Flutamide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Flutamide, sold under the brand name Eulexin among others, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which is used primarily to treat

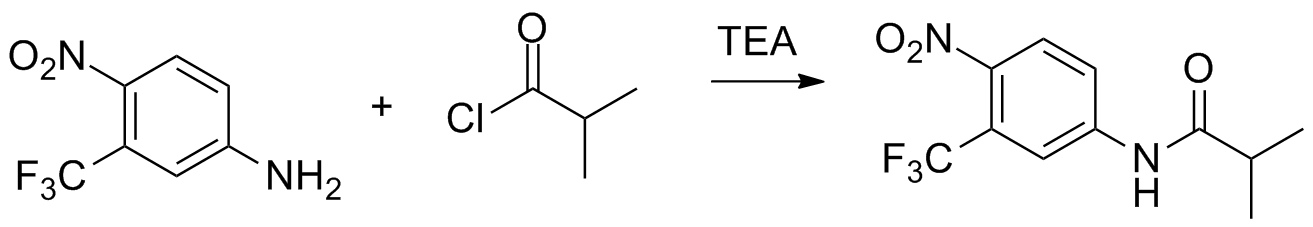 Schotten–Baumann reaction between 4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline 93-11-3(1) with isobutanoyl chloride 9-30-1(2) in the presence of triethylamine.
Schotten–Baumann reaction between 4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline 93-11-3(1) with isobutanoyl chloride 9-30-1(2) in the presence of triethylamine.
prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
. It is also used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions like acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
, excessive hair growth, and high androgen levels in women. It is taken by mouth, usually three times per day.
Side effects in men include breast tenderness and enlargement, feminization, sexual dysfunction, and hot flash
Hot flashes (also known as hot flushes) are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, an ...
es. Conversely, the medication has fewer side effects and is better-tolerated in women with the most common side effect being dry skin. Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
and elevated liver enzymes
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), may be an indicator of liver dysfunction. Other terms include transaminasemia, transaminitis, and elevated ...
can occur in both sexes. Rarely, flutamide can cause liver damage, lung disease, sensitivity to light, elevated methemoglobin, elevated sulfhemoglobin, and deficient neutrophils. Numerous cases of liver failure and death have been reported, which has limited the use of flutamide.
Flutamide acts as a selective antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist.
Etymology
The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, ri ...
of the androgen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in ...
(AR), competing with androgens like testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
and dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues includi ...
(DHT) for binding to ARs in tissues like the prostate gland
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physi ...
. By doing so, it prevents their effects and stops them from stimulating prostate cancer cells to grow. Flutamide is a prodrug
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the dru ...
to a more active form. Flutamide and its active form stay in the body for a relatively short time, which makes it necessary to take flutamide multiple times per day.
Flutamide was first described in 1967 and was first introduced for medical use in 1983. It became available in the United States in 1989. The medication has largely been replaced by newer and improved NSAAs, namely bicalutamide and enzalutamide, due to their better efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as ''effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made between ...
, tolerability, safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are two slightly di ...
, and dosing frequency (once per day), and is now relatively little-used. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Medical uses
Prostate cancer
GnRH is released by thehypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
in a pulsatile fashion; this causes the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. Th ...
pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The h ...
to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, ...
(FSH). LH stimulates the testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
to produce testosterone, which is metabolized to DHT by the enzyme 5α-reductase
5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes o ...
.
DHT, and to a significantly smaller extent, testosterone, stimulate prostate cancer cells to grow. Therefore, blocking these androgens can provide powerful treatment for prostate cancer, especially metastatic disease. Normally administered are GnRH analogues, such as leuprorelin
Leuprorelin, also known as leuprolide, is a manufactured version of a hormone used to treat prostate cancer, breast cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, as part of transgender hormone therapy, for early puberty, or to perform chemical c ...
or cetrorelix. Although GnRH agonists stimulate the same receptors that GnRH does, since they are present continuously and not in a pulsatile manner, they serve to inhibit the pituitary gland and therefore block the whole chain. However, they initially cause a surge in activity; this is not solely a theoretical risk but may cause the cancer to flare. Flutamide was initially used at the beginning of GnRH agonist therapy to block this surge, and it and other NSAAs continue in this use. In contrast to GnRH agonists, GnRH antagonists don't cause an initial androgen surge, and are gradually replacing GnRH agonists in clinical use.
