milk the cows and stay at home. Sons rear and herd cattle along with the domesticated cows. If either of these two misbehave they are similarly punished by their elders. Also, it is disrespectful look an adult in the eyes.Eating
Sudan is well known for its Guhwahcoffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
served from a ''jebena'', a special Sudanese pot. The coffee beans are roasted in this pot over charcoal, then ground with cloves
Cloves are the aromatic flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae, ''Syzygium aromaticum'' (). They are native to the Maluku Islands (or Moluccas) in Indonesia, and are commonly used as a spice, flavoring or Aroma compound, fragrance in fi ...
and other spices. The grounds are steeped in hot water and the coffee is served in tiny cups after straining it through a grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns a ...
sieve
A sieve, fine mesh strainer, or sift, is a device for separating wanted elements from unwanted material or for controlling the particle size distribution of a sample, using a screen such as a woven mesh or net or perforated sheet materia ...
.
Tea or ''chai'' is also very popular and served in small glasses without milk. Some beverages enjoyed in the non-Islamic areas are Aragi, a clear strong spirit made from dates, merissa, a type of beer and tedj, or wines, made from dates or honey.
Sudanese cuisine is as varied as its cultures, especially in the south, but it has certain unique characteristics. Millet porridge and fool medamas, a savory dish of mashed fava beans, are popular breakfast foods in the north. Lamb and chicken are often eaten, but pork is prohibited to Muslims.
Wheat and dura sorghum are the staple starches. Breads include the Arabian khubz, and kisra, an omelette-like pancake which is part of the Sudanese dinner. Maschi, a beef and tomato dish, is also typical. Fruits are peeled for dessert and a favourite treat is creme caramel.
In the south, dinner is served on a low, bare table. There may be five or six dishes to dip into with large pieces of flatbread. These dishes are accompanied by a salad and shata, a red-hot spice mixture served in small dishes. After the meal, dessert is served, then tea. On special occasions incense may be lit. The ritual of hospitality is important in Sudan.
Economic base
The Fur people have many types of families. Porundia, or nuclear families, are a very common type. They normally have 2 or more children. In a typical Fur family the parents of the groom and wife will be taken care of until they die. In a Fur marriage, the groom's father goes to the bride's father and asks for his son's permission to marry. The bride's father does not give an answer immediately, but then asks the village for its opinion. If everyone approves, the bride's father accepts. The whole village gathers for the announcement of the marriage, and preparations are made. Then the marriage starts in the groom's house. Theimam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve ...
recites words from the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
. The groom and bride hold hands during this time. After the wedding, the family and guests have lunch, then they start a lively dance called firalubia. Then the bride and groom are taken to the bride's house and given food during which everyone says congratulations (''mabrouk'' in Arabic).
Institutions
Islam is the major religion among the Fur people, although some still practice their own religion. The schools called (Kalwa) in this region teach theQuran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
. Classes begin at 6–7 years and they continue learning the Quran (though not entirely in school) for the rest of their lives. Normal schooling is also practiced in these schools.
The main occupation here is farming. The Fur people are excellent farmers. They grow and harvest wheat, herbs, spices, etc. Wealth is not really important for the Fur people. Only his knowledge of the Quran determines his altitude.
History
The Fur people came from southern Africa, specifically Central African Republic to the northwest of Sudan, where they settled in Darfur. They had 36 sultanates. The Fur were also one of the first people from other ethnic groups in the country who were picked to build the wall covering and mosque surrounding theKaaba
The Kaaba (, ), also spelled Ka'bah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah ( ar, ٱلْكَعْبَة ٱلْمُشَرَّفَة, lit=Honored Ka'bah, links=no, translit=al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah), is a building at the c ...
.Moreover, they managed to send conveys informs of aid every year to Makkah.
Political situation
Until 1916, the Fur were ruled by an independent sultanate and were oriented politically to peoples in Chad. Though the ruling dynasty before that time, as well as the common people, had long been Muslims they have not beenarabized
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, تعريب, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, ...
. They are now incorporated into the Sudan political system.
The Fur had been basically independent from the 17th century. After British reconquest in 1899, the British approved the re-establishment of the Fur Sultanate, assumed by Ali Dinar when the Mahdist movement crumbled.
Mahdi
The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad w ...
st revolts continued to break out in Sudan until 1916. The fall of Darfur was decided when Ali Dinar declared loyalty to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. The British abolished the Fur Sultanate in 1916 after Dinar died in battle.
In World War I Darfur made a bid for independence by allying with Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
against the British. The British conquered Darfur in 1916, and since then it has been part of Sudan. Since the 1970s, the Darfur area has suffered some of the effects of the northern Arab war prosecuted in the south against Southern ethnic groups who wanted to secede from the Sudan.
War has been the primary factor in the last few decades of the Darfur area. A civil war lasted about 20 years until the end of the 20th Century. A new conflict arose in 2003, involving local Arab militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
called Janjaweed
The Janjaweed ( ar, جنجويد, Janjawīd, lit=mounted gunman; also transliterated ''Janjawid'') are a Sudanese Arab militia group that operate in Sudan, particularly Darfur, and eastern Chad. Using the United Nations definition, the Janjaweed ...
attacking the African peoples village by village in a campaign of terror, reportedly supported by the Sudanese military.
Genetics
Analysis of classic genetic markers and DNA polymorphisms by Tay and Saha (1988) found that the Fur are most closely related to the Hawazma of Sudan. Both populations have gene frequencies intermediate between those of theAfro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic s ...
-speaking Beja, Gaalin and Gulf Arab populations and those of the local Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. ...
-speaking Nuba and Nilotes.
According to Hassan et al. (2008), around 59.4% of Fur are carriers of the E1b1b paternal haplogroup. Of these, 68.4% bear the V32 subclade. Approximately 6.3% also belong to the haplogroup J1. This points to significant patrilineal gene flow from neighbouring Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic s ...
-speaking populations. The remaining Fur individuals are primarily carriers of the A3b2 lineage (31.3%), which is instead common among Nilotes.
Maternally, the Fur entirely belong to African-based derivatives of the macrohaplogroup L according to Hassan (2010). Of these mtDNA clades, the L0a1 (15.3%) and L1c (11.5%) lineages are most frequent. This altogether suggests that the genetic introgression into the Fur's ancestral population was asymmetrical, occurring primarily through Afro-Asiatic-speaking males rather than females.
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Fur People Ethnic groups in Chad Ethnic groups in Sudan Darfur Society of Sudan African diaspora Muslim communities in Africa