Foreign Exchange Market on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.
The main participants in this market are the larger international banks.
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.
The main participants in this market are the larger international banks.
(2007), UNCTAD Trade and development report 2007 (Chapter 1B). In a typical foreign exchange transaction, a party purchases some quantity of one currency by paying with some quantity of another currency. The modern foreign exchange market began forming during the 1970s. This followed three decades of government restrictions on foreign exchange transactions under the
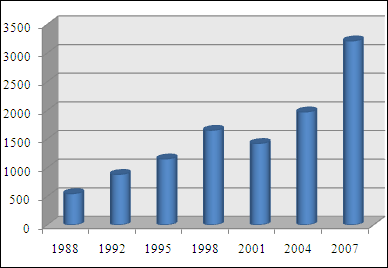 The foreign exchange market is the most
The foreign exchange market is the most
 Risk aversion is a kind of trading behavior exhibited by the foreign exchange market when a potentially adverse event happens that may affect market conditions. This behavior is caused when risk averse traders liquidate their positions in risky assets and shift the funds to less risky assets due to uncertainty.
In the context of the foreign exchange market, traders liquidate their positions in various currencies to take up positions in safe-haven currencies, such as the US dollar. Sometimes, the choice of a safe haven currency is more of a choice based on prevailing sentiments rather than one of economic statistics. An example would be the financial crisis of 2008. The value of equities across the world fell while the US dollar strengthened (see Fig.1). This happened despite the strong focus of the crisis in the US.
Risk aversion is a kind of trading behavior exhibited by the foreign exchange market when a potentially adverse event happens that may affect market conditions. This behavior is caused when risk averse traders liquidate their positions in risky assets and shift the funds to less risky assets due to uncertainty.
In the context of the foreign exchange market, traders liquidate their positions in various currencies to take up positions in safe-haven currencies, such as the US dollar. Sometimes, the choice of a safe haven currency is more of a choice based on prevailing sentiments rather than one of economic statistics. An example would be the financial crisis of 2008. The value of equities across the world fell while the US dollar strengthened (see Fig.1). This happened despite the strong focus of the crisis in the US.
A user's guide to the Triennial Central Bank Survey of foreign exchange market activity, Bank for International Settlements
London Foreign Exchange Committee with links (on right) to committees in NY, Tokyo, Canada, Australia, HK, Singapore
United States Federal Reserve daily update of exchange rates
Bank of Canada historical (10-year) currency converter and data download
OECD Exchange rate statistics (monthly averages)
* National Futures Association (2010).
Trading in the Retail Off-Exchange Foreign Currency Market
'. Chicago, Illinois. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Foreign Exchange Market
 The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.
The main participants in this market are the larger international banks.
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.
The main participants in this market are the larger international banks. Financial center
A financial centre ( BE), financial center ( AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial markets with venues and supporting services for these activities to t ...
s around the world function as anchors of trading between a wide range of multiple types of buyers and sellers around the clock, with the exception of weekends. Since currencies are always traded in pairs, the foreign exchange market does not set a currency's absolute value but rather determines its relative value by setting the market price of one currency if paid for with another. Ex: USD 1 is worth X CAD, or CHF, or JPY, etc.
The foreign exchange market works through financial institutions and operates on several levels. Behind the scenes, banks turn to a smaller number of financial firms known as "dealers", who are involved in large quantities of foreign exchange trading. Most foreign exchange dealers are banks, so this behind-the-scenes market is sometimes called the " interbank market" (although a few insurance companies and other kinds of financial firms are involved). Trades between foreign exchange dealers can be very large, involving hundreds of millions of dollars. Because of the sovereignty issue when involving two currencies, Forex has little (if any) supervisory entity regulating its actions.
The foreign exchange market assists international trade and investments by enabling currency conversion. For example, it permits a business in the United States to import goods from European Union member states, especially Eurozone members, and pay Euros, even though its income is in United States dollars. It also supports direct speculation and evaluation relative to the value of currencies and the carry trade speculation, based on the differential interest rate between two currencies.Global imbalances and destabilizing speculation(2007), UNCTAD Trade and development report 2007 (Chapter 1B). In a typical foreign exchange transaction, a party purchases some quantity of one currency by paying with some quantity of another currency. The modern foreign exchange market began forming during the 1970s. This followed three decades of government restrictions on foreign exchange transactions under the
Bretton Woods system
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretto ...
of monetary management, which set out the rules for commercial and financial relations among the world's major industrial states after World War II. Countries gradually switched to floating exchange rate
In macroeconomics and economic policy, a floating exchange rate (also known as a fluctuating or flexible exchange rate) is a type of exchange rate regime in which a currency's value is allowed to fluctuate in response to foreign exchange mar ...
s from the previous exchange rate regime, which remained fixed per the Bretton Woods system.
The foreign exchange market is unique because of the following characteristics:
* its huge trading volume, representing the largest asset class in the world leading to high liquidity;
* its geographical dispersion;
* its continuous operation: 24 hours a day except for weekends, i.e., trading from 22:00 UTC on Sunday (Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
) until 22:00 UTC Friday (New York);
* the variety of factors that affect exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
s;
* the low margins of relative profit compared with other markets of fixed income; and
* the use of leverage to enhance profit and loss margins and with respect to account size.
