French Huguenot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of
 A term used originally in derision, ''Huguenot'' has unclear origins. Various hypotheses have been promoted. The term may have been a combined reference to the Swiss politician
A term used originally in derision, ''Huguenot'' has unclear origins. Various hypotheses have been promoted. The term may have been a combined reference to the Swiss politician
, ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'', 1911 The ('supposedly 'reformed) were said to gather at night at
 The Huguenot cross is the distinctive emblem of the Huguenots (). It is now an official symbol of the (French Protestant church). Huguenot descendants sometimes display this symbol as a sign of (recognition) between them.
The Huguenot cross is the distinctive emblem of the Huguenots (). It is now an official symbol of the (French Protestant church). Huguenot descendants sometimes display this symbol as a sign of (recognition) between them.
 The issue of demographic strength and geographical spread of the
The issue of demographic strength and geographical spread of the
 The availability of the Bible in
The availability of the Bible in
p. 389 They were suppressed by
 These tensions spurred eight civil wars, interrupted by periods of relative calm, between 1562 and 1598. With each break in peace, the Huguenots' trust in the Catholic throne diminished, and the violence became more severe, and Protestant demands became grander, until a lasting cessation of open hostility finally occurred in 1598. The wars gradually took on a dynastic character, developing into an extended feud between the Houses of Bourbon and Guise, both of which—in addition to holding rival religious views—staked a claim to the French throne. The crown, occupied by the
These tensions spurred eight civil wars, interrupted by periods of relative calm, between 1562 and 1598. With each break in peace, the Huguenots' trust in the Catholic throne diminished, and the violence became more severe, and Protestant demands became grander, until a lasting cessation of open hostility finally occurred in 1598. The wars gradually took on a dynastic character, developing into an extended feud between the Houses of Bourbon and Guise, both of which—in addition to holding rival religious views—staked a claim to the French throne. The crown, occupied by the  The
The
 In what became known as the St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre of 24 August – 3 October 1572, Catholics killed thousands of Huguenots in Paris and similar massacres took place in other towns in the following weeks. The main provincial towns and cities experiencing massacres were
In what became known as the St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre of 24 August – 3 October 1572, Catholics killed thousands of Huguenots in Paris and similar massacres took place in other towns in the following weeks. The main provincial towns and cities experiencing massacres were
 The pattern of warfare, followed by brief periods of peace, continued for nearly another quarter-century. The warfare was definitively quelled in 1598, when Henry of Navarre, having succeeded to the French throne as Henry IV, and having recanted Protestantism in favour of Roman Catholicism in order to obtain the French crown, issued the
The pattern of warfare, followed by brief periods of peace, continued for nearly another quarter-century. The warfare was definitively quelled in 1598, when Henry of Navarre, having succeeded to the French throne as Henry IV, and having recanted Protestantism in favour of Roman Catholicism in order to obtain the French crown, issued the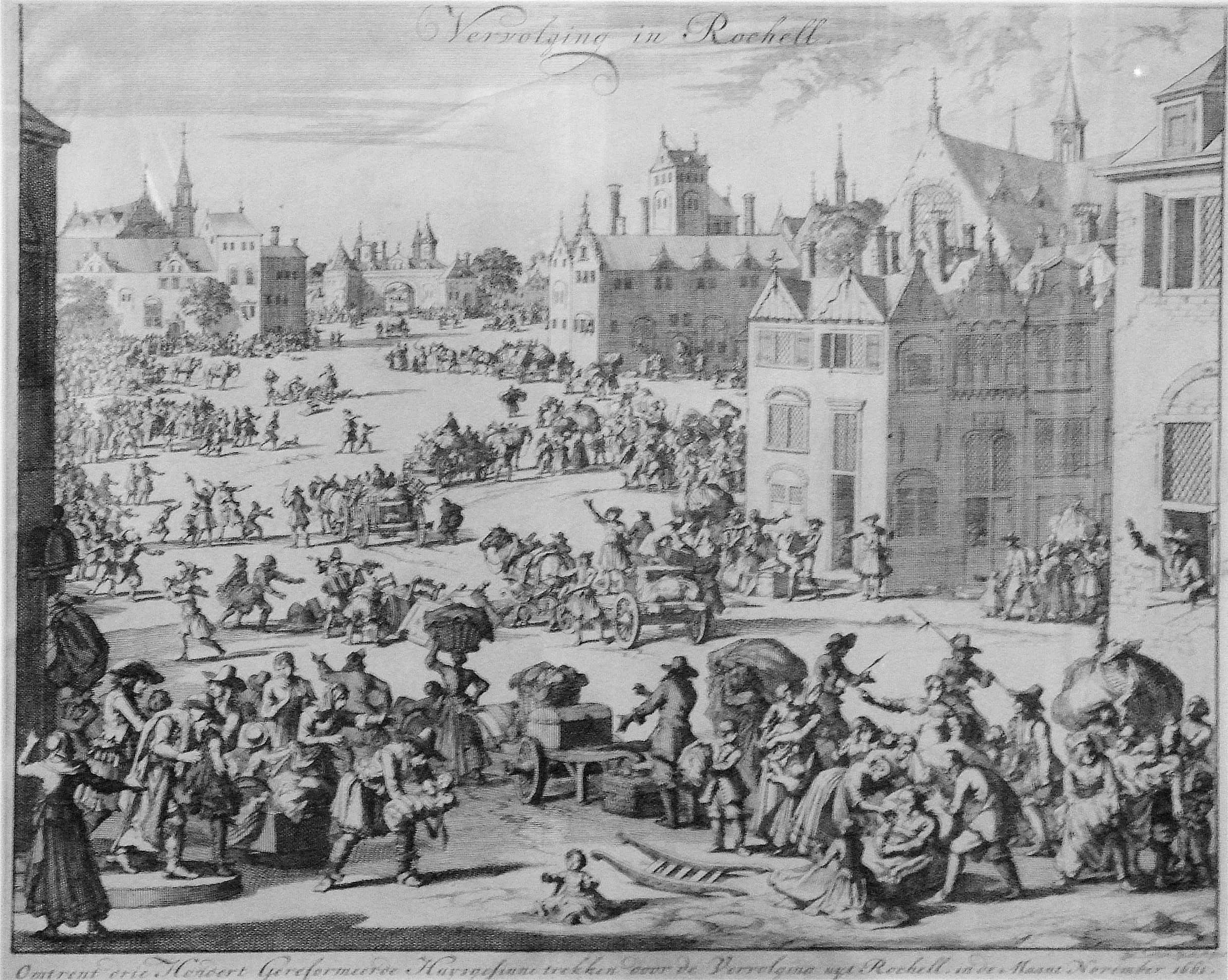  By 1620, the Huguenots were on the defensive, and the government increasingly applied pressure. A series of three small civil wars known as the
By 1620, the Huguenots were on the defensive, and the government increasingly applied pressure. A series of three small civil wars known as the
 By the 1760s Protestantism was no longer a favourite religion of the elite. By then, most Protestants were Cévennes peasants. It was still illegal, and, although the law was seldom enforced, it could be a threat or a nuisance to Protestants. Calvinists lived primarily in the
By the 1760s Protestantism was no longer a favourite religion of the elite. By then, most Protestants were Cévennes peasants. It was still illegal, and, although the law was seldom enforced, it could be a threat or a nuisance to Protestants. Calvinists lived primarily in the
 Many of these settlers were given land in an area that was later called (
Many of these settlers were given land in an area that was later called (
 French Huguenots made two attempts to establish a haven in North America. In 1562, naval officer
French Huguenots made two attempts to establish a haven in North America. In 1562, naval officer  Barred by the government from settling in
Barred by the government from settling in  Huguenot immigrants did not disperse or settle in different parts of the country, but rather, formed three societies or congregations; one in the city of New York, another 21 miles north of New York in a town which they named
Huguenot immigrants did not disperse or settle in different parts of the country, but rather, formed three societies or congregations; one in the city of New York, another 21 miles north of New York in a town which they named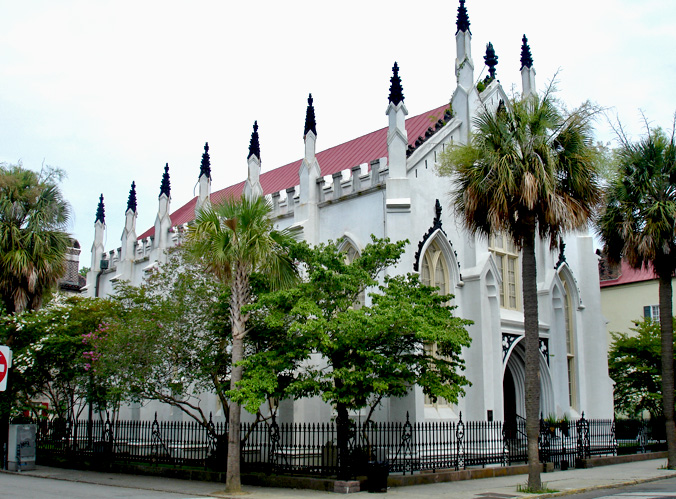  In the early years, many Huguenots also settled in the area of present-day
In the early years, many Huguenots also settled in the area of present-day
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster
Burgomaster (alternatively spelled burgermeister, literally "master of the town, master of the borough, master of the fortress, master of the citizens") is the English form of various terms in or derived from Germanic languages for the chie ...
Bezanson Hugues (1491–1532?), was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
, Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; german: Mosel ; lb, Musel ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it joins at Koblenz. A ...
, and Montbéliard
Montbéliard (; traditional ) is a town in the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in eastern France, about from the border with Switzerland. It is one of the two subprefectures of the department.
History
Montbéliard is ...
, were mainly Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
.
In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
, who instituted the ''dragonnades
The ''Dragonnades'' were a French government policy instituted by King Louis XIV in 1681 to intimidate Huguenot (Protestant) families into converting to Catholicism. This involved the billeting of ill-disciplined dragoons in Protestant household ...
'' to forcibly convert Protestants, and then finally revoked all Protestant rights in his Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without ...
of 1685.
The Huguenots were concentrated in the southern and western parts of the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
. As Huguenots gained influence and more openly displayed their faith, Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
hostility grew. A series of religious conflicts followed, known as the French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholics and Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four mil ...
, fought intermittently from 1562 to 1598. The Huguenots were led by Jeanne d'Albret
Jeanne d'Albret ( Basque: ''Joana Albretekoa''; Occitan: ''Joana de Labrit''; 16 November 1528 – 9 June 1572), also known as Jeanne III, was Queen of Navarre from 1555 to 1572.
Jeanne was the daughter of Henry II of Navarre and Margar ...
; her son, the future Henry IV (who would later convert to Catholicism in order to become king); and the princes of Condé
The Most Serene House of Bourbon-Condé (), named after Condé-en-Brie now in the Aisne ', was a French princely house and a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon. The name of the house was derived from the title of Prince of Condé (French: ''p ...
. The wars ended with the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed pr ...
, which granted the Huguenots substantial religious, political and military autonomy.
Huguenot rebellions
The Huguenot rebellions, sometimes called the Rohan Wars after the Huguenot leader Henri de Rohan, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which French Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted agains ...
in the 1620s resulted in the abolition of their political and military privileges. They retained the religious provisions of the Edict of Nantes until the rule of Louis XIV, who gradually increased persecution of Protestantism until he issued the Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without ...
(1685). This ended legal recognition of Protestantism in France
Protestantism in France has existed in its various forms, starting with Calvinism and Lutheranism since the Protestant Reformation. John Calvin was a Frenchman, as were numerous other Protestant Reformers including William Farel, Pierre Viret ...
and the Huguenots were forced to either convert to Catholicism (possibly as Nicodemite
A Nicodemite () is a person suspected of publicly misrepresenting their religious faith to conceal their true beliefs. The term is sometimes defined as referring to a Protestant Christian who lived in a Roman Catholic country and escaped persecuti ...
s) or flee as refugees; they were subject to violent dragonnades
The ''Dragonnades'' were a French government policy instituted by King Louis XIV in 1681 to intimidate Huguenot (Protestant) families into converting to Catholicism. This involved the billeting of ill-disciplined dragoons in Protestant household ...
. Louis XIV claimed that the French Huguenot population was reduced from about 900,000 or 800,000 adherents to just 1,000 or 1,500. He exaggerated the decline, but the dragonnades were devastating for the French Protestant community. The exodus of Huguenots from France created a brain drain, as many of them had occupied important places in society.
The remaining Huguenots faced continued persecution under Louis XV. By the time of his death in 1774, Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
had been nearly eliminated from France. Persecution of Protestants officially ended with the Edict of Versailles
The Edict of Versailles, also known as the Edict of Tolerance, was an official act that gave non-Catholics in France the access to civil rights formerly denied to them, which included the right to contract marriages without having to convert to t ...
, signed by Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
in 1787. Two years later, with the Revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective, to refer to something that has a major, sudden impact on society or on some aspect of human endeavor.
...
Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen
The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (french: Déclaration des droits de l'homme et du citoyen de 1789, links=no), set by France's National Constituent Assembly in 1789, is a human civil rights document from the French Revol ...
of 1789, Protestants gained equal rights as citizens.Aston, ''Religion and Revolution in France, 1780–1804'' (2000) pp 245–50
Etymology
Besançon Hugues
Besançon Hugues (b. 1487 - d. 1532) was a member of the Grand Council of Geneva and participated in the rebellion against the rule of the Savoy dynasty, which led to the independence of Geneva in 1526.
He was a supporter of Philibert Berthelie ...
(died 1532) and the religiously conflicted nature of Swiss republicanism in his time. It used a derogatory pun
A pun, also known as paronomasia, is a form of word play that exploits multiple meanings of a term, or of similar-sounding words, for an intended humorous or rhetorical effect. These ambiguities can arise from the intentional use of homophoni ...
on the name by way of the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
word (literally 'housemates'), referring to the connotations of a somewhat related word in German ('Confederate' in the sense of 'a citizen of one of the states of the Swiss Confederacy').''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 11th ed, Frank Puaux, ''Huguenot''
Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situa ...
was John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
's adopted home and the centre of the Calvinist movement. In Geneva, Hugues, though Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, was a leader of the "Confederate Party", so called because it favoured independence from the Duke of Savoy
The titles of count, then of duke of Savoy are titles of nobility attached to the historical territory of Savoy. Since its creation, in the 11th century, the county was held by the House of Savoy. The County of Savoy was elevated to a duchy at ...
. It sought an alliance between the city-state of Geneva and the Swiss Confederation. The label ''Huguenot'' was purportedly first applied in France to those conspirators (all of them aristocratic members of the Reformed Church) who were involved in the Amboise plot of 1560: a foiled attempt to wrest power in France from the influential and zealously Catholic House of Guise
The House of Guise (pronunciation: �ɥiz Dutch: ''Wieze, German: Wiese'') was a prominent French noble family, that was involved heavily in the French Wars of Religion. The House of Guise was the founding house of the Principality of Joinvil ...
. This action would have fostered relations with the Swiss.
