fuel cell vehicle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an
Global EV Data Explorer
tool and choose "EV Stock", "Cars" and "World" for global stock, and "Country" for the country stock.'' , there were only two models of fuel cell cars publicly available in select markets: the Toyota Mirai (2014-present) and the
 The concept of the fuel cell was first demonstrated by
The concept of the fuel cell was first demonstrated by
“Smithsonian Institution”, 2004, accessed August 2, 2011 Fuel cell development continued with the Apollo Program. The electrical power systems in the Apollo capsules and lunar modules used alkali fuel cells. In 1966, General Motors developed the first fuel cell road vehicle, the Chevrolet Electrovan. It had a
. Environmental Leader: Environmental & Energy Management News, July 20, 2011, accessed August 2, 2011
TÜV SÜD Industrie Service GmbH, accessed on August 2, 2011 including the GM HydroGen4, and Mercedes-Benz F-Cell. The
"2019 Hyundai Nexo Fuel Cell Vehicle Features 370 Miles of Range"
AutoEvolution, January 9, 2018 Sales of the Toyota Mirai to government and corporate customers began in Japan in December 2014. Pricing started at (~) before taxes and a government incentive of (~). Former European Parliament President
Sales of the Toyota Mirai to government and corporate customers began in Japan in December 2014. Pricing started at (~) before taxes and a government incentive of (~). Former European Parliament President
"Toyota To Lose $100,000 On Every Hydrogen FCV Sold?"
CleanTechnica.com, November 19, 2014; and Blanco, Sebastian
"Bibendum 2014: Former EU President says Toyota could lose 100,000 euros per hydrogen FCV sedan"
GreenAutoblog.com, November 12, 2014 , global sales totaled 5,300 Mirais. The top selling markets were the U.S. with 2,900 units, Japan with 2,100 and Europe with 200. The Honda Clarity Fuel Cell was produced from 2016 to 2021. The 2017 Clarity had the highest combined and city fuel economy ratings among all hydrogen fuel cell cars rated by the EPA that year, with a combined city/highway rating of 67 miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe), and 68 MPGe in city driving. In 2019, Katsushi Inoue, the president of Honda Europe, stated, "Our focus is on hybrid and electric vehicles now. Maybe hydrogen fuel cell cars will come, but that's a technology for the next era."Allen, James
"Honda: Now Is The Right Time to Embrace Electric Cars"
'' The Sunday Times'', November 4, 2019 By 2017, Daimler phased out its FCEV development, citing declining battery costs and increasing range of EVs, and most of the automobile companies developing hydrogen cars had switched their focus to battery electric vehicles. By 2020, only three car makers were still manufacturing, or had active manufacturing programs for hydrogen cars.Morris, Charles
"Why Are 3 Automakers Still Hyping Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles?"
CleanTechnica, October 14, 2021
. Calstart. Accessed 12 August 2011 although a Whistler, British Columbia project was discontinued in 2015. In 2022, the city of


.www.theengineer.co.uk. 20 June 2011. Accessed August 2, 2011. Fuel cells are also being used to provide auxiliary power for aircraft, replacing fossil fuel generators that were previously used to start the engines and power on board electrical needs. Fuel cells can help airplanes reduce CO2 and other pollutant emissions and noise.
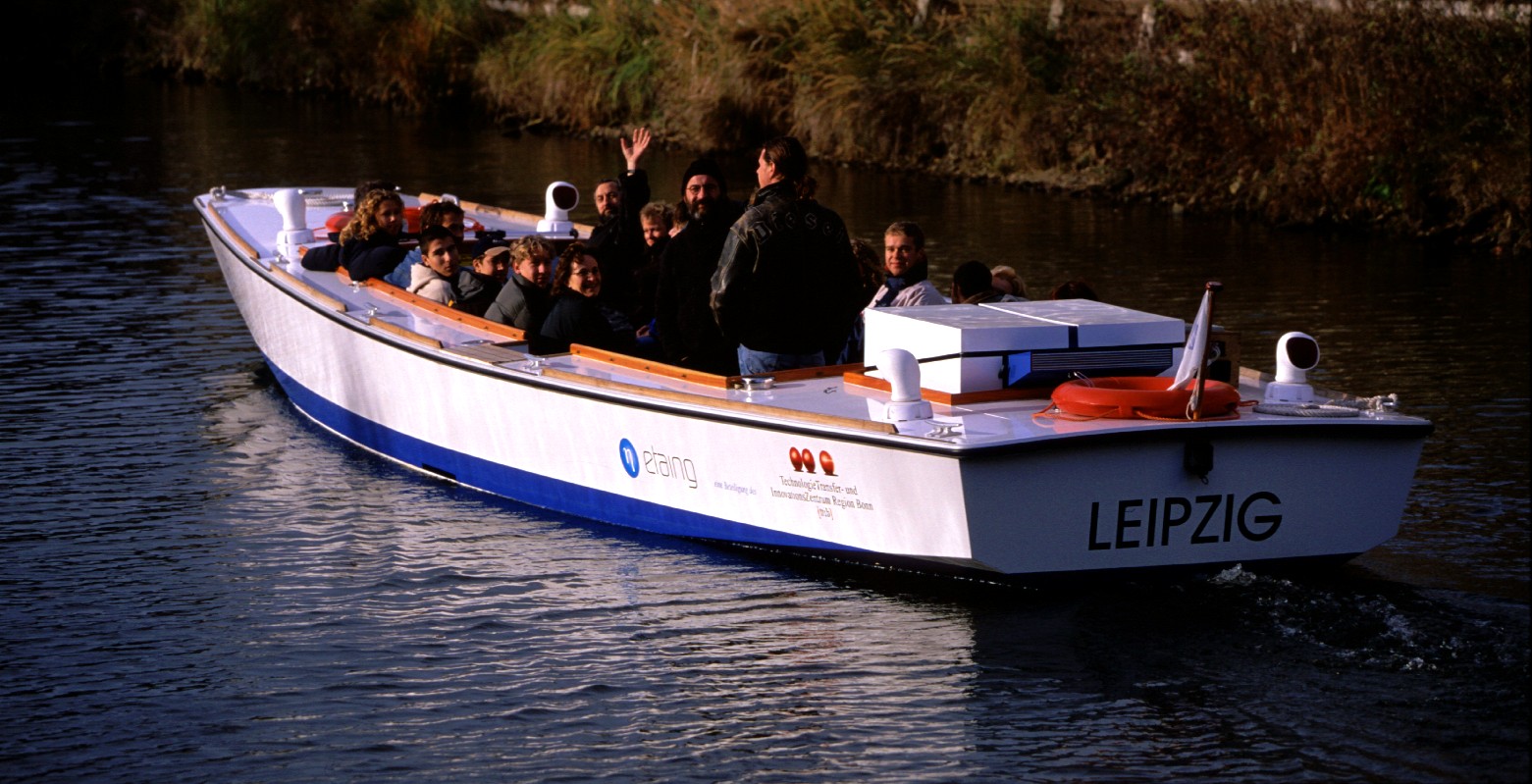 The world's first Fuel Cell Boat HYDRA used an AFC system with 6.5 kW net output. For each liter of fuel consumed, the average outboard motor produces 140 times less the hydrocarbons produced by the average modern car. Fuel cell engines have higher energy efficiencies than combustion engines, and therefore offer better range and significantly reduced emissions."Fuel Cell Basics: Applications"
The world's first Fuel Cell Boat HYDRA used an AFC system with 6.5 kW net output. For each liter of fuel consumed, the average outboard motor produces 140 times less the hydrocarbons produced by the average modern car. Fuel cell engines have higher energy efficiencies than combustion engines, and therefore offer better range and significantly reduced emissions."Fuel Cell Basics: Applications"
Amsterdam introduced its first fuel cell powered boat in 2011 that ferries people around the city's canals.
