Fraser syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fraser syndrome (also known as Meyer-Schwickerath's syndrome, Fraser-François syndrome, or Ullrich-Feichtiger syndrome) is an
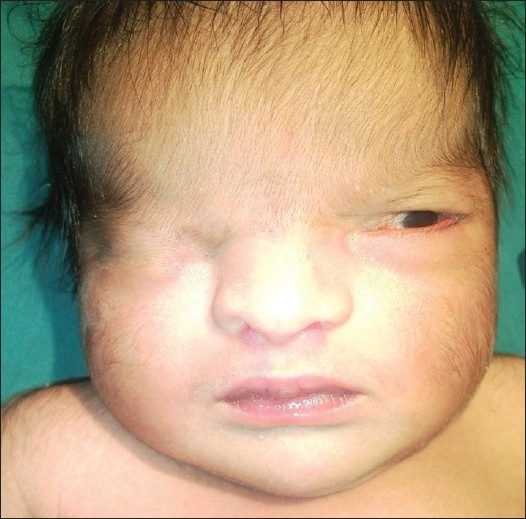 It is characterized by developmental defects including
It is characterized by developmental defects including
 The diagnosis of this syndrome can be made on
The diagnosis of this syndrome can be made on
autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in au ...
recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
congenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
, identified by several developmental anomalies. Fraser syndrome is named for the geneticist George R. Fraser, who first described the syndrome in 1962.
Signs and symptoms
 It is characterized by developmental defects including
It is characterized by developmental defects including cryptophthalmos
Cryptophthalmos is a rare congenital anomaly in which the skin is continuous over the eyeball with absence of Palpebral fissure, palpebral fissures and presence of eyelashes. It is classified into three types: complete, incomplete and abortive. Fai ...
(where the eyelids fail to separate in each eye), and intersex
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical bina ...
development in the genitals
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
(such as micropenis
Micropenis is an unusually small penis. A common criterion is a dorsal (measured on top) penile length of at least 2.5 standard deviations smaller than the mean human penis size (stretched penile length less than 9.3 cm (3.67 in) in adults). ...
, or clitoromegaly
Clitoromegaly (or macroclitoris) is an abnormal enlargement of the clitoris that is mostly congenital or acquired, though deliberately induced clitoris enlargement as a form of genital body modification is achieved through various uses of anabo ...
) and cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is from Greek () 'hidden' and () 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of ...
Congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
malformation
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can r ...
s of the nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes th ...
, ear
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of ...
s, larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
and renal
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
system, as well as developmental delays
Specific developmental disorders (SDD) was a classification of disorders characterized by delayed development in one specific area or areas.Ahuja Vyas: ''Textbook of Postgraduate Psychiatry'' (2 Vols.), 2nd ed. 1999 Specific developmental disorders ...
, manifest occasionally. Syndactyly
Syndactyly is a condition wherein two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammals, such as the siamang and diprotodontia, but is an unusual condition in humans. The term is from Greek σύν, ''syn'' 'together' and δάκ� ...
(fused fingers or toes) has also been noted.
Genetics
The genetic background of this disease has been linked to a gene called FRAS1, which seems to be involved in skin epithelialmorphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of devel ...
during early development. It has also been associated with FREM2 and with GRIP1.
Mapping
By autozygosity mapping, McGregor et al. (2003) located the Fraser syndrome locus to chromosome 4q21.Genetic Heterogeneity
In 6 of 18 consanguineous families with Fraser syndrome, van Haelst et al. (2008) excluded linkage to both the FRAS1 and FREM2 genes, indicating genetic heterogeneity.Molecular genetics
In 5 families with Fraser syndrome, McGregor et al. (2003) identified 5 homozygous mutations in the FRAS1 gene (e.g., 607830.0001), which encodes a putative extracellular matrix (ECM) protein. In 2 families with Fraser syndrome unlinked to the FRAS1 gene, Jadeja et al. (2005) found a homozygous missense mutation in the FREM2 gene (608945.0001). In an infant girl with Fraser syndrome, Slavotinek et al. (2006) identified compound heterozygosity for a deletion (607830.0006) and an insertion (607830.0007) in the FRAS1 gene, inherited from her mother and her father, respectively. Cavalcanti et al. (2007) described 2 stillborn Brazilian male siblings, born at 25 and 29 weeks' gestation, respectively. One sibling appeared to have a lethal form of ablepharon-macrostomia syndrome (AMS; 200110) or an intermediate phenotype between AMS and Fraser syndrome, and the other had classic Fraser syndrome. Analysis of the FRAS1 gene revealed homozygosity for a splice site mutation (607830.0008), resulting in a severely truncated protein in both siblings and heterozygosity for the mutation in both parents. Cavalcanti et al. (2007) concluded that a phenotype resembling AMS is a rare clinical expression of Fraser syndrome, with no obvious genotype/phenotype correlation. In a female fetus with a normal karyotype and cryptophthalmos, ambiguous external