O. I. A. Roche promoted this idea among historians. He wrote in his book, ''The Days of the Upright, A History of the Huguenots'' (1965), that ''Huguenot'' is:
a combination of a Dutch and a German word. In the Dutch-speaking North of France, Bible students who gathered in each other's houses to study secretly were called ("housemates") while on the Swiss and German borders they were termed , or "oath fellows", that is, persons bound to each other by anSome disagree with such double or triple non-French linguistic origins. Janet Gray argues that for the word to have spread into common use in France, it must have originated there in French. The "Hugues hypothesis" argues that the name was derived by association with Hugues Capet, king of France, who reigned long before the Reformation. He was regarded by the Gallicians as a noble man who respected people's dignity and lives. Janet Gray and other supporters of the hypothesis suggest that the name would be roughly equivalent to 'little Hugos', or 'those who want Hugo'. In this last connection, the name could suggest the derogatory inference of superstitious worship; popular fancy held that , the gate of King Hugo, was haunted by the ghost of (regarded by Roman Catholics as an infamous scoundrel) and other spirits. Instead of being inoath Traditionally an oath (from Anglo-Saxon ', also called plight) is either a statement of fact or a promise taken by a sacrality as a sign of verity. A common legal substitute for those who conscientiously object to making sacred oaths is to g .... Gallicised into , often used deprecatingly, the word became, during two and a half centuries of terror and triumph, a badge of enduring honour and courage.
Purgatory
Purgatory (, borrowed into English via Anglo-Norman and Old French) is, according to the belief of some Christian denominations (mostly Catholic), an intermediate state after physical death for expiatory purification. The process of purgatory ...
after death, according to Catholic doctrine, they came back to harm the living at night.Antoine Dégert, "Huguenots", ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'', 1911 The ('supposedly 'reformed) were said to gather at night at
Tours
Tours ( , ) is one of the largest cities in the region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is the prefecture of the department of Indre-et-Loire. The commune of Tours had 136,463 inhabitants as of 2018 while the population of the whole metro ...
, both for political purposes, and for prayer and singing psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived ...
. Reguier de la Plancha (d. 1560) in his offered the following account as to the origin of the name, as cited by ''The Cape Monthly'':
Reguier de la Plancha accounts for itSome have suggested the name was derived, with similar intended scorn, from (the 'monkeys' or 'apes ofhe name He or HE may refer to: Language * He (pronoun), an English pronoun * He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ * He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets * He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...as follows: "The name was given to those of the religion during the affair of Amboyse, and they were to retain it ever since. I'll say a word about it to settle the doubts of those who have strayed in seeking its origin. The superstition of our ancestors, to within twenty or thirty years thereabouts, was such that in almost all the towns in the kingdom they had a notion that certain spirits underwent their Purgatory in this world after death, and that they went about the town at night, striking and outraging many people whom they found in the streets. But the light of the Gospel has made them vanish, and teaches us that these spirits were street-strollers and ruffians. In Paris the spirit was called ; at Orléans, ; at Blois ; at Tours, ; and so on in other places. Now, it happens that those whom they called Lutherans were at that time so narrowly watched during the day that they were forced to wait till night to assemble, for the purpose of praying God, for preaching and receiving the Holy Sacrament; so that although they did not frighten nor hurt anybody, the priests, through mockery, made them the successors of those spirits which roam the night; and thus that name being quite common in the mouth of the populace, to designate the evangelical in the country of Tourraine and Amboyse, it became in vogue after that enterprise."''De l'Estat de France'' 1560, by Reguier de la Plancha, quoted by ''The Cape Monthly'' (February 1877), No. 82 Vol. XIV on page 126,
Jan Hus
Jan Hus (; ; 1370 – 6 July 1415), sometimes anglicized as John Hus or John Huss, and referred to in historical texts as ''Iohannes Hus'' or ''Johannes Huss'', was a Czech theologian and philosopher who became a Church reformer and the insp ...
'). By 1911, there was still no consensus in the United States on this interpretation.
Symbol
Demographics
Reformed tradition
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Calv ...
in France has been covered in a variety of sources. Most of them agree that the Huguenot population reached as many as 10% of the total population, or roughly 2 million people, on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572.Hans J. Hillerbrand, ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism: 4-volume Set'', paragraphs "France" and "Huguenots"
The new teaching of John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
attracted sizeable portions of the nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The character ...
and urban bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. Th ...
. After John Calvin introduced the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in France, the number of French Protestants steadily swelled to ten percent of the population, or roughly 1.8 million people, in the decade between 1560 and 1570. During the same period there were some 1,400 Reformed churches operating in France. Hans J. Hillerbrand, an expert on the subject, in his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism: 4-volume Set'' claims the Huguenot community reached as much as 10% of the French population on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre, declining to 7 to 8% by the end of the 16th century, and further after heavy persecution began once again with the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without s ...
by Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
in 1685.
Among the nobles, Calvinism peaked on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre. Since then, it sharply decreased as the Huguenots were no longer tolerated by both the French royalty and the Catholic masses. By the end of the sixteenth century, Huguenots constituted 7-8% of the whole population, or 1.2 million people. By the time Louis XIV revoked the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed pr ...
in 1685, Huguenots accounted for 800,000 to 1 million people.
Huguenots controlled sizeable areas in southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and western France. In addition, many areas, especially in the central part of the country, were also contested between the French Reformed and Catholic nobles. Demographically, there were some areas in which the whole populations had been Reformed. These included villages in and around the Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.
Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,0 ...
, as well as the area around Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; oc, Dordonha ) is a large rural department in Southwestern France, with its prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and the Pyrenees, it is named ...
, which used to be almost entirely Reformed too. John Calvin was a Frenchman and himself largely responsible for the introduction and spread of the Reformed tradition in France. He wrote in French, but unlike the Protestant development in Germany, where Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
writings were widely distributed and could be read by the common man, it was not the case in France, where only nobles adopted the new faith and the folk remained Catholic. This is true for many areas in the west and south controlled by the Huguenot nobility. Although relatively large portions of the peasant population became Reformed there, the people, altogether, still remained majority Catholic.
Overall, Huguenot presence was heavily concentrated in the western and southern portions of the French kingdom, as nobles there secured practise of the new faith. These included Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-Roussillon (; oc, Lengadòc-Rosselhon ; ca, Llenguadoc-Rosselló) is a former administrative region of France. On 1 January 2016, it joined with the region of Midi-Pyrénées to become Occitania. It comprised five departments, and b ...
, Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part ...
and even a strip of land that stretched into the Dauphiné
The Dauphiné (, ) is a former province in Southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was originally the Dauphiné of Viennois.
In the 12th centu ...
. Huguenots lived on the Atlantic coast in La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. Wi ...
, and also spread across provinces of Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
and Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
. In the south, towns like Castres, Montauban
Montauban (, ; oc, Montalban ) is a commune in the Tarn-et-Garonne department, region of Occitania, Southern France. It is the capital of the department and lies north of Toulouse. Montauban is the most populated town in Tarn-et-Garonne, ...
, Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people l ...
and Nimes were Huguenot strongholds. In addition, a dense network of Protestant villages permeated the rural mountainous region of the Cevennes. Inhabited by Camisards, it continues to be the backbone of French Protestantism. Historians estimate that roughly 80% of all Huguenots lived in the western and southern areas of France.
Today, there are some Reformed communities around the world that still retain their Huguenot identity. In France, Calvinists in the United Protestant Church of France and also some in the Protestant Reformed Church of Alsace and Lorraine consider themselves Huguenots. A rural Huguenot community in the Cevennes that rebelled in 1702 is still being called '' Camisards'', especially in historical contexts. Huguenot exiles in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, and a number of other countries still retain their identity.
Emigration and diaspora
The bulk of Huguenot émigrés moved to Protestant states such as theDutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
, England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is En ...
, Protestant-controlled Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, the Channel Islands
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, the Electorate of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 square ...
and Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine o ...
in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
, and the Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establish ...
. Some fled as refugees to the Dutch Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie) was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and its successive states that the colony was inco ...
in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, the Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, whic ...
, the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
colonies, and several of the Dutch and English colonies in North America. A few families went to Orthodox Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
and Catholic Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
.
After centuries, most Huguenots have assimilated into the various societies and cultures where they settled. Remnant communities of Camisards in the Cévennes, most Reformed members of the United Protestant Church of France, French members of the largely German Protestant Reformed Church of Alsace and Lorraine, and the Huguenot diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
in England and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, all still retain their beliefs and Huguenot designation.
History
Origins
 The availability of the Bible in
The availability of the Bible in vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
languages was important to the spread of the Protestant movement and development of the Reformed church in France. The country had a long history of struggles with the papacy (see the Avignon Papacy
The Avignon Papacy was the period from 1309 to 1376 during which seven successive popes resided in Avignon – at the time within the Kingdom of Arles, part of the Holy Roman Empire; now part of France – rather than in Rome. The situation a ...
, for example) by the time the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
finally arrived. Around 1294, a French version of the Scriptures was prepared by the Roman Catholic priest, Guyard des Moulins. A two-volume illustrated folio paraphrase version based on his manuscript, by Jean de Rély, was printed in Paris in 1487.
The first known translation of the Bible into one of France's regional languages, Arpitan or Franco-Provençal, had been prepared by the 12th-century pre-Protestant reformer Peter Waldo
Peter Waldo (; c. 1140 – c. 1205; also ''Valdo'', ''Valdes'', ''Waldes''; , ) was the leader of the Waldensians, a Christian spiritual movement of the Middle Ages.
The tradition that his first name was "Peter" can only be traced back to the f ...
(Pierre de Vaux). The Waldensians created fortified areas, as in Cabrières, perhaps attacking an abbey.Malcolm D. Lambert, ''Medieval Heresy: Popular Movements from the Gregorian Reform to the Reformation''p. 389 They were suppressed by
Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
in 1545 in the Massacre of Mérindol
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
.
Other predecessors of the Reformed church included the pro-reform and Gallican Roman Catholics, such as Jacques Lefevre (c. 1455–1536). The Gallicans briefly achieved independence for the French church, on the principle that the religion of France could not be controlled by the Bishop of Rome, a foreign power. During the Protestant Reformation, Lefevre, a professor at the University of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of Arms
, latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis
, motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin)
, mottoeng = Here and a ...
, published his French translation of the New Testament in 1523, followed by the whole Bible in the French language in 1530. William Farel was a student of Lefevre who went on to become a leader of the Swiss Reformation
The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matt ...
, establishing a Protestant republican government in Geneva. Jean Cauvin (John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
), another student at the University of Paris, also converted to Protestantism. Long after the sect was suppressed by Francis I, the remaining French Waldensians
The Waldensians (also known as Waldenses (), Vallenses, Valdesi or Vaudois) are adherents of a church tradition that began as an ascetic movement within Western Christianity before the Reformation.
Originally known as the "Poor Men of Lyon" in ...
, then mostly in the Luberon
The Luberon ( or ; Provençal: ''Leberon'' or ''Leberoun'' ) is a massif in central Provence in Southern France, part of the French Prealps. It has a maximum elevation of and an area of about . It is composed of three mountain ranges (from w ...
region, sought to join Farel, Calvin and the Reformation, and Olivétan published a French Bible for them. The French Confession of 1559 shows a decidedly Calvinistic influence.
Although usually Huguenots are lumped into one group, there were actually two types of Huguenots that emerged. Since the Huguenots had political and religious goals, it was commonplace to refer to the Calvinists as "Huguenots of religion" and those who opposed the monarchy as "Huguenots of the state", who were mostly nobles.
* The Huguenots of religion were influenced by John Calvin's works and established Calvinist synods. They were determined to end religious oppression.
* The Huguenots of the state opposed the monopoly of power the Guise family had and wanted to attack the authority of the crown. This group of Huguenots from southern France had frequent issues with the strict Calvinist tenets that are outlined in many of John Calvin's letters to the synods of the Languedoc.
Criticism and conflict with the Catholic Church
Like other religious reformers of the time, Huguenots felt that the Catholic Church needed a radical cleansing of its impurities, and that the Pope represented a worldly kingdom, which sat in mocking tyranny over the things of God, and was ultimately doomed. Rhetoric like this became fiercer as events unfolded, and eventually stirred up a reaction in the Catholic establishment. Fanatically opposed to the Catholic Church, the Huguenots killed priests, monks, and nuns, attacked monasticism, and destroyed sacred images, relics, and church buildings. Most of the cities in which the Huguenots gained a hold saw iconoclastriot
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people.
Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targete ...
s in which altars and images in churches, and sometimes the buildings themselves torn down. Ancient relics and texts were destroyed; the bodies of saints exhumed and burned. The cities of Bourges, Montauban and Orléans saw substantial activity in this regard.
The Huguenots transformed themselves into a definitive political movement thereafter. Protestant preachers rallied a considerable army and a formidable cavalry, which came under the leadership of Admiral Gaspard de Coligny. Henry of Navarre and the House of Bourbon allied themselves to the Huguenots, adding wealth and territorial holdings to the Protestant strength, which at its height grew to sixty fortified cities, and posed a serious and continuous threat to the Catholic crown and Paris over the next three decades.
The Catholic Church in France and many of its members opposed the Huguenots. Some Huguenot preachers and congregants were attacked as they attempted to meet for worship. The height of this persecution was the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in August, 1572, when 5,000 to 30,000 were killed, although there were also underlying political reasons for this as well, as some of the Huguenots were nobles trying to establish separate centres of power in southern France. Retaliating against the French Catholics, the Huguenots had their own militia.
Reformation and growth
Early in his reign,Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
() persecuted the old, pre-Protestant movement of Waldensians
The Waldensians (also known as Waldenses (), Vallenses, Valdesi or Vaudois) are adherents of a church tradition that began as an ascetic movement within Western Christianity before the Reformation.
Originally known as the "Poor Men of Lyon" in ...
in southeastern France. Francis initially protected the Huguenot dissidents from Parlement
A ''parlement'' (), under the French Ancien Régime, was a provincial appellate court of the Kingdom of France. In 1789, France had 13 parlements, the oldest and most important of which was the Parlement of Paris. While both the modern Fr ...
ary measures seeking to exterminate them. After the 1534 Affair of the Placards
The Affair of the Placards (french: Affaire des Placards) was an incident in which anti-Catholic posters appeared in public places in Paris and in four major provincial cities, Blois, Rouen, Tours and Orléans, in the night of the 17 to 18 October ...
, however, he distanced himself from Huguenots and their protection.
Huguenot numbers grew rapidly between 1555 and 1561, chiefly amongst nobles and city dwellers. During this time, their opponents first dubbed the Protestants ''Huguenots''; but they called themselves , or "Reformed". They organised their first national synod in 1558 in Paris.
By 1562, the estimated number of Huguenots peaked at approximately two million, concentrated mainly in the western, southern, and some central parts of France, compared to approximately sixteen million Catholics during the same period. Persecution diminished the number of Huguenots who remained in France.
Wars of religion
As the Huguenots gained influence and displayed their faith more openly, Roman Catholic hostility towards them grew, even though the French crown offered increasingly liberal political concessions and edicts of toleration. Following the accidental death of Henry II in 1559, his son succeeded as King Francis II along with his wife, the Queen Consort, also known asMary, Queen of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
The only surviving legitimate child of James V of S ...
. During the eighteen months of the reign of Francis II, Mary encouraged a policy of rounding up French Huguenots on charges of heresy and putting them in front of Catholic judges, and employing torture and burning as punishments for dissenters. Mary returned to Scotland a widow, in the summer of 1561.
In 1561, the Edict of Orléans declared an end to the persecution, and the Edict of Saint-Germain of January 1562 formally recognised the Huguenots for the first time. However, these measures disguised the growing tensions between Protestants and Catholics.