As such, it has been referred to as the market closest to the ideal of perfect competition
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In Economic model, theoret ...
, notwithstanding currency intervention by central banks.
According to the Bank for International Settlements, the preliminary global results from the 2022 Triennial Central Bank Survey of Foreign Exchange and OTC Derivatives Markets Activity show that trading in foreign exchange markets averaged per day in April 2022. This is up from in April 2019. Measured by value, foreign exchange swaps were traded more than any other instrument in April 2022, at per day, followed by spot trading at .
The break-down is as follows:
* in spot transactions
* in outright forwards
* in foreign exchange swap
In finance, a foreign exchange swap, forex swap, or FX swap is a simultaneous purchase and sale of identical amounts of one currency for another with two different value dates (normally spot to forward) and may use foreign exchange derivatives. ...
s
* currency swaps
* in options
Option or Options may refer to:
Computing
*Option key, a key on Apple computer keyboards
*Option type, a polymorphic data type in programming languages
* Command-line option, an optional parameter to a command
*OPTIONS, an HTTP request method
...
and other products
History
Ancient
Currency trading and exchange first occurred in ancient times. Money-changers (people helping others to change money and also taking a commission or charging a fee) were living in theHoly Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
in the times of the Talmudic writings (''Biblical times''). These people (sometimes called "kollybistẻs") used city stalls, and at feast times the Temple's Court of the Gentiles instead. Money-changers were also the silversmiths and/or goldsmiths of more recent ancient times.
During the 4th century AD, the Byzantine government kept a monopoly on the exchange of currency.
Papyri PCZ I 59021 (c.259/8 BC), shows the occurrences of exchange of coinage in Ancient Egypt.
Currency and exchange were important elements of trade in the ancient world, enabling people to buy and sell items like food, pottery, and raw materials. If a Greek coin held more gold than an Egyptian coin due to its size or content, then a merchant could barter fewer Greek gold coins for more Egyptian ones, or for more material goods. This is why, at some point in their history, most world currencies in circulation today had a value fixed to a specific quantity of a recognized standard like silver and gold.
Medieval and later
During the 15th century, the Medici family were required to open banks at foreign locations in order to exchange currencies to act on behalf of textile merchants. To facilitate trade, the bank created the ''nostro
''Nostro'' and ''vostro'' (from Italian, ''nostro'' and ''vostro''; English, 'ours' and 'yours') are accounting terms used to distinguish an account held for another entity from an account another entity holds. The entities in question are usually ...
'' (from Italian, this translates to "ours") account book which contained two columned entries showing amounts of foreign and local currencies; information pertaining to the keeping of an account with a foreign bank. During the 17th (or 18th) century, Amsterdam maintained an active Forex market. In 1704, foreign exchange took place between agents acting in the interests of the Kingdom of England and the County of Holland.
Early modern
Alex. Brown & Sons traded foreign currencies around 1850 and was a leading currency trader in the USA. In 1880, J.M. do Espírito Santo de Silva ( Banco Espírito Santo) applied for and was given permission to engage in a foreign exchange trading business. The year 1880 is considered by at least one source to be the beginning of modern foreign exchange: the gold standard began in that year. Prior to the First World War, there was a much more limited control of international trade. Motivated by the onset of war, countries abandoned the gold standard monetary system.Modern to post-modern
From 1899 to 1913, holdings of countries' foreign exchange increased at an annual rate of 10.8%, while holdings of gold increased at an annual rate of 6.3% between 1903 and 1913. At the end of 1913, nearly half of the world's foreign exchange was conducted using thepound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
. The number of foreign banks operating within the boundaries of London increased from 3 in 1860, to 71 in 1913. In 1902, there were just two London foreign exchange brokers. At the start of the 20th century, trades in currencies was most active in Paris, New York City and Berlin; Britain remained largely uninvolved until 1914. Between 1919 and 1922, the number of foreign exchange brokers in London increased to 17; and in 1924, there were 40 firms operating for the purposes of exchange.
During the 1920s, the Kleinwort family were known as the leaders of the foreign exchange market, while Japheth, Montagu & Co. and Seligman still warrant recognition as significant FX traders. The trade in London began to resemble its modern manifestation. By 1928, Forex trade was integral to the financial functioning of the city. Continental exchange controls, plus other factors in Europe and Latin America, hampered any attempt at wholesale prosperity from trade for those of 1930s London.
After World War II
In 1944, theBretton Woods Accord
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bret ...
was signed, allowing currencies to fluctuate within a range of ±1% from the currency's par exchange rate. In Japan, the Foreign Exchange Bank Law was introduced in 1954. As a result, the Bank of Tokyo became a center of foreign exchange by September 1954. Between 1954 and 1959, Japanese law was changed to allow foreign exchange dealings in many more Western currencies.
U.S. President, Richard Nixon is credited with ending the Bretton Woods Accord and fixed rates of exchange, eventually resulting in a free-floating currency system. After the Accord ended in 1971, the Smithsonian Agreement allowed rates to fluctuate by up to ±2%. In 1961–62, the volume of foreign operations by the U.S. Federal Reserve was relatively low. Those involved in controlling exchange rates found the boundaries of the Agreement were not realistic and so ceased this in March 1973, when sometime afterward none of the major currencies were maintained with a capacity for conversion to gold, organizations relied instead on reserves of currency. From 1970 to 1973, the volume of trading in the market increased three-fold. At some time (according to ''Gandolfo'' during February–March 1973) some of the markets were "split", and a two-tier currency market was subsequently introduced, with dual currency rates. This was abolished in March 1974.
