Flea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless
Koehler, P.G.; Oi, F.M. Printed July 1993, revised February 2003. Provided by the
 Flea larvae emerge from the eggs to feed on any available organic material such as dead insects, faeces,
Flea larvae emerge from the eggs to feed on any available organic material such as dead insects, faeces,

 Fleas likely descended from fluid feeding insects that probably fed on plants. Fossils of large, wingless
Fleas likely descended from fluid feeding insects that probably fed on plants. Fossils of large, wingless
 Fleas feed on a wide variety of
Fleas feed on a wide variety of
 In many species, fleas are principally a nuisance to their hosts, causing an
In many species, fleas are principally a nuisance to their hosts, causing an
File:HookeFlea01.jpg, Robert Hooke's drawing of a flea in ''

Parasitic Insects, Mites and Ticks: Genera of Medical and Veterinary Importance
{{Authority control Extant Middle Jurassic first appearances Hematophages Insect vectors of human pathogens Insects in culture Parasites of cats Parasites of dogs Veterinary entomology
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s that live as external parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
of mammals and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, are usually brown, and have bodies that are "flattened" sideways or narrow, enabling them to move through their hosts' fur or feathers. They lack wings; their hind legs are extremely well adapted for jumping. Their claws keep them from being dislodged, and their mouthparts are adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
. They can leap 50 times their body length, a feat second only to jumps made by another group of insects, the superfamily of froghoppers. Flea larvae are worm-like, with no limbs; they have chewing mouthparts and feed on organic debris left on their hosts' skin.
Genetic evidence indicates that fleas are a specialised lineage of parasitic scorpionflies (Mecoptera) ''sensu lato'', most closely related to the family Nannochoristidae
Nannochoristidae is a family of scorpionflies with many unusual traits. It is a tiny, relict family with a single extant genus, '' Nannochorista'', with eight species occurring in New Zealand, southeastern Australia, Tasmania, Argentina and Chil ...
. The earliest known fleas are lived in the Middle Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
; modern-looking forms appeared in the Cenozoic. Fleas probably originated on mammals first and expanded their reach to birds. Each species of flea specializes, more or less, on one species of host: many species of flea never breed on any other host; some are less selective. Some families of fleas are exclusive to a single host group; for example, the Malacopsyllidae are found only on armadillos, the Ischnopsyllidae
Ischnopsyllidae is a family of fleas belonging to the order Siphonaptera
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live ...
only on bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
s, and the Chimaeropsyllidae only on elephant shrew
Elephant shrews, also called jumping shrews or sengis, are small insectivorous mammals native to Africa, belonging to the family Macroscelididae, in the order Macroscelidea. Their traditional common English name "elephant shrew" comes from a perc ...
s.
The oriental rat flea, ''Xenopsylla cheopis
The Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''), also known as the tropical rat flea or the rat flea, is a parasite of rodents, primarily of the genus ''Rattus'', and is a primary vector for bubonic plague and murine typhus. This occurs when a fl ...
'', is a vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
of ''Yersinia pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly '' Pasteurella pestis'') is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium without spores that is related to both ''Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'' and ''Yersinia enterocolitica''. It is a facult ...
'', the bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were amon ...
that causes bubonic plague. The disease was spread to humans by rodents, such as the black rat, which were bitten by infected fleas. Major outbreaks included the Plague of Justinian
The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague (541–549 AD) was the first recorded major outbreak of the first plague pandemic, the first Old World pandemic of plague, the contagious disease caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. The dis ...
, about 540, and the Black Death, about 1350, each of which killed a sizeable fraction of the world's people.
Fleas appear in human culture in such diverse forms as flea circus
A flea circus is a circus sideshow attraction in which fleas are attached (or appear to be attached) to miniature carts and other items, and encouraged to perform circus acts within a small housing.
History
The first records of flea perform ...
es; poems, such as John Donne's erotic " The Flea"; works of music, such as those by Modest Mussorgsky
Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky ( rus, link=no, Модест Петрович Мусоргский, Modest Petrovich Musorgsky , mɐˈdɛst pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈmusərkskʲɪj, Ru-Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky version.ogg; – ) was a Russian compo ...
; and a film by Charlie Chaplin.
Morphology and behavior
Fleas are wingless insects, long, that are agile, usually dark colored (for example, the reddish-brown of thecat flea
The cat flea (scientific name ''Ctenocephalides felis'') is an extremely common parasitic insect whose principal host is the domestic cat, although a high proportion of the fleas found on dogs also belong to this species. This is despite the wid ...
), with a proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elong ...
, or stylet, adapted to feeding by piercing the skin and sucking their host's blood through their epipharynx. Flea legs end in strong claws that are adapted to grasp a host.