Civil wars
 These tensions spurred eight civil wars, interrupted by periods of relative calm, between 1562 and 1598. With each break in peace, the Huguenots' trust in the Catholic throne diminished, and the violence became more severe, and Protestant demands became grander, until a lasting cessation of open hostility finally occurred in 1598. The wars gradually took on a dynastic character, developing into an extended feud between the Houses of Bourbon and Guise, both of which—in addition to holding rival religious views—staked a claim to the French throne. The crown, occupied by the
These tensions spurred eight civil wars, interrupted by periods of relative calm, between 1562 and 1598. With each break in peace, the Huguenots' trust in the Catholic throne diminished, and the violence became more severe, and Protestant demands became grander, until a lasting cessation of open hostility finally occurred in 1598. The wars gradually took on a dynastic character, developing into an extended feud between the Houses of Bourbon and Guise, both of which—in addition to holding rival religious views—staked a claim to the French throne. The crown, occupied by the House of Valois
The Capetian house of Valois ( , also , ) was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. They succeeded the House of Capet (or "Direct Capetians") to the French throne, and were the royal house of France from 1328 to 1589. Junior members of the f ...
, generally supported the Catholic side, but on occasion switched over to the Protestant cause when politically expedient.
 The
The French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholics and Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four mil ...
began with the Massacre of Vassy on 1 March 1562, when dozens (some sources say hundreds) of Huguenots were killed, and about 200 were wounded. It was in this year that some Huguenots destroyed the tomb and remains of Saint Irenaeus
Irenaeus (; grc-gre, Εἰρηναῖος ''Eirēnaios''; c. 130 – c. 202 AD) was a Greek bishop noted for his role in guiding and expanding Christian communities in the southern regions of present-day France and, more widely, for the de ...
(d. 202), an early Church father and bishop who was a disciple of Polycarp
Polycarp (; el, Πολύκαρπος, ''Polýkarpos''; la, Polycarpus; AD 69 155) was a Christian bishop of Smyrna. According to the ''Martyrdom of Polycarp'', he died a martyr, bound and burned at the stake, then stabbed when the fire failed ...
. The Michelade by Huguenotes against Catholics was later on 29 September 1567.
St. Bartholomew's Day massacre
 In what became known as the St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre of 24 August – 3 October 1572, Catholics killed thousands of Huguenots in Paris and similar massacres took place in other towns in the following weeks. The main provincial towns and cities experiencing massacres were
In what became known as the St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre of 24 August – 3 October 1572, Catholics killed thousands of Huguenots in Paris and similar massacres took place in other towns in the following weeks. The main provincial towns and cities experiencing massacres were Aix
Aix or AIX may refer to:
Computing
* AIX, a line of IBM computer operating systems
*An Alternate Index, for a Virtual Storage Access Method Key Sequenced Data Set
* Athens Internet Exchange, a European Internet exchange point
Places Belgiu ...
, Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectu ...
, Bourges
Bourges () is a commune in central France on the river Yèvre. It is the capital of the department of Cher, and also was the capital city of the former province of Berry.
History
The name of the commune derives either from the Bituriges, ...
, Lyons
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of t ...
, Meaux
Meaux () is a Communes of France, commune on the river Marne (river), Marne in the Seine-et-Marne Departments of France, department in the Île-de-France Regions of France, region in the Functional area (France), metropolitan area of Paris, Franc ...
, Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and Rouen Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population ...
, (US) and Rouen Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population ...
Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and fr ...
, and Troyes
Troyes () is a commune and the capital of the department of Aube in the Grand Est region of north-central France. It is located on the Seine river about south-east of Paris. Troyes is situated within the Champagne wine region and is near ...
.
Although the exact number of fatalities throughout the country is not known, on 23–24 August, between 2,000 and 3,000 Protestants were killed in Paris and a further 3,000 to 7,000 more in the French provinces. By 17 September, almost 25,000 Protestants had been massacred in Paris alone.Partner, P. (1999), ''Two Thousand Years: The Second Millennium'', Granda Media (Andre Deutsch), Britain, hardback, pp. ; Beyond Paris, the killings continued until 3 October. An amnesty granted in 1573 pardoned the perpetrators.
Edict of Nantes
 The pattern of warfare, followed by brief periods of peace, continued for nearly another quarter-century. The warfare was definitively quelled in 1598, when Henry of Navarre, having succeeded to the French throne as Henry IV, and having recanted Protestantism in favour of Roman Catholicism in order to obtain the French crown, issued the
The pattern of warfare, followed by brief periods of peace, continued for nearly another quarter-century. The warfare was definitively quelled in 1598, when Henry of Navarre, having succeeded to the French throne as Henry IV, and having recanted Protestantism in favour of Roman Catholicism in order to obtain the French crown, issued the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed pr ...
. The Edict reaffirmed Roman Catholicism as the state religion of France, but granted the Protestants equality with Catholics under the throne and a degree of religious and political freedom within their domains. The Edict simultaneously protected Catholic interests by discouraging the founding of new Protestant churches in Catholic-controlled regions.
With the proclamation of the Edict of Nantes, and the subsequent protection of Huguenot rights, pressures to leave France abated. However, enforcement of the Edict grew increasingly irregular over time, making life so intolerable that many fled the country. The Huguenot population of France dropped to 856,000 by the mid-1660s, of which a plurality lived in rural areas. The greatest concentrations of Huguenots at this time resided in the regions of Guienne
Guyenne or Guienne (, ; oc, Guiana ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of ''Aquitania Secunda'' and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transformation of ...
, Saintonge-Aunis
Aunis () is a historical province of France, situated in the north-west of the department of Charente-Maritime. Its historic capital is La Rochelle, which took over from Castrum Allionis (Châtelaillon) the historic capital which gives its name ...
-Angoumois
Angoumois (), historically the County of Angoulême, was a county and province of France, originally inferior to the parent duchy of Aquitaine, similar to the Périgord to its east but lower and generally less forested, equally with occasional ...
and Poitou
Poitou (, , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical c ...
.
Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people l ...
was among the most important of the 66 ('cities of protection' or 'protected cities') that the Edict of 1598 granted to the Huguenots. The city's political institutions and the university were all handed over to the Huguenots. Tension with Paris led to a siege by the royal army in 1622. Peace terms called for the dismantling of the city's fortifications. A royal citadel was built and the university and consulate were taken over by the Catholic party. Even before the Edict of Alès (1629), Protestant rule was dead and the was no more.
 By 1620, the Huguenots were on the defensive, and the government increasingly applied pressure. A series of three small civil wars known as the
By 1620, the Huguenots were on the defensive, and the government increasingly applied pressure. A series of three small civil wars known as the Huguenot rebellions
The Huguenot rebellions, sometimes called the Rohan Wars after the Huguenot leader Henri de Rohan, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which French Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted agains ...
broke out, mainly in southwestern France, between 1621 and 1629 in which the Reformed areas revolted against royal authority. The uprising occurred a decade following the death of Henry IV, who was assassinated by a Catholic fanatic in 1610. His successor Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
, under the regency of his Italian Catholic mother Marie de' Medici
Marie de' Medici (french: link=no, Marie de Médicis, it, link=no, Maria de' Medici; 26 April 1575 – 3 July 1642) was Queen of France and Navarre as the second wife of King Henry IV of France of the House of Bourbon, and Regent of the Kingdom ...
, was more intolerant of Protestantism. The Huguenots responded by establishing independent political and military structures, establishing diplomatic contacts with foreign powers, and openly revolting against central power. The rebellions were implacably suppressed by the French crown.
Edict of Fontainebleau
Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
inherited the throne in 1643 and acted increasingly aggressively to force the Huguenots to convert. At first he sent missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
, backed by a fund to financially reward converts to Roman Catholicism. Then he imposed penalties, closed Huguenot schools and excluded them from favoured professions. Escalating, he instituted dragonnades
The ''Dragonnades'' were a French government policy instituted by King Louis XIV in 1681 to intimidate Huguenot (Protestant) families into converting to Catholicism. This involved the billeting of ill-disciplined dragoons in Protestant household ...
, which included the occupation and looting of Huguenot homes by military troops, in an effort to forcibly convert them. In 1685, he issued the Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without ...
, revoking the Edict of Nantes and declaring Protestantism illegal.
The revocation forbade Protestant services, required education of children as Catholics, and prohibited emigration. It proved disastrous to the Huguenots and costly for France. It precipitated civil bloodshed, ruined commerce, and resulted in the illegal flight from the country of hundreds of thousands of Protestants, many of whom were intellectuals, doctors and business leaders whose skills were transferred to Britain as well as Holland, Prussia, South Africa and other places they fled to. 4,000 emigrated to the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centu ...
, where they settled, especially in New York, the Delaware River Valley in Eastern Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Virginia. The English authorities welcomed the French refugees, providing money from both government and private agencies to aid their relocation. Those Huguenots who stayed in France were subsequently forcibly converted to Roman Catholicism and were called "new converts".
After this, the Huguenots (with estimates ranging from 200,000 to 1,000,000) fled to Protestant countries: England, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Norway, Denmark, and Prussia—whose Calvinist Great Elector Frederick William welcomed them to help rebuild his war-ravaged and underpopulated country. Following this exodus, Huguenots remained in large numbers in only one region of France: the rugged Cévennes region in the south. There were also some Calvinists in the Alsace region, which then belonged to the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. In the early 18th century, a regional group known as the Camisards (who were Huguenots of the mountainous Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.
Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,0 ...
region) rioted against the Catholic Church, burning churches and killing the clergy. It took French troops years to hunt down and destroy all the bands of Camisards, between 1702 and 1709.
End of persecution
 By the 1760s Protestantism was no longer a favourite religion of the elite. By then, most Protestants were Cévennes peasants. It was still illegal, and, although the law was seldom enforced, it could be a threat or a nuisance to Protestants. Calvinists lived primarily in the
By the 1760s Protestantism was no longer a favourite religion of the elite. By then, most Protestants were Cévennes peasants. It was still illegal, and, although the law was seldom enforced, it could be a threat or a nuisance to Protestants. Calvinists lived primarily in the Midi
MIDI (; Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and ...
; about 200,000 Lutherans accompanied by some Calvinists lived in the newly acquired Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
, where the 1648 Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought ...
effectively protected them.
Persecution of Protestants diminished in France after 1724, finally ending with the Edict of Versailles
The Edict of Versailles, also known as the Edict of Tolerance, was an official act that gave non-Catholics in France the access to civil rights formerly denied to them, which included the right to contract marriages without having to convert to t ...
, commonly called the Edict of Tolerance
An edict of toleration is a declaration, made by a government or ruler, and states that members of a given religion will not be persecuted for engaging in their religious practices and traditions. The edict implies tacit acceptance of the religion ...
, signed by Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
in 1787. Two years later, with the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen of 1789
The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (french: Déclaration des droits de l'homme et du citoyen de 1789, links=no), set by France's National Constituent Assembly in 1789, is a human civil rights document from the French Revolu ...
, Protestants gained equal rights as citizens.
Right of return to France in the 19th and 20th centuries
The government encouraged descendants of exiles to return, offering them French citizenship in a 15 December 1790 law:All persons born in a foreign country and descending in any degree of a French man or woman expatriated for religious reason are declared French nationals () and will benefit from rights attached to that quality if they come back to France, establish their domicile there and take the civic oath.Article 4 of 26 June 1889 Nationality Law stated: "Descendants of families proscribed by the revocation of the Edict of Nantes will continue to benefit from the benefit of 15 December 1790 Law, but on the condition that a nominal decree should be issued for every petitioner. That decree will only produce its effects for the future." Foreign descendants of Huguenots lost the automatic right to French citizenship in 1945 (by force of the , which revoked the 1889 Nationality Law). It states in article 3: "This application does not, however, affect the validity of past acts by the person or rights acquired by third parties on the basis of previous laws."
Modern times
In the 1920s and 1930s, members of the extreme-right movement expressed strong animus against Huguenots and otherProtestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
in general, as well as against Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and Freemasons
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
. They were regarded as groups supporting the French Republic, which sought to overthrow.
In World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Huguenots led by in the village of in helped save many Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
. They hid them in secret places or helped them get out of Vichy
Vichy (, ; ; oc, Vichèi, link=no, ) is a city in the Allier department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of central France, in the historic province of Bourbonnais.
It is a spa and resort town and in World War II was the capital of ...
France. André Trocmé preached against discrimination as the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
were gaining power in neighbouring Germany and urged his Protestant Huguenot congregation to hide Jewish refugees from the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europ ...
.
In the early 21st century, there were approximately one million Protestants in France, representing some 2% of its population. Most are concentrated in Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
in northeast France and the mountain region in the south, who still regard themselves as Huguenots to this day. Surveys suggest that Protestantism has grown in recent years, though this is due primarily to the expansion of evangelical Protestant
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "born again", in which an individual exper ...
churches which particularly have adherents among immigrant groups that are generally considered distinct from the French Huguenot population.
A diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
of French Australians
French Australians (french: link=no, Australiens d'origine française), some of whom refer to themselves as Huguenots, are Australian citizens or residents of French ancestry, or French-born people who reside in Australia. According to the 201 ...
still considers itself Huguenot, even after centuries of exile. Long integrated into Australian society, it is encouraged by the Huguenot Society of Australia to embrace and conserve its cultural heritage, aided by the Society's genealogical research services.
In the United States there are several Huguenot worship groups and societies. The Huguenot Society of America has headquarters in New York City and has a broad national membership. One of the most active Huguenot groups is in Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina, the county seat of Charleston County, and the principal city in the Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint o ...
. While many American Huguenot groups worship in borrowed churches, the congregation in Charleston has its own church. Although services are conducted largely in English, every year the church holds an Annual French Service, which is conducted entirely in French using an adaptation of the Liturgies of Neufchatel (1737) and Vallangin (1772). Typically the Annual French Service takes place on the first or second Sunday after Easter in commemoration of the signing of the Edict of Nantes.
Exodus
Most French Huguenots were either unable or unwilling to emigrate to avoid forced conversion to Roman Catholicism.Early emigration to colonies
The first Huguenots to leave France sought freedom from persecution in Switzerland and the Netherlands. A group of Huguenots was part of the French colonisers who arrived in Brazil in 1555 to found . A couple of ships with around 500 people arrived at the Guanabara Bay, present-dayRio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, and settled on a small island. A fort, named Fort Coligny, was built to protect them from attack from the Portuguese troops and Brazilian natives. It was an attempt to establish a French colony in South America. The fort was destroyed in 1560 by the Portuguese, who captured some of the Huguenots. The Portuguese threatened their Protestant prisoners with death if they did not convert to Roman Catholicism. The Huguenots of Guanabara, as they are now known, produced what is known as the Guanabara Confession of Faith
The Guanabara Confession of Faith was a Calvinist creed from 1558. The first Protestant writing in Brazil, and in all of the Americas, it was written by the French Huguenots Jean du Bourdel, Matthieu Verneuil, Pierre Bourdon and André la Fon, who ...
to explain their beliefs. The Portuguese executed them.
South Africa
Individual Huguenots settled at theCape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is ...
from as early as 1671; the first documented was the wagonmaker François Vilion (Viljoen
Viljoen is an Afrikaans surname, derived from the French ''Villion''. It was brought to South Africa in 1671 by French Huguenots who subsequently intermarried with the local Dutch population.
The progenitors of the extended Viljoen clan are Fran� ...
). The first Huguenot to arrive at the Cape of Good Hope was Maria de la Quellerie
Maria van Riebeeck (née de la Queillerie; 28 October 1629 – 2 November 1664) was a French Huguenot who was the first wife of Jan van Riebeeck, the Dutch colonial administrator and first commander of the settlement at the Cape.
