Fort Carillon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fort Carillon, presently known as Fort Ticonderoga, was constructed by
 Fort Carillon was situated south of
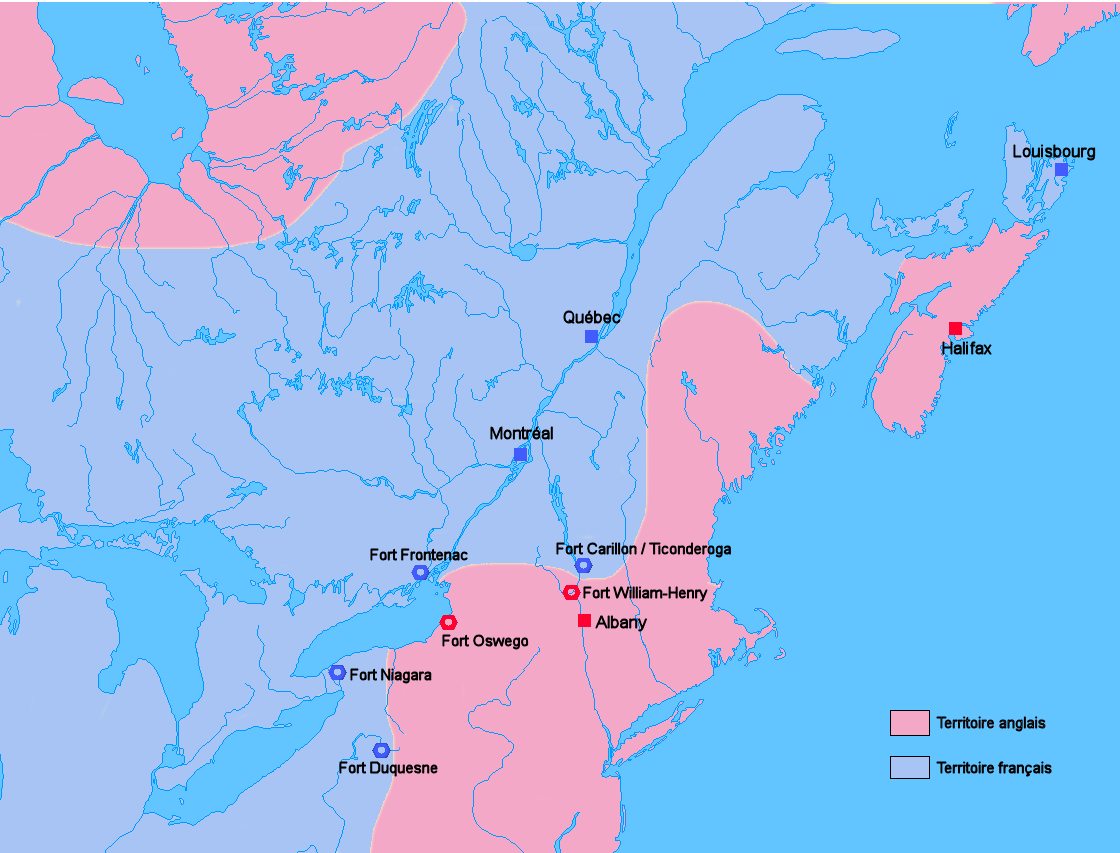
Fort Carillon was situated south of
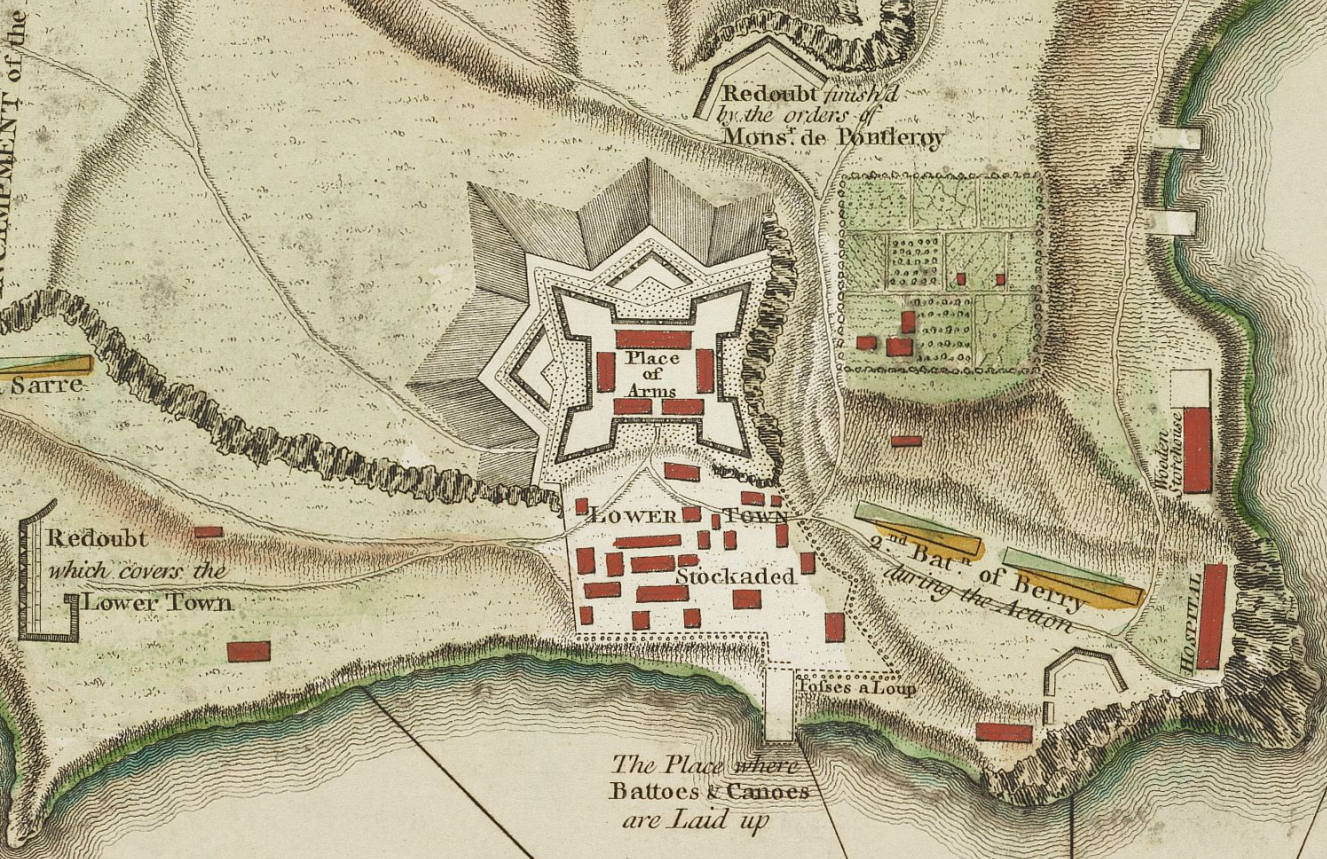 In 1756, the Canadian and French troops developed "le Jardin du Roi" on the sandy plain below the heights. It was intended to feed the summer garrison charged with constructing the new fort.The bulletin of Fort Carillon, p.141-142
By 1758, Fort Carillon and its surroundings were composed of a lower town, an upper town, two hospitals, hangars, and barracks for the soldiers. The lower town itself took the form of a triangle with the fort as its northern tip, and the lower town the southern part of the triangle. There, taverns with wine cellars for the soldiers, bakeries, and nine ovens were located.
It was important to construct batteries for the lower town, and the earth removed for construction of the lower town was taken closer to the fort.
On July 22, 1759, when orders were given to set fire to the town, the Indians could not believe that the French and Canadians would abandon what they had worked so hard to build. Heavy smoke rose from the two hospitals, the hangars of the lower and upper town, and the soldiers' barracks. All was to be abandoned to the advancing British army. None of the buildings were ever reconstructed as was the case in
In 1756, the Canadian and French troops developed "le Jardin du Roi" on the sandy plain below the heights. It was intended to feed the summer garrison charged with constructing the new fort.The bulletin of Fort Carillon, p.141-142
By 1758, Fort Carillon and its surroundings were composed of a lower town, an upper town, two hospitals, hangars, and barracks for the soldiers. The lower town itself took the form of a triangle with the fort as its northern tip, and the lower town the southern part of the triangle. There, taverns with wine cellars for the soldiers, bakeries, and nine ovens were located.