There have been studies to investigate the benefit of adding an antiandrogen to surgical orchiectomy or its continued use with a GnRH analogue (combined androgen blockade Maximum or maximal androgen blockade (MAB) or complete or combined androgen blockade (CAB) is a medical treatment involving the combination of both androgen receptor (AR) antagonism and inhibition or suppression of androgen production to attain ma ...
(CAB)). Adding antiandrogens to orchiectomy showed no benefit, while a small benefit was shown with adding antiandrogens to GnRH analogues.
Unfortunately, therapies which lower testosterone levels, such as orchiectomy or GnRH analogue administration, also have significant side effects. Compared to these therapies, treatment with antiandrogens exhibits "fewer hot flashes, less of an effect on libido, less muscle wasting, fewer personality changes, and less bone loss." However, antiandrogen therapy alone is less effective than surgery. Nevertheless, given the advanced age of many with prostate cancer, as well as other features, many men may choose antiandrogen therapy alone for a better quality of life.Scher, Howard I. (2005). "Hyperplastic and Malignant Diseases of the Prostate". In Dennis L. Kasper, Anthony S. Fauci, Dan L. Longo, Eugene Braunwald, Stephen L. Hauser, & J. Larry Jameson (Eds.), '' Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine'' (16th edition), pp. 548–9. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Flutamide has been found to be similarly effective in the treatment of prostate cancer to bicalutamide, although indications of inferior efficacy, including greater compensatory increases in testosterone levels and greater reductions in PSA levels with bicalutamide, were observed. The medication, at a dosage of 750 mg/day (250 mg three times daily), has also been found to be equivalent in effectiveness to 250 mg/day oral cyproterone acetate as a monotherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer in a large-scale clinical trial of 310 patients, though its side effect and toxicity profiles (including gynecomastia, diarrhea, nausea, loss of appetite, and liver disturbances) were regarded as considerably worse than those of cyproterone acetate.
A dosage of 750 mg/day flutamide (250 mg/three times a day) is roughly equivalent in terms of effectiveness to 50 mg/day bicalutamide when used as the antiandrogen component in combined androgen blockade Maximum or maximal androgen blockade (MAB) or complete or combined androgen blockade (CAB) is a medical treatment involving the combination of both androgen receptor (AR) antagonism and inhibition or suppression of androgen production to attain ma ...
in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
Flutamide has been used to prevent the effects of the testosterone flare at the start of GnRH agonist therapy in men with prostate cancer.
The combination of flutamide with an estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
such as ethinylestradiol sulfonate has been used as a form of combined androgen blockade and as an alternative to the combination of flutamide with surgical or medical castration.
Skin and hair conditions
Flutamide has been researched and used extensively in the treatment of androgen-dependentskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and hair conditions in women including acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
, seborrhea, hirsutism, and scalp hair loss
Pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia (AGA)) is a hair loss condition that primarily affects the top and front of the scalp. In male-pattern hair loss (MPHL), the hair loss typically presents itself as either a receding front ...
, as well as in hyperandrogenism (e.g., in polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
or congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex ...
), and is effective in improving the symptoms of these conditions. The dosages used are lower than those used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Although flutamide continues to be used for these indications, its use in recent years has been limited due to the risk of potentially fatal hepatotoxicity, and it is no longer recommended as a first- or second-line therapy. The related NSAA bicalutamide has also been found to be effective in the treatment of hirsutism in women and appears to have comparable effectiveness to that of flutamide, but has a far lower and only small risk of hepatotoxicity in comparison.
Aside from its risk of liver toxicity and besides other nonsteroidal antiandrogens, it has been said that flutamide is likely the best typically used antiandrogen medication for the treatment of androgen-dependent symptoms in women. This is related to its high effectiveness and minimal side effects.