Life
She w ...
, wife of commander Jan van Riebeeck
Johan Anthoniszoon "Jan" van Riebeeck (21 April 1619 – 18 January 1677) was a Dutch navigator and colonial administrator of the Dutch East India Company.
Life
Early life
Jan van Riebeeck was born in Culemborg, as the son of a surgeon. ...
(and daughter of a Walloon church minister), who arrived on 6 April 1652 to establish a settlement at what is today Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. The couple left for Batavia ten years later.
But it was not until 31 December 1687 that the first organised group of Huguenots set sail from the Netherlands to the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
post at the Cape of Good Hope. The largest portion of the Huguenots to settle in the Cape arrived between 1688 and 1689 in seven ships as part of the organised migration, but quite a few arrived as late as 1700; thereafter, the numbers declined and only small groups arrived at a time.
 Many of these settlers were given land in an area that was later called (
Many of these settlers were given land in an area that was later called (Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
for 'French Corner'), in the present-day Western Cape
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , and the third most populous, with an estimated 7 million inhabitants in 202 ...
province of South Africa. A large monument to commemorate the arrival of the Huguenots in South Africa was inaugurated on 7 April 1948 at Franschhoek. The Huguenot Memorial Museum was also erected there and opened in 1957.
The official policy of the Dutch East India governors was to integrate the Huguenot and the Dutch communities. When Paul Roux, a pastor who arrived with the main group of Huguenots, died in 1724, the Dutch administration, as a special concession, permitted another French cleric to take his place "for the benefit of the elderly who spoke only French". But with assimilation
Assimilation may refer to:
Culture
* Cultural assimilation, the process whereby a minority group gradually adapts to the customs and attitudes of the prevailing culture and customs
** Language shift, also known as language assimilation, the prog ...
, within three generations the Huguenots had generally adopted Dutch as their first and home language.
Many of the farms in the Western Cape province in South Africa still bear French names. Many families, today, mostly Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gr ...
-speaking, have surnames indicating their French Huguenot ancestry. Examples include: Blignaut, Cilliers, Cronje (Cronier), de Klerk (Le Clercq), de Villiers de Villiers is a common French language, French and Afrikaans surname. It may refer to:
*De Villiers (playwright) (c. 1600–1681), French playwright and actor
*AB de Villiers, a former South Africa national cricket team, South African international ...
, du Plessis, Du Preez (Des Pres), du Randt (Durand), du Toit, Duvenhage (Du Vinage), Franck, Fouché, Fourie (Fleurit), Gervais, Giliomee (Guilliaume), Gous/Gouws (Gauch), Hugo, Jordaan (Jourdan), Joubert
Joubert is a French surname. It is a regional variant form of Jaubert, originating in the centre west and centre south of France.Albert Dauzat (Foreword by Marie-Thérèse Morlet), ''Noms et prénoms de France'', éditions Larousse 1980. p. 346b. ...
, Kriek, Labuschagne (la Buscagne), le Roux, Lombard, Malan, Malherbe, Marais, Maree, Minnaar (Mesnard), Nel (Nell), Naudé, Nortjé (Nortier), Pienaar Pienaar is a well-known Afrikaans surname, derived from the French '' Pinard''. It was brought to South Africa in 1688 by Huguenot settlers traveling with the Dutch East India Company. The extended progenitors of the Pienaar clan are Jacques Pinard ...
(Pinard), Retief (Retif), Roux, Rossouw (Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
), Taljaard (Taillard), TerBlanche, Theron, Viljoen
Viljoen is an Afrikaans surname, derived from the French ''Villion''. It was brought to South Africa in 1671 by French Huguenots who subsequently intermarried with the local Dutch population.
The progenitors of the extended Viljoen clan are Fran� ...
(Vilion) and Visagie (Visage). The wine industry in South Africa owes a significant debt to the Huguenots, some of whom had vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyard ...
s in France, or were brandy distillers, and used their skills in their new home.
North America
 French Huguenots made two attempts to establish a haven in North America. In 1562, naval officer
French Huguenots made two attempts to establish a haven in North America. In 1562, naval officer Jean Ribault
Jean Ribault (also spelled ''Ribaut'') (1520 – October 12, 1565) was a French naval officer, navigator, and a colonizer of what would become the southeastern United States. He was a major figure in the French attempts to colonize Florida. A ...
led an expedition that explored Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
and the present-day Southeastern US, and founded the outpost of Charlesfort on Parris Island, South Carolina
Parris Island is a district of the city of Port Royal, South Carolina on an island of the same name. It became part of the city with the annexation of the Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island on October 11, 2002. For statistical purposes, the ...
. The French Wars of Religion precluded a return voyage, and the outpost was abandoned. In 1564, Ribault's former lieutenant René Goulaine de Laudonnière launched a second voyage to build a colony; he established Fort Caroline
Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June, 1564, follow ...
in what is now Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the seat of Duval County, with which th ...
. War at home again precluded a resupply mission, and the colony struggled. In 1565 the Spanish decided to enforce their claim to , and sent Pedro Menéndez de Avilés
Pedro Menéndez de Avilés (; ast, Pedro (Menéndez) d'Avilés; 15 February 1519 – 17 September 1574) was a Spanish admiral, explorer and conquistador from Avilés, in Asturias, Spain. He is notable for planning the first regular trans-ocean ...
, who established the settlement of St. Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
near Fort Caroline. Menéndez' forces routed the French and executed most of the Protestant captives.
 Barred by the government from settling in
Barred by the government from settling in New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
, Huguenots led by Jessé de Forest Jessé de Forest (1576 – October 22, 1624) was the leader of a group of Walloon Huguenots who fled Europe due to religious persecutions. They emigrated to the New World, where he planned to found New-Amsterdam, which is currently New York Ci ...
, sailed to North America in 1624 and settled instead in the Dutch colony of New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva ...
(later incorporated into New York and New Jersey); as well as Great Britain's colonies, including Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
. A number of New Amsterdam's families were of Huguenot origin, often having immigrated as refugees to the Netherlands in the previous century. In 1628 the Huguenots established a congregation as (the French church in New Amsterdam). This parish continues today as , now a part of the Episcopal Church (Anglican) communion, and welcomes Francophone New Yorkers from all over the world. Upon their arrival in New Amsterdam, Huguenots were offered land directly across from Manhattan on Long Island for a permanent settlement and chose the harbour at the end of Newtown Creek
Newtown Creek, a long tributary of the East River, is an estuary that forms part of the border between the boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens, in New York City. Channelization made it one of the most heavily-used bodies of water in the Port of N ...
, becoming the first Europeans to live in Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
, then known as Boschwick, in the neighbourhood now known as Bushwick
Bushwick is a neighborhood in the northern part of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. It is bounded by the neighborhood of Ridgewood, Queens, to the northeast; Williamsburg to the northwest; East New York and the cemeteries of Highland Pa ...
.
 Huguenot immigrants did not disperse or settle in different parts of the country, but rather, formed three societies or congregations; one in the city of New York, another 21 miles north of New York in a town which they named
Huguenot immigrants did not disperse or settle in different parts of the country, but rather, formed three societies or congregations; one in the city of New York, another 21 miles north of New York in a town which they named New Rochelle
New Rochelle (; older french: La Nouvelle-Rochelle) is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States, in the southeastern portion of the state. In 2020, the city had a population of 79,726, making it the seventh-largest in the state o ...
, and a third further upstate in New Paltz
New Paltz () is an incorporated U.S. town in Ulster County, New York. The population was 14,003 at the 2010 U.S. Census. The town is located in the southeastern part of the county and is south of Kingston. New Paltz contains a village, also wit ...
. The "Huguenot Street Historic District
Historic Huguenot Street is located in New Paltz, New York, approximately north of New York City. The seven stone houses and several accompanying structures in the 10-acre National Landmark Historic District were likely built in the early 18th c ...
" in New Paltz has been designated a National Historic Landmark site and contains one of the oldest streets in the United States of America. A small group of Huguenots also settled on the south shore of Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey b ...
along the New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in ...
, for which the current neighbourhood of Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
was named. Huguenot refugees also settled in the Delaware River Valley of Eastern Pennsylvania and Hunterdon County, New Jersey in 1725. Frenchtown in New Jersey bears the mark of early settlers.
New Rochelle
New Rochelle (; older french: La Nouvelle-Rochelle) is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States, in the southeastern portion of the state. In 2020, the city had a population of 79,726, making it the seventh-largest in the state o ...
, located in the county of Westchester on the north shore of Long Island Sound
Long Island Sound is a marine sound and tidal estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It lies predominantly between the U.S. state of Connecticut to the north and Long Island in New York to the south. From west to east, the sound stretches from the Eas ...
, seemed to be the great location of the Huguenots in New York. It is said that they landed on the coastline peninsula of Davenports Neck called "Bauffet's Point" after travelling from England where they had previously taken refuge on account of religious persecution, four years before the revocation of the Edict of Nantes. They purchased from John Pell, Lord of Pelham Manor
Pelham Manor is an affluent village located in Westchester County, New York. As of the 2020 census, the village had a total population of 5,752. It is located in the town of Pelham.
History
The Bolton Priory, Edgewood House, and Pelhamdale are ...
, a tract of land consisting of six thousand one hundred acres with the help of Jacob Leisler
Jacob Leisler ( – May 16, 1691) was a German-born colonist who served as a politician in the Province of New York. He gained wealth in New Amsterdam (later New York City) in the fur trade and tobacco business. In what became known as Leisler ...
. It was named New Rochelle after La Rochelle, their former strong-hold in France. A small wooden church was first erected in the community, followed by a second church that was built of stone. Previous to the erection of it, the strong men would often walk twenty-three miles on Saturday evening, the distance by the road from New Rochelle to New York, to attend the Sunday service. The church was eventually replaced by a third, Trinity-St. Paul's Episcopal Church, which contains heirlooms including the original bell from the French Huguenot Church on Pine Street in New York City, which is preserved as a relic in the tower room. The Huguenot cemetery, or the "Huguenot Burial Ground", has since been recognised as a historic cemetery that is the final resting place for a wide range of the Huguenot founders, early settlers and prominent citizens dating back more than three centuries.
Some Huguenot immigrants settled in central and eastern Pennsylvania. They assimilated with the predominantly Pennsylvania German
The Pennsylvania Dutch ( Pennsylvania Dutch: ), also known as Pennsylvania Germans, are a cultural group formed by German immigrants who settled in Pennsylvania during the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. They emigrated primarily from German-spe ...
settlers of the area.
In 1700 several hundred French Huguenots migrated from England to the colony of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, where the King William III of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic f ...
had promised them land grants in Lower Norfolk County Lower Norfolk County is a long-extinct county which was organized in colonial Virginia, operating from 1637 until 1691.
New Norfolk County was formed in 1636 from Elizabeth City Shire, one of the eight original shires (or counties) formed in 1634 ...
. When they arrived, colonial authorities offered them instead land 20 miles above the falls of the James River, at the abandoned Monacan village known as Manakin Town, now in Goochland County
Goochland County is a county located in the Piedmont of the Commonwealth of Virginia. Its southern border is formed by the James River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 24,727. Its county seat is Goochland.
Goochland County is inc ...
. Some settlers landed in present-day Chesterfield County. On 12 May 1705, the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, the first elected legislative assembly in the New World, and was established on July 30, 16 ...
passed an act to naturalise the 148 Huguenots still resident at Manakintown. Of the original 390 settlers in the isolated settlement, many had died; others lived outside town on farms in the English style; and others moved to different areas. Gradually they intermarried with their English neighbours. Through the 18th and 19th centuries, descendants of the French migrated west into the Piedmont, and across the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
into the West of what became Kentucky, Tennessee, Missouri, and other states. In the Manakintown area, the Huguenot Memorial Bridge
Huguenot Memorial Bridge is located in Henrico County and the independent city of Richmond, Virginia. It carries State Route 147 across the former Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (now the James River Line of CSX Transportation), the James River and K ...
across the James River
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 to Chesap ...
and Huguenot Road were named in their honour, as were many local features, including several schools, including Huguenot High School
Huguenot High School, part of the Richmond Public Schools system, is a high school located in Richmond, Virginia, United States, with grades 9–12.
Huguenot High School was named in honor of the Huguenots, French Protestants who emigrated to ...
.
 In the early years, many Huguenots also settled in the area of present-day
In the early years, many Huguenots also settled in the area of present-day Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina, the county seat of Charleston County, and the principal city in the Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint o ...
. In 1685, Rev. Elie Prioleau from the town of Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
in France, was among the first to settle there. He became pastor of the first Huguenot church in North America in that city. After the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed pr ...
in 1685, several Huguenots including Edmund Bohun of Suffolk, England, Pierre Bacot
Pierre Bacot (1671–1730) was a prominent French Huguenot planter in colonial South Carolina.
Biography
Born in Tours, France, Pierre was the son of Pierre Bacot (1637-1702) and Jacquine Mercier (1649-1709), and grandson of Pierre Bacot (1597 ...
of Touraine France, Jean Postell of Dieppe France, Alexander Pepin
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
, Antoine Poitevin of Orsement France, and Jacques de Bordeaux of Grenoble, immigrated to the Charleston Orange district. They were very successful at marriage and property speculation. After petitioning the British Crown in 1697 for the right to own land in the Baronies, they prospered as slave owners on the Cooper, Ashepoo, Ashley and Santee River plantations they purchased from the British Landgrave Edmund Bellinger. Some of their descendants moved into the Deep South and Texas, where they developed new plantations.
The French Huguenot Church
The Huguenot Church, also called the French Huguenot Church or the French Protestant Church, is a Gothic Revival church located at 136 Church Street in Charleston, South Carolina. Built in 1844 and designed by architect Edward Brickell White, ...
of Charleston, which remains independent, is the oldest continuously active Huguenot congregation in the United States. in New York, founded in 1628, is older, but it left the French Reformed movement in 1804 to become part of the Episcopal Church.
Most of the Huguenot congregations (or individuals) in North America eventually affiliated with other Protestant denominations with more numerous members. The Huguenots adapted quickly and often married outside their immediate French communities, which led to their assimilation. Their descendants in many families continued to use French first names and surnames for their children well into the nineteenth century. Assimilated, the French made numerous contributions to United States economic life, especially as merchants and artisans in the late Colonial and early Federal periods. For example, E.I. du Pont EI or Ei may refer to:
Arts and media
* "E.I." (song), a single by Nelly
* E/I, a type of children's television programming shown in the United States
* ''Ei'' (album), an album by Maija Vilkkumaa
** "Ei" (song), its first single
* ''Eerie, Ind ...
, a former student of Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS ( Eleutherian gunpowder mills.