 For transport applications such as long-haul trucks, fuel cells are a potential solution for zero emission transport. A 2022 study in ''Energies'' magazine cites relatively fast refueling times compared with electric truck charging times and the current limitations of the energy density of batteries, but they note that "operating constraints" include the "high amount of CO2 emissions aused byhydrogen production", the lack of storage and refueling infrastructure, H2 leakage and safety challenges, efficiency "losses in compression, storage and dispensing", .
In 2020,
For transport applications such as long-haul trucks, fuel cells are a potential solution for zero emission transport. A 2022 study in ''Energies'' magazine cites relatively fast refueling times compared with electric truck charging times and the current limitations of the energy density of batteries, but they note that "operating constraints" include the "high amount of CO2 emissions aused byhydrogen production", the lack of storage and refueling infrastructure, H2 leakage and safety challenges, efficiency "losses in compression, storage and dispensing", .
In 2020,
"Sustainable transportation based on electric vehicle concepts: a brief overview"
Energy & Environmental Science, Royal Society of Chemistry, May 14, 2010, accessed August 2, 2011 , there were 43 publicly accessible hydrogen refueling stations in the US, 41 of which were located in California.Alternative Fueling Station Counts by State
''Alternative Fuels Data Center'', accessed July 2, 2020 In 2013, Governor
"Governor Brown Signs AB 8"
, California Fuel Cell Partnership, September 30, 2013 In 2014, the
"Energy use for hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles: higher than electrics, even hybrids (analysis)"
''Green Car Reports'', May 4, 2017 Germany had 18 public hydrogen fueling stations in July 2015. The German government hoped to increase this number to 50 by end of 2016, but only 30 were open in June 2017.
electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes ch ...
that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate electricity generally using oxygen from the air and compressed hydrogen. Most fuel cell vehicles are classified as zero-emissions vehicles that emit only water and heat. As compared with internal combustion vehicles, hydrogen vehicles centralize pollutants at the site of the hydrogen production
Hydrogen production is the family of industrial methods for generating hydrogen gas. As of 2020, the majority of hydrogen (∼95%) is produced from fossil fuels by steam reforming of natural gas and other light hydrocarbons, partial oxidation of h ...
, where hydrogen is typically derived from reformed natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon di ...
. Transporting and storing hydrogen may also create pollutants.
Fuel cells have been used in various kinds of vehicles including forklift
A forklift (also called lift truck, jitney, hi-lo, fork truck, fork hoist, and forklift truck) is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials over short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th century by various c ...
s, especially in indoor applications where their clean emissions are important to air quality, and in space applications. The first commercially produced hydrogen fuel cell automobile, the Hyundai ix35 FCEV
The Hyundai ix35 FCEV or Tucson FCEV is a hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicle developed by Hyundai. The model is a left-hand drive only conversion to the SUV platform it is based on and was the first of its type to be mass-produced and sold comm ...
, was introduced in 2013, the Toyota Mirai followed in 2015, and then Honda entered the market. Fuel cells are being developed and tested in trucks, buses, boats, ships, motorcycles and bicycles, among other kinds of vehicles.
, 31,225 passenger FCEVs powered with hydrogen had been sold worldwide. ''Go to thGlobal EV Data Explorer
tool and choose "EV Stock", "Cars" and "World" for global stock, and "Country" for the country stock.'' , there were only two models of fuel cell cars publicly available in select markets: the Toyota Mirai (2014-present) and the
Hyundai Nexo
The Hyundai Nexo ( ko, 현대 넥쏘, translit=Hyeondae Negso) is a hydrogen fuel cell powered crossover SUV that was revealed at the 2018 Consumer Electronics Show on January 8, 2018. Replacing the Hyundai Tucson FCEV, the Nexo is the flagsh ...
(2018–present). The Honda Clarity was produced from 2016 to 2021, when it was discontinued. As of 2020, there was limited hydrogen infrastructure, with fewer than fifty hydrogen fueling stations for automobiles publicly available in the U.S. Critics doubt whether hydrogen will be efficient or cost-effective for automobiles, as compared with other zero emission technologies, and in 2019, '' The Motley Fool'' opined: "What's tough to dispute is that the hydrogen fuel cell dream is all but dead for the passenger vehicle market."
Description and purpose of fuel cells in vehicles
All fuel cells are made up of three parts: an electrolyte, an anode and a cathode. In principle, a hydrogen fuel cell functions like a battery, producing electricity, which can run an electric motor. Instead of requiring recharging, however, the fuel cell can be refilled with hydrogen. Different types of fuel cells include polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells, direct methanol fuel cells, phosphoric acid fuel cells,molten carbonate fuel cell
Molten-carbonate fuel cells (MCFCs) are high-temperature fuel cells that operate at temperatures of 600 °C and above.
Molten carbonate fuel cells (MCFCs) were developed for natural gas, biogas (produced as a result of anaerobic digestion or ...
s, solid oxide fuel cells, reformed methanol fuel cell and Regenerative Fuel Cells.
History
 The concept of the fuel cell was first demonstrated by
The concept of the fuel cell was first demonstrated by Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for the ...
in 1801, but the invention of the first working fuel cell is credited to William Grove, a chemist, lawyer, and physicist. Grove's experiments with what he called a "gas voltaic battery" proved in 1842 that an electric current could be produced by an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen over a platinum catalyst. English engineer Francis Thomas Bacon expanded on Grove's work, creating and demonstrating various alkaline fuel cells from 1939 to 1959.