Acne and seborrhea
Flutamide has been found to be effective in the treatment of acne and seborrhea in women in a number of studies. In a long-term study of 230 women with acne, 211 of whom also had seborrhea, very-low-dose flutamide alone or in combination with an oral contraceptive caused a marked decrease in acne and seborrhea after 6 months of treatment, with maximal effect by 1 year of treatment and benefits maintained in the years thereafter. In the study, 97% of the women reported satisfaction with the control of their acne with flutamide. In another study, flutamide decreased acne and seborrhea scores by 80% in only 3 months. In contrast, spironolactone decreased symptoms by only 40% in the same time period, suggesting superior effectiveness for flutamide for these indications. Flutamide has, in general, been found to reduce symptoms of acne by as much as 90% even at low doses, with several studies showing complete acne clearance.Excessive hair growth
Flutamide has been found to be effective in the treatment of hirsutism (excessive body/facial hair
Facial hair is hair grown on the face, usually on the chin, cheeks, and upper lip region. It is typically a secondary sex characteristic of human males. Men typically start developing facial hair in the later stages of puberty or adolescenc ...
growth) in numerous studies.Müderri̇s, İ. İ., & Öner, G. (2009). Flutamide and Bicalutamide Treatment in Hirsutism. Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Endocrinology-Special Topics, 2(2), 110. http://www.turkiyeklinikleri.com/article/en-hirsutizm-tedavisinde-flutamid-ve-bikalutamid-kullanimi-55753.html It possesses moderate effectiveness for this indication, and the overall quality of the evidence is considered to be moderate. The medication shows equivalent or superior effectiveness to other antiandrogens including spironolactone, cyproterone acetate, and finasteride in the treatment of hirsutism, although its relatively high risk of hepatotoxicity makes it unfavorable compared to these other options. It has been used to treat hirsutism at dosages ranging from 62.5 mg/day to 750 mg/day. A study found that multiple dosages of flutamide significantly reduced hirsutism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and that there were no significant differences in the effectiveness for dosages of 125 mg/day, 250 mg/day, and 375 mg/day. In addition, a study found that combination of 125 mg/day flutamide with finasteride was no more effective than 125 mg/day flutamide alone in the treatment of hirsutism. These findings support the use of flutamide at lower doses for hirsutism without loss of effectiveness, which may help to lower the risk of hepatotoxicity. However, the risk has been found to remain even at very low doses.
Scalp hair loss
Flutamide has been found to be effective in the treatment of female pattern hair loss in a number of studies. In one study of 101 pre- and postmenopausal women, flutamide alone or in combination with an oral contraceptive produced a marked decrease in hair loss scores after 1 year of treatment, with maximum effect after 2 years of treatment and benefits maintained for another 2 years. In a small study of flutamide with an oral contraceptive, the medication caused an increase in cosmetically acceptance hair density in 6 of 7 women with diffuse scalp hair loss. In a comparative study, flutamide significantly improved scalp hair growth (21% reduction in Ludwig scores) in hyperandrogenic women after 1 year of treatment, whereas cyproterone acetate andfinasteride
Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat excessive hair growth in women and as a part of h ...
were ineffective.
Other uses
Flutamide has been used incase report In medicine, a case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports may contain a demographic profile of the patient, but usually describe an unusual or novel occur ...
s to decrease the frequency of spontaneous orgasms, for instance in men with post-orgasmic illness syndrome.
Available forms
Flutamide is available in the form of 125 mgoral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
** Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or or ...
capsules and 250 mg oral tablet
Tablet may refer to:
Medicine
* Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill"
Computing
* Tablet computer, a mobile computer that is primarily operated by touching the ...
s.
Side effects
The side effects of flutamide are sex-dependent. In men, a variety of side effects related to androgen deprivation may occur, the most common being gynecomastia and breast tenderness. Others includehot flash
Hot flashes (also known as hot flushes) are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, an ...
es, decreased muscle mass, decreased bone mass and an associated increased risk of fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displ ...
s, depression, and sexual dysfunction including reduced libido and erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, is the type of sexual dysfunction in which the penis fails to become or stay erect during sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in men.Cunningham GR, Rosen RC. Overview of ma ...
. In women, flutamide is, generally, relatively well tolerated, and does not interfere with ovulation. The only common side effect of flutamide in women is dry skin (75%), which can be attributed to a reduction of androgen-mediated sebum production. General side effects that may occur in either sex include dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a common medical c ...
, lack of appetite, gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of th ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenter ...
, and diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
, a greenish-bluish discoloration of the urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
, and hepatic changes. Because flutamide is a pure antiandrogen, unlike steroidal antiandrogens like cyproterone acetate and megestrol acetate (which additionally possess progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the bod ...
ic activity), it does not appear to have a risk of cardiovascular side effects (e.g., thromboembolism
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets ...