Reuters introduced computer monitors during June 1973, replacing the telephones and telex used previously for trading quotes.
Markets close
Due to the ultimate ineffectiveness of the Bretton Woods Accord and the European Joint Float, the forex markets were forced to close sometime during 1972 and March 1973. The largest purchase of US dollars in the history of 1976 was when the West German government achieved an almost 3 billion dollar acquisition (a figure is given as 2.75 billion in total by The Statesman: Volume 18 1974). This event indicated the impossibility of balancing of exchange rates by the measures of control used at the time, and the monetary system and the foreign exchange markets in West Germany and other countries within Europe closed for two weeks (during February and, or, March 1973. ''Giersch, Paqué, & Schmieding'' state closed after purchase of "7.5 million Dmarks" ''Brawley'' states "... Exchange markets had to be closed. When they re-opened ... March 1 " that is a large purchase occurred after the close).After 1973
In developed nations, state control of foreign exchange trading ended in 1973 when complete floating and relatively free market conditions of modern times began. Other sources claim that the first time a currency pair was traded by U.S. retail customers was during 1982, with additional currency pairs becoming available by the next year. On 1 January 1981, as part of changes beginning during 1978, the People's Bank of China allowed certain domestic "enterprises" to participate in foreign exchange trading. Sometime during 1981, the South Korean government endedForex controls
Foreign exchange controls are various forms of controls imposed by a government on the purchase/sale of foreign currencies by residents, on the purchase/sale of local currency by nonresidents, or the transfers of any currency across national bor ...
and allowed free trade to occur for the first time. During 1988, the country's government accepted the IMF quota for international trade.
Intervention by European banks (especially the Bundesbank) influenced the Forex market on 27 February 1985. The greatest proportion of all trades worldwide during 1987 were within the United Kingdom (slightly over one quarter). The United States had the second highest involvement in trading.
During 1991, Iran changed international agreements with some countries from oil-barter to foreign exchange.
Market size and liquidity
 The foreign exchange market is the most
The foreign exchange market is the most liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
financial market in the world. Traders include governments and central banks, commercial banks, other institutional investor
An institutional investor is an entity which pools money to purchase securities, real property, and other investment assets or originate loans. Institutional investors include commercial banks, central banks, credit unions, government-linked co ...
s and financial institutions, currency speculators, other commercial corporations, and individuals. According to the 2019 Triennial Central Bank Survey, coordinated by the Bank for International Settlements, average daily turnover was in April 2022 (compared to in 2004). Of this , was spot transactions and $5.4 trillion was traded in outright forwards, swaps, and other derivatives
The derivative of a function is the rate of change of the function's output relative to its input value.
Derivative may also refer to:
In mathematics and economics
* Brzozowski derivative in the theory of formal languages
* Formal derivative, an ...
.
Foreign exchange is traded in an over-the-counter market where brokers/dealers negotiate directly with one another, so there is no central exchange or clearing house. The biggest geographic trading center is the United Kingdom, primarily London. In April 2022, trading in the United Kingdom accounted for 38.1% of the total, making it by far the most important center for foreign exchange trading in the world. Owing to London's dominance in the market, a particular currency's quoted price is usually the London market price. For instance, when the International Monetary Fund calculates the value of its special drawing rights every day, they use the London market prices at noon that day. Trading in the United States accounted for 19.4%, Singapore and Hong Kong account for 9.4% and 7.1%, respectively, and Japan accounted for 4.4%.
Turnover of exchange-traded foreign exchange futures and options was growing rapidly in 2004-2013, reaching in April 2013 (double the turnover recorded in April 2007). As of April 2022, exchange-traded currency derivatives represent 2% of OTC foreign exchange turnover. Foreign exchange futures contracts were introduced in 1972 at the Chicago Mercantile Exchange
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) (often called "the Chicago Merc", or "the Merc") is a global derivatives marketplace based in Chicago and located at 20 S. Wacker Drive. The CME was founded in 1898 as the Chicago Butter and Egg Board, an a ...
and are traded more than to most other futures contracts.
Most developed countries permit the trading of derivative products (such as futures and options on futures) on their exchanges. All these developed countries already have fully convertible capital accounts. Some governments of emerging markets do not allow foreign exchange derivative products on their exchanges because they have capital controls. The use of derivatives is growing in many emerging economies. Countries such as South Korea, South Africa, and India have established currency futures exchanges, despite having some capital controls.
Foreign exchange trading increased by 20% between April 2007 and April 2010 and has more than doubled since 2004. The increase in turnover is due to a number of factors: the growing importance of foreign exchange as an asset class, the increased trading activity of high-frequency traders
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic financial trading characterized by high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios that leverages high-frequency financial data and electronic trading tools. While there is no ...