The first modern fuel cell vehicle was a modified Allis-Chalmers
Allis-Chalmers was a U.S. manufacturer of machinery for various industries. Its business lines included agricultural equipment, construction equipment, power generation and power transmission equipment, and machinery for use in industrial sett ...
farm tractor, fitted with a 15 kilowatt fuel cell, around 1959. The Cold War Space Race drove further development of fuel cell technology. Project Gemini tested fuel cells to provide electrical power during crewed space missions.“PEM Fuel Cells”“Smithsonian Institution”, 2004, accessed August 2, 2011 Fuel cell development continued with the Apollo Program. The electrical power systems in the Apollo capsules and lunar modules used alkali fuel cells. In 1966, General Motors developed the first fuel cell road vehicle, the Chevrolet Electrovan. It had a
PEM fuel cell
Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC), also known as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells, are a type of fuel cell being developed mainly for transport applications, as well as for stationary fuel-cell applications and portable ...
, a range of 120 miles and a top speed of 70 mph. There were only two seats, as the fuel cell stack and large tanks of hydrogen and oxygen took up the rear portion of the van. Only one was built, as the project was deemed cost-prohibitive.
General Electric and others continued working on PEM fuel cells in the 1970s. Fuel cell stacks were still limited principally to space applications in the 1980s, including the Space Shuttle. However, the closure of the Apollo Program sent many industry experts to private companies. By the 1990s, automobile manufacturers were interested in fuel cell applications, and demonstration vehicles were readied. In 2001, the first 700 Bar (10000 PSI) hydrogen tanks were demonstrated, reducing the size of the fuel tanks that could be used in vehicles and extending the range.
Applications
There are fuel cell vehicles for all modes of transport. The most prevalent fuel cell vehicles are cars, buses, forklifts and material handling vehicles."Hydrogen Fueling Stations Could Reach 5,200 by 2020". Environmental Leader: Environmental & Energy Management News, July 20, 2011, accessed August 2, 2011
Automobiles
TheHonda FCX Clarity
The Honda Clarity is a nameplate used by Honda on alternative fuel vehicles. It was initially used only on hydrogen fuel-cell electric vehicles such as the 2008 Honda FCX Clarity, but in 2017 the nameplate was expanded to include the battery-elec ...
concept car was introduced in 2008 for leasing by customers in Japan and Southern California and discontinued by 2015. From 2008 to 2014, Honda leased a total of 45 FCX units in the US. Over 20 other FCEV prototypes and demonstration cars were released in that time period,"Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Vehicles Worldwide"TÜV SÜD Industrie Service GmbH, accessed on August 2, 2011 including the GM HydroGen4, and Mercedes-Benz F-Cell. The
Hyundai ix35 FCEV
The Hyundai ix35 FCEV or Tucson FCEV is a hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicle developed by Hyundai. The model is a left-hand drive only conversion to the SUV platform it is based on and was the first of its type to be mass-produced and sold comm ...
Fuel Cell vehicle was available for lease from 2014 to 2018, when 54 units were leased. In 2018, Hyundai introduced the Nexo.Panait, Mircea"2019 Hyundai Nexo Fuel Cell Vehicle Features 370 Miles of Range"
AutoEvolution, January 9, 2018
 Sales of the Toyota Mirai to government and corporate customers began in Japan in December 2014. Pricing started at (~) before taxes and a government incentive of (~). Former European Parliament President
Sales of the Toyota Mirai to government and corporate customers began in Japan in December 2014. Pricing started at (~) before taxes and a government incentive of (~). Former European Parliament President Pat Cox
Patrick Cox (born 28 November 1952) is a former Irish Fine Gael politician, journalist and television current affairs presenter who served as President of the European Parliament from 2002 to 2004 and Leader of the European Liberal Democrat a ...
estimated that Toyota initially would lose about $100,000 on each Mirai sold.Ayre, James"Toyota To Lose $100,000 On Every Hydrogen FCV Sold?"
CleanTechnica.com, November 19, 2014; and Blanco, Sebastian
"Bibendum 2014: Former EU President says Toyota could lose 100,000 euros per hydrogen FCV sedan"
GreenAutoblog.com, November 12, 2014 , global sales totaled 5,300 Mirais. The top selling markets were the U.S. with 2,900 units, Japan with 2,100 and Europe with 200. The Honda Clarity Fuel Cell was produced from 2016 to 2021. The 2017 Clarity had the highest combined and city fuel economy ratings among all hydrogen fuel cell cars rated by the EPA that year, with a combined city/highway rating of 67 miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe), and 68 MPGe in city driving. In 2019, Katsushi Inoue, the president of Honda Europe, stated, "Our focus is on hybrid and electric vehicles now. Maybe hydrogen fuel cell cars will come, but that's a technology for the next era."Allen, James
"Honda: Now Is The Right Time to Embrace Electric Cars"
'' The Sunday Times'', November 4, 2019 By 2017, Daimler phased out its FCEV development, citing declining battery costs and increasing range of EVs, and most of the automobile companies developing hydrogen cars had switched their focus to battery electric vehicles. By 2020, only three car makers were still manufacturing, or had active manufacturing programs for hydrogen cars.Morris, Charles
"Why Are 3 Automakers Still Hyping Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles?"
CleanTechnica, October 14, 2021
Fuel economy
The following table compares EPA's fuel economy expressed in miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe) for the two models of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles rated by the EPA , and available in California. ''One kg of hydrogen is roughly equivalent to one U.S. gallon of gasoline.''Fuel cells powered by an ethanol reformer
In June 2016, Nissan announced plans to develop fuel cell vehicles powered by ethanol rather than hydrogen. Nissan claims this technical approach would be cheaper, and that it would be easier to deploy the fueling infrastructure than a hydrogen infrastructure. The vehicle would include a tank holding a blend of water and ethanol, which is fed into an onboard reformer that splits it into hydrogen and carbon dioxide. The hydrogen is then fed into a solid oxide fuel cell. According to Nissan, the liquid fuel could be an ethanol-water blend at a 55:45 ratio.Buses
In 2011 there were over 100fuel cell bus
A fuel cell bus is a bus that uses a hydrogen fuel cell as its power source for electrically driven wheels, sometimes augmented in a hybrid fashion with batteries or a supercapacitor. The only emission from the bus is water. Several cities aroun ...
es deployed around the world. Most of these buses were produced by UTC Power, Toyota, Ballard, Hydrogenics
Hydrogenics is a developer and manufacturer of hydrogen generation and fuel cell products based on water electrolysis and proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology. Hydrogenics is divided into two business units: OnSite Generation and Power Syst ...
, and Proton Motor. UTC buses had accumulated over of driving. Fuel cell buses have a 30–141% higher fuel economy than diesel buses and natural gas buses. Fuel cell buses have been deployed in cities around the world,"National Fuel Cell Bus Program Awards". Calstart. Accessed 12 August 2011 although a Whistler, British Columbia project was discontinued in 2015. In 2022, the city of
Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people l ...