 As a major Protestant nation, England patronised and helped protect Huguenots, starting with
As a major Protestant nation, England patronised and helped protect Huguenots, starting with
 Following the French crown's revocation of the
Following the French crown's revocation of the
 Around 1685, Huguenot refugees found a safe haven in the Lutheran and Reformed states in Germany and Scandinavia. Nearly 50,000 Huguenots established themselves in Germany, 20,000 of whom were welcomed in
Around 1685, Huguenot refugees found a safe haven in the Lutheran and Reformed states in Germany and Scandinavia. Nearly 50,000 Huguenots established themselves in Germany, 20,000 of whom were welcomed in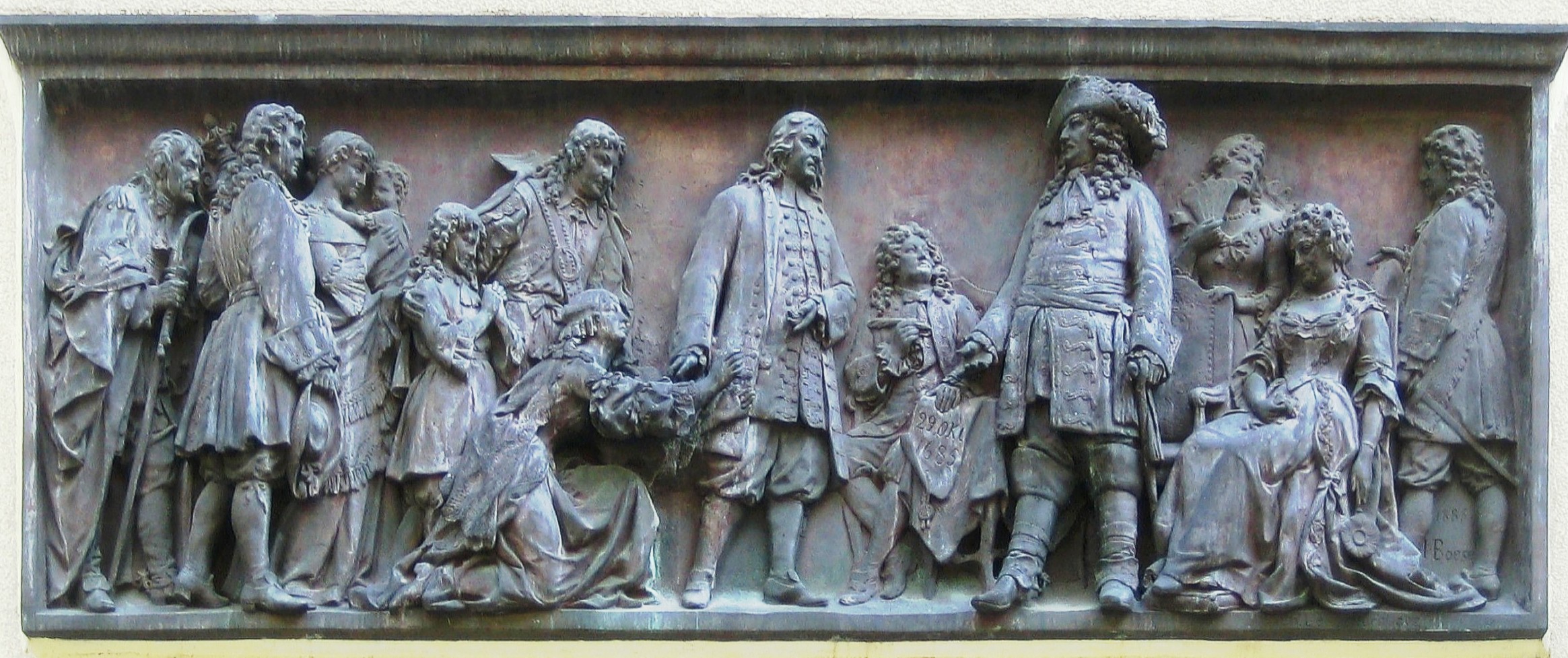  In Berlin the Huguenots created two new neighbourhoods:
In Berlin the Huguenots created two new neighbourhoods:
 In October 1985, to commemorate the tricentenary of the
In October 1985, to commemorate the tricentenary of the
excerpt and text search
* Gilman, C. Malcolm. ''The Huguenot Migration in Europe and America, its Cause and Effect'' (1962) * Glozier, Matthew and David Onnekink, eds. ''War, Religion and Service. Huguenot Soldiering, 1685–1713'' (2007) * Glozier, Matthew ''The Huguenot soldiers of William of Orange and the Glorious Revolution of 1688: the lions of Judah'' (Brighton, 2002) * Gwynn, Robin D. ''Huguenot Heritage: The History and Contribution of the Huguenots in England'' (Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1985). * Kamil, Neil. ''Fortress of the Soul: Violence, Metaphysics, and Material Life in the Huguenots' New World, 1517–1751'' Johns Hopkins U. Press, 2005. 1058 pp. * Lachenicht, Susanne. "Huguenot Immigrants and the Formation of National Identities, 1548–1787", ''Historical Journal'' 2007 50(2): 309–331, * Lotz-Heumann, Ute
''Confessional Migration of the Reformed: The Huguenots''
excerpt and text search
* Murdoch, Tessa, and Randolph Vigne. The '' French Hospital in England: Its Huguenot History and Collections'' Cambridge: John Adamson, 2009 * Ruymbeke, Bertrand Van. ''New Babylon to Eden: The Huguenots and Their Migration to Colonial South Carolina.'' U. of South Carolina Press, 2006. 396 pp * Scoville, Warren Candler. ''The persecution of Huguenots and French economic development, 1680-1720'' (U of California Press, 1960). * Scoville, Warren C. "The Huguenots and the diffusion of technology. I." ''Journal of political economy'' 60.4 (1952): 294–311
part I online
Part2: Vol. 60, No. 5 (Oct., 1952), pp. 392–41
online part 2
* Soman, Alfred. ''The Massacre of St. Bartholomew: Reappraisals and Documents'' (The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff, 1974) * Treasure, G. R. R. ''Seventeenth Century France'' (2nd ed., 1981) pp. 371–96. * VanRuymbeke, Bertrand and Sparks, Randy J., eds. ''Memory and Identity: The Huguenots in France and the Atlantic Diaspora'', U. of South Carolina Press, 2003. 352 pp. * Wijsenbeek, Thera. "Identity Lost: Huguenot Refugees in the Dutch Republic and its Former Colonies in North America and South Africa, 1650 To 1750: A Comparison", ''South African Historical Journal'' 2007 (59): 79–102 * Wolfe, Michael. ''The Conversion of Henri IV: Politics, Power, and Religious Belief in Early Modern France'' (1993).
The Huguenot Library
at
Historic Huguenot Street
Huguenot Fellowship
The Huguenot Society of Australia
Library for Huguenot History, Germany
The National Huguenot Society
The Huguenot Society of America
Huguenot Society of Great Britain & Ireland
Huguenots of Spitalfields
''Huguenots and Jews of the Languedoc''
About the inhabitants of Southern France and how they came to be called French Protestants
''Early Prayer Books of America: Being a Descriptive Account of Prayer Books Published in the United States, Mexico and Canada''
by Rev. John Wright, D.D. St Paul, MN: Privately Printed, 1898. Pages 188 to 210 are entitled "The Prayer Book of the French Protestants, Charleston, South Carolina." (597 pdfs)
''The French Protestant (Huguenot) Church in the city of Charleston, South Carolina''
Includes history, text of memorial tablets, and the rules adopted in 1869. (1898, 40 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de célébrer le service Divin; Qui est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin''
(1713, 160 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de célébrer le service Divin; Qui est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin''
Revised and corrected second edition. (1737, 302 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de Célébrer le Service Divin, Comme elle est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin. Nouvelle édition, Augmentée de quelques Prieres, Collectes & Cantiques''
(1772, 256 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de Célébrer le Service Divin, qui est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin. Cinquieme édition, revue, corrigée & augmentée''
(1799, 232 pdfs)
''La Liturgie, ou La Manière de Célébrer le Service Divin, dans le églises du Canton de Vaud''
(1807, 120 pdfs)
''The Liturgy of the French Protestant Church, Translated from the Editions of 1737 and 1772, Published at Neufchatel, with Additional Prayers, Carefully Selected, and Some Alterations: Arranged for the Use of the Congregation in the City of Charleston, S. C.''
Charleston, SC: James S. Burgess, 1835. (205 pdfs)
''The Liturgy of the French Protestant Church, Translated from the Editions of 1737 and 1772, Published at Neufchatel, with Additional Prayers Carefully Selected, and Some Alterations. Arranged for the Use of the Congregation in the City of Charleston, S. C.''
New York, NY: Charles M. Cornwell, Steam Printer, 1869. (186 pdfs) * ''The Liturgy, or Forms of Divine Service, of the French Protestant Church, of Charleston, S. C., Translated from the Liturgy of the Churches of Neufchatel and Vallangin: editions of 1737 and 1772. With Some Additional Prayers, Carefully Selected. The Whole Adapted to Public Worship in the United States of America.'' Third edition. New York, NY: Anson D. F. Randolph & Company, 1853. 228 pp
Google Books
and th
Internet Archive
Available also fro
Making of America Books
as a DLXS file or in hardcover.
''The Liturgy Used in the Churches of the Principality of Neufchatel: with a Letter from the Learned Dr. Jablonski, Concerning the Nature of Liturgies: To which is Added, The Form of Prayer lately introduced into the Church of Geneva''
(1712, 143 pdfs)
Manifesto, (or Declaration of Principles), of the French Protestant Church of London, Founded by Charter of Edward VI. 24 July, A.D. 1550.
By Order of the Consistory. London, England: Messrs. Seeleys, 1850.
''Preamble and rules for the government of the French Protestant Church of Charleston: adopted at meetings of the corporation held on the 12th and the 19th of November, 1843''
(1845, 26 pdfs)
''Synodicon in Gallia Reformata: or, the Acts, Decisions, Decrees, and Canons of those Famous National Councils of the Reformed Churches in France''
by John Quick. Volume 1 of 2. (1692, 693 pdfs)
Synodicon in Gallia Reformata: or, the Acts, Decisions, Decrees, and Canons of those Famous National Councils of the Reformed Churches in France
by John Quick. Volume 2 of 2. (1692, 615 pdfs) * {{Authority control Anti-Catholicism in France Ethnoreligious groups French diaspora French Wars of Religion Huguenot history in France Religion in the Ancien Régime
CNRS ( Eleutherian gunpowder mills.
Howard Hughes
Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American business magnate, record-setting pilot, engineer, film producer, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most influential and richest people in t ...
, famed investor, pilot, film director, and philanthropist, was also of Huguenot descent and descendant from Rev. John Gano.
Paul Revere
Paul Revere (; December 21, 1734 O.S. (January 1, 1735 N.S.)May 10, 1818) was an American silversmith, engraver, early industrialist, Sons of Liberty member, and Patriot and Founding Father. He is best known for his midnight ride to a ...
was descended from Huguenot refugees, as was Henry Laurens, who signed the Articles of Confederation for South Carolina; Jack Jouett
John Jouett Jr. (December 7, 1754 – March 1, 1822) was an American farmer and politician in Virginia and Kentucky best known for his ride during the American Revolution. Sometimes called the "Paul Revere of the South", Jouett rode to warn Tho ...
, who made the ride from Cuckoo Tavern to warn Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
and others that Tarleton and his men were on their way to arrest him for crimes against the king; Reverend John Gano was a Revolutionary War chaplain and spiritual advisor to George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
; Francis Marion
Brigadier-General Francis Marion ( 1732 – February 27, 1795), also known as the Swamp Fox, was an American military officer, planter and politician who served during the French and Indian War and the Revolutionary War. During the Amer ...
, and a number of other leaders of the American Revolution and later statesmen. The last active Huguenot congregation in North America worships in Charleston, South Carolina, at a church that dates to 1844. The Huguenot Society of America maintains the Manakin Episcopal Church
The manakins are a Family (biology), family, Pipridae, of small Tyranni, suboscine passerine birds. The group contains some 54 species distributed through the American tropics. The name is from Middle Dutch ''mannekijn'' "little man" (also the so ...
in Virginia as a historic shrine with occasional services. The Society has chapters in numerous states, with the one in Texas being the largest.
After the British Conquest of New France
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, ...
, British authorities in Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec ...
tried to encourage Huguenot immigration in an attempt to promote a Francophone Protestant Church in the region, hoping that French-speaking Protestants would be more loyal clergy than those of Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. While a small amount of Huguenots did come, the majority switched from speaking French to English. As a result Protestants are still a religious minority in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
today.
Spoken language
The Huguenots originally spoke French on their arrival in the American colonies, but after two or three generations, they had switched to English. They did not promote French-language schools or publications and "lost" their historic identity. In upstate New York they merged with the Dutch Reformed community and switched first to Dutch and then in the early 19th century to English. In colonial New York city they switched from French to English or Dutch by 1730.Netherlands
Some Huguenots fought in the Low Countries alongside the Dutch against Spain during the first years of theDutch Revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Ref ...
(1568–1609). The Dutch Republic rapidly became a destination for Huguenot exiles. Early ties were already visible in the of William the Silent
William the Silent (24 April 153310 July 1584), also known as William the Taciturn (translated from nl, Willem de Zwijger), or, more commonly in the Netherlands, William of Orange ( nl, Willem van Oranje), was the main leader of the Dutch Re ...
, condemning the Spanish Inquisition, which was written by his court minister, the Huguenot Pierre L'Oyseleur, lord of Villiers. Louise de Coligny
Louise de Coligny (23 September 1555 – 9 November 1620) was a Princess consort of Orange as the fourth and last spouse of William the Silent. She was the daughter of Gaspard II de Coligny and Charlotte de Laval.
Biography
Louise was born at ...
, daughter of the murdered Huguenot leader Gaspard de Coligny, married William the Silent, leader of the Dutch (Calvinist) revolt against Spanish (Catholic) rule. As both spoke French in daily life, their court church in the Prinsenhof
The Prinsenhof ("The Court of the Prince") in the city of Delft in the Netherlands is an urban palace built in the Middle Ages as a monastery. Later it served as a residence for William the Silent. William was assassinated in the Prinsenhof by B ...
in Delft
Delft () is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. It is located between Rotterdam, to the southeast, and The Hague, to the northwest. Together with them, it is part of both the Rotterdam–The Hague metropolita ...
held services in French. The practice has continued to the present day. The Prinsenhof is one of the 14 active Walloon churches of the Dutch Reformed Church
The Dutch Reformed Church (, abbreviated NHK) was the largest Christian denomination in the Netherlands from the onset of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century until 1930. It was the original denomination of the Dutch Royal Family and ...
(now of the Protestant Church in the Netherlands
The Protestant Church in the Netherlands ( nl, de Protestantse Kerk in Nederland, abbreviated PKN) is the largest Protestant denomination in the Netherlands, being both Calvinist and Lutheran.
It was founded on 1 May 2004 as the merger of the ...
). The ties between Huguenots and the Dutch Republic's military and political leadership, the House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau ( Dutch: ''Huis van Oranje-Nassau'', ) is the current reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the politics and government of the Netherland ...
, which existed since the early days of the Dutch Revolt, helped support the many early settlements of Huguenots in the Dutch Republic's colonies. They settled at the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is ...
in South Africa and New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva ...
in North America.
Stadtholder William III of Orange
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from ...
, who later became King of England, emerged as the strongest opponent of king Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Ver ...
after the French attacked the Dutch Republic in 1672. William formed the League of Augsburg
The Grand Alliance was the anti-French coalition formed on 20 December 1689 between the Dutch Republic, England and the Holy Roman Empire. It was signed by the two leading opponents of France: William III, Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic and ( ...
as a coalition to oppose Louis and the French state. Consequently, many Huguenots considered the wealthy and Calvinist-controlled Dutch Republic, which also happened to lead the opposition to Louis XIV, as the most attractive country for exile after the revocation of the Edict of Nantes. They also found many French-speaking Calvinist churches there (which were called the " Walloon churches").