) or fluid retention.
Gynecomastia
Flutamide, as a monotherapy, causes gynecomastia in 30 to 79% of men, and also produces breast tenderness. However, more than 90% of cases of gynecomastia with NSAAs including flutamide are mild to moderate.Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and treat breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has b ...
, a selective estrogen receptor modulator
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonist/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on the estrogen receptor (ER). A characteristic that distinguishes these substances from pure ER agonists ...
(SERM) with predominantly antiestrogenic actions, can counteract flutamide-induced gynecomastia and breast pain in men.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea is more common and sometimes more severe with flutamide than with other NSAAs. In a comparative trial ofcombined androgen blockade Maximum or maximal androgen blockade (MAB) or complete or combined androgen blockade (CAB) is a medical treatment involving the combination of both androgen receptor (AR) antagonism and inhibition or suppression of androgen production to attain ma ...
for prostate cancer, the rate of diarrhea was 26% for flutamide and 12% for bicalutamide. Moreover, 6% of flutamide-treated patients discontinued the medication due to diarrhea, whereas only 0.5% of bicalutamide-treated patients did so. In the case of antiandrogen monotherapy for prostate cancer, the rates of diarrhea are 5 to 20% for flutamide, 2 to 5% for bicalutamide, and 2 to 4% for nilutamide. In contrast to diarrhea, the rates of nausea and vomiting are similar among the three medications.
Rare reactions
Liver toxicity
Although rare, flutamide has been associated with severe hepatotoxicity and death. By 1996, 46 cases of severe cholestatichepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
had been reported, with 20 fatalities. There have been continued case reports since, including liver transplants and death. A 2021 review of the literature found 15 cases of serious hepatotoxicity in women treated with flutamide, including 7 liver transplantations and 2 deaths.
Based on the number of prescriptions written and the number of cases reported in the MedWatch database, the rate of serious hepatotoxicity associated with flutamide treatment was estimated in 1996 as approximately 0.03% (3 per 10,000). However, other research has suggested that the true incidence of significant hepatotoxicity with flutamide may be much greater, as high as 0.18 to 10%.
Flutamide is also associated with liver enzyme elevations in up to 42 to 62% of patients, although marked elevations in liver enzymes (above 5 times upper normal limit) occur only in 3 to 5%. The risk of hepatotoxicity with flutamide is much higher than with nilutamide or bicalutamide. Lower doses of the medication appear to have a possibly reduced but still significant risk. Liver function should be monitored regularly with liver function test
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
s during flutamide treatment. In addition, due to the high risk of serious hepatotoxicity, flutamide should not be used in the absence of a serious indication.
The mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targ ...
of flutamide-induced hepatotoxicity is thought to be due to mitochondrial toxicity. Specifically, flutamide and particularly its major metabolite hydroxyflutamide inhibit enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s in the mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
l electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples ...
in hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
s, including respiratory complexes I ( NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase), II (succinate dehydrogenase
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase (SQR) or respiratory complex II is an enzyme complex, found in many bacterial cells and in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. It is the only enzyme that participates ...
), and V (ATP synthase
ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation ...
), and thereby reduce cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
via ATP depletion and hence decrease cell survival. Inhibition of taurocholate
Taurocholic acid, known also as cholaic acid, cholyltaurine, or acidum cholatauricum, is a deliquescent yellowish crystalline bile acid involved in the emulsification of fats. It occurs as a sodium salt in the bile of mammals. It is a conjugate ...
(a bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Primar ...
) efflux has also been implicated in flutamide-induced hepatotoxicity. In contrast to flutamide and hydroxyflutamide, which severely compromise hepatocyte cellular respiration ''in vitro'', bicalutamide does not significantly do so at the same concentrations and is regarded as non-mitotoxic. It is thought that the nitroaromatic group of flutamide and hydroxyflutamide enhance their mitochondrial toxicity; bicalutamide, in contrast, possesses a cyano group
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a ...
in place of the nitro moiety
Moiety may refer to:
Chemistry
* Moiety (chemistry), a part or functional group of a molecule
** Moiety conservation, conservation of a subgroup in a chemical species
Anthropology
* Moiety (kinship), either of two groups into which a society is ...
, greatly reducing the potential for such toxicity.