, France, cancelled a contract to procure 51 buses powered by hydrogen fuel cells, when it found that "the cost of operation for hydrogen uses
Use may refer to:
* Use (law), an obligation on a person to whom property has been conveyed
* Use (liturgy), a special form of Roman Catholic ritual adopted for use in a particular diocese
* Use–mention distinction, the distinction between usin ...
is 6 times the cost of electricity".
Fuel cell bus projects have included:
*12 Fuel cell buses were deployed in the Oakland and San Francisco Bay area of California in 2007.
* Daimler AG, with thirty-six experimental buses powered by Ballard Power Systems fuel cells, completed a successful three-year trial, in eleven cities, in 2007.
*A fleet of Thor buses with UTC Power fuel cells was deployed in California, operated by SunLine Transit Agency, in 2011.
*The first hydrogen fuel cell bus prototype in Brazil was deployed in São Paulo in 2009. The bus was manufactured in Caxias do Sul
Caxias do Sul (), is a city in Rio Grande do Sul, Southern Brazil, situated in the state's mountainous Serra Gaúcha region. It was established by Italian immigrants on June 20, 1890. Today it is the second largest city in the state of Rio Gra ...
, and the hydrogen fuel was to be produced in São Bernardo do Campo from water through electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from na ...
. The program, called (Brazilian Hydrogen Autobus), included three buses.
*Three hydrogen fuel cell buses were introduced in Vienna, Austria, in 2022. Manufactured by Hyundai Motor Company
Hyundai Motor Company, often abbreviated to Hyundai Motors ( )
and commonly known as Hyundai (, ; ), is a South Korean multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, and founded in 1967. Currently, the company o ...
and called Elec-city FCEV, the units were supplied as part of the Austrian government's HyBus Project. Further units are planned to be sent to Graz and Salzburg.
Forklifts
A fuel cell forklift (also called a fuel cell lift truck or a fuel cell forklift) is a fuel cell-powered industrial forklift truck used to lift and transport materials. Most fuel cells used in forklifts are powered by PEM fuel cells. In 2013, there were over 4,000 fuel cell forklifts used in material handling in the US from which only 500 received funding from DOE (2012). Fuel cell fleets are operated by a large number of companies, including Sysco Foods, FedEx Freight, GENCO (at Wegmans, Coca-Cola, Kimberly Clark, and Whole Foods), and H-E-B Grocers. Europe demonstrated 30 fuel cell forklifts with Hylift and extended it with HyLIFT-EUROPE to 200 units, with other projects in France and Austria. Pike Research stated in 2011 that fuel-cell-powered forklifts will be the largest driver of hydrogen fuel demand by 2020. PEM fuel-cell-powered forklifts provide significant benefits over petroleum powered forklifts as they produce no local emissions. Fuel-cell forklifts can work for a full 8-hour shift on a single tank of hydrogen, can be refueled in 3 minutes and have a lifetime of 8–10 years. Fuel cell-powered forklifts are often used in refrigerated warehouses as their performance is not degraded by lower temperatures. In design the FC units are often made as drop-in replacements.
Motorcycles and bicycles
In 2005, the British firm Intelligent Energy produced the first working hydrogen run motorcycle called the ENV (Emission Neutral Vehicle). It holds enough fuel to run for four hours, and to travel in an urban area, at a top speed of . There are other examples of bikes and bicycles with a hydrogen fuel cell engine. The Suzuki Burgman received "whole vehicle type" approval in the EU. The PHB was a hydrogen bicycle with an electric motor. It debuted in Shanghai in 2008, but it was discontinued due to lack of hydrogen fuel services. Its predecessor was a hydrogen bicycle called Palcan, based in Vancouver, Canada.Airplanes
Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and produc ...
researchers and industry partners throughout Europe conducted experimental flight tests in February 2008 of a crewed airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectr ...
powered only by a fuel cell and lightweight batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
. The Fuel Cell Demonstrator Airplane, as it was called, used a Proton-Exchange Membrane (PEM) fuel cell/lithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also see ...
hybrid system to power an electric motor, which was coupled to a conventional propeller.
In 2003, the world's first propeller driven airplane to be powered entirely by a fuel cell was flown. The fuel cell was a unique FlatStack stack design which allowed the fuel cell to be integrated with the aerodynamic surfaces of the plane.
There have been several fuel cell powered unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV). A Horizon fuel cell UAV set the record distance flown by a small UAV in 2007. The military is especially interested in this application because of the low noise, low thermal signature and ability to attain high altitude. In 2009, the Naval Research Laboratory's (NRL's) Ion Tiger utilized a hydrogen-powered fuel cell and flew for 23 hours and 17 minutes. Boeing is completing tests on the Phantom Eye, a high-altitude, long endurance (HALE) to be used to conduct research and surveillance flying at for up to four days at a time."Hydrogen-powered unmanned aircraft completes set of tests".www.theengineer.co.uk. 20 June 2011. Accessed August 2, 2011. Fuel cells are also being used to provide auxiliary power for aircraft, replacing fossil fuel generators that were previously used to start the engines and power on board electrical needs. Fuel cells can help airplanes reduce CO2 and other pollutant emissions and noise.
Boats
 The world's first Fuel Cell Boat HYDRA used an AFC system with 6.5 kW net output. For each liter of fuel consumed, the average outboard motor produces 140 times less the hydrocarbons produced by the average modern car. Fuel cell engines have higher energy efficiencies than combustion engines, and therefore offer better range and significantly reduced emissions."Fuel Cell Basics: Applications"
The world's first Fuel Cell Boat HYDRA used an AFC system with 6.5 kW net output. For each liter of fuel consumed, the average outboard motor produces 140 times less the hydrocarbons produced by the average modern car. Fuel cell engines have higher energy efficiencies than combustion engines, and therefore offer better range and significantly reduced emissions."Fuel Cell Basics: Applications"Amsterdam introduced its first fuel cell powered boat in 2011 that ferries people around the city's canals.
Submarines
The first submersible application of fuel cells is the German Type 212 submarine. Each Type 212 contains nine PEM fuel cells, spread throughout the ship, providing between 30 kW and 50 kW each of electrical power. This allows the Type 212 to remain submerged longer and makes them more difficult to detect. Fuel cell powered submarines are also easier to design, manufacture, and maintain than nuclear-powered submarines.Trains
In March 2015, China South Rail Corporation (CSR) demonstrated the world's first hydrogen fuel cell-powered tramcar at an assembly facility in Qingdao. 83 miles of tracks for the new vehicle were built in seven Chinese cities. China had plans to spend 200 billion yuan ($32 billion) over the next five years to increase tram tracks to more than 1,200 miles. In 2016,Alstom
Alstom SA is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer operating worldwide in rail transport markets, active in the fields of passenger transportation, signalling, and locomotives, with products including the AGV, TGV, Eurostar, Avel ...
debuted the Coradia iLint, a regional train powered by hydrogen fuel cells. It was designed to reach and travel on a full tank of hydrogen. The train entered service in Germany in 2018 and is expected to be tested in the Netherlands beginning in 2019.