After the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685, the Dutch Republic received the largest group of Huguenot refugees, an estimated total of 75,000 to 100,000 people. Amongst them were 200 pastors. Most came from northern France (Brittany, Normandy, and Picardy, as well as West Flanders (subsequently French Flanders), which had been annexed from the Southern Netherlands by Louis XIV in 1668-78). Many came from the region of the Cévennes, for instance, the village of Fraissinet-de-Lozère. This was a huge influx as the entire population of the Dutch Republic amounted to at that time. Around 1700, it is estimated that nearly 25% of the Amsterdam population was Huguenot. In 1705, Amsterdam and the area of West Frisia were the first areas to provide full citizens rights to Huguenot immigrants, followed by the whole Dutch Republic in 1715. Huguenots intermarried with Dutch from the outset.
One of the most prominent Huguenot refugees in the Netherlands was Pierre Bayle
Pierre Bayle (; 18 November 1647 – 28 December 1706) was a French philosopher, author, and lexicographer. A Huguenot, Bayle fled to the Dutch Republic in 1681 because of religious persecution in France. He is best known for his '' Histori ...
. He started teaching in Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte (river), Rotte'') is the second largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the Prov ...
, where he finished writing and publishing his multi-volume masterpiece, '' Historical and Critical Dictionary''. It became one of the 100 foundational texts of the US Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The libra ...
. Some Huguenot descendants in the Netherlands may be noted by French family names, although they typically use Dutch given names. Due to the Huguenots' early ties with the leadership of the Dutch Revolt and their own participation, some of the Dutch patriciate are of part-Huguenot descent. Some Huguenot families have kept alive various traditions, such as the celebration and feast of their patron , similar to the Dutch (Sinterklaas
Sinterklaas () or Sint-Nicolaas () is a legendary figure based on Saint Nicholas, patron saint of children. Other Dutch names for the figure include ''De Sint'' ("The Saint"), ''De Goede Sint'' ("The Good Saint") and ''De Goedheiligman'' ("The ...
) feast.
Great Britain and Ireland
England
 As a major Protestant nation, England patronised and helped protect Huguenots, starting with
As a major Protestant nation, England patronised and helped protect Huguenots, starting with Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
in 1562, with the first Huguenots settling in Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
in 1565. There was a small naval Anglo-French War (1627–1629)
The Anglo-French War () was a military conflict fought between the Kingdom of France and the Kingdom of England between 1627 and 1629. It mainly involved actions at sea.''Warfare at sea, 1500-1650: maritime conflicts and the transformation of E ...
, in which the English supported the French Huguenots against King Louis XIII. London financed the emigration of many to England and its colonies around 1700. Some 40,000-50,000 settled in England, mostly in towns near the sea in the southern districts, with the largest concentration in London where they constituted about 5% of the total population in 1700. Many others went to the American colonies, especially South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. The immigrants included many skilled craftsmen and entrepreneurs who facilitated the economic modernisation of their new home, in an era when economic innovations were transferred by people rather than through printed works. The British government ignored the complaints made by local craftsmen about the favouritism shown to foreigners. The immigrants assimilated well in terms of using English, joining the Church of England, intermarriage and business success. They founded the silk industry in England. Many became private tutors, schoolmasters, travelling tutors and owners of riding schools, where they were hired by the upper class.
Both before and after the 1708 passage of the Foreign Protestants Naturalization Act, an estimated 50,000 Protestant Walloons
Walloons (; french: Wallons ; wa, Walons) are a Gallo-Romance ethnic group living native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of France. Walloons primarily speak '' langues d'oïl'' such as Belgian French, Picard and Walloon. Wallo ...
and French Huguenots fled to England, with many moving on to Ireland and elsewhere. In relative terms, this was one of the largest waves of immigration ever of a single ethnic community to Britain. Andrew Lortie (born André Lortie), a leading Huguenot theologian and writer who led the exiled community in London, became known for articulating their criticism of the Pope and the doctrine of transubstantiation
Transubstantiation (Latin: ''transubstantiatio''; Greek: μετουσίωσις '' metousiosis'') is, according to the teaching of the Catholic Church, "the change of the whole substance of bread into the substance of the Body of Christ and of ...
during Mass.
Of the refugees who arrived on the Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
coast, many gravitated towards Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of t ...
, then the county's Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
hub. Many Walloon and Huguenot families were granted asylum
Asylum may refer to:
Types of asylum
* Asylum (antiquity), places of refuge in ancient Greece and Rome
* Benevolent Asylum, a 19th-century Australian institution for housing the destitute
* Cities of Refuge, places of refuge in ancient Judea
...
there. Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first E ...
granted them the whole of the western crypt of Canterbury Cathedral
Canterbury Cathedral in Canterbury, Kent, is one of the oldest and most famous Christian structures in England. It forms part of a World Heritage Site. It is the cathedral of the Archbishop of Canterbury, currently Justin Welby, leader of the ...
for worship. In 1825, this privilege was reduced to the south aisle and in 1895 to the former chantry
A chantry is an ecclesiastical term that may have either of two related meanings:
# a chantry service, a Christian liturgy of prayers for the dead, which historically was an obiit, or
# a chantry chapel, a building on private land, or an area i ...
chapel of the Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock, known to history as the Black Prince (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), was the eldest son of King Edward III of England, and the heir apparent to the English throne. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II, suc ...
. Services are still held there in French according to the Reformed tradition every Sunday at 3 pm.
Other evidence of the Walloons and Huguenots in Canterbury includes a block of houses in Turnagain Lane, where weavers' windows survive on the top floor, as many Huguenots worked as weavers. The Weavers, a half-timbered
Timber framing (german: Holzfachwerk) and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and joined timbers with joints secured by large woode ...
house by the river, was the site of a weaving school from the late 16th century to about 1830. (It has been adapted as a restaurant—see illustration above. The house derives its name from a weaving school which was moved there in the last years of the 19th century, reviving an earlier use.) Other refugees practised the variety of occupations necessary to sustain the community as distinct from the indigenous population. Such economic separation was the condition of the refugees' initial acceptance in the city. They also settled elsewhere in Kent, particularly Sandwich
A sandwich is a food typically consisting of vegetables, sliced cheese or meat, placed on or between slices of bread, or more generally any dish wherein bread serves as a container or wrapper for another food type. The sandwich began as a po ...
, Faversham
Faversham is a market town in Kent, England, from London and from Canterbury, next to the Swale, a strip of sea separating mainland Kent from the Isle of Sheppey in the Thames Estuary. It is close to the A2, which follows an ancient Briti ...
and Maidstone
Maidstone is the largest town in Kent, England, of which it is the county town. Maidstone is historically important and lies 32 miles (51 km) east-south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town, linking it wi ...
—towns in which there used to be refugee churches.
The French Protestant Church of London
The French Protestant Church of London (''Église protestante française de Londres'') is a Reformed / Presbyterian church that has catered to the French-speaking community of London since 1550. It is the last remaining Huguenot church of Lon ...
was established by Royal Charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, b ...
in 1550. It is now located at Soho Square
Soho Square is a garden square in Soho, London, hosting since 1954 a ''de facto'' public park let by the Soho Square Garden Committee to Westminster City Council. It was originally called King Square after Charles II, and a much weathered ...
. Huguenot refugees flocked to Shoreditch
Shoreditch is a district in the East End of London in England, and forms the southern part of the London Borough of Hackney. Neighbouring parts of Tower Hamlets are also perceived as part of the area.
In the 16th century, Shoreditch was an imp ...
, London. They established a major weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal ...
industry in and around Spitalfields
Spitalfields is a district in the East End of London and within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The area is formed around Commercial Street (on the A1202 London Inner Ring Road) and includes the locale around Brick Lane, Christ Church, ...
(see Petticoat Lane
Petticoat Lane Market is a fashion and clothing market in Spitalfields, London. It consists of two adjacent street markets. Wentworth Street Market is open six days a week and Middlesex Street Market is open on Sunday only.
The modern market
...
and the Tenterground
A tenterground, tenter ground or teneter-field was an area used for drying newly manufactured cloth after fulling. The wet cloth was hooked onto frames called " tenters" and stretched taut using "tenter hooks", so that the cloth would dry fl ...
) in East London. In Wandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
Toponymy
Wandsworth takes its nam ...
, their gardening skills benefited the Battersea
Battersea is a large district in south London, part of the London Borough of Wandsworth, England. It is centred southwest of Charing Cross and extends along the south bank of the River Thames. It includes the Battersea Park.
History
Batt ...
market gardens. The flight of Huguenot refugees from Tours
Tours ( , ) is one of the largest cities in the region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is the prefecture of the department of Indre-et-Loire. The commune of Tours had 136,463 inhabitants as of 2018 while the population of the whole metro ...
, France drew off most of the workers of its great silk mills which they had built. Some of these immigrants moved to Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of ...
, which had accommodated an earlier settlement of Walloon weavers. The French added to the existing immigrant population, then comprising about a third of the population of the city.
Some Huguenots settled in Bedfordshire, one of the main centres of the British lace industry at the time. Although 19th-century sources have asserted that some of these refugees were lacemakers and contributed to the East Midlands lace industry, this is contentious. The only reference to immigrant lacemakers in this period is of twenty-five widows who settled in Dover, and there is no contemporary documentation to support there being Huguenot lacemakers in Bedfordshire. The implication that the style of lace known as 'Bucks Point' demonstrates a Huguenot influence, being a "combination of Mechlin patterns on Lille ground", is fallacious: what is now known as Mechlin lace did not develop until the first half of the eighteenth century and lace with Mechlin patterns and Lille ground did not appear until the end of the 18th century, when it was widely copied throughout Europe.
Many Huguenots from the Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gra ...
region also eventually settled in the area around Stourbridge
Stourbridge is a market town in the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley in the West Midlands, England, situated on the River Stour. Historically in Worcestershire, it was the centre of British glass making during the Industrial Revolution. The ...
in the modern-day West Midlands, where they found the raw materials and fuel to continue their glassmaking tradition. Anglicised names such as Tyzack, Henzey and Tittery are regularly found amongst the early glassmakers, and the region went on to become one of the most important glass regions in the country.
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
was the most prominent Briton of Huguenot descent, deriving from the Huguenots who went to the colonies; his American grandfather was Leonard Jerome.
Ireland
 Following the French crown's revocation of the
Following the French crown's revocation of the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed pr ...
, many Huguenots settled in Ireland in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, encouraged by an act of parliament for Protestants' settling in Ireland. Huguenot regiments fought for William of Orange in the Williamite War in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland (1688–1691; ga, Cogadh an Dá Rí, "war of the two kings"), was a conflict between Jacobite supporters of deposed monarch James II and Williamite supporters of his successor, William III. It is also called th ...
, for which they were rewarded with land grants and titles, many settling in Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
. Significant Huguenot settlements were in Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
, Cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
, Portarlington, Lisburn
Lisburn (; ) is a city in Northern Ireland. It is southwest of Belfast city centre, on the River Lagan, which forms the boundary between County Antrim and County Down. First laid out in the 17th century by English and Welsh settlers, with ...
, Waterford
"Waterford remains the untaken city"
, mapsize = 220px
, pushpin_map = Ireland#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption = Location within Ireland##Location within Europe
, pushpin_relief = 1
, coordinates ...
and Youghal
Youghal ( ; ) is a seaside resort town in County Cork, Ireland. Located on the estuary of the River Blackwater, the town is a former military and economic centre. Located on the edge of a steep riverbank, the town has a long and narrow layout. ...
. Smaller settlements, which included Killeshandra
Killeshandra or Killashandra (), is a village in County Cavan, Ireland. It is northwest of Cavan Town in the centre of County Cavan's lakeland and geopark region and the Erne catchment environment of rivers, lakes, wetlands and woodland. Tog ...
in County Cavan, contributed to the expansion of flax cultivation and the growth of the Irish linen industry.
For over 150 years, Huguenots were allowed to hold their services in Lady Chapel in St. Patrick's Cathedral. A Huguenot cemetery
The Huguenot Cemetery (also known as the St. Augustine Public Burying Ground) in St. Augustine, Florida located across from the historic City Gate was a Protestant burial ground between the years 1821 and 1884. The Spanish colonial city of St. Augu ...
is located in the centre of Dublin, off St. Stephen's Green. Prior to its establishment, Huguenots used the Cabbage Garden near the cathedral. Another Huguenot cemetery
The Huguenot Cemetery (also known as the St. Augustine Public Burying Ground) in St. Augustine, Florida located across from the historic City Gate was a Protestant burial ground between the years 1821 and 1884. The Spanish colonial city of St. Augu ...
is located off French Church Street in Cork.
A number of Huguenots served as mayors in Dublin, Cork, Youghal and Waterford in the 17th and 18th centuries. Numerous signs of Huguenot presence can still be seen with names still in use, and with areas of the main towns and cities named after the people who settled there. Examples include the Huguenot District and French Church Street in Cork City
Cork ( , from , meaning 'marsh') is the second largest city in Ireland and third largest city by population on the island of Ireland. It is located in the south-west of Ireland, in the province of Munster. Following an extension to the city's ...
; and D'Olier Street
D'Olier Street ( ) is a street in the southern city-centre of Dublin, the capital of Ireland. It and Westmoreland Street are two broad streets whose northern ends meet at the southern end of O'Connell Bridge over the River Liffey. Its southern e ...
in Dublin, named after a High Sheriff and one of the founders of the Bank of Ireland. A French church in Portarlington dates back to 1696, and was built to serve the significant new Huguenot community in the town. At the time, they constituted the majority of the townspeople.
One of the more notable Huguenot descendants in Ireland was Seán Lemass
Seán Francis Lemass (born John Francis Lemass; 15 July 1899 – 11 May 1971) was an Irish Fianna Fáil politician who served as Taoiseach and Leader of Fianna Fáil from 1959 to 1966. He also served as Tánaiste from 1957 to 1959, 1951 to 1954 ...
(1899–1971), who was appointed as ''Taoiseach
The Taoiseach is the head of government, or prime minister, of Ireland. The office is appointed by the president of Ireland upon the nomination of Dáil Éireann (the lower house of the Oireachtas, Ireland's national legislature) and the of ...
'', serving from 1959 until 1966.
Scotland
With the precedent of a historical alliance — theAuld Alliance
The Auld Alliance ( Scots for "Old Alliance"; ; ) is an alliance made in 1295 between the kingdoms of Scotland and France against England. The Scots word ''auld'', meaning ''old'', has become a partly affectionate term for the long-lasting a ...
— between Scotland and France; Huguenots were mostly welcomed to, and found refuge in the nation from around the year 1700. Although they did not settle in Scotland in such significant numbers as in other regions of Britain and Ireland, Huguenots have been romanticised, and are generally considered to have contributed greatly to Scottish culture. John Arnold Fleming wrote extensively of the French Protestant group's impact on the nation in his 1953 ''Huguenot Influence in Scotland'', while sociologist Abraham Lavender
Abraham Donald Lavender (November 14, 1940 – June 26, 2022) was a professor of sociology at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, where his special areas of interest include ethnic relations, Judaica, political sociology, urban soc ...
, who has explored how the ethnic group transformed over generations "from Mediterranean Catholics to White Anglo-Saxon Protestants", has analyzed how Huguenot adherence to Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
customs helped facilitate compatibility with the Scottish people.