The hepatotoxicity of flutamide appears to depend on hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
of flutamide catalyzed by an arylacetamide deacetalyse enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
. This is analogous to the hepatotoxicity that occurs with the withdrawn paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferio ...
(acetominophen)-related medication phenacetin
Phenacetin (acetophenetidin, ''N''-(4-ethoxyphenyl)acetamide) is a pain-relieving and fever-reducing drug, which was widely used following its introduction in 1887. It was withdrawn from medicinal use as dangerous from the 1970s (e.g., withdrawn ...
. In accordance, the combination of paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferio ...
(acetaminophen) and flutamide appears to result in additive to synergistic hepatotoxicity, indicating a potential drug interaction.
Others
Flutamide has also been associated withinterstitial pneumonitis
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs)) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pul ...
(which can progress to pulmonary fibrosis). The incidence of interstitial pneumonitis with flutamide was found to be 0.04% (4 per 10,000) in a large clinical cohort of 41,700 prostate cancer patients. A variety of case report In medicine, a case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports may contain a demographic profile of the patient, but usually describe an unusual or novel occur ...
s have associated flutamide with photosensitivity. Flutamide has been associated with several case reports of methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia, or methaemoglobinaemia, is a condition of elevated methemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, poor muscle coordination, and blue-colored skin (cyanosis). Complications ...
. Bicalutamide does not appear to share this risk with flutamide. Flutamide has also been associated with reports of sulfhemoglobinemia
Sulfhemoglobinemia is a rare condition in which there is excess sulfhemoglobin (SulfHb) in the blood. The pigment is a greenish derivative of hemoglobin which cannot be converted back to normal, functional hemoglobin. It causes cyanosis even at ...
and neutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteri ...
.
Birth defects
Out of the available endocrine-disrupting compounds looked at, flutamide has a notable effect onanogenital distance
Anogenital distance (AGD) is the distance from the midpoint of the anus to the genitalia, the underside of the vagina, the clitoris or the scrotum. It is considered medically significant for a number of reasons, in both humans and other animals ...
in rats.)
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Antiandrogenic activity
Flutamide acts as a selective, competitive, silent antagonist of theandrogen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in ...
(AR). Its active form, hydroxyflutamide, has between 10- to 25-fold higher affinity for the AR than does flutamide, and hence is a much more potent AR antagonist in comparison. However, at high concentrations, unlike flutamide, hydroxyflutamide is able to weakly activate the AR. Flutamide has far lower affinity for the AR than do steroidal antiandrogens like spironolactone and cyproterone acetate, and it is a relatively weak antiandrogen in terms of potency by weight, but the large dosages at which flutamide is used appear to compensate for this. In accordance with its selectivity for the AR, flutamide does not interact with the progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the majo ...
, estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
, glucocorticoid, or mineralocorticoid receptor, and possesses no intrinsic progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the bod ...
ic, estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
ic, glucocorticoid, or antigonadotropic
An antigonadotropin is a drug which suppresses the activity and/or downstream effects of one or both of the gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). This results in an inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituita ...
activity. However, it can have some indirect estrogenic effects via increased levels of estradiol secondary to AR blockade, and this involved in the gynecomastia it can produce. Because flutamide does not have any estrogenic, progestogenic, or antigonadotropic activity, the medication does not cause menstrual irregularities in women. This is in contrast to steroidal antiandrogens like spironolactone and cyproterone acetate. Similarly to nilutamide, bicalutamide, and enzalutamide, flutamide crosses the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where ne ...
and exerts central antiandrogen actions.
Flutamide has been found to be equal to slightly more potent than cyproterone acetate and substantially more potent than spironolactone as an antiandrogen in bioassays. This is in spite of the fact that hydroxyflutamide has on the order of 10-fold lower affinity for the AR relative to cyproterone acetate.Feau, C. (2009). Novel Small Molecule Antagonists of the Interaction of the Androgen Receptor and Transcriptional Co-regulators. Saint Jude Children's Research Hospital Memphis TN. http://www.dtic.mil/docs/citations/ADA499611 Hydroxyflutamide shows about 2- to 4-fold lower affinity for the rat and human AR than does bicalutamide. In addition, whereas bicalutamide has an elimination half-life of around 6 days, hydroxyflutamide has an elimination half-life of only 8 to 10 hours, a roughly 17-fold difference. In accordance, at dosages of 50 mg/day bicalutamide and 750 mg/day flutamide (a 15-fold difference), circulating levels of flutamide at steady-state
In systems theory, a system or a process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties '' ...