It was important to construct batteries for the lower town, and the earth removed for construction of the lower town was taken closer to the fort.
On July 22, 1759, when orders were given to set fire to the town, the Indians could not believe that the French and Canadians would abandon what they had worked so hard to build. Heavy smoke rose from the two hospitals, the hangars of the lower and upper town, and the soldiers' barracks. All was to be abandoned to the advancing British army. None of the buildings were ever reconstructed as was the case in
 The ''troupes de la terre'' were composed of professional soldiers of the
The ''troupes de la terre'' were composed of professional soldiers of the
 Louis-Joseph de Montcalm, in command of the French troops at Fort Carillon decided to attack Fort William Henry from Fort Carillon. On August 9, 1757, Montcalm, with an army of 7,000 men consisting of French soldiers, Canadian militia, and Indians from various tribes, took Fort William Henry, situated at the southern point of Lake George. The Indians, who thought that an agreement had been made without their consent, revolted. What ensued were violent attacks by the Indians intoxicated by alcohol. There were, according to sources, between 70 and 150 people killed, scalped, and decapitated. After this massacre, the French soldiers accompanied the survivors to Fort Edward to avoid further bloodshed.Jacques Lacoursière, Tome I de son Histoire populaire du Québec page 345.
After his victory, Montcalm could have taken Fort Edward, but he took instead the destroyed Fort William Henry, and returned to Fort Carillon. The British had been humiliated and Montcalm had shown the compassion of a great general by stopping any further bloodshed by the Indians and accompanying the survivors. However, Montcalm knew that he had to withdraw because of the anger and loss of the Indians as allies, as well as a shortage of provisions.
In 1756,
Louis-Joseph de Montcalm, in command of the French troops at Fort Carillon decided to attack Fort William Henry from Fort Carillon. On August 9, 1757, Montcalm, with an army of 7,000 men consisting of French soldiers, Canadian militia, and Indians from various tribes, took Fort William Henry, situated at the southern point of Lake George. The Indians, who thought that an agreement had been made without their consent, revolted. What ensued were violent attacks by the Indians intoxicated by alcohol. There were, according to sources, between 70 and 150 people killed, scalped, and decapitated. After this massacre, the French soldiers accompanied the survivors to Fort Edward to avoid further bloodshed.Jacques Lacoursière, Tome I de son Histoire populaire du Québec page 345.
After his victory, Montcalm could have taken Fort Edward, but he took instead the destroyed Fort William Henry, and returned to Fort Carillon. The British had been humiliated and Montcalm had shown the compassion of a great general by stopping any further bloodshed by the Indians and accompanying the survivors. However, Montcalm knew that he had to withdraw because of the anger and loss of the Indians as allies, as well as a shortage of provisions.
In 1756,
 Although the French government knew that the British had dispatched 8,000 men to North America, Canada had only received 1,800 men, most of whom were assigned to
Although the French government knew that the British had dispatched 8,000 men to North America, Canada had only received 1,800 men, most of whom were assigned to
 The British were alarmed by the outcome of losing Fort William Henry, which was their northernmost fort. They decided to prepare for a massive attack against Fort Carillon. Close to 16,000 men (the largest troop deployment ever assembled on the North American continent) was united under the orders of General James Abercrombie, commander in chief of the British forces in
The British were alarmed by the outcome of losing Fort William Henry, which was their northernmost fort. They decided to prepare for a massive attack against Fort Carillon. Close to 16,000 men (the largest troop deployment ever assembled on the North American continent) was united under the orders of General James Abercrombie, commander in chief of the British forces in
File:Fort ticonderoga 1759.jpg
File:Fort Ticonderoga 1775.jpg
File:Fort ticonderoga exterior detail.jpg
File:Fort ticonderoga place d arms.jpg
File:Fort ticonderoga vault in bakery.jpg
File:Fort ticonderoga guns on bastion.jpg
File:Fort ticonderoga drawbridge to demilune.jpg
File:Fort Carillon.jpg
 * Battle on Snowshoes (1757)
* Battle on Snowshoes (1758)
*
* Battle on Snowshoes (1757)
* Battle on Snowshoes (1758)
*
Pierre de Rigaud de Vaudreuil
Pierre is a masculine given name. It is a French form of the name Peter. Pierre originally meant "rock" or "stone" in French (derived from the Greek word πέτρος (''petros'') meaning "stone, rock", via Latin "petra"). It is a translatio ...