, and the emergence of retail investors as an important market segment. The growth of electronic execution
In finance, an electronic trading platform also known as an online trading platform, is a computer software program that can be used to place orders for financial products over a network with a financial intermediary. Various financial products c ...
and the diverse selection of execution venues has lowered transaction costs, increased market liquidity, and attracted greater participation from many customer types. In particular, electronic trading via online portals has made it easier for retail traders to trade in the foreign exchange market. By 2010, retail trading was estimated to account for up to 10% of spot turnover, or $150 billion per day (see below: Retail foreign exchange traders).
Market participants
Unlike a stock market, the foreign exchange market is divided into levels of access. At the top is the interbank foreign exchange market, which is made up of the largest commercial banks and securities dealers. Within the interbank market, spreads, which are the difference between the bid and ask prices, are razor sharp and not known to players outside the inner circle. The difference between the bid and ask prices widens (for example from 0 to 1 pip to 1–2 pips for currencies such as the EUR) as you go down the levels of access. This is due to volume. If a trader can guarantee large numbers of transactions for large amounts, they can demand a smaller difference between the bid and ask price, which is referred to as a better spread. The levels of access that make up the foreign exchange market are determined by the size of the "line" (the amount of money with which they are trading). The top-tier interbank market accounts for 51% of all transactions. From there, smaller banks, followed by large multi-national corporations (which need to hedge risk and pay employees in different countries), large hedge funds, and even some of the retail market makers. According to Galati and Melvin, “Pension fund
A pension fund, also known as a superannuation fund in some countries, is any plan, fund, or scheme which provides retirement income.
Pension funds typically have large amounts of money to invest and are the major investors in listed and priva ...
s, insurance companies, mutual funds, and other institutional investors have played an increasingly important role in financial markets in general, and in FX markets in particular, since the early 2000s.” (2004) In addition, he notes, “Hedge funds have grown markedly over the 2001–2004 period in terms of both number and overall size”. Central banks also participate in the foreign exchange market to align currencies to their economic needs.
Commercial companies
An important part of the foreign exchange market comes from the financial activities of companies seeking foreign exchange to pay for goods or services. Commercial companies often trade fairly small amounts compared to those of banks or speculators, and their trades often have a little short-term impact on market rates. Nevertheless, trade flows are an important factor in the long-term direction of a currency's exchange rate. Some multinational corporations (MNCs) can have an unpredictable impact when very large positions are covered due to exposures that are not widely known by other market participants.Central banks
National central banks play an important role in the foreign exchange markets. They try to control the money supply, inflation, and/or interest rates and often have official or unofficial target rates for their currencies. They can use their often substantial foreign exchange reserves to stabilize the market. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of central bank "stabilizing speculation" is doubtful because central banks do not go bankrupt if they make large losses as other traders would. There is also no convincing evidence that they actually make a profit from trading.Foreign exchange fixing
Foreign exchange fixing
A fixed exchange rate, often called a pegged exchange rate, is a type of exchange rate regime in which a currency's value is fixed or pegged by a monetary authority against the value of another currency, a basket of other currencies, or another m ...
is the daily monetary exchange rate fixed by the national bank of each country. The idea is that central banks use the fixing time and exchange rate to evaluate the behavior of their currency. Fixing exchange rates reflect the real value of equilibrium in the market. Banks, dealers, and traders use fixing rates as a market trend indicator.
The mere expectation or rumor of a central bank foreign exchange intervention might be enough to stabilize the currency. However, aggressive intervention might be used several times each year in countries with a dirty float
Managed float regime is an international financial environment in which exchange rates fluctuate from day to day, but central banks attempt to influence their countries' exchange rates by buying and selling currencies to maintain a certain rang ...
currency regime. Central banks do not always achieve their objectives. The combined resources of the market can easily overwhelm any central bank. Several scenarios of this nature were seen in the 1992–93 European Exchange Rate Mechanism collapse, and in more recent times in Asia.
Investment management firms
Investment management
Investment management is the professional asset management of various securities, including shareholdings, bonds, and other assets, such as real estate, to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of investors. Investors may be institut ...
firms (who typically manage large accounts on behalf of customers such as pension funds and endowments) use the foreign exchange market to facilitate transactions in foreign securities. For example, an investment manager bearing an international equity portfolio needs to purchase and sell several pairs of foreign currencies to pay for foreign securities purchases.
Some investment management firms also have more speculative specialist currency overlay operations, which manage clients' currency exposures with the aim of generating profits as well as limiting risk. While the number of this type of specialist firms is quite small, many have a large value of assets under management and can, therefore, generate large trades.
Retail foreign exchange traders
Individual retail speculative traders constitute a growing segment of this market. Currently, they participate indirectly through brokers or banks. Retail brokers, while largely controlled and regulated in the US by theCommodity Futures Trading Commission
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) is an independent agency of the US government created in 1974 that regulates the U.S. derivatives markets, which includes futures, swaps, and certain kinds of options.
The Commodity Exchange Ac ...
and National Futures Association, have previously been subjected to periodic foreign exchange fraud. To deal with the issue, in 2010 the NFA required its members that deal in the Forex markets to register as such (i.e., Forex CTA instead of a CTA). Those NFA members that would traditionally be subject to minimum net capital requirements, FCMs and IBs, are subject to greater minimum net capital requirements if they deal in Forex. A number of the foreign exchange brokers operate from the UK under Financial Services Authority
The Financial Services Authority (FSA) was a quasi-judicial body accountable for the financial regulation, regulation of the financial services industry in the United Kingdom between 2001 and 2013. It was founded as the Securities and Investmen ...
regulations where foreign exchange trading using margin is part of the wider over-the-counter derivatives trading industry that includes contracts for difference and financial spread betting.