have been found to be approximately 7.5-fold lower than those of bicalutamide. Moreover, whereas flutamide at this dosage has been found to produce a 75% reduction in prostate-specific antigen levels in men with prostate cancer, a fall of 90% has been demonstrated with this dosage of bicalutamide. In accordance, 50 mg/day bicalutamide has been found to possess equivalent or superior effectiveness to 750 mg/day flutamide in a large clinical trial for prostate cancer. Also, bicalutamide has been shown to be 5-fold more potent than flutamide in rats and 50-fold more potent than flutamide in dogs. Taken together, flutamide appears to be a considerably less potent and efficacious antiandrogen than is bicalutamide.
Dose-ranging studies of flutamide in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer alone and in combination with a GnRH agonist have been performed.
Flutamide increases testosterone levels by 5- to 10-fold in gonadally intact male rats.
CYP17A1 inhibition
Flutamide and hydroxyflutamide have been found ''in vitro'' to inhibit CYP17A1 (17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase), anenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
which is required for the biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecul ...
of androgens. In accordance, flutamide has been found to slightly but significantly lower androgen levels in GnRH analogue-treated male prostate cancer patients and women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
. In a directly comparative study of flutamide monotherapy (375mg once daily) versus bicalutamide monotherapy (80mg once daily) in Japanese men with prostate cancer, after 24weeks of treatment flutamide decreased dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) levels by about 44% while bicalutamide increased them by about 4%. As such, flutamide is a weak inhibitor of androgen biosynthesis. However, the clinical significance of this action may be limited when flutamide is given without a GnRH analogue to non-castrated men, as the medication markedly elevates testosterone levels into the high normal male range via prevention of AR activation-mediated negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by othe ...
on the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis in this context.
Other activities
Flutamide has been identified as anagonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. This may be involved in the hepatotoxicity of flutamide.
Pharmacokinetics
Theabsorption
Absorption may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
*Absorption (biology), digestion
**Absorption (small intestine)
*Absorption (chemistry), diffusion of particles of gas or liquid into liquid or solid materials
*Absorption (skin), a route by which s ...
of flutamide is complete upon oral ingestion. Food has no effect on the bioavailability of flutamide. Steady-state
In systems theory, a system or a process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties '' ...
levels of hydroxyflutamide, the active form of flutamide, are achieved after 2 to 4 days administration. Levels of hydroxyflutamide are approximately 50-fold higher than those of flutamide at steady-state
In systems theory, a system or a process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties '' ...
.
The plasma protein binding of flutamide and hydroxyflutamide are high; 94 to 96% and 92 to 94%, respectively. Flutamide and its metabolite hydroxyflutamide are known to be transported by the multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1; ABCC1).
Flutamide is metabolized
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
by CYP1A2 (via α-hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to:
*(i) most commonly, hydroxylation describes a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound.
*(ii) the ''degree of hydroxylation'' refers to the number of OH groups in a ...
) in the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
during first-pass metabolism to its main metabolite hydroxyflutamide (which accounts for 23% of an oral dose of flutamide one hour post-ingestion), and to at least five other, minor metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
s. Flutamide has at least 10 inactive metabolites total, including 4-nitro-3-fluoro-methylaniline.
Flutamide is excreted in various forms in the urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
, the primary form being 2-amino-5-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenol.
Flutamide and hydroxyflutamide have elimination half-lives of 4.7 hours and 6 hours in adults, respectively. However, the half-life of hydroxyflutamide is extended to 8 hours after a single dose and to 9.6 hours at steady state) in elderly
Old age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms for people at this age include old people, the elderly (worldwide usage), OAPs (British usage ...
individuals. The elimination half-lives of flutamide and hydroxyflutamide are regarded as too short to allow for once-daily dosing, and for this reason, flutamide is instead administered three times daily at 8-hour intervals. In contrast, the newer NSAAs nilutamide, bicalutamide, and enzalutamide all have much longer half-lives, and this allows for once-daily administration in their cases.