, Governor of French Canada
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fre ...
, to protect Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/ Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type ...
from a British invasion. Situated on the lake some south of Fort Saint Frédéric, it was built to prevent an attack on Canada and slow the advance of the enemy long enough for reinforcements to arrive.
Assigned to remedy Fort Saint Frédéric's inability to resist a constant British threat to the south, French King's Engineer Michel Chartier de Lotbinière began construction of Fort Carillon where Lake George, at that time called Lac Saint Sacrement, joins Lake Champlain by the La Chute river
The La Chute River, also known as Ticonderoga Creek, is a short, fast-moving river, near the Vermont–New York border. It is now almost wholly contained within the municipality of Ticonderoga, New York, connecting the northern end and outlet ...
. Construction began in October 1755.Boréal Express, Canada-Québec, Éditions du Renouveau Pédagogique Inc. 1977
Location
Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/ Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type ...
and north of Lake George, a natural point of conflict between the French forces, which were advancing south from Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
through the Richelieu River towards Lake Champlain and the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
, and the British forces, which were hoping to move north. The area was chosen so as to control the southern point of Lake Champlain as well as access to the Hudson Valley. The fort is surrounded by water on three sides, and on half of the fourth side by a moat. The portion remaining was strongly fortified by deep trenches, sustained by three batteries of cannon and, in front of the fort, blocked by trees which had been cut down and the pointed ends strengthened by fire, creating a formidable defensive system.
Handicapped by corruption, the construction continued at a slow pace. By mid-July 1756, four bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
s with cannon were placed at a height of . Two of the bastions were directed to the northeast and northwest, away from the lake. They were the Reine and Germaine bastions, with two demilunes (an outwork in front of a fort, shaped like a crescent moon) further extending the works on the land side. The two other bastions provided cover for the landing area outside the fort. They were the Joannes and Languedoc bastions, which overlooked the lake to the south. The walls were high and thick, and the whole works was surrounded by a glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glacis ...
and a dry moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
deep and wide. The fort was armed with cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
brought in from Fort St. Frédéric and Montréal.Kaufmann
Kaufmann is a surname with many variants such as Kauffmann, Kaufman, and Kauffman. In German, the name means '' merchant''. It is the cognate of the English ''Chapman'' (which had a similar meaning in the Middle Ages, though it disappeared from ...
, pp. 75–76 Lonergan (1959), p. 19
By fall, the fort was still not finished when an important discovery was made: as soon as the trees of the peninsula were cut, the French realized that the location they chose did not join well with the junction between the two lakes. To correct this, a second but smaller fort was built closer to the lake, known as ''Redoute des Grenadiers.'' By January 1757, the fort was still incomplete and composed of earth and moats, mounted by 36 cannon waiting for an attack that the French were anticipating. The French and Canadians did not want to wait passively for the British assault however, and decided to attack first. In April, 8,000 men, under the command of Marquis de Montcalm, mustered at Fort Carillon. In August 1757, they crossed Lake George to take Fort William Henry. The operation was a success and Montcalm brought back his men to Fort Carillon for the summer.
Lower and upper town of Carillon
Louisbourg
Louisbourg is an unincorporated community and former town in Cape Breton Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia.
History
The French military founded the Fortress of Louisbourg in 1713 and its fortified seaport on the southwest part of the harbour ...
, Cape Breton.
Garrison at Fort Carillon
''Les troupes de terre''
French Army
History
Early history
The first permanent army, paid with regular wages, instead of feudal levies, was established under Charles VII of France, Charles VII in the 1420 to 1430s. The Kings of France needed reliable troops during and after the ...
, sent from France to America, who were disciplined and well trained. At Fort Carillon in 1758, these troops were made up of the second battalions of seven regiments sent from different regions of France.Germain, Jean-Claude ''Nous étions le Nouveau Monde'', Hurtibise, p. 142 (2009) The regiments represented in the garrison were those of La Reine La Reine can refer to
Organizations
* Régiment de La Reine, a regiment of the French Army of the Ancien Régime
Places
* La Reine, Quebec, a municipality in Quebec, Canada
* La Reine, a populated place in the commune of Saint-Priest-des-Champs, ...
