Frisian languages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Frisian (, ) languages are a closely related group of
Ried fan de Fryske Beweging
is an organization which works for the preservation of the West Frisian language and culture in the Dutch province of
Fryske Academy
also plays a large role, since its foundation in 1938, to conduct research on Frisian language, history, and society, including attempts at forming a larger dictionary. Recent attempts have allowed Frisian be used somewhat more in some of the domains of education, media and public administration. Nevertheless, Saterland Frisian and most dialects of North Frisian are seriously
 ** Island dialects
***
** Island dialects
***
* See also West Frisian language#Sample text.
** ''Which'' was changed to "who", ''in earth'' to "on earth," and ''them that'' to "those who" in the 1928 version of the Church of England prayer book and used in other later Anglican prayer books too. However, the words given here are those of the original 1662 book as stated.
Omniglot links to various Frisian resourcesTresoar - Historical and Literary Centre of Friesland Province of the Netherlands
Ferring Stiftung, a foundation from North Frisia
West-Frisian-English dictionary
[PDF]Hewett, Waterman Thomas, The Frisian language and literature
and compare with equivalents in English and other Germanic languages. *
Radio in West Frisian
Radio news in North Frisian
Online (German-Frisian) Dictionary for multiple North Frisian dialects
{{DEFAULTSORT:Frisian Languages Languages attested from the 8th century Languages of the Netherlands Languages of Germany
West Germanic languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into ...
, spoken by about 500,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
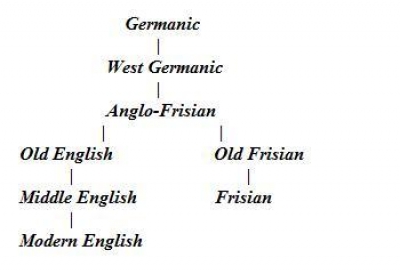
. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages
The Anglo-Frisian languages are the Anglic (English, Scots, and Yola) and Frisian varieties of the West Germanic languages.
The Anglo-Frisian languages are distinct from other West Germanic languages due to several sound changes: besides th ...
group and together with the Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle ...
dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as a ...
, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and foreign influences.
There are three different Frisian branches, which are usually called the Frisian languages, despite the fact that their so-called dialects are often not mutually intelligible even within these branches. These branches are: West Frisian, which is by far the most spoken of the three and is an official language in the Dutch province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
of Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
, where it is spoken on the mainland and on two of the West Frisian Islands
The West Frisian Islands (; fry, Waadeilannen) are a chain of islands in the North Sea off the Dutch coast, along the edge of the Wadden Sea. They continue further east as the German East Frisian Islands and are part of the Frisian Islands.
...
: Terschelling
Terschelling (; fry, Skylge; Terschelling dialect: ''Schylge'') is a municipality and an island in the northern Netherlands, one of the West Frisian Islands. It is situated between the islands of Vlieland and Ameland.
Wadden Islanders are k ...
and Schiermonnikoog
Schiermonnikoog (; fry, ) is an island, a municipality and national park in the Northern Netherlands. Schiermonnikoog is one of the West Frisian Islands, and is part of the province of Friesland. It is situated between the islands of Ameland ...
. It is also spoken in four villages in the Westerkwartier
The Westerkwartier (; en, Western Quarter) is a historical region in the Dutch province of Groningen, at the border with the provinces of Drenthe and Friesland. In the past the area was part of the historical region of Frisia. The West Frisian ...
of the neighbouring province of Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of t ...
. North Frisian, the second branch, is spoken in the northernmost German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivision ...
of Nordfriesland
Nordfriesland (; da, Nordfrisland; frr, Nordfraschlönj ), also known as North Frisia, is the northernmost district of Germany, part of the state of Schleswig-Holstein. It includes almost all of traditional North Frisia (with the exception ...
in the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
: on the North Frisian mainland, and on the North Frisian Islands of Sylt
Sylt (; da, Sild; Sylt North Frisian, Söl'ring North Frisian: ) is an island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, and well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian ...