There are two main types of retail FX brokers offering the opportunity for speculative currency trading: ''brokers'' and ''dealers'' or ''market makers''. ''Brokers'' serve as an agent of the customer in the broader FX market, by seeking the best price in the market for a retail order and dealing on behalf of the retail customer. They charge a commission or "mark-up" in addition to the price obtained in the market. ''Dealers'' or ''market makers'', by contrast, typically act as principals in the transaction versus the retail customer, and quote a price they are willing to deal at.
Non-bank foreign exchange companies
Non-bankforeign exchange companies
A non-bank foreign exchange company also known as foreign exchange broker or simply forex broker is a company that offers currency exchange and international payments to private individuals and companies. The term is typically used for currency ex ...
offer currency exchange and international payments to private individuals and companies. These are also known as "foreign exchange brokers" but are distinct in that they do not offer speculative trading but rather currency exchange with payments (i.e., there is usually a physical delivery of currency to a bank account).
It is estimated that in the UK, 14% of currency transfers/payments are made via Foreign Exchange Companies. These companies' selling point is usually that they will offer better exchange rates or cheaper payments than the customer's bank. These companies differ from Money Transfer/Remittance Companies in that they generally offer higher-value services.
The volume of transactions done through Foreign Exchange Companies in India amounts to
about US$2 billion per day This does not compete favorably with any well developed foreign exchange market of international repute, but with the entry of online Foreign Exchange Companies the market is steadily growing. Around 25% of currency transfers/payments in India are made via non-bank Foreign Exchange Companies. Most of these companies use the USP of better exchange rates than the banks. They are regulated by FEDAI and any transaction in foreign Exchange is governed by the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA), is an Act of the Parliament of India "to consolidate and amend the law relating to foreign exchange with the objective of facilitating external trade and payments and for promoting the orderly d ...
(FEMA).
Money transfer/remittance companies and bureaux de change
Money transfer companies/remittance companies perform high-volume low-value transfers generally by economic migrants back to their home country. In 2007, the Aite Group estimated that there were $369 billion of remittances (an increase of 8% on the previous year). The four largest foreign markets ( India,China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Mexico, and the Philippines) receive $95 billion. The largest and best-known provider is Western Union with 345,000 agents globally, followed by UAE Exchange. Bureaux de change or currency transfer companies provide low-value foreign exchange services for travelers. These are typically located at airports and stations or at tourist locations and allow physical notes to be exchanged from one currency to another. They access foreign exchange markets via banks or non-bank foreign exchange companies.
Most traded currencies by value
There is no unified or centrally cleared market for the majority of trades, and there is very little cross-border regulation. Due to the over-the-counter (OTC) nature of currency markets, there are rather a number of interconnected marketplaces, where different currenciesinstruments
Instrument may refer to:
Science and technology
* Flight instruments, the devices used to measure the speed, altitude, and pertinent flight angles of various kinds of aircraft
* Laboratory equipment, the measuring tools used in a scientific l ...
are traded. This implies that there is not a ''single'' exchange rate but rather a number of different rates (prices), depending on what bank or market maker is trading, and where it is. In practice, the rates are quite close due to arbitrage
In economics and finance, arbitrage (, ) is the practice of taking advantage of a difference in prices in two or more markets; striking a combination of matching deals to capitalise on the difference, the profit being the difference between the ...
. Due to London's dominance in the market, a particular currency's quoted price is usually the London market price. Major trading exchanges include Electronic Broking Services (EBS) and Thomson Reuters Dealing, while major banks also offer trading systems. A joint venture of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange and Reuters, called Fxmarketspace
FXMarketSpace (FXMS) was a centrally cleared, global foreign exchange (FX) platform for the over the counter (OTC) cash market. It was launched in May 2006 as a joint venture between Reuters and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange but they decided ...
opened in 2007 and aspired but failed to the role of a central market clearing mechanism.
The main trading centers are London and New York City, though Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Singapore are all important centers as well. Banks throughout the world participate. Currency trading happens continuously throughout the day; as the Asian trading session ends, the European session begins, followed by the North American session and then back to the Asian session.
Fluctuations in exchange rates are usually caused by actual monetary flows as well as by expectations of changes in monetary flows. These are caused by changes in gross domestic product (GDP) growth, inflation (purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currency, currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of ...
theory), interest rates ( interest rate parity, Domestic Fisher effect, International Fisher effect), budget and trade deficits or surpluses, large cross-border M&A deals and other macroeconomic conditions. Major news is released publicly, often on scheduled dates, so many people have access to the same news at the same time. However, large banks have an important advantage; they can see their customers' order flow
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
.