Swiss manufacturer Stadler Rail
Stadler Rail is a Swiss manufacturer of railway rolling stock, with an emphasis on regional train multiple units and trams. It is also focused on niche products, such as being one of the last European manufacturers of rack railway rolling stock. ...
signed a contract in California to supply a hydrogen fuel cell train in the US, the FLIRT H2 train, in 2024 as part of the Arrow rail project.
Trucks
 For transport applications such as long-haul trucks, fuel cells are a potential solution for zero emission transport. A 2022 study in ''Energies'' magazine cites relatively fast refueling times compared with electric truck charging times and the current limitations of the energy density of batteries, but they note that "operating constraints" include the "high amount of CO2 emissions aused byhydrogen production", the lack of storage and refueling infrastructure, H2 leakage and safety challenges, efficiency "losses in compression, storage and dispensing", .
In 2020,
For transport applications such as long-haul trucks, fuel cells are a potential solution for zero emission transport. A 2022 study in ''Energies'' magazine cites relatively fast refueling times compared with electric truck charging times and the current limitations of the energy density of batteries, but they note that "operating constraints" include the "high amount of CO2 emissions aused byhydrogen production", the lack of storage and refueling infrastructure, H2 leakage and safety challenges, efficiency "losses in compression, storage and dispensing", .
In 2020, Hyundai Hyundai is a South Korean industrial conglomerate (" chaebol"), which was restructured into the following groups:
* Hyundai Group, parts of the former conglomerate which have not been divested
** Hyundai Mobis, Korean car parts company
** Hyundai A ...
started to manufacture hydrogen powered 34-ton cargo trucks under the model name XCIENT, making an initial shipment of 10 of the vehicles to Switzerland. They are able to travel on a full tank and take 8 to 20 minutes to fill up.
In 2022, Total Transportation Services (TTSI), Toyota Logistics Services (TLS), UPS, and Southern Counties Express (SCE) are operating a 12-month "Shore-to-Store (S2S) project" running hydrogen fuel cell trucks on trips from Los Angeles area ports. The Kenworth T680 hydrogen prototype used in Los Angeles and Long Beach was unveiled in 2018 and has also been tested in the Seattle area.
Hydrogen infrastructure
Eberle and Rittmar von Helmolt stated in 2010 that challenges remain before fuel cell cars can become competitive with other technologies and cite the lack of an extensive hydrogen infrastructure in the U.S.:Eberle, Ulrich and Rittmar von Helmolt"Sustainable transportation based on electric vehicle concepts: a brief overview"
Energy & Environmental Science, Royal Society of Chemistry, May 14, 2010, accessed August 2, 2011 , there were 43 publicly accessible hydrogen refueling stations in the US, 41 of which were located in California.Alternative Fueling Station Counts by State
''Alternative Fuels Data Center'', accessed July 2, 2020 In 2013, Governor
Jerry Brown
Edmund Gerald Brown Jr. (born April 7, 1938) is an American lawyer, author, and politician who served as the 34th and 39th governor of California from 1975 to 1983 and 2011 to 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he was elected Secretary of St ...
signed AB 8, a bill to fund $20 million a year for 10 years to build up to 100 stations.Xiong, Ben"Governor Brown Signs AB 8"
, California Fuel Cell Partnership, September 30, 2013 In 2014, the
California Energy Commission
The California Energy Commission, formally the Energy Resources Conservation and Development Commission, is the primary energy policy and planning agency for California.
Created in 1974 and headquartered in Sacramento, the Commission'core respo ...
funded $46.6 million to build 28 stations.
Japan got its first commercial hydrogen fueling station in 2014. By March 2016, Japan had 80 hydrogen fueling stations, and the Japanese government aims to double this number to 160 by 2020. In May 2017, there were 91 hydrogen fueling stations in Japan.Voelcker, John"Energy use for hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles: higher than electrics, even hybrids (analysis)"
''Green Car Reports'', May 4, 2017 Germany had 18 public hydrogen fueling stations in July 2015. The German government hoped to increase this number to 50 by end of 2016, but only 30 were open in June 2017.
Codes and standards
Under United Nations global technical regulations for wheeled vehicles, specifically regarding hydrogen usage, there are international standards which define aspects of engineering and overall integrity, performance, safety, part lifecycle, and various other categories. One notable area of these regulations is regarding the compressed hydrogen storage systems that typically reach the end of qualified service life at 15 or fewer years in use.US programs
In 2003, US President George Bush proposed the Hydrogen Fuel Initiative (HFI). The HFI aimed to further develop hydrogen fuel cells and infrastructure technologies to accelerate the commercial introduction of fuel cell vehicles. By 2008, the U.S. had contributed 1 billion dollars to this project. In 2009,Steven Chu
Steven ChuUS Secretary of Energy, asserted that hydrogen vehicles "will not be practical over the next 10 to 20 years".Bullis, Kevin
"Q & A: Steven Chu"
''Technology Review'', May 14, 2009 In 2012, however, Chu stated that he saw fuel cell cars as more economically feasible as natural gas prices had fallen and hydrogen reforming technologies had improved. In June 2013, the
"VIII.0 Technology Validation Sub-Program Overview"
DOE Fuel Cell Technologies Program, FY 2010 Annual Progress Report, accessed August 2, 2011 In 2010, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) estimated that the cost of automobile fuel cells had fallen 80% since 2002 and that such fuel cells could potentially be manufactured for $51/kW, assuming high-volume manufacturing cost savings."Accomplishments and Progress"
. Fuel Cell Technology Program, U.S. Dept. of Energy, June 24, 2011 Fuel cell electric vehicles have been produced with "a driving range of more than 250 miles between refueling". They can be refueled in less than 5 minutes. Deployed fuel cell buses have a 40% higher fuel economy than diesel buses.