, Föhr, Amrum
Amrum (; ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and ha ...
, and the Halligs. It is also spoken on the islands of Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possession ...
, in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
. The third Frisian branch, East Frisian, has only one remaining variant, Sater Frisian, spoken in the municipality of Saterland
Saterland (; Saterland Frisian: , ) is a municipality in the district of Cloppenburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated between the cities of Leer, Cloppenburg, and Oldenburg. It is home to Saterland Frisians, who speak Frisian in add ...
in the Lower Saxon district of Cloppenburg. Surrounded by bogs
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
, the four Saterlandic villages lie just outside the borders of East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
, in the Oldenburg Münsterland
The Oldenburg Münsterland, otherwise called Oldenburger Münsterland or Oldenburgisches Münsterland, is a region in Lower Saxony, Germany and the administrative area that comprises the federal districts of Cloppenburg and Vechta. Unofficiall ...
region. In East Frisia proper, East Frisian Low Saxon is spoken today, which is not a Frisian language, but a variant of Low German/Low Saxon.
Depending upon their location, the six Frisian languages have been heavily influenced by and bear similarities to Dutch and Low German/Low Saxon, and in addition North Frisian has a Danish substrate. However, Frisian is still unintelligible to Dutch, for instance, a cloze test in 2005 revealed the Dutch understood 31.9% of a West Frisian newspaper, 66.4% of an Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gr ...
newspaper and 97.1% of a Dutch newspaper. Additional shared linguistic characteristics between Friesland and the Great Yarmouth
Great Yarmouth (), often called Yarmouth, is a seaside town and unparished area in, and the main administrative centre of, the Borough of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England; it straddles the River Yare and is located east of Norwich. A pop ...
area in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
are likely to have resulted from the close trading relationship these areas maintained during the centuries-long Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label= Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
of the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
.
Division
There are three main groups of Frisian varieties: West Frisian, Saterland Frisian, and North Frisian. Some linguists consider these three varieties, despite theirmutual unintelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as a ...
, to be dialects of one single Frisian language, whereas others consider them to be a number of separate languages equal to or greater than the number of main branches discussed here. Indeed, the insular varieties of West Frisian are not intelligible to the mainland, and by that standard are additional languages, and North Frisian is also divided into several strongly diverse dialects, which are not all mutually intelligible among themselves. West Frisian is strongly influenced by Dutch. The other Frisian languages, meanwhile, have been influenced by Low German and German. Stadsfries
Stadsfries () or Town Frisian ( fy, Stedsk, link=no, ) is a set of dialects spoken in certain cities in the province of Friesland in the northern Netherlands, namely Leeuwarden, Sneek, Bolsward, Franeker, Dokkum, Harlingen, Stavoren, and to som ...
and West Frisian Dutch are not Frisian, but Dutch dialects influenced by West Frisian. Frisian is called ''Frysk'' in West Frisian, ''Fräisk'' in Saterland Frisian, and ''Friisk'', ''fresk'', ''freesk'', ''frasch'', ''fräisch'', and ''freesch'' in the varieties of North Frisian.
The situation in the Dutch province of Groningen and the German region of East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
is similar: The local Low German/Low Saxon dialects of Gronings and East Frisian Low Saxon still bear some Frisian elements due to East Frisian substrate. Frisian was spoken there at one time, only to have been gradually replaced by Low Saxon since the Middle Ages. This local language is now, like Frisian, under threat by standard Dutch and German.
Speakers
Most Frisian speakers live in theNetherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, primarily in the province of Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
, which since 1997 officially uses its West Frisian name of Fryslân, where the number of native speakers is about 400,000, which is about 75% of the inhabitants of Friesland. An increasing number of native Dutch speakers in the province are learning Frisian as a second language.
In Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, there are about 2,000 speakers of Saterland Frisian in the marshy Saterland
Saterland (; Saterland Frisian: , ) is a municipality in the district of Cloppenburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated between the cities of Leer, Cloppenburg, and Oldenburg. It is home to Saterland Frisians, who speak Frisian in add ...
region of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
. Saterland Frisian has resisted encroachment from Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle ...
and Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
, but Saterland Frisian still remains seriously endangered because of the small size of the speech community
A speech community is a group of people who share a set of linguistic norms and expectations regarding the use of language. It is a concept mostly associated with sociolinguistics and anthropological linguistics.