(345 soldiers), Guyenne
Guyenne or Guienne (, ; oc, Guiana ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of '' Aquitania Secunda'' and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transformation o ...
(470 soldiers), Berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, rasp ...
(450 soldiers), Béarn
The Béarn (; ; oc, Bearn or ''Biarn''; eu, Bearno or ''Biarno''; or ''Bearnia'') is one of the traditional provinces of France, located in the Pyrenees mountains and in the plain at their feet, in southwest France. Along with the three B ...
(410 soldiers), La Sarre
La Sarre is a town in northwestern Quebec, Canada, and is the most populous town and seat of the Abitibi-Ouest Regional County Municipality. It is located at the intersection of Routes 111 and 393, on the La Sarre River, a tributary of Lake ...
(460 soldiers), Royal Roussillon (480 soldiers), and Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (; , ; oc, Lengadòc ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately ...
(426 soldiers). The Berry regiment also had a second battalion, but their numbers were not known.
The requisite white uniform of the French regular infantry is likely to have been similarly modified for all the battalions. The uniform of the ''Régiment de Guyenne'' and ''Régiment Berry'' was a bit like the ''Régiment de la Reine'': a white-grey coat with red reversed sleeves with three ornate buttons, red vest, white-grey pants, and black shoes with metallic buckles. However, contrary to ''La Reine'', the tricorn hat was black felt with a gold medallion.Nous étions le Nouveau Monde, Jean-Claude Germain, Hurtibise, p. 143 (2009) The uniforms of the other regiments had blue vests and blue cuffs, except for ''Régiment de La Sarre'' which had red vests and blue cuffs. The French musket was of a smaller caliber than the British musket.
''Les troupes de la Marine''
The Troupes de la Marine were led by Chevalier de Lévis with 150 Canadians. There were also about 250 Canadian Indians at Fort Carillon, for a total of 3,500 soldiers. The French and Canadians often made use of guns placed on the walls of the fort, although for the Battle of Carillon, because the fighting took place 3/4 of a mile from the fort, it was essentially a battle of musket and bayonet.Fort Carillon 1757
 Louis-Joseph de Montcalm, in command of the French troops at Fort Carillon decided to attack Fort William Henry from Fort Carillon. On August 9, 1757, Montcalm, with an army of 7,000 men consisting of French soldiers, Canadian militia, and Indians from various tribes, took Fort William Henry, situated at the southern point of Lake George. The Indians, who thought that an agreement had been made without their consent, revolted. What ensued were violent attacks by the Indians intoxicated by alcohol. There were, according to sources, between 70 and 150 people killed, scalped, and decapitated. After this massacre, the French soldiers accompanied the survivors to Fort Edward to avoid further bloodshed.Jacques Lacoursière, Tome I de son Histoire populaire du Québec page 345.
After his victory, Montcalm could have taken Fort Edward, but he took instead the destroyed Fort William Henry, and returned to Fort Carillon. The British had been humiliated and Montcalm had shown the compassion of a great general by stopping any further bloodshed by the Indians and accompanying the survivors. However, Montcalm knew that he had to withdraw because of the anger and loss of the Indians as allies, as well as a shortage of provisions.
In 1756,
Louis-Joseph de Montcalm, in command of the French troops at Fort Carillon decided to attack Fort William Henry from Fort Carillon. On August 9, 1757, Montcalm, with an army of 7,000 men consisting of French soldiers, Canadian militia, and Indians from various tribes, took Fort William Henry, situated at the southern point of Lake George. The Indians, who thought that an agreement had been made without their consent, revolted. What ensued were violent attacks by the Indians intoxicated by alcohol. There were, according to sources, between 70 and 150 people killed, scalped, and decapitated. After this massacre, the French soldiers accompanied the survivors to Fort Edward to avoid further bloodshed.Jacques Lacoursière, Tome I de son Histoire populaire du Québec page 345.
After his victory, Montcalm could have taken Fort Edward, but he took instead the destroyed Fort William Henry, and returned to Fort Carillon. The British had been humiliated and Montcalm had shown the compassion of a great general by stopping any further bloodshed by the Indians and accompanying the survivors. However, Montcalm knew that he had to withdraw because of the anger and loss of the Indians as allies, as well as a shortage of provisions.