genitalia, syndactyly, bilobed lungs, bilateral renal agenesis, hypoplastic bladder, and agenesis of internal genitalia with streak ovaries, Shafeghati et al. (2008) identified homozygosity for a splice site mutation in the FREM2 gene (608945.0002). The consanguineous Iranian parents were heterozygous for the mutation. An earlier pregnancy had resulted in the intrauterine death at 30 weeks of gestation of a male fetus with a normal karyotype in whom the diagnosis of Fraser syndrome was suggested by the presence of cryptophthalmos, syndactyly, ambiguous genitalia, imperforate anus, bilateral renal agenesis, pulmonary hypoplasia, and hydrocephalus. The authors noted that the findings in the sibs were consistent with classic Fraser syndrome. Among 18 consanguineous families with Fraser syndrome, van Haelst et al. (2008) found 9 families with linkage to FRAS1, 3 families to FREM2, and 3 families to both genes. Six families did not link to either locus, indicating genetic heterogeneity. Among a larger group of 33 families, including the 18 consanguineous families, molecular analysis identified 11 novel mutations in the FRAS1 gene in 10 families and 1 mutation in the FREM2 gene (608945.0003) in 1 family. A literature review of genotype/phenotype correlations suggested that patients with FRAS1 mutations have more frequent skull ossification defects and a low insertion of the umbilical cord compared to patients without a FRAS1 mutation, but the findings were not statistically significant.Diagnosis
 The diagnosis of this syndrome can be made on
The diagnosis of this syndrome can be made on clinical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient ...
and perinatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any di ...
.
Koenig and Spranger (1986) noted that eye lesions are apparently nonobligatory components of the syndrome. The diagnosis of Fraser syndrome should be entertained in patients with a combination of acrofacial and urogenital malformations with or without cryptophthalmos. Thomas et al. (1986) also emphasized the occurrence of the cryptophthalmos syndrome without cryptophthalmos and proposed diagnostic criteria for Fraser syndrome. Major criteria consisted of cryptophthalmos, syndactyly, abnormal genitalia, and positive family history. Minor criteria were congenital malformation of the nose, ears, or larynx, cleft lip and/or palate, skeletal defects, umbilical hernia, renal agenesis, and mental retardation. Diagnosis was based on the presence of at least 2 major and 1 minor criteria, or 1 major and 4 minor criteria.
Boyd et al. (1988) suggested that prenatal diagnosis by ultrasound examination of eyes, digits, and kidneys should detect the severe form of the syndrome. Serville et al. (1989) demonstrated the feasibility of ultrasonographic diagnosis of the Fraser syndrome at 18 weeks' gestation. They suggested that the diagnosis could be made if 2 of the following signs are present: obstructive uropathy, microphthalmia, syndactyly, and oligohydramnios
Oligohydramnios is a medical condition in pregnancy characterized by a deficiency of amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds the fetus in the abdomen, in the amniotic sac. It is typically diagnosed by ultrasound when the amniotic fluid index (A ...
. Schauer et al. (1990) made the diagnosis at 18.5 weeks' gestation on the basis of sonography. Both the female fetus and the phenotypically normal father had a chromosome anomaly: inv(9)(p11q21). An earlier born infant had Fraser syndrome and the same chromosome 9 inversion.
Van Haelst et al. (2007) provided a revision of the diagnostic criteria for Fraser syndrome according to Thomas et al. (1986) through the addition of airway tract and urinary tract anomalies to the major criteria and removal of mental retardation and clefting as criteria. Major criteria included syndactyly, cryptophthalmos spectrum, urinary tract abnormalities, ambiguous genitalia, laryngeal and tracheal anomalies, and positive family history. Minor criteria included anorectal defects, dysplastic ears, skull ossification defects, umbilical abnormalities, and nasal anomalies. Cleft lip and/or palate, cardiac malformations, musculoskeletal anomalies, and mental retardation were considered uncommon. Van Haelst et al. (2007) suggested that the diagnosis of Fraser syndrome can be made if either 3 major criteria, or 2 major and 2 minor criteria, or 1 major and 3 minor criteria are present in a patient.
Epidemiology
The incidence of Fraser syndrome is 0.043 per 10,000 live born infants and 1.1 in 10,000 stillbirths, making it a rare syndrome.References
External links
{{Medical resources , DiseasesDB = 32241 , ICD10 = {{ICD10, Q, 87, 0, q, 87 , ICD9 = , ICDO = , OMIM = 219000 , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = , eMedicineTopic = , MeshID = , SNOMED CT = 204102004 , Orphanet = 2052 Autosomal recessive disorders Syndromes affecting the eye Syndromes with intellectual disability Rare syndromes Syndromes affecting female reproductive system