Exactly how to define ''speech ...
and of the lack of institutional support to help preserve and spread the language.
In the North Frisia (''Nordfriesland'') region of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, there were 10,000 North Frisian speakers. Although many of these live on the mainland, most are found on the islands, notably Sylt
Sylt (; da, Sild; Sylt North Frisian, Söl'ring North Frisian: ) is an island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, and well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian ...
, Föhr, Amrum
Amrum (; ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and ha ...
, and Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possession ...
. The local corresponding North Frisian dialects are still in use.
West Frisian-Dutch bilinguals are split into two categories: Speakers who had Dutch as their first language tended to maintain the Dutch system of homophony between plural and linking suffixes when speaking West Frisian, by using the West Frisian plural as a linking morpheme. Speakers who had West Frisian as their first language often maintained the West Frisian system of no homophony when speaking West Frisian.
Status
Saterland and North Frisian are officially recognised and protected asminority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) ...
s in Germany, and West Frisian is one of the two official languages in the Netherlands, the other being Dutch.
ISO 639-1 code fy and ISO 639-2
ISO 639- 2:1998, ''Codes for the representation of names of languages — Part 2: Alpha-3 code'', is the second part of the ISO 639 standard, which lists codes for the representation of the names of languages. The three-letter codes given for ea ...
code fry were assigned to "Frisian", but that was changed in November 2005 to " Western Frisian". According to the ISO 639 Registration Authority the "previous usage of hiscode has been for Western Frisian, although helanguage name was 'Frisian'".
The new ISO 639
ISO 639 is a set of standards by the International Organization for Standardization that is concerned with representation of names for languages and language groups.
It was also the name of the original standard, approved in 1967 (as ''ISO 639/ ...
code stq is used for the Saterland Frisian language
Saterland Frisian, also known as Sater Frisian, Saterfrisian or Saterlandic (), is the last living dialect of the East Frisian language. It is closely related to the other Frisian languages: North Frisian, spoken in Germany as well, and West Fr ...
, a variety of Eastern Frisian (not to be confused with East Frisian Low Saxon, a West Low German
Low Saxon, also known as West Low German ( nds, Nedersassisch, Nedersaksies; nl, Nedersaksisch) are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark (in North Schleswig by parts o ...
dialect). The new ISO 639 code frr is used for the North Frisian language
North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are th ...
variants spoken in parts of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
.
ThRied fan de Fryske Beweging
is an organization which works for the preservation of the West Frisian language and culture in the Dutch province of
Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
. ThFryske Academy
also plays a large role, since its foundation in 1938, to conduct research on Frisian language, history, and society, including attempts at forming a larger dictionary. Recent attempts have allowed Frisian be used somewhat more in some of the domains of education, media and public administration. Nevertheless, Saterland Frisian and most dialects of North Frisian are seriously
endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and in ...
and West Frisian is considered as vulnerable to being endangered. Moreover, for all advances in integrating Frisian in daily life, there is still a lack of education and media awareness of the Frisian language, perhaps reflecting its rural origins and its lack of prestige Therefore, in a sociological sense it is considered more a dialect than a standard language, even though linguistically it is a separate language.
For L2 speakers, both the quality and amount of time Frisian is taught in the classroom is low, concluding that Frisian lessons do not contribute meaningfully to the linguistic and cultural development of the students. Moreover, Frisian runs the risk of dissolving into Dutch, especially in Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
, where both languages are used.
History
Old Frisian
In theEarly Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
the Frisian lands stretched from the area around Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
, in what is now Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, to the river Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
, in northern Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
. At that time, the Frisian language was spoken along the entire southern North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
coast. Today this region is sometimes referred to as Great Frisia or Frisia Magna, and many of the areas within it still treasure their Frisian heritage, even though in most places the Frisian languages have been lost.