In 1756, New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
had suffered a disastrous crop failure. Montcalm was forced to release the Canadian militiamen who made up more than half of his force. The Canadians were urgently needed to return home for the harvest. However, in 1757, disaster struck again and the harvest was the worst in Canadian history. Conditions were particularly bad around Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
, which was "the granary of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
." By late September, the inhabitants were subsisting on a half-pound of bread a day, and those at Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
on a quarter-pound of bread. A month later, there was no bread at all. "The distress is so great that some of the inhabitants are living on grass," Bougainville wrote. There was a feeling of dispirited despair in the colony and the conclusion was that its military prospects would soon become indefensible.Jacques Lacoursière, Tome I de son Histoire populaire du Québec page 346.
After a string of French victories in 1757, the British were prompted to organize a large-scale attack on the fort as part of a multifaceted campaign strategy against Canada. Anderson (2005), p. 126 In June 1758, British General James Abercrombie began amassing a large force at Fort William Henry in preparation for the military campaign
A military campaign is large-scale long-duration significant military strategy plan incorporating a series of interrelated military operations or battles forming a distinct part of a larger conflict often called a war. The term derives from the ...
directed up the Champlain Valley. These forces landed at the north end of Lake George, only four miles from the fort, on July 6. Anderson (2005), p. 132 The French general Louis-Joseph de Montcalm, who had only arrived at Carillon in late June, engaged his troops in a flurry of work to improve the fort's outer defenses. They built, over two days, entrenchments around a rise between the fort and Mount Hope, about three-quarters of a mile (one kilometer) northwest of the fort, and then constructed an abatis (felled trees with sharpened branches pointing out) below these entrenchments. Anderson (2000), p. 242 Abercrombie's failure to advance directly to the fort on July 7 made much of this defensive work possible. Brigadier General George Howe, Abercromby's second-in-command, had been killed when his column encountered a French reconnaissance troop. Abercrombie "felt owe's deathmost heavily" and may have been unwilling to act immediately. Anderson (2005), p. 135
1757 was therefore a bad year for the British in North America, not only because of their defeat in northern New York, but in the Ohio Valley and Nova Scotia as well. That year, British Prime-Minister William Pitt named General James Wolfe commander of the British troops in North America.
British force sent against Fort Carillon
The British force sent against Fort Carillon was made up of regular British regiments and provincial regiments. The British units were the 27th (Enniskillen) Regiment of Foot, the 42nd (Highland) Regiment of Foot, the 44th Regiment of Foot,46th Regiment of Foot
The 46th (South Devonshire) Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in 1741. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 32nd (Cornwall) Regiment of Foot to form the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry in 1881, b ...
, the 55th Regiment of Foot
The 55th Regiment of Foot was a British Army infantry regiment, raised in 1755. After 1782 it had a county designation added, becoming known as the 55th (Westmorland) Regiment of Foot. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 34th (Cu ...
, the 1st and 4th battalions of 60th (Royal American) Regiment
The King's Royal Rifle Corps was an infantry rifle regiment of the British Army that was originally raised in British North America as the Royal American Regiment during the phase of the Seven Years' War in North America known in the United ...
, and Gage's Light Infantry.
The British regiments were in their customary red coats with the exception of Gage's light infantry, which wore grey. The soldiers were armed with musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually di ...
s, bayonets, hatchets or tomahawks, and knives. The standard battle issue for British soldiers was 24 rounds of ammunition; Howe may have ordered his soldiers to carry as many rounds as they could. The provincial regiments wore blue, but extensive modification of uniform was made to suit forest warfare with coats being cut back and any form of headgear and equipment permitted. Rogers' Rangers
Rogers' Rangers was a company of soldiers from the Province of New Hampshire raised by Major Robert Rogers and attached to the British Army during the Seven Years' War ( French and Indian War). The unit was quickly adopted into the British arm ...
most likely wore their distinctive green. Along with Rogers' Rangers, there were regiments from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
, Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the ...
, and New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
.
Early preparations to the Battle of Carillon (1758)
 Although the French government knew that the British had dispatched 8,000 men to North America, Canada had only received 1,800 men, most of whom were assigned to
Although the French government knew that the British had dispatched 8,000 men to North America, Canada had only received 1,800 men, most of whom were assigned to Louisbourg
Louisbourg is an unincorporated community and former town in Cape Breton Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia.