Wales
A number of French Huguenots settled in Wales, in the upperRhymney
Rhymney (; cy, Rhymni ) is a town and a community in the county borough of Caerphilly, South Wales. It is within the historic boundaries of Monmouthshire. With the villages of Pontlottyn, Fochriw, Abertysswg, Deri and New Tredegar, Rhymney ...
valley of the current Caerphilly County Borough
Caerphilly County Borough ( cy, Bwrdeistref Sirol Caerffili) is a county borough in the south-east of Wales. It is governed by Caerphilly County Borough Council.
Its main and largest town is Caerphilly. Other towns in the county borough are B ...
. The community they created there is still known as ''Fleur de Lys'' (the symbol of France), an unusual French village name in the heart of the valleys of Wales. Nearby villages are Hengoed
Hengoed () is a village on the west side of the Rhymney Valley - between Ystrad Mynach to the south and Cefn Hengoed to the north. Across the valley it looks towards Maesycwmmer. The village is in the county borough of Caerphilly, in the trad ...
, and Ystrad Mynach. Apart from the French village name and that of the local rugby team, Fleur De Lys RFC
Fleur De Lys RFC is a Welsh rugby union club based in south-east Wales and are a feeder club for Newport Gwent Dragons. The 1st XV Team currently play in Division 4 East
History
Fleur De Lys RFC reformed into their current guise in 1966. In 1 ...
, little remains of the French heritage.
Germany and Scandinavia
 Around 1685, Huguenot refugees found a safe haven in the Lutheran and Reformed states in Germany and Scandinavia. Nearly 50,000 Huguenots established themselves in Germany, 20,000 of whom were welcomed in
Around 1685, Huguenot refugees found a safe haven in the Lutheran and Reformed states in Germany and Scandinavia. Nearly 50,000 Huguenots established themselves in Germany, 20,000 of whom were welcomed in Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohe ...
, where Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, h ...
and Duke of Prussia (), granted them special privileges ( Edict of Potsdam of 1685) and churches in which to worship (such as the Church of St. Peter and St. Paul, Angermünde and the French Cathedral, Berlin). The Huguenots furnished two new regiments of his army: the Altpreußische Infantry Regiments No. 13 (Regiment on foot Varenne) and 15 (Regiment on foot Wylich). Another 4,000 Huguenots settled in the German territories of Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
, Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper ...
(Principality of Bayreuth
The Principality of Bayreuth (german: Fürstentum Bayreuth) or Margraviate of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (''Markgraftum Brandenburg-Bayreuth'') was an immediate territory of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a Franconian branch of the Hohenzollern dynas ...
, Principality of Ansbach
The Principality or Margraviate of (Brandenburg-)Ansbach (german: Fürstentum Ansbach or ) was a principality in the Holy Roman Empire centered on the Franconian city of Ansbach. The ruling Hohenzollern princes of the land were known as margrav ...
), Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Kassel), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, was a state in the Holy Roman Empire that was directly subject to the Emperor. The state was created in 1567 when the La ...
, Duchy of Württemberg
The Duchy of Württemberg (german: Herzogtum Württemberg) was a duchy located in the south-western part of the Holy Roman Empire. It was a member of the Holy Roman Empire from 1495 to 1806. The dukedom's long survival for over three centuries ...
, in the Wetterau Association of Imperial Counts Wetterau Association of Imperial Counts was an association of comital families in the Wetterau and surrounding areas. It originated in the late Middle Ages and was formally disbanded when the Holy Roman Empire was dissolved in 1806.
400px, Map ...
, in the Palatinate
The Palatinate (german: Pfalz; Palatine German: ''Palz'') is a region of Germany. In the Middle Ages it was known as the Rhenish Palatinate (''Rheinpfalz'') and Lower Palatinate (''Unterpfalz''), which strictly speaking designated only the we ...
and Palatine Zweibrücken
Palatine Zweibrücken (), or the County Palatine of Zweibrücken, is a former state of the Holy Roman Empire. Its capital was Zweibrücken (french: Deux-Ponts). Its reigning house, a branch of the Wittelsbach dynasty, was also the Royal House of S ...
, in the Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
), in modern-day Saarland
The Saarland (, ; french: Sarre ) is a state of Germany in the south west of the country. With an area of and population of 990,509 in 2018, it is the smallest German state in area apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, a ...
; and 1,500 found refuge in Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, Bremen
Bremen ( Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state cons ...
and Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
. Three hundred refugees were granted asylum at the court of George William, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg
George William (german: Georg Wilhelm; 26 January 1624 – 28 August 1705) was the first Welf Duke of Lauenburg after its occupation in 1689. From 1648 to 1665, he was the ruler of the Principality of Calenberg as an appanage from his eldest ...
in Celle
Celle () is a town and capital of the district of Celle, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town is situated on the banks of the river Aller, a tributary of the Weser, and has a population of about 71,000. Celle is the southern gateway to the Lü ...
.
 In Berlin the Huguenots created two new neighbourhoods:
In Berlin the Huguenots created two new neighbourhoods: Dorotheenstadt
is a historic zone or neighbourhood (''Stadtviertel'') of central Berlin, Germany, which forms part of the locality (''Ortsteil'') of Mitte within the borough (''Bezirk'') also called Mitte. It contains several famous Berlin landmarks: the ...
and Friedrichstadt
Friedrichstadt (; da, Frederiksstad) is a town in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated on the river Eider approx. 12 km south of Husum.
History
The town was founded in 1621 by Dutch settlers. D ...
. By 1700 one fifth of the city's population was French-speaking. The Berlin Huguenots preserved the French language in their church services for nearly a century. They ultimately decided to switch to German in protest against the occupation of Prussia by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in 1806–07. Many of their descendants rose to positions of prominence. Several congregations were founded throughout Germany and Scandinavia, such as those of Fredericia (Denmark), Berlin, Stockholm
Stockholm () is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropo ...
, Hamburg, Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
, Helsinki, and Emden
Emden () is an independent city and seaport in Lower Saxony in the northwest of Germany, on the river Ems. It is the main city of the region of East Frisia and, in 2011, had a total population of 51,528.
History
The exact founding date of ...
.
Prince Louis de Condé, along with his sons Daniel and Osias, arranged with Count Ludwig von Nassau-Saarbrücken to establish a Huguenot community in present-day Saarland
The Saarland (, ; french: Sarre ) is a state of Germany in the south west of the country. With an area of and population of 990,509 in 2018, it is the smallest German state in area apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, a ...
in 1604. The Count supported mercantilism and welcomed technically skilled immigrants into his lands, regardless of their religion. The Condés established a thriving glass-making works, which provided wealth to the principality for many years. Other founding families created enterprises based on textiles and such traditional Huguenot occupations in France. The community and its congregation remain active to this day, with descendants of many of the founding families still living in the region. Some members of this community emigrated to the United States in the 1890s.
In Bad Karlshafen, Hessen, Germany is the Huguenot Museum and Huguenot archive. The collection includes family histories, a library, and a picture archive.
Effects
The exodus of Huguenots from France created a brain drain, as many of them had occupied important places in society. The kingdom did not fully recover for years. The French crown's refusal to allow non-Catholics to settle inNew France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
may help to explain that colony's low population compared to that of the neighbouring British colonies, which opened settlement to religious dissenters. By the start of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
, the North American front of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
, a sizeable population of Huguenot descent lived in the British colonies, and many participated in the British defeat of New France in 1759–1760.
Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, h ...
, invited Huguenots to settle in his realms, and a number of their descendants rose to positions of prominence in Prussia. Several prominent German military, cultural and political figures were ethnic Huguenot, including the poet Theodor Fontane
Theodor Fontane (; 30 December 1819 – 20 September 1898) was a German novelist and poet, regarded by many as the most important 19th-century German-language realist author. He published the first of his novels, for which he is best known to ...
, General Hermann von François, the hero of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
's Battle of Tannenberg
The Battle of Tannenberg, also known as the Second Battle of Tannenberg, was fought between Russia and Germany between 26 and 30 August 1914, the first month of World War I. The battle resulted in the almost complete destruction of the Russ ...
, Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
general and fighter ace
A flying ace, fighter ace or air ace is a military aviator credited with shooting down five or more enemy aircraft during aerial combat. The exact number of aerial victories required to officially qualify as an ace is varied, but is usually co ...
Adolf Galland
Adolf Josef Ferdinand Galland (19 March 1912 – 9 February 1996) was a German Luftwaffe general and flying ace who served throughout the Second World War in Europe. He flew 705 combat missions, and fought on the Western Front and in the Defenc ...
,Galland 1954, p. vii. the Luftwaffe flying ace Hans-Joachim Marseille
Hans-Joachim Marseille (; 13 December 1919 – 30 September 1942) was a German Luftwaffe fighter pilot and flying ace during World War II. He is noted for his aerial battles during the North African Campaign and his Bohemian lifestyle. One o ...
and the famed U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
Captains Lothar von Arnauld de la Perière and Wilhelm Souchon. The last prime minister of East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In t ...
, Lothar de Maizière, is also a descendant of a Huguenot family, as is the former German Federal Minister of the Interior, Thomas de Maizière
Karl Ernst Thomas de Maizière (; born 21 January 1954) is a German politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) who served as Federal Minister of the Interior from 2009 to 2011 and 2013 to 2018, as well as Federal Minister of Defence f ...
.
The persecution and the flight of the Huguenots greatly damaged the reputation of Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
abroad, particularly in England. Both kingdoms, which had enjoyed peaceful relations until 1685, became bitter enemies and fought each other in a series of wars, called the " Second Hundred Years' War" by some historians, from 1689 onward.
1985 apology
 In October 1985, to commemorate the tricentenary of the
In October 1985, to commemorate the tricentenary of the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without s ...
, President François Mitterrand
François Marie Adrien Maurice Mitterrand (26 October 19168 January 1996) was President of France, serving under that position from 1981 to 1995, the longest time in office in the history of France. As First Secretary of the Socialist Party, he ...
of France announced a formal apology to the descendants of Huguenots around the world. At the same time, the government released a special postage stamp in their honour reading "France ''is'' the home of the Huguenots" ().
Legacy
Huguenot legacy persists both in France and abroad.France
Several French Protestant churches are descended from or tied to the Huguenots, including: * Reformed Church of France (), founded in 1559, the historical and principal Reformed church in France since the Protestant Reformation until its 2013 merger into the United Protestant Church of France * Evangelical Reformed Church of France (), founded in 1938 * some French members of the largely German Protestant Reformed Church of Alsace and LorraineUnited States
*Bayonne, New Jersey
Bayonne ( ) is a city in Hudson County, New Jersey, United States. Located in the Gateway Region, Bayonne is situated on a peninsula located between Newark Bay to the west, the Kill Van Kull to the south, and New York Bay to the east. As ...
* Four-term Republican United States Representative Howard Homan Buffett was of Huguenot descent.
* Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina, the county seat of Charleston County, and the principal city in the Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint o ...
, is home to the only active Huguenot congregation in the United States
* John Sevier
John Sevier (September 23, 1745 September 24, 1815) was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennes ...
, the first governor of the state of Tennessee, and the only governor of the State of Franklin
The State of Franklin (also the Free Republic of Franklin or the State of Frankland)Landrum, refers to the proposed state as "the proposed republic of Franklin; while Wheeler has it as ''Frankland''." In ''That's Not in My American History Boo ...
was of Huguenot descent.
* In 1924, the US issued a commemorative
A commemorative is an object made to memorialize something.
Commemorative may refer to:
* Commemorative coin, coins that issued to commemorate something
* Commemorative medal, a medal to commemorate something
* Commemorative plaque, a plate typic ...
half-dollar
The term "half dollar" refers to a half-unit of several currencies that are named "dollar". One dollar ( $1) is normally divided into subsidiary currency of 100 cents, so a half dollar is equal to 50 cents. These half dollars (aka 50 cent pieces) ...
, known as the " Huguenot-Walloon half-dollar", to celebrate the 300th anniversary of the Huguenots' settlement in what is now the United States.
* Frenchtown, New Jersey
Frenchtown is a borough in Hunterdon County, New Jersey, United States. Frenchtown is located along the banks of the Delaware River on the Hunterdon Plateau thirty two miles northwest of the state capital Trenton. As of the 2010 United States ...
, part of the larger Delaware River Valley, was a settling area in the early 1700s.
* The Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
neighbourhood in New York City's borough of Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey b ...
, straddling Huguenot Avenue
*Huguenot Memorial Park in Jacksonville, Florida.
* The early leaders John Jay
John Jay (December 12, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, patriot, diplomat, abolitionist, signatory of the Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served as the second governor of New York and the f ...
and Paul Revere
Paul Revere (; December 21, 1734 O.S. (January 1, 1735 N.S.)May 10, 1818) was an American silversmith, engraver, early industrialist, Sons of Liberty member, and Patriot and Founding Father. He is best known for his midnight ride to a ...
were of Huguenot descent.
* Francis Marion
Brigadier-General Francis Marion ( 1732 – February 27, 1795), also known as the Swamp Fox, was an American military officer, planter and politician who served during the French and Indian War and the Revolutionary War. During the Amer ...
, an American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
guerrilla fighter in South Carolina, was of predominantly Huguenot ancestry.
* New Paltz, New York
New Paltz () is an incorporated U.S. town in Ulster County, New York. The population was 14,003 at the 2010 U.S. Census. The town is located in the southeastern part of the county and is south of Kingston. New Paltz contains a village, also wi ...
* New Rochelle, New York
New Rochelle (; older french: La Nouvelle-Rochelle) is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States, in the southeastern portion of the state. In 2020, the city had a population of 79,726, making it the seventh-largest in the state o ...
, named for the city of La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. Wi ...
, a known former Huguenot stronghold in France. The Huguenot and Historical Association of New Rochelle was organised in 1885 for the purpose of perpetuating the history of its original Huguenot settlers. The mascot of New Rochelle High School is the Huguenot; and one of the main streets in the city is called Huguenot Street.
* John Pintard
John Pintard, Jr. (May 18, 1759 – June 21, 1844) was an American merchant and philanthropist.
Biography
He was a descendant of Antoine Pintard, a Huguenot from La Rochelle, France. He was orphaned when his mother died when he was "a fortnight ...
(1759–1854), a descendant of Huguenots and prosperous New York City merchant who was involved in various New York City organisations. Pintard was credited with establishing the modern conception of Santa Claus
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnigh ...
.
* Arthur C. Mellette (June 23, 1842 – May 25, 1896), the last governor of the Dakota territory and the first governor of South Dakota is of Huguenot descent.
* In Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
and the neighbouring Chesterfield County, there is a Huguenot Road. A Huguenot High School in Richmond and Huguenot Park in Chesterfield County, along with several other uses of the name throughout the region, commemorate the early refugee settlers.
*The Manakintown Episcopal Church in Midlothian, Virginia serves as a National Huguenot Memorial.
* Walloon Settlers Memorial (located in Battery Park
The Battery, formerly known as Battery Park, is a public park located at the southern tip of Manhattan Island in New York City facing New York Harbor. It is bounded by Battery Place on the north, State Street on the east, New York Harbor to ...
) is a monument given to the City of New York by the Belgian Province of Hainaut in honour of the inspiration of Jessé de Forest Jessé de Forest (1576 – October 22, 1624) was the leader of a group of Walloon Huguenots who fled Europe due to religious persecutions. They emigrated to the New World, where he planned to found New-Amsterdam, which is currently New York Ci ...
in founding New York City. Baron de Cartier de Marchienne, representing the government and Albert I, King of Belgium, presented the monument to Mayor John F. Hylan, for the City of New York 18 May 1924.