Chemistry
Unlike the hormones with which it competes, flutamide is not asteroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
; rather, it is a substituted anilide. Hence, it is described as ''nonsteroidal'' in order to distinguish it from older steroidal antiandrogens such as cyproterone acetate and megestrol acetate.
Synthesis
 Schotten–Baumann reaction between 4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline 93-11-3(1) with isobutanoyl chloride 9-30-1(2) in the presence of triethylamine.
Schotten–Baumann reaction between 4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline 93-11-3(1) with isobutanoyl chloride 9-30-1(2) in the presence of triethylamine.
History
Flutamide was first synthesized in 1967 by Neri and colleagues at Schering Plough Corporation. It was originally synthesized as abacteriostatic agent
A bacteriostatic agent or bacteriostat, abbreviated Bstatic, is a biological or chemical agent that stops bacteria from reproducing, while not necessarily killing them otherwise. Depending on their application, bacteriostatic antibiotics, disinfect ...
, but was subsequently, and serendipitously found to possess antiandrogen activity. The code name of flutamide during development was SCH-13521. Clinical research of the medication began in 1971, and it was first marketed in 1983, specifically in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
under the brand name Drogenil and in West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
under the brand name Flugerel. Flutamide was not introduced in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
until 1989; it was specifically approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer in combination with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released ...
(GnRH) analogue. The medication was first studied for the treatment of hirsutism in women in 1989. It was the first "pure antiandrogen" to be studied in the treatment of hirsutism. Flutamide was the first NSAA to be introduced, and was followed by nilutamide in 1989 and then bicalutamide in 1995.
Society and culture
Generic names
''Flutamide'' is the generic name of the drug and its , , , , and . Its names inLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, and Spanish are ''flutamidum'', ''flutamid'', and ''flutamida'', respectively. The medication has also been referred to by the name ''niftolide''.
Brand names
Brand names of flutamide include or have included Cebatrol, Cytomid, Drogenil, Etaconil, Eulexin, Flucinom, Flumid, Flutacan, Flutamid, Flutamida, Flutamin, Flutan, Flutaplex, Flutasin, Fugerel, Profamid, and Sebatrol, among others.Availability
Flutamide is marketed widely throughout the world, including in theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
, East and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
.
Research
Prostate cancer
The combination of anestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
and flutamide as a form of combined androgen blockade Maximum or maximal androgen blockade (MAB) or complete or combined androgen blockade (CAB) is a medical treatment involving the combination of both androgen receptor (AR) antagonism and inhibition or suppression of androgen production to attain ma ...
for the treatment of prostate cancer has been researched.
Enlarged prostate
Flutamide has been studied in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH; enlarged prostate) in men in several clinical studies. It has been found to reduce prostate volume by about 25%, which is comparable to the reduction achieved with the5α-reductase inhibitor
5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes o ...
finasteride
Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat excessive hair growth in women and as a part of h ...
. Unfortunately, it has been associated with side effects in these studies including gynecomastia and breast tenderness (in about 50% of patients), gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, diarrhea, and flatulence
Flatulence, in humans, is the expulsion of gas from the intestines via the anus, commonly referred to as farting. "Flatus" is the medical word for gas generated in the stomach or bowels. A proportion of intestinal gas may be swallowed enviro ...
, and hepatotoxicity, although sexual function including libido and erectile potency were maintained.
Breast cancer
Flutamide was studied for the treatment of advanced breast cancer in two phase IIclinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s but was found to be ineffective. Out of a total of 47 patients, only three short-term responses occurred. However, the patients in the studies were selected irrespective of AR, , , or HER2 status, which were all unknown.
Psychiatric disorders
Flutamide has been studied in the treatment ofbulimia nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. The aim of this activity is to expel the body of calories eaten ...
in women.
Flutamide was found to be effective in the treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) in men with comorbid Tourette's syndrome in one small randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical t ...
. Conversely, it was ineffective in patients with OCD in another study. More research is necessary to determine whether flutamide is effective in the treatment of OCD.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * {{Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulators Anilides Anti-acne preparations Aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists CYP17A1 inhibitors Enantiopure drugs Hair loss medications Hair removal Hepatotoxins Hormonal antineoplastic drugs Nitrobenzenes Nonsteroidal antiandrogens Prodrugs Progonadotropins Propionamides Prostate cancer Trifluoromethyl compounds