Currencies are traded against one another in pairs. Each currency pair thus constitutes an individual trading product and is traditionally noted XXXYYY or XXX/YYY, where XXX and YYY are the ISO 4217 international three-letter code of the currencies involved. The first currency (XXX) is the base currency that is quoted relative to the second currency (YYY), called the counter currency (or quote currency). For instance, the quotation ''EURUSD (EUR/USD) 1.5465'' is the price of the Euro expressed in US dollars, meaning 1 euro = 1.5465 dollars. The market convention is to quote most exchange rates against the USD with the US dollar as the base currency (e.g. USDJPY, USDCAD, USDCHF). The exceptions are the British pound (GBP), Australian dollar (AUD), the New Zealand dollar (NZD) and the euro (EUR) where the USD is the counter currency (e.g. GBPUSD, AUDUSD, NZDUSD, EURUSD).
The factors affecting XXX will affect both XXXYYY and XXXZZZ. This causes a positive currency correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics ...
between XXXYYY and XXXZZZ.
On the spot market, according to the 2022 Triennial Survey, the most heavily traded bilateral currency pairs were:
* EURUSD: 22.7%
* USDJPY: 13.5%
* GBPUSD (also called '' cable''): 9.5%
The U.S. currency was involved in 88.5% of transactions, followed by the euro (30.5%), the yen (16.7%), and sterling (12.9%) (see table). Volume percentages for all individual currencies should add up to 200%, as each transaction involves two currencies.
Trading in the euro has grown considerably since the currency's creation in January 1999, and how long the foreign exchange market will remain dollar-centered is open to debate. Until recently, trading the euro versus a non-European currency ZZZ would have usually involved two trades: EURUSD and USDZZZ. The exception to this is EURJPY, which is an established traded currency pair in the interbank spot market.
Determinants of exchange rates
In a fixed exchange rate regime, exchange rates are decided by the government, while a number of theories have been proposed to explain (and predict) the fluctuations in exchange rates in afloating exchange rate
In macroeconomics and economic policy, a floating exchange rate (also known as a fluctuating or flexible exchange rate) is a type of exchange rate regime in which a currency's value is allowed to fluctuate in response to foreign exchange mar ...
regime, including:
* International parity conditions: Relative purchasing power parity, interest rate parity, Domestic Fisher effect
In economics, the Fisher effect is the tendency for nominal interest rates to change to follow the inflation rate. It is named after the economist Irving Fisher, who first observed and explained this relationship. Fisher proposed that the real i ...
, International Fisher effect. To some extent the above theories provide logical explanation for the fluctuations in exchange rates, yet these theories falter as they are based on challengeable assumptions (e.g., free flow of goods, services, and capital) which seldom hold true in the real world.
* Balance of payments
In international economics, the balance of payments (also known as balance of international payments and abbreviated BOP or BoP) of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time (e.g., a ...
model: This model, however, focuses largely on tradable goods and services, ignoring the increasing role of global capital flows. It failed to provide any explanation for the continuous appreciation of the US dollar during the 1980s and most of the 1990s, despite the soaring US current account deficit.
* Asset market model: views currencies as an important asset class for constructing investment portfolios. Asset prices are influenced mostly by people's willingness to hold the existing quantities of assets, which in turn depends on their expectations on the future worth of these assets. The asset market model of exchange rate determination states that “the exchange rate between two currencies represents the price that just balances the relative supplies of, and demand for, assets denominated in those currencies.”
None of the models developed so far succeed to explain exchange rates and volatility in the longer time frames. For shorter time frames (less than a few days), algorithms can be devised to predict prices. It is understood from the above models that many macroeconomic factors affect the exchange rates and in the end currency prices are a result of dual forces of supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a Market (economics), market. It postulates that, Ceteris paribus, holding all else equal, in a perfect competition, competitive market, the unit price for a ...
. The world's currency markets can be viewed as a huge melting pot: in a large and ever-changing mix of current events, supply and demand factors are constantly shifting, and the price of one currency in relation to another shifts accordingly. No other market encompasses (and distills) as much of what is going on in the world at any given time as foreign exchange.
Supply and demand for any given currency, and thus its value, are not influenced by any single element, but rather by several. These elements generally fall into three categories: economic factors, political conditions, and market psychology.
Economic factors
Economic factors include: (a) economic policy, disseminated by government agencies and central banks, (b) economic conditions, generally revealed through economic reports, and other economic indicators. * Economic policy comprises government fiscal policy (budget/spending practices) and monetary policy (the means by which a government's central bank influences the supply and "cost" of money, which is reflected by the level of interest rates). * Government budget deficits or surpluses: The market usually reacts negatively to widening government budget deficits, and positively to narrowing budget deficits. The impact is reflected in the value of a country's currency. * Balance of trade levels and trends: The trade flow between countries illustrates the demand for goods and services, which in turn indicates demand for a country's currency to conduct trade. Surpluses and deficits in trade of goods and services reflect the competitiveness of a nation's economy. For example, trade deficits may have a negative impact on a nation's currency. * Inflation levels and trends: Typically a currency will lose value if there is a high level of inflation in the country or if inflation levels are perceived to be rising. This is because inflation erodes purchasing power, thus demand, for that particular currency. However, a currency may sometimes strengthen when inflation rises because of expectations that the central bank will raise short-term interest rates to combat rising inflation. * Economic growth and health: Reports such as GDP, employment levels, retail sales,capacity utilization
Capacity utilization or capacity utilisation is the extent to which a firm or nation employs its installed productive capacity. It is the relationship between output that ''is'' produced with the installed equipment, and the potential output whic ...
and others, detail the levels of a country's economic growth and health. Generally, the more healthy and robust a country's economy, the better its currency will perform, and the more demand for it there will be.