"The Great Compression: the Future of the Hydrogen Economy"
Lux Research, Inc. January 2012
PVBuzz.com, November 15, 2016
"Getting Back Into Gear: Fuel Cell Development After the Hype"
The Electrochemical Society ''Interface'', Winter 2008, pp. 36–39, accessed August 7, 2011 Also in 2008, '' Wired News'' reported that "experts say it will be 40 years or more before hydrogen has any meaningful impact on gasoline consumption or global warming, and we can't afford to wait that long. In the meantime, fuel cells are diverting resources from more immediate solutions." In 2008, Robert Zubrin, the author of '' Energy Victory'', said: "Hydrogen is 'just about the worst possible vehicle fuel.Wrigglesworth, Phil
"The car of the perpetual future"'
September 4, 2008, retrieved on September 15, 2008 If hydrogen could be produced using renewable energy, "it would surely be easier simply to use this energy to charge the batteries of all-electric or plug-in hybrid vehicles." The ''Los Angeles Times'' wrote in 2009, "Any way you look at it, hydrogen is a lousy way to move cars." '' The Washington Post'' asked in November 2009, " y would you want to store energy in the form of hydrogen and then use that hydrogen to produce electricity for a motor, when electrical energy is already waiting to be sucked out of sockets all over America and stored in auto batteries...?" '' The Motley Fool'' stated in 2013 that "there are still cost-prohibitive obstacles or hydrogen carsrelating to transportation, storage, and, most importantly, production." Volkswagen's Rudolf Krebs said in 2013 that "no matter how excellent you make the cars themselves, the laws of physics hinder their overall efficiency. The most efficient way to convert energy to mobility is electricity." He elaborated: "Hydrogen mobility only makes sense if you use green energy", but ... you need to convert it first into hydrogen "with low efficiencies" where "you lose about 40 percent of the initial energy". You then must compress the hydrogen and store it under high pressure in tanks, which uses more energy. "And then you have to convert the hydrogen back to electricity in a fuel cell with another efficiency loss". Krebs continued: "in the end, from your original 100 percent of electric energy, you end up with 30 to 40 percent." In 2014, electric automotive and energy futurist Julian Cox wrote that producing hydrogen from methane "is significantly more carbon intensive per unit of energy than coal. Mistaking fossil hydrogen from the hydraulic fracturing of shales for an environmentally sustainable energy pathway threatens to encourage energy policies that will dilute and potentially derail global efforts to head-off climate change due to the risk of diverting investment and focus from vehicle technologies that are economically compatible with renewable energy."Cox, Julian
"Time To Come Clean About Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles"
CleanTechnica.com, June 4, 2014 In 2014, former Dept. of Energy official
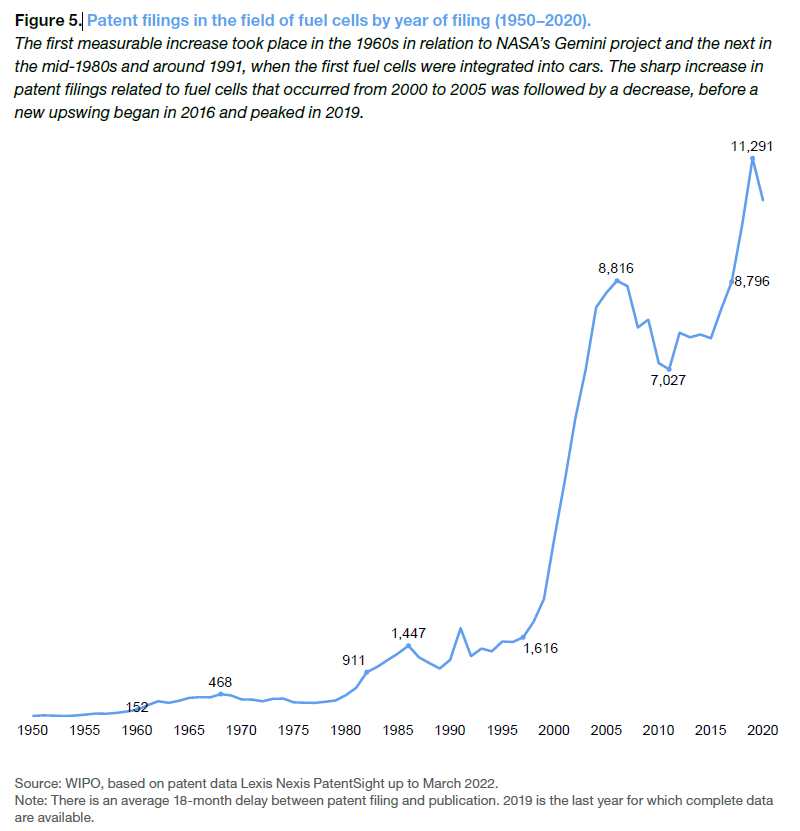 Fuel cell patent fillings in the area of hydrogen fuel cells increased in the 1960s, partly due to NASAs space program; another increase in the 80s was driven by research for automobiles. This was followed by a surge in filings from 2000 to 2005 by inventors in Japan, US and South Korea. Since then, China has dominated patent fillings in the field, with a smaller number in Japan, Germany, South Korea and the US. Between 2016 and 2020, annual filings, particularly for transportation applications, increased by a further 23%.
Almost 80% of the patents in the area of fuel cells for transportation were filed by car companies. Academia is collaborating actively with the industry. Although filings related to road vehicles such as cars and trucks dominate, inventions in other areas like shipping, aviation, rail and other special vehicles is increasing.
Fuel cell patent fillings in the area of hydrogen fuel cells increased in the 1960s, partly due to NASAs space program; another increase in the 80s was driven by research for automobiles. This was followed by a surge in filings from 2000 to 2005 by inventors in Japan, US and South Korea. Since then, China has dominated patent fillings in the field, with a smaller number in Japan, Germany, South Korea and the US. Between 2016 and 2020, annual filings, particularly for transportation applications, increased by a further 23%.
Almost 80% of the patents in the area of fuel cells for transportation were filed by car companies. Academia is collaborating actively with the industry. Although filings related to road vehicles such as cars and trucks dominate, inventions in other areas like shipping, aviation, rail and other special vehicles is increasing.
"A vision on a sustainable electric society supported by Electric Vehicles"
Olino Renewable Energy, June 5, 2009
Ulrich Hottelet: State funding for hybrid dreams
The Asia Pacific Times, October 2009
Fuel cell market size
per Prescient & Strategic Market Research 2021 {{Authority control
"Q & A: Steven Chu"
''Technology Review'', May 14, 2009 In 2012, however, Chu stated that he saw fuel cell cars as more economically feasible as natural gas prices had fallen and hydrogen reforming technologies had improved. In June 2013, the
California Energy Commission
The California Energy Commission, formally the Energy Resources Conservation and Development Commission, is the primary energy policy and planning agency for California.
Created in 1974 and headquartered in Sacramento, the Commission'core respo ...
granted $18.7M for hydrogen fueling stations. In 2013, Governor Brown signed AB 8, a bill to fund $20 million a year for 10 years for up to 100 stations. In 2013, the US DOE announced up to $4 million planned for "continued development of advanced hydrogen storage systems". On May 13, 2013, the Energy Department launched H2USA, which is focused on advancing hydrogen infrastructure in the US.