Frisian is the language most closely related to English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
and Scots, but after at least five hundred years of being subject to the influence of Dutch, modern Frisian in some aspects bears a greater similarity to Dutch than to English; one must also take into account the centuries-long drift of English away from Frisian. Thus the two languages have become less mutually intelligible over time, partly due to the marks which Dutch and Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle ...
have left on Frisian, and partly due to the vast influence some languages (in particular Norman French
Norman or Norman French (, french: Normand, Guernésiais: , Jèrriais: ) is a Romance language which can be classified as one of the Oïl languages along with French, Picard and Walloon. The name "Norman French" is sometimes used to descri ...
) have had on English throughout the centuries.
Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries along the North Sea coast, roughly between the mouths of the Rhine and Weser rivers. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland (today's Northern Fries ...
, however, was very similar to Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
. Historically, both English and Frisian are marked by the loss of the Germanic nasal in words like ''us'' (''ús''; ''uns'' in German), ''soft'' (''sêft''; ''sanft'') or ''goose'' (''goes''; ''Gans''): see Anglo-Frisian nasal spirant law. Also, when followed by some vowels, the Germanic ''k'' softened to a ''ch'' sound; for example, the Frisian for ''cheese'' and ''church'' is ''tsiis'' and ''tsjerke'', whereas in Dutch it is ''kaas'' and ''kerk'', and in High German the respective words are ''Käse'' and ''Kirche''. Contrarily, this did not happen for ''chin'' and ''choose'', which are ''kin'' and ''kieze''.
One rhyme demonstrates the palpable similarity between Frisian and English: "Butter, bread and green cheese is good English and good Frisian," which is pronounced more or less the same in both languages (West Frisian: "Bûter, brea en griene tsiis is goed Ingelsk en goed Frysk.")
One major difference between Old Frisian and modern Frisian is that in the Old Frisian period (c.1150-c.1550) grammatical cases still existed. Some of the texts that are preserved from this period are from the 12th or 13th, but most are from the 14th and 15th centuries. Generally, all these texts are restricted to legalistic writings. Although the earliest definite written examples of Frisian are from approximately the 9th century, there are a few examples of runic
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were used to write various Germanic languages (with some exceptions) before they adopted the Latin alphabet, and for specialised ...
inscriptions from the region which are probably older and possibly in the Frisian language. These runic writings however usually do not amount to more than single- or few-word inscriptions, and cannot be said to constitute literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
as such. The transition from the Old Frisian to the Middle Frisian period (c.1550-c.1820) in the 16th century is based on the fairly abrupt halt in the use of Frisian as a written language.
Middle West Frisian
Up until the 15th century, Frisian was a language widely spoken and written, but from 1500 onwards it became an almost exclusively oral language, mainly used in rural areas. This was in part due to the occupation of its stronghold, the Dutch province ofFriesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
(Fryslân), in 1498, by Albert III, Duke of Saxony, who replaced West Frisian as the language of government with Dutch.
Afterwards this practice was continued under the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
rulers of the Netherlands (the German Emperor Charles V and his son, the Spanish King Philip II), and even when the Netherlands became independent, in 1585, West Frisian did not regain its former status. The reason for this was the rise of Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former Provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
as the dominant part of the Netherlands, and its language, Dutch, as the dominant language in judicial, administrative and religious affairs.
In this period the great Frisian poet Gysbert Japiks (1603–66), a schoolteacher and cantor from the city of Bolsward
Bolsward (, West Frisian: ''Boalsert'') is a city in Súdwest-Fryslân in the province of Friesland, the Netherlands. Bolsward has a population of just under 10,200. It is located 10 km W.N.W. of Sneek.
History
The town is founded o ...
, who largely fathered modern West Frisian literature and orthography, was really an exception to the rule.
His example was not followed until the 19th century, when entire generations of West Frisian authors and poets appeared. This coincided with the introduction of the so-called newer breaking system, a prominent grammatical feature in almost all West Frisian dialects, with the notable exception of Southwest Frisian. Therefore, the Modern West Frisian period is considered to have begun at this point in time, around 1820.