History
The French military founded the Fortress of Louisbourg in 1713 and its fortified seaport on the southwest part of the harbour ...
. The army's small size forced Major-General Louis-Joseph de Montcalm
Louis-Joseph de Montcalm-Grozon, Marquis de Montcalm de Saint-Veran (28 February 1712 – 14 September 1759) was a French soldier best known as the commander of the forces in North America during the Seven Years' War (whose North American th ...
, commander of French forces in Canada, to rely on Indians, and although traditional French allies like the Nipissing, Algonkin, and Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
contributed a thousand warriors, it was not enough. Determined to capture both Fort William Henry and Fort Edward, Governor Vaudreuil also recruited a thousand warriors from tribes around the upper Great Lakes. The large number of different tribes meant that there were not enough interpreters, and potentially dangerous tribal rivalries needed attention. Dealing with Indians was never an easy matter, but these Indians did not see themselves as subjects of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
, just temporary allies in search of loot. However, even traditional French allies had scalped wounded British when the garrison at Oswego surrendered, and then forced the French to buy back a number of English prisoners.
While Montcalm and Vaudreuil were raising an army, American rangers proved to be too few to stop Indians from raiding the area around Fort William Henry at will. In late June, a powerful Indian raiding party discovered that the road between the two forts was basically unguarded. The French had a clear picture of the strategic situation in June, but six separate scouting parties were unable to penetrate the Indian screen to learn anything more detailed than that there was a large force at Fort Carillon.
The destruction of Fort William Henry should have guaranteed the safety of Fort Carillon, but the British government had made North America the priority, while France had not, so another attempt was made at Fort Carillon.
Battle of Fort Carillon
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
. The actual officer in charge of the land operation was Brigadier-General Lord Howe. On July 8, 1758, the British army of General James Abercrombie with 16,000 men, (6,000 British soldiers and 10,000 colonials) and their allies the Mohawks
The Mohawk people ( moh, Kanienʼkehá꞉ka) are the most easterly section of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and northern Ne ...
(who did not participate in the battle), attacked Fort Carillon commanded by Louis-Joseph de Montcalm
Louis-Joseph de Montcalm-Grozon, Marquis de Montcalm de Saint-Veran (28 February 1712 – 14 September 1759) was a French soldier best known as the commander of the forces in North America during the Seven Years' War (whose North American th ...
with 3,600 soldiers, including 400 Canadians from Lévis and 300 Abenakis. Abercrombie was determined to go ahead with his advancement before he lost the advantage. The British however faced a well-fortified position. While the fort was still under construction,, the French forces dug deep trenches flanked by three batteries of cannon. The fort was also defended by a line of sharpened trees pointed towards the exterior and intertwined with branches and spikes installed during the night on orders from Montcalm. Part of the French forces were dispersed in the adjoining forest. The land around the fort gave way to only one opening, since the fort was surrounded on three sides by water and at half of the rear by a moat.
Abercrombie could have gone around the French, but wanting a quick victory, he decided against this maneuver. Informed by his lieutenant that it would be possible to take the French by assault, he opted for a massive frontal attack. However, the French defenses proved to be well prepared and they were not in danger of enemy fire. The French easily decimated the British ranks with cannon fire. (The French were lined up in 3 rows: the first row fired while the third was reloading their rifles, permitting a strong even fire).
The British soldiers had to climb on each other's shoulders in order to reach the top of the trenches, so it was easy for the French to repulse them as they arrived near the summit of the defenses. Only one time were the British capable of breaking through the French defenses, only to be repulsed by a charge of bayonets. The British tried to take the fort, but were driven back time and time again by the French artillery. Abercrombie sent his men to assail the fort several times; he lost 551 soldiers, 1,356 were wounded and 77 disappeared. They retreated to Fort William Henry. As for the French and Canadians, they had 104 killed and 273 wounded.