Cost
By 2010, advancements in fuel cell technology had reduced the size, weight and cost of fuel cell electric vehicles.Garbak, John"VIII.0 Technology Validation Sub-Program Overview"
DOE Fuel Cell Technologies Program, FY 2010 Annual Progress Report, accessed August 2, 2011 In 2010, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) estimated that the cost of automobile fuel cells had fallen 80% since 2002 and that such fuel cells could potentially be manufactured for $51/kW, assuming high-volume manufacturing cost savings."Accomplishments and Progress"
. Fuel Cell Technology Program, U.S. Dept. of Energy, June 24, 2011 Fuel cell electric vehicles have been produced with "a driving range of more than 250 miles between refueling". They can be refueled in less than 5 minutes. Deployed fuel cell buses have a 40% higher fuel economy than diesel buses.
EERE
The Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) is an office within the United States Department of Energy. Formed from other energy agencies after the 1973 energy crisis, EERE is led by the Assistant Secretary of Energy Efficiency an ...
's Fuel Cell Technologies Program claims that, as of 2011, fuel cells achieved a 42 to 53% fuel cell electric vehicle efficiency at full power, and a durability of over 75,000 miles with less than 10% voltage degradation, double that achieved in 2006. In 2012, Lux Research, Inc. issued a report that concluded that "Capital cost ... will limit adoption to a mere 5.9 GW" by 2030, providing "a nearly insurmountable barrier to adoption, except in niche applications". Lux's analysis concluded that by 2030, PEM stationary fuel cell applications Stationary fuel-cell applications (or stationary fuel-cell power systems) are applications for fuel cells that are either connected to the electric grid (distributed generation) to provide supplemental power and as emergency power system for critic ...
will reach $1 billion, while the vehicle market, including fuel cell forklifts, will reach a total of $2 billion.Brian Warshay, Brian"The Great Compression: the Future of the Hydrogen Economy"
Lux Research, Inc. January 2012
Environmental impact
The environmental impact of fuel cell vehicles depends on the primary energy with which the hydrogen was produced. Fuel cell vehicles are only environmentally benign when the hydrogen was produced with renewable energy. If this is the case fuel cell cars are cleaner and more efficient than fossil fuel cars. However, they are not as efficient asbattery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, wi ...
s which consume much less energy. Usually a fuel cell car consumes 2.4 times more energy than a battery electric car, because electrolysis and storage of hydrogen is much less efficient than using electricity to directly load a battery.
As of 2009, motor vehicles used most of the petroleum consumed in the U.S. and produced over 60% of the carbon monoxide emissions and about 20% of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, however production of hydrogen for hydro cracking used in gasoline production chief amongst its industrial uses was responsible for approximately 10% of fleet wide greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, a vehicle fueled with pure hydrogen emits few pollutants, producing mainly water and heat, although the production of the hydrogen would create pollutants unless the hydrogen used in the fuel cell were produced using only renewable energy.
In a 2005 well-to-wheels analysis, the DOE estimated that fuel cell electric vehicles using hydrogen produced from natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon di ...
would result in emissions of approximately 55% of the CO2 per mile of internal combustion engine vehicles and have approximately 25% less emissions than hybrid vehicles. In 2006, Ulf Bossel stated that the large amount of energy required to isolate hydrogen from natural compounds (water, natural gas, biomass), package the light gas by compression or liquefaction, transfer the energy carrier to the user, plus the energy lost when it is converted to useful electricity with fuel cells, leaves around 25% for practical use." Richard Gilbert, co-author of ''Transport Revolutions: Moving People and Freight without Oil'' (2010), comments similarly, that producing hydrogen gas ends up using some of the energy it creates. Then, energy is taken up by converting the hydrogen back into electricity within fuel cells. This means that only a quarter of the initially available energy reaches the electric motor' ... Such losses in conversion don't stack up well against, for instance, recharging an electric vehicle (EV) like the Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
or Chevy Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid manufactured by General Motors, also marketed in rebadged variants as the Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand and the Buick Velite 5 in China, and with a different fascia as the Vauxhall Ampera in th ...
from a wall socket". A 2010 well-to-wheels analysis of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles report from Argonne National Laboratory states that renewable H2 pathways offer much larger green house gas benefits. This result has recently been confirmed. In 2010, a US DOE well-to-wheels publication assumed that the efficiency of the single step of compressing hydrogen to at the refueling station is 94%. A 2016 study in the November issue of the journal '' Energy'' by scientists at Stanford University and the Technical University of Munich concluded that, even assuming local hydrogen production, "investing in all-electric battery vehicles is a more economical choice for reducing carbon dioxide emissions, primarily due to their lower cost and significantly higher energy efficiency.""Battery electric cars are a better choice for emissions reduction"PVBuzz.com, November 15, 2016
Criticism of fuel cell cars
In 2008, professor Jeremy P. Meyers, in the Electrochemical Society journal ''Interface'' wrote that fuel cells "are not as efficient as batteries, due primarily to the inefficiency of the oxygen reduction reaction. ... ey make the most sense for operation disconnected from the grid, or when fuel can be provided continuously. For applications that require frequent and relatively rapid start-ups ... where zero emissions are a requirement, as in enclosed spaces such as warehouses."Meyers, Jeremy P"Getting Back Into Gear: Fuel Cell Development After the Hype"
The Electrochemical Society ''Interface'', Winter 2008, pp. 36–39, accessed August 7, 2011 Also in 2008, '' Wired News'' reported that "experts say it will be 40 years or more before hydrogen has any meaningful impact on gasoline consumption or global warming, and we can't afford to wait that long. In the meantime, fuel cells are diverting resources from more immediate solutions." In 2008, Robert Zubrin, the author of '' Energy Victory'', said: "Hydrogen is 'just about the worst possible vehicle fuel.Wrigglesworth, Phil
"The car of the perpetual future"'
September 4, 2008, retrieved on September 15, 2008 If hydrogen could be produced using renewable energy, "it would surely be easier simply to use this energy to charge the batteries of all-electric or plug-in hybrid vehicles." The ''Los Angeles Times'' wrote in 2009, "Any way you look at it, hydrogen is a lousy way to move cars." '' The Washington Post'' asked in November 2009, " y would you want to store energy in the form of hydrogen and then use that hydrogen to produce electricity for a motor, when electrical energy is already waiting to be sucked out of sockets all over America and stored in auto batteries...?" '' The Motley Fool'' stated in 2013 that "there are still cost-prohibitive obstacles or hydrogen carsrelating to transportation, storage, and, most importantly, production." Volkswagen's Rudolf Krebs said in 2013 that "no matter how excellent you make the cars themselves, the laws of physics hinder their overall efficiency. The most efficient way to convert energy to mobility is electricity." He elaborated: "Hydrogen mobility only makes sense if you use green energy", but ... you need to convert it first into hydrogen "with low efficiencies" where "you lose about 40 percent of the initial energy". You then must compress the hydrogen and store it under high pressure in tanks, which uses more energy. "And then you have to convert the hydrogen back to electricity in a fuel cell with another efficiency loss". Krebs continued: "in the end, from your original 100 percent of electric energy, you end up with 30 to 40 percent." In 2014, electric automotive and energy futurist Julian Cox wrote that producing hydrogen from methane "is significantly more carbon intensive per unit of energy than coal. Mistaking fossil hydrogen from the hydraulic fracturing of shales for an environmentally sustainable energy pathway threatens to encourage energy policies that will dilute and potentially derail global efforts to head-off climate change due to the risk of diverting investment and focus from vehicle technologies that are economically compatible with renewable energy."Cox, Julian
"Time To Come Clean About Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles"
CleanTechnica.com, June 4, 2014 In 2014, former Dept. of Energy official
Joseph Romm
Joseph J. Romm (born June 27, 1960) is an American author, editor, physicist and climate expert, who advocates reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit global warming and increasing energy security through energy efficiency, green energy techno ...