England
* There is a Huguenot society in London, as well as aFrench Protestant Church of London
The French Protestant Church of London (''Église protestante française de Londres'') is a Reformed / Presbyterian church that has catered to the French-speaking community of London since 1550. It is the last remaining Huguenot church of Lon ...
, founded in 1550 in Soho Square
Soho Square is a garden square in Soho, London, hosting since 1954 a ''de facto'' public park let by the Soho Square Garden Committee to Westminster City Council. It was originally called King Square after Charles II, and a much weathered ...
, which is still active, and has also been a registered charity since 1926.
* Huguenots of Spitalfields is a registered charity promoting public understanding of the Huguenot heritage and culture in Spitalfields, the City of London and beyond. They arrange tours, talks, events and schools programmes to raise the Huguenot profile in Spitalfields and raise funds for a permanent memorial to the Huguenots.
* Huguenot Place in Wandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
Toponymy
Wandsworth takes its nam ...
is named after the Huguenot Burial Site
The Huguenot Burial Site (also known as Mount Nod Cemetery) is a former burial ground for Huguenots in Wandsworth, London. It was in use from 1687 to 1854. The burial site is located between East Hill and Huguenot Place in the London Borough of W ...
or Mount Nod Cemetery, which was used by the Huguenots living in the area. The site was in use from 1687 to 1854 and graves can still be observed today.
*Canterbury Cathedral
Canterbury Cathedral in Canterbury, Kent, is one of the oldest and most famous Christian structures in England. It forms part of a World Heritage Site. It is the cathedral of the Archbishop of Canterbury, currently Justin Welby, leader of the ...
retains a Huguenot Chapel in the 'Black Prince's Chantry', part of the Crypt which is accessible from the exterior of the cathedral. The chapel was granted to Huguenot refugees on the orders of Queen Elizabeth I in 1575. To this day, the chapel still holds services in French every Sunday at 3pm.
*Strangers' Hall
Strangers' Hall is a museum of domestic history located in Norwich, Norfolk, UK. It is a Grade I listed building.
The oldest parts of the building date back to the fourteenth century, although many additions have been made to the structure ...
in Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of ...
got its name from the Protestant refugees from the Spanish Netherlands who settled in the city from the 16th century onwards and were referred to by the locals as the ' Strangers'. The Strangers brought with them their pet canaries, and over the centuries the birds became synonymous with the city. In the early 20th century, Norwich City F.C. adopted the canary
Canary originally referred to the island of Gran Canaria on the west coast of Africa, and the group of surrounding islands (the Canary Islands). It may also refer to:
Animals Birds
* Canaries, birds in the genera '' Serinus'' and ''Crithagra'' ...
as their emblem and nickname.
Prussia
*Huguenot refugees inPrussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
are thought to have contributed significantly to the development of the textile industry in that country. One notable example was Marthe de Roucoulle, governess of Prussian kings Frederick William I and Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
.
Ireland
* Sean Francis Lemass,Taoiseach
The Taoiseach is the head of government, or prime minister, of Ireland. The office is appointed by the president of Ireland upon the nomination of Dáil Éireann (the lower house of the Oireachtas, Ireland's national legislature) and the of ...
of Ireland from 1959 to 1966, was of Huguenot descent.
* The Poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or w ...
Samuel Beckett
Samuel Barclay Beckett (; 13 April 1906 – 22 December 1989) was an Irish novelist, dramatist, short story writer, theatre director, poet, and literary translator. His literary and theatrical work features bleak, impersonal and Tragicomedy, tr ...
was also of Huguenot descent.
South Africa
* Most South African Huguenots settled in theCape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with ...
, where they became assimilated into the Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a South African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers first arriving at the Cape of Good Hope in the 17th and 18th centuries.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: Brain to Cast ...
and Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gr ...
population. Many modern Afrikaners have French surnames, which are given Afrikaans pronunciation and orthography. The early immigrants settled in ("French Corner") near Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. The Huguenots contributed greatly to the wine industry in South Africa.
Australia
* The majority of Australians with French ancestry are descended from Huguenots. Some of the earliest to arrive in Australia held prominent positions in English society, notablyJane Franklin
Jane, Lady Franklin (née Griffin; 4 December 1791 – 18 July 1875) was the second wife of the English explorer Sir John Franklin. During her husband's period as Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen's Land, she became known for her philanthropic ...
and Charles La Trobe
Charles la Trobe, CB (20 March 18014 December 1875), commonly Latrobe, was appointed in 1839 superintendent of the Port Phillip District of New South Wales and, after the establishment in 1851 of the colony of Victoria (now a state of Austra ...
.
* Others who came later were from poorer families, migrating from England in the 19th and early 20th centuries to escape the poverty of London's East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have u ...
Huguenot enclaves of Spitalfields
Spitalfields is a district in the East End of London and within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The area is formed around Commercial Street (on the A1202 London Inner Ring Road) and includes the locale around Brick Lane, Christ Church, ...
and Bethnal Green
Bethnal Green is an area in the East End of London northeast of Charing Cross. The area emerged from the small settlement which developed around the Green, much of which survives today as Bethnal Green Gardens, beside Cambridge Heath Road. By ...
. Their impoverishment had been brought on by the Industrial Revolution, which caused the collapse of the Huguenot-dominated silk-weaving industry. Many French Australian
French Australians (french: link=no, Australiens d'origine française), some of whom refer to themselves as Huguenots, are Australian citizens or residents of French ancestry, or French-born people who reside in Australia. According to the 201 ...
descendants of Huguenots still consider themselves very much Huguenots or French, even in the 21st century.
See also
*Bible translations into French
Bible translations into French date back to the Medieval era. After a number of French Bible translations in the Middle Ages, the first printed translation of the Bible into French was the work of the French theologian Jacques Lefèvre d'Étaples ...
* French Confession of Faith The French Confession of Faith (1559) or Confession de La Rochelle or Gallic Confession of Faith or La Rochelle Confession of Faith is a Reformed confession of faith.
Under the sponsorship of Geneva a Calvinist church was organised in Paris N.V. ...
* Guillebeau House
Guillebeau House is a historic home located in Hickory Knob State Resort Park near Willington in McCormick County, South Carolina. It was built in about 1764 and is a double-pen log house with one exterior chimney and two front entrances. It ha ...
* Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
* Les Huguenots (opera)
* List of Huguenots
Some notable French Huguenots or people with French Huguenot ancestry include:
Actors and film-makers
*James Agee (1909–1955), American screenwriter, Pulitzer Prize-winning author.
* René Allio (1924–1995), French film-maker.
*Humphrey Bo ...
* Salzburg Protestants—German Protestants expelled from the Archbishopric of Salzburg
The Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg (german: Fürsterzbistum Salzburg; Erzstift Salzburg; Erzbistum Salzburg) was an ecclesiastical principality and state of the Holy Roman Empire. It comprised the secular territory ruled by the archbishops o ...
Notes
Further reading
* Baird, Charles W. "History of the Huguenot Emigration to America." Genealogical Publishing Company, Published: 1885, Reprinted: 1998, * Butler, Jon. ''The Huguenots in America: A Refugee People in New World Society'' (1992) * Cottret, Bernard, ''The Huguenots in England. Immigration and Settlement'', Cambridge & Paris, Cambridge University Press, 1991. * Diefendorf, Barbara B. ''Beneath the Cross: Catholics and Huguenots in Sixteenth-Century Paris'' (1991excerpt and text search
* Gilman, C. Malcolm. ''The Huguenot Migration in Europe and America, its Cause and Effect'' (1962) * Glozier, Matthew and David Onnekink, eds. ''War, Religion and Service. Huguenot Soldiering, 1685–1713'' (2007) * Glozier, Matthew ''The Huguenot soldiers of William of Orange and the Glorious Revolution of 1688: the lions of Judah'' (Brighton, 2002) * Gwynn, Robin D. ''Huguenot Heritage: The History and Contribution of the Huguenots in England'' (Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1985). * Kamil, Neil. ''Fortress of the Soul: Violence, Metaphysics, and Material Life in the Huguenots' New World, 1517–1751'' Johns Hopkins U. Press, 2005. 1058 pp. * Lachenicht, Susanne. "Huguenot Immigrants and the Formation of National Identities, 1548–1787", ''Historical Journal'' 2007 50(2): 309–331, * Lotz-Heumann, Ute
''Confessional Migration of the Reformed: The Huguenots''
European History Online
European History Online (''Europäische Geschichte Online, EGO'') is an academic website that publishes articles on the history of Europe between the period of 1450 and 1950 according to the principle of open access.
Organisation
EGO is issued ...
, Mainz: Institute of European History The Leibniz Institute of European History (IEG) in Mainz, Germany, is an independent, public research institute that carries out and promotes historical research on the foundations of Europe in the early and late Modern period. Though autonomous i ...
, 2012, retrieved: 11 July 2012.
* McClain, Molly. "A Letter from Carolina, 1688: French Huguenots in the New World." William and Mary Quarterly. 3rd. ser., 64 (April 2007): 377–394.
* Mentzer, Raymond A. and Andrew Spicer. ''Society and Culture in the Huguenot World, 1559–1685'' (2007excerpt and text search
* Murdoch, Tessa, and Randolph Vigne. The '' French Hospital in England: Its Huguenot History and Collections'' Cambridge: John Adamson, 2009 * Ruymbeke, Bertrand Van. ''New Babylon to Eden: The Huguenots and Their Migration to Colonial South Carolina.'' U. of South Carolina Press, 2006. 396 pp * Scoville, Warren Candler. ''The persecution of Huguenots and French economic development, 1680-1720'' (U of California Press, 1960). * Scoville, Warren C. "The Huguenots and the diffusion of technology. I." ''Journal of political economy'' 60.4 (1952): 294–311
part I online
Part2: Vol. 60, No. 5 (Oct., 1952), pp. 392–41
online part 2
* Soman, Alfred. ''The Massacre of St. Bartholomew: Reappraisals and Documents'' (The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff, 1974) * Treasure, G. R. R. ''Seventeenth Century France'' (2nd ed., 1981) pp. 371–96. * VanRuymbeke, Bertrand and Sparks, Randy J., eds. ''Memory and Identity: The Huguenots in France and the Atlantic Diaspora'', U. of South Carolina Press, 2003. 352 pp. * Wijsenbeek, Thera. "Identity Lost: Huguenot Refugees in the Dutch Republic and its Former Colonies in North America and South Africa, 1650 To 1750: A Comparison", ''South African Historical Journal'' 2007 (59): 79–102 * Wolfe, Michael. ''The Conversion of Henri IV: Politics, Power, and Religious Belief in Early Modern France'' (1993).
In French
* Augeron Mickaël, Didier Poton et Bertrand Van Ruymbeke, dir., ''Les Huguenots et l'Atlantique'', vol. 1: ''Pour Dieu, la Cause ou les Affaires'', préface de Jean-Pierre Poussou, Paris, Presses de l'Université Paris-Sorbonne (PUPS), Les Indes savantes, 2009 * Augeron Mickaël, Didier Poton et Bertrand Van Ruymbeke, dir., ''Les Huguenots et l'Atlantique'', vol. 2: ''Fidélités, racines et mémoires'', Paris, Les Indes savantes, 2012. * Augeron Mickaël, John de Bry, Annick Notter, dir., ''Floride, un rêve français (1562–1565)'', Paris, Illustria, 2012.External links
The Huguenot Library
at
University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
contains approximate 6500 books and pamphlets including 1500 rare books
Historic Huguenot Street
Huguenot Fellowship
The Huguenot Society of Australia
Library for Huguenot History, Germany
The National Huguenot Society
The Huguenot Society of America
Huguenot Society of Great Britain & Ireland
Huguenots of Spitalfields
Texts
''Huguenots and Jews of the Languedoc''
About the inhabitants of Southern France and how they came to be called French Protestants
''Early Prayer Books of America: Being a Descriptive Account of Prayer Books Published in the United States, Mexico and Canada''
by Rev. John Wright, D.D. St Paul, MN: Privately Printed, 1898. Pages 188 to 210 are entitled "The Prayer Book of the French Protestants, Charleston, South Carolina." (597 pdfs)
''The French Protestant (Huguenot) Church in the city of Charleston, South Carolina''
Includes history, text of memorial tablets, and the rules adopted in 1869. (1898, 40 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de célébrer le service Divin; Qui est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin''
(1713, 160 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de célébrer le service Divin; Qui est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin''
Revised and corrected second edition. (1737, 302 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de Célébrer le Service Divin, Comme elle est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin. Nouvelle édition, Augmentée de quelques Prieres, Collectes & Cantiques''
(1772, 256 pdfs)
''La Liturgie: ou La Manière de Célébrer le Service Divin, qui est établie Dans le Eglises de la Principauté de Neufchatel & Vallangin. Cinquieme édition, revue, corrigée & augmentée''
(1799, 232 pdfs)
''La Liturgie, ou La Manière de Célébrer le Service Divin, dans le églises du Canton de Vaud''
(1807, 120 pdfs)
''The Liturgy of the French Protestant Church, Translated from the Editions of 1737 and 1772, Published at Neufchatel, with Additional Prayers, Carefully Selected, and Some Alterations: Arranged for the Use of the Congregation in the City of Charleston, S. C.''
Charleston, SC: James S. Burgess, 1835. (205 pdfs)
''The Liturgy of the French Protestant Church, Translated from the Editions of 1737 and 1772, Published at Neufchatel, with Additional Prayers Carefully Selected, and Some Alterations. Arranged for the Use of the Congregation in the City of Charleston, S. C.''
New York, NY: Charles M. Cornwell, Steam Printer, 1869. (186 pdfs) * ''The Liturgy, or Forms of Divine Service, of the French Protestant Church, of Charleston, S. C., Translated from the Liturgy of the Churches of Neufchatel and Vallangin: editions of 1737 and 1772. With Some Additional Prayers, Carefully Selected. The Whole Adapted to Public Worship in the United States of America.'' Third edition. New York, NY: Anson D. F. Randolph & Company, 1853. 228 pp
Google Books
and th
Internet Archive
Available also fro
Making of America Books
as a DLXS file or in hardcover.
''The Liturgy Used in the Churches of the Principality of Neufchatel: with a Letter from the Learned Dr. Jablonski, Concerning the Nature of Liturgies: To which is Added, The Form of Prayer lately introduced into the Church of Geneva''
(1712, 143 pdfs)
Manifesto, (or Declaration of Principles), of the French Protestant Church of London, Founded by Charter of Edward VI. 24 July, A.D. 1550.
By Order of the Consistory. London, England: Messrs. Seeleys, 1850.
''Preamble and rules for the government of the French Protestant Church of Charleston: adopted at meetings of the corporation held on the 12th and the 19th of November, 1843''
(1845, 26 pdfs)
''Synodicon in Gallia Reformata: or, the Acts, Decisions, Decrees, and Canons of those Famous National Councils of the Reformed Churches in France''
by John Quick. Volume 1 of 2. (1692, 693 pdfs)
Synodicon in Gallia Reformata: or, the Acts, Decisions, Decrees, and Canons of those Famous National Councils of the Reformed Churches in France
by John Quick. Volume 2 of 2. (1692, 615 pdfs) * {{Authority control Anti-Catholicism in France Ethnoreligious groups French diaspora French Wars of Religion Huguenot history in France Religion in the Ancien Régime