* Productivity of an economy: Increasing productivity in an economy should positively influence the value of its currency. Its effects are more prominent if the increase is in the traded sector.
Political conditions
Internal, regional, and international political conditions and events can have a profound effect on currency markets. All exchange rates are susceptible to political instability and anticipations about the new ruling party. Political upheaval and instability can have a negative impact on a nation's economy. For example, destabilization ofcoalition government
A coalition government is a form of government in which political parties cooperate to form a government. The usual reason for such an arrangement is that no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an election, an atypical outcome in ...
s in Pakistan and Thailand can negatively affect the value of their currencies. Similarly, in a country experiencing financial difficulties, the rise of a political faction that is perceived to be fiscally responsible can have the opposite effect. Also, events in one country in a region may spur positive/negative interest in a neighboring country and, in the process, affect its currency.
Market psychology
Market psychology
Behavioral economics studies the effects of Psychology, psychological, cognitive bias, cognitive, emotional, cultural and social factors on the decision making, decisions of individuals or institutions, such as how those decisions vary from t ...
and trader perceptions influence the foreign exchange market in a variety of ways:
* Flights to quality: Unsettling international events can lead to a "flight-to-quality
A flight-to-quality, or flight-to-safety, is a financial market phenomenon occurring when investors sell what they perceive to be higher-risk investments and purchase safer investments, such as gold and other precious metals. This is considered a s ...
", a type of capital flight whereby investors move their assets to a perceived "safe haven
Safe haven may refer to:
* Sanctuary
Arts and entertainment
* ''Safe Haven'' (novel), a 2010 American novel by Nicholas Sparks
** ''Safe Haven'' (film), a 2013 American film adapted from the novel
* ''Safe Haven'' (short film), a 2009 American ...
". There will be a greater demand, thus a higher price, for currencies perceived as stronger over their relatively weaker counterparts. The US dollar, Swiss franc and gold have been traditional safe havens during times of political or economic uncertainty.
* Long-term trends: Currency markets often move in visible long-term trends. Although currencies do not have an annual growing season like physical commodities, business cycles do make themselves felt. Cycle analysis looks at longer-term price trends that may rise from economic or political trends.
* "Buy the rumor, sell the fact": This market truism can apply to many currency situations. It is the tendency for the price of a currency to reflect the impact of a particular action before it occurs and, when the anticipated event comes to pass, react in exactly the opposite direction. This may also be referred to as a market being "oversold" or "overbought". To buy the rumor or sell the fact can also be an example of the cognitive bias
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the objective input, m ...
known as Anchoring
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ἄγ ...
, when investors focus too much on the relevance of outside events to currency prices.
* Economic numbers: While economic numbers can certainly reflect economic policy, some reports and numbers take on a talisman-like effect: the number itself becomes important to market psychology and may have an immediate impact on short-term market moves. "What to watch" can change over time. In recent years, for example, money supply, employment, trade balance figures and inflation numbers have all taken turns in the spotlight.
* Technical trading
In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis use many of the same ...
considerations: As in other markets, the accumulated price movements in a currency pair such as EUR/USD can form apparent patterns that traders may attempt to use. Many traders study price charts in order to identify such patterns.
Financial instruments
Spot
A spot transaction is a two-day delivery transaction (except in the case of trades between the US dollar, Canadian dollar, Turkish lira, euro and Russian ruble, which settle the next business day), as opposed to the futures contracts, which are usually three months. This trade represents a “direct exchange” between two currencies, has the shortest time frame, involves cash rather than a contract, and interest is not included in the agreed-upon transaction. Spot trading is one of the most common types of forex trading. Often, a forex broker will charge a small fee to the client to roll-over the expiring transaction into a new identical transaction for a continuation of the trade. This roll-over fee is known as the "swap" fee.Forward
One way to deal with theforeign exchange risk
Foreign exchange risk (also known as FX risk, exchange rate risk or currency risk) is a financial risk that exists when a financial transaction is denominated in a currency other than the domestic currency of the company. The exchange risk arises ...
is to engage in a forward transaction. In this transaction, money does not actually change hands until some agreed upon future date. A buyer and seller agree on an exchange rate for any date in the future, and the transaction occurs on that date, regardless of what the market rates are then. The duration of the trade can be one day, a few days, months or years. Usually the date is decided by both parties. Then the forward contract is negotiated and agreed upon by both parties.