British capture
Jeffery Amherst, now commander in chief of the British forces in America with 12,000 soldiers, prepared to move against Fort Carillon on July 21, 1759. On July 22 and 23, Bourlamaque left the fort with 3,600 men and deployed 400 soldiers to set fire to the two hospitals, hangars, barracks, and to the lower part of the town. During four days, from July 23 to 26, the British bombed the fort, using artillery positioned where Captain Hébécourt and his men were retrenched. On July 26, they left at 10 PM, and at midnight, the explosives demolished most of the fort. They then moved out to Fort Saint Frédéric with the regiment of Hébécourt, captain of the La Reine regiment. Bourlamaque did the same to Fort Saint Frédéric on July 31. After that, they moved up to Isle-aux-Noix where Amherst declined to advance against them, preferring to consolidate his forces in the lower Lake Champlain area. In withdrawing, the French used explosives to destroy what they could of the fort andspiked
Spiked may refer to:
* A drink to which alcohol, recreational drugs, or a date rape drug has been added
**Spiked seltzer, seltzer with alcohol
** Mickey Finn (drugs), a drink laced with a drug
* Spiked (hairstyle), hairstyles featuring spikes
* ' ...
or dumped cannon they did not take with them. Lonergan (1959), p. 56 The British moved in on July 27 and, though they worked in 1759 and 1760 to repair and improve the fort (which they renamed Fort Ticonderoga),Kaufmann
Kaufmann is a surname with many variants such as Kauffmann, Kaufman, and Kauffman. In German, the name means '' merchant''. It is the cognate of the English ''Chapman'' (which had a similar meaning in the Middle Ages, though it disappeared from ...
, pp. 90–91 the fort saw no more significant action in the war. After the war, the British garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mili ...
ed it with a small number of troops but allowed it to fall into disrepair. Colonel Frederick Haldimand, in command of the fort in 1773, wrote that it was in "ruinous condition". Lonergan (1959), p. 59
Photos of Fort Carillon
Legacy of Fort Carillon
The importance of Fort Carillon, theBattle of Carillon
The Battle of Carillon, also known as the 1758 Battle of Ticonderoga, Chartrand (2000), p. 57 was fought on July 8, 1758, during the French and Indian War (which was part of the global Seven Years' War). It was fought near Fort Carillon (now ...
, and the Flag of Carillon; have long been a source of pride for French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fren ...
and to the people of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
.H.-J.-J.-B. Chouinard, ''Annales de la Société Saint-Jean-Baptiste de Québec'', volume IV, Québec, la Cie d'imprimerie du «Soleil», 1903, p. 562 The Flag of Quebec was modeled after the Carillon flag and the Fort and its history bring honor to Canada as well as the province of Quebec.
See also
Fort Chambly
Fort Chambly is a historic fort in La Vallée-du-Richelieu Regional County Municipality, Quebec. It is designated as a National Historic Site of Canada. Fort Chambly was formerly known as Fort St. Louis. It was part of a series of five fortificat ...
* Fort Île-aux-Noix
* Fort Saint Frédéric
* Fort Saint-Jean (Quebec)
Fort Saint-Jean is a fort in the Canadian province of Quebec located on the Richelieu River. The fort was first built in 1666 by soldiers of the Carignan-Salières Regiment of France who had travelled to New France to assist the young colon ...
* Fort Sainte Thérèse
Fort Sainte Thérèse is the name given to three different forts built successively on one site, among a series of fortifications constructed during the 17th century by France along the Richelieu River, in the province of Quebec, in Montérégie.
...
* List of French forts in North America
* Military of New France
The military of New France consisted of a mix of regular soldiers from the French Army ( Carignan-Salières Regiment) and French Navy ( Troupes de la marine, later Compagnies Franches de la Marine) supported by small local volunteer militia unit ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
* Visit to Fort Carillon 2008 http://www.lestafette.net/t1760-vv-86-visite-au-fort-carillon * Béarn regiment at Fort Carillon http://reconstitution.fr/histoire_fort_carillon.html * Artwork depicting Fort Carillon in 1759 http://faculty.marianopolis.edu/c.belanger/quebechistory/encyclopedia/FortCarillon.htmlCarillon
A carillon ( , ) is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 cast-bronze bells. The bells are hung in fixed suspension and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoni ...
Military history of Canada
National Historic Landmarks in New York (state)
Carillon
A carillon ( , ) is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 cast-bronze bells. The bells are hung in fixed suspension and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoni ...
Carillon
A carillon ( , ) is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 cast-bronze bells. The bells are hung in fixed suspension and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoni ...
Carillon
A carillon ( , ) is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 cast-bronze bells. The bells are hung in fixed suspension and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoni ...
New France
1755 establishments in the French colonial empire