Modern West Frisian
The revival of the West Frisian Language comes from the poet Gysbert Japiks, who had begun to write in the language as a way to show that it was possible, and created a collective West Frisian identity and West Frisian standard of writing through his poetry. Later on, Johannes Hilarides would build off Gysbert Japik's work by building on West Frisian orthography, particularly on its pronunciation; he also, unlike Japiks, set a standard of the West Frisian language that focused more heavily on how the common people used it as an everyday language. Perhaps the most important figure in the spreading of the West Frisian language was J. H. Halbertsma (1789–1869), who translated many works into the West Frisian language, such as the New Testament He had however, like Hilarides, focused mostly on the vernacular of the West Frisian language, where he focused on translating texts, plays and songs for the lower and middle classes in order to teach and expand the West Frisian language. This had begun the effort to continuously preserve the West Frisian language, which continues unto this day. It was however not until the first half of the 20th century that the West Frisian revival movement began to gain strength, not only through its language, but also through its culture and history, supporting singing and acting in West Frisian in order to facilitate West Frisian speaking. It was not until 1960 that Dutch began to dominate West Frisian in Friesland; with many non-Frisian immigrants into Friesland, the language gradually began to diminish, and only survives now due to the constant effort of scholars and organisations. In recent years, it has been the province of Friesland, rather than the language itself, that has become a more important part of the West Frisian identity; as such, the language has become less important for cultural preservation purposes. It is especially written West Frisian that seems to have trouble surviving, with only 30% of the West Frisian population competent in it; it went out of use in the 16th century and continues to be barely taught today.Family tree
Frisian languages belong to the West Germanic branch of theIndo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, D ...
, the most widespread language family in Europe and the world. Its closest living genealogical relatives are the Anglic languages, i.e. English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
and Scots (Anglo-Frisian languages
The Anglo-Frisian languages are the Anglic (English, Scots, and Yola) and Frisian varieties of the West Germanic languages.
The Anglo-Frisian languages are distinct from other West Germanic languages due to several sound changes: besides th ...
); together with the also closely related Low Saxon dialects the two groups make up the group of North Sea Germanic languages.
*West Frisian language
West Frisian, or simply Frisian ( fy, link=no, Frysk or ; nl, Fries , also ), is a West Germanic language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland () in the north of the Netherlands, mostly by those of Frisian ancestry. It is the most wid ...
, spoken in the Netherlands.
** Hindeloopen Frisian
** Schiermonnikoogs
**Westlauwers–Terschelling Frisian
*** Terschellings (Oosterend and West-Terschelling dialects)
***Western Frisian proper
**** Clay Frisian (Klaaifrysk, incl. Westereendersk
Westereendersk is a local variety of Wood Frisian and is spoken in De Westereen, Zwagerbosch and Twijzelerheide. The most remarkable feature is the use of ''ee'' where Wood Frisian and most other West Frisian dialects use ''ei'' or ''ij'' .
T ...
)
**** Wood Frisian
West Frisian, or simply Frisian ( fy, link=no, Frysk or ; nl, Fries , also ), is a West Germanic language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland () in the north of the Netherlands, mostly by those of Frisian ancestry. It is the most wid ...
(Wâldfrysk)
**** South Frisian (Súdhoeks)
*East Frisian language
East Frisian is one of the Frisian languages. Its last surviving dialect is spoken in Saterland in Germany.
There were once two main dialects, ''Ems'' and ''Weser''. Weser, including the Wursten and Wangerooge dialects, held out until the 20t ...
, spoken in Lower Saxony, Germany.
** Ems Frisian dialects
*** Saterland Frisian
*** Several extinct dialects
** Weser Frisian dialects
*** Wangerooge Frisian
Wangerooge Frisian is an extinct dialect of the East Frisian language, formerly spoken on the East Frisian island of Wangerooge. Wangerooge Frisian was a part of the Weser group of dialects which included the Wangerooge and the equally extinct ...