Non-deliverable forward (NDF)
Forex banks, ECNs, and prime brokers offer NDF contracts, which are derivatives that have no real deliver-ability. NDFs are popular for currencies with restrictions such as the Argentinian peso. In fact, a forex hedger can only hedge such risks with NDFs, as currencies such as the Argentinian peso cannot be traded on open markets like major currencies.Swap
The most common type of forward transaction is the foreign exchange swap. In a swap, two parties exchange currencies for a certain length of time and agree to reverse the transaction at a later date. These are not standardized contracts and are not traded through an exchange. A deposit is often required in order to hold the position open until the transaction is completed.Futures
Futures are standardized forward contracts and are usually traded on an exchange created for this purpose. The average contract length is roughly 3 months. Futures contracts are usually inclusive of any interest amounts. Currency futures contracts are contracts specifying a standard volume of a particular currency to be exchanged on a specific settlement date. Thus the currency futures contracts are similar to forward contracts in terms of their obligation, but differ from forward contracts in the way they are traded. In addition, Futures are daily settled removing credit risk that exist in Forwards. They are commonly used by MNCs to hedge their currency positions. In addition they are traded by speculators who hope to capitalize on their expectations of exchange rate movements.Option
A foreign exchange option (commonly shortened to just FX option) is a derivative where the owner has the right but not the obligation to exchange money denominated in one currency into another currency at a pre-agreed exchange rate on a specified date. The FX options market is the deepest, largest and most liquid market for options of any kind in the world.Speculation
Controversy about currency speculators and their effect on currency devaluations and national economies recurs regularly. Economists, such as Milton Friedman, have argued that speculators ultimately are a stabilizing influence on the market, and that stabilizing speculation performs the important function of providing a market for hedgers and transferring risk from those people who don't wish to bear it, to those who do. Other economists, such asJoseph Stiglitz
Joseph Eugene Stiglitz (; born February 9, 1943) is an American New Keynesian economist, a public policy analyst, and a full professor at Columbia University. He is a recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (2001) and the Joh ...
, consider this argument to be based more on politics and a free market philosophy than on economics.
Large hedge funds and other well capitalized "position traders" are the main professional speculators. According to some economists, individual traders could act as " noise traders" and have a more destabilizing role than larger and better informed actors.
Currency speculation is considered a highly suspect activity in many countries. While investment in traditional financial instruments like bonds or stocks often is considered to contribute positively to economic growth by providing capital, currency speculation does not; according to this view, it is simply gambling that often interferes with economic policy. For example, in 1992, currency speculation forced Sweden's central bank, the Riksbank
Sveriges Riksbank, or simply the ''Riksbank'', is the central bank of Sweden. It is the world's oldest central bank and the fourth oldest bank in operation.
Etymology
The first part of the word ''riksbank'', ''riks'', stems from the Swedish w ...
, to raise interest rates for a few days to 500% per annum, and later to devalue the krona. Mahathir Mohamad
Mahathir bin Mohamad ( ms, محاضير بن محمد, label= Jawi, script=arab, italic=unset; ; born 10 July 1925) is a Malaysian politician, author, and physician who served as the 4th and 7th Prime Minister of Malaysia. He held the office ...
, one of the former Prime Ministers of Malaysia, is one well-known proponent of this view. He blamed the devaluation of the Malaysian ringgit in 1997 on George Soros and other speculators.
Gregory Millman reports on an opposing view, comparing speculators to "vigilantes" who simply help "enforce" international agreements and anticipate the effects of basic economic "laws" in order to profit. In this view, countries may develop unsustainable economic bubble
An economic bubble (also called a speculative bubble or a financial bubble) is a period when current asset prices greatly exceed their intrinsic valuation, being the valuation that the underlying long-term fundamentals justify. Bubbles can be c ...
s or otherwise mishandle their national economies, and foreign exchange speculators made the inevitable collapse happen sooner. A relatively quick collapse might even be preferable to continued economic mishandling, followed by an eventual, larger, collapse. Mahathir Mohamad and other critics of speculation are viewed as trying to deflect the blame from themselves for having caused the unsustainable economic conditions.
Risk aversion
Carry trade
Currency carry trade refers to the act of borrowing one currency that has a low interest rate in order to purchase another with a higher interest rate. A large difference in rates can be highly profitable for the trader, especially if high leverage is used. However, with all levered investments this is a double edged sword, and large exchange rateprice fluctuation
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by ''σ'') is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns.
Historic volatility measures a time series of past market pric ...
s can suddenly swing trades into huge losses.
See also
* Balance of trade *Currency codes
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual cu ...
* Currency strength
* Foreign currency mortgage
A foreign currency mortgage is a mortgage which is repayable in a currency other than the currency of the country in which the borrower is a resident. Foreign currency mortgages can be used to finance both personal mortgages and corporate mortgages ...
* Foreign exchange controls
* Foreign exchange derivative
A foreign exchange derivative is a financial derivative whose payoff depends on the foreign exchange rates of two (or more) currencies. These instruments are commonly used for currency speculation and arbitrage or for hedging foreign exchange ri ...
* Foreign exchange hedge
* Foreign-exchange reserves
* Leads and lags
* Money market
* Nonfarm payrolls
* Tobin tax
* World currency
Notes
References
External links
A user's guide to the Triennial Central Bank Survey of foreign exchange market activity, Bank for International Settlements
London Foreign Exchange Committee with links (on right) to committees in NY, Tokyo, Canada, Australia, HK, Singapore
United States Federal Reserve daily update of exchange rates
Bank of Canada historical (10-year) currency converter and data download
OECD Exchange rate statistics (monthly averages)
* National Futures Association (2010).
Trading in the Retail Off-Exchange Foreign Currency Market
'. Chicago, Illinois. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Foreign Exchange Market