concluded that renewable energy cannot economically be used to make hydrogen for an FCV fleet "either now or in the future." GreenTech Media
Greentech Media, a subsidiary of Wood Mackenzie, is a media company based in Massachusetts, United States, that generates daily reports, market research studies, and news on electricity systems and green technology and green jobs.
It was founded ...
's analyst reached similar conclusions in 2014. In 2015, ''Clean Technica'' listed some of the disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
A 2017 analysis published in ''Green Car Reports'' found that the best hydrogen fuel cell vehicles consume "more than three times more electricity per mile than an electric vehicle ... generate more greenhouse-gas emissions than other powertrain technologies ... nd havevery high fuel costs. ... Considering all the obstacles and requirements for new infrastructure (estimated to cost as much as $400 billion), fuel-cell vehicles seem likely to be a niche technology at best, with little impact on U.S. oil consumption. In 2017, Michael Barnard, writing in '' Forbes'', listed the continuing disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cell cars and concluded that "by about 2008, it was very clear that hydrogen was and would be inferior to battery technology as a storage of energy for vehicles. 2025 the last hold outs should likely be retiring their fuel cell dreams.” A 2019 video by ''Real Engineering'' noted that using hydrogen as a fuel for cars does not help to reduce carbon emissions from transportation. The 95% of hydrogen still produced from fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide, and producing hydrogen from water is an energy-consuming process. Storing hydrogen requires more energy either to cool it down to the liquid state or to put it into tanks under high pressure, and delivering the hydrogen to fueling stations requires more energy and may release more carbon. The hydrogen needed to move a FCV a kilometer costs approximately eight times as much as the electricity needed to move a BEV the same distance. Also in 2019, Katsushi Inoue, the president of Honda Europe, stated, "Our focus is on hybrid and electric vehicles now. Maybe hydrogen fuel cell cars will come, but that's a technology for the next era."
Assessments since 2020 have concluded that hydrogen vehicles are still only 38% efficient, while battery EVs from 80% to 95% efficient. A 2021 assessment by CleanTechnica
''CleanTechnica'' is a US-based website dedicated to aggregating news in clean technology, sustainable energy, and electric vehicles, with a focus on Tesla.
Content
CleanTechnica publishes stories on a wide range of topics that are cited by m ...
concluded that while hydrogen cars are far less efficient than electric cars, the vast majority of hydrogen being produced is polluting grey hydrogen
Hydrogen production is the family of industrial methods for generating hydrogen gas. As of 2020, the majority of hydrogen (∼95%) is produced from fossil fuels by steam reforming of natural gas and other light hydrocarbons, partial oxidation of h ...
, and delivering hydrogen would require building a vast and expensive new infrastructure, the remaining two "advantages of fuel cell vehicles – longer range and fast fueling times – are rapidly being eroded by improving battery and charging technology." A 2022 study in '' Nature Electronics'' agreed.
Innovation
 Fuel cell patent fillings in the area of hydrogen fuel cells increased in the 1960s, partly due to NASAs space program; another increase in the 80s was driven by research for automobiles. This was followed by a surge in filings from 2000 to 2005 by inventors in Japan, US and South Korea. Since then, China has dominated patent fillings in the field, with a smaller number in Japan, Germany, South Korea and the US. Between 2016 and 2020, annual filings, particularly for transportation applications, increased by a further 23%.
Almost 80% of the patents in the area of fuel cells for transportation were filed by car companies. Academia is collaborating actively with the industry. Although filings related to road vehicles such as cars and trucks dominate, inventions in other areas like shipping, aviation, rail and other special vehicles is increasing.
Fuel cell patent fillings in the area of hydrogen fuel cells increased in the 1960s, partly due to NASAs space program; another increase in the 80s was driven by research for automobiles. This was followed by a surge in filings from 2000 to 2005 by inventors in Japan, US and South Korea. Since then, China has dominated patent fillings in the field, with a smaller number in Japan, Germany, South Korea and the US. Between 2016 and 2020, annual filings, particularly for transportation applications, increased by a further 23%.
Almost 80% of the patents in the area of fuel cells for transportation were filed by car companies. Academia is collaborating actively with the industry. Although filings related to road vehicles such as cars and trucks dominate, inventions in other areas like shipping, aviation, rail and other special vehicles is increasing. Airbus
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft throughout the world. The company has three divisions: '' ...
, a major aircraft manufacturer, has increased its patenting activity in the area since 2019. The number of fuel cell patents for shipping applications is comparable in size to the one for aviation and similarly slow in growth.
A World Intellectual Property Organization report argues that because heavy-duty vehicles, such as construction vehicles, forklifts
A forklift (also called lift truck, jitney, hi-lo, fork truck, fork hoist, and forklift truck) is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials over short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th century by various ...
, and airport tugs require a higher payload, the high energy density of hydrogen can make fuel cells a more advantageous solution than battery applications.
See also
* Hydrogen vehicle * Glossary of fuel cell terms *Proton-exchange membrane fuel cell
Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC), also known as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells, are a type of fuel cell being developed mainly for transport applications, as well as for stationary fuel-cell applications and portable ...
* Reformed methanol fuel cell
*Fuel cell auxiliary power unit A fuel cell auxiliary power unit (FC-APU) is a fuel cell based auxiliary power unit on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are mainly used in trucking, aviation, marine and recreational vehicles.
Market
In 2010 ...
* Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Energy Association
*Water-fuelled car
A water-fuelled car is an automobile that hypothetically derives its energy directly from water. Water-fuelled cars have been the subject of numerous international patents, newspaper and popular science magazine articles, local television news ...
Notes
External links
*Heetebrij, Jan"A vision on a sustainable electric society supported by Electric Vehicles"
Olino Renewable Energy, June 5, 2009
Ulrich Hottelet: State funding for hybrid dreams
The Asia Pacific Times, October 2009
Fuel cell market size
per Prescient & Strategic Market Research 2021 {{Authority control