(extinct)
*** Wursten Frisian
Wursten Frisian was a dialect of the East Frisian language that is thought to have been spoken until the early 18th century in the landscape of Wursten between Bremerhaven and Cuxhaven, Germany. Together with Harlingen Frisian and Wangerooge F ...
(extinct)
*** Several extinct dialects
*North Frisian language
North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are th ...
, spoken in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
** Mainland dialects
*** Bökingharde Frisian
*** Northern Goesharde Frisian
***Middle Goesharde Frisian
***Southern Goesharde Frisian (extinct)
***Wiedingharde Frisian
Wiedingharde Frisian (North Frisian: ''Wiringhiirder freesk'', Danish: ''Vidingherredfrisisk'') is a dialect of the North Frisian language spoken in the German ''amt'' of Wiedingharde south of the border to Denmark in North Frisia (''historic s ...
*** Halligen Frisian
***Karrharde Frisian
Karrharde Frisian is a dialect of the North Frisian language spoken in the municipalities of Stedesand and Enge-Sande in the German '' Amt'' of Südtondern (formerly Karrharde) in the district of Nordfriesland, Schleswig-Holstein. It is a mai ...
 ** Island dialects
***
** Island dialects
***Söl'ring
Sylt Frisian, or ''Söl'ring'', is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the island of Sylt in the German region of North Frisia. ''Söl'ring'' refers to the ''Söl'ring'' Frisian word for Sylt, ''Söl''. Together with the Fering ...
*** Fering-Öömrang
Amrum Frisian, or ''Öömrang'', is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the island of Amrum in the German region of North Frisia. ''Öömrang'' refers to the ''Öömrang'' Frisian name of Amrum, ''Oomram''. Together with the Fe ...
*** Heligolandic (Halunder)
** Extinct dialects
***Strand Frisian
Strand Frisian was a dialect of the North Frisian language which was originally spoken on Strand island, Duchy of Schleswig. Strand was destroyed in the Burchardi flood of 1634 with its remnants forming the islands Pellworm and Nordstrand which ...
*** Eiderstedt Frisian
Text samples
The Lord's Prayer
NB:* See also West Frisian language#Sample text.
** ''Which'' was changed to "who", ''in earth'' to "on earth," and ''them that'' to "those who" in the 1928 version of the Church of England prayer book and used in other later Anglican prayer books too. However, the words given here are those of the original 1662 book as stated.
Comparative sentences
* en, The boy stroked the girl about the chin and kissed her on the cheeks. * Saterland Frisian: * North Frisian ( Mooring dialect): * Nordfriesisch (Söl'ring): ''Di Dreeng strekt dit faamen om't Ken en taatjet / kleepet höör üp di Sjaken'' * West Frisian: * Gronings: ''t Jong fleerde t wicht om kinne tou en smokte heur op wange.'' * East Frisian Low Saxon: * german: Der Junge streichelte das Mädchen ums Kinn und küsste es (sie) auf die Wange. * nl, De jongen aaide (streelde, streek) het meisje langs/over haar/de kin en kuste/zoende haar op de wangen. *Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gr ...
:
* da, Drengen strøg/aede pigen på hagen og kyssede hende på kinden.
* Norwegian:
NB: These are not always literal translations of each other.
See also
* East Frisian Low Saxon *Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West G ...
* Frisian Islands
*Frisians
The Frisians are a Germanic ethnic group native to the coastal regions of the Netherlands and northwestern Germany. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, ...
* Imperativus Pro Infinitivo
References
Notes
General references
Omniglot links to various Frisian resources
External links
Ferring Stiftung, a foundation from North Frisia
West-Frisian-English dictionary
[PDF]Hewett, Waterman Thomas, The Frisian language and literature
and compare with equivalents in English and other Germanic languages. *
Radio in West Frisian
Radio news in North Frisian
Online (German-Frisian) Dictionary for multiple North Frisian dialects
{{DEFAULTSORT:Frisian Languages Languages attested from the 8th century Languages of the Netherlands Languages of Germany