Unlike other insects, fleas do not possess compound eye
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which disti ...
s but instead only have simple eyespots with a single biconvex lens; some species lack eyes altogether. Their bodies are laterally compressed, permitting easy movement through the hairs or feathers on the host's body. The flea body is covered with hard plates called sclerites. These sclerites are covered with many hairs and short spines directed backward, which also assist its movements on the host. The tough body is able to withstand great pressure, likely an adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
to survive attempts to eliminate them by scratching.FleasKoehler, P.G.; Oi, F.M. Printed July 1993, revised February 2003. Provided by the
University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
Fleas lay tiny, white, oval eggs. The larvae are small and pale, have bristles covering their worm-like bodies, lack eyes, and have mouth parts adapted to chewing. The larvae feed on organic matter, especially the feces of mature fleas, which contain dried blood. Adults feed only on fresh blood.
Jumping
Their legs are long, the hind pair well adapted for jumping; a flea can jump vertically up to and horizontally up to , making the flea one of the best jumpers of all known animals (relative to body size), second only to the froghopper. A flea can jump more than 100 times its length (vertically up to 7 inches and horizontally 13 inches). That's equivalent to an adult human jumping 250 feet vertically and 450 feet horizontally. Rarely do fleas jump from dog to dog. Most flea infestations come from newly developed fleas from the pet's environment. The flea jump is so rapid and forceful that it exceeds the capabilities of muscle, and instead of relying on direct muscle power, fleas store muscle energy in a pad of the elastic protein namedresilin
Resilin is an elastomeric protein found in many insects and other arthropods. It provides soft rubber-elasticity to mechanically active organs and tissue; for example, it enables insects of many species to jump or pivot their wings efficiently ...
before releasing it rapidly (like a human using a bow and arrow). Immediately before the jump, muscles contract and deform the resilin pad, slowly storing energy which can then be released extremely rapidly to power leg extension for propulsion. To prevent premature release of energy or motions of the leg, the flea employs a "catch mechanism". Early in the jump, the tendon of the primary jumping muscle passes slightly behind the coxa-trochanter joint, generating a torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
which holds the joint closed with the leg close to the body. To trigger jumping, another muscle pulls the tendon forward until it passes the joint axis, generating the opposite torque to extend the leg and power the jump by release of stored energy. The actual take off has been shown by high-speed video to be from the tibiae and tarsi rather than from the trochantera (knees).
Life cycle and development
Fleas areholometabolous
Holometabolism, also called complete metamorphosis, is a form of insect development which includes four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and imago (or adult). Holometabolism is a synapomorphic trait of all insects in the superorder Endopterygota. ...
insects, going through the four lifecycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
* Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
*Life-cycle hypothesis ...
stages of egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
, larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
, pupa
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in thei ...
, and imago
In biology, the imago (Latin for "image") is the last stage an insect attains during its metamorphosis, its process of growth and development; it is also called the imaginal stage, the stage in which the insect attains maturity. It follows the f ...
(adult). In most species, neither female nor male fleas are fully mature when they first emerge but must feed on blood before they become capable of reproduction. The first blood meal triggers the maturation of the ovaries in females and the dissolution of the testicular plug in males, and copulation soon follows. Some species breed all year round while others synchronise their activities with their hosts' life cycles or with local environmental factors and climatic conditions. Flea populations consist of roughly 50% eggs, 35% larvae, 10% pupae, and 5% adults.
Egg
The number of eggs laid depends on species, with batch sizes ranging from two to several dozen. The total number of eggs produced in a female's lifetime (fecundity) varies from around one hundred to several thousand. In some species, the flea lives in the host's nest or burrow and the eggs are deposited on the substrate, but in others, the eggs are laid on the host itself and can easily fall off onto the ground. Because of this, areas where the host rests and sleeps become one of the primaryhabitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
s of eggs and developing larvae. The eggs take around two days to two weeks to hatch.
Larva
 Flea larvae emerge from the eggs to feed on any available organic material such as dead insects, faeces,
Flea larvae emerge from the eggs to feed on any available organic material such as dead insects, faeces, conspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species.
Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organis ...
eggs, and vegetable matter. In laboratory studies, some dietary diversity seems necessary for proper larval development. Blood-only diets allow only 12% of larvae to mature, whereas blood and yeast or dog chow diets allow almost all larvae to mature. Another study also showed that 90% of larvae matured into adults when the diet included nonviable eggs. They are blind and avoid sunlight, keeping to dark, humid places such as sand or soil, cracks and crevices, under carpets and in bedding. The entire larval stage lasts between four and 18 days.
Pupa
Given an adequate supply of food, larvaepupate
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their ...
and weave silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
en cocoons after three larval stages. Within the cocoon, the larva molts for a final time and undergoes metamorphosis into the adult form. This can take just four days, but may take much longer under adverse conditions, and there follows a variable-length stage during which the pre-emergent adult awaits a suitable opportunity to emerge. Trigger factors for emergence include vibrations (including sound), heat (in warm-blooded hosts), and increased levels of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
, all of which may indicate the presence of a suitable host. Large numbers of pre-emergent fleas may be present in otherwise flea-free environments, and the introduction of a suitable host may trigger a mass emergence.
Adult
Once the flea reaches adulthood, its primary goal is to find blood and then to reproduce. Female fleas can lay 5000 or more eggs over their life, permitting rapid increase in numbers. Generally speaking, an adult flea only lives for 2 or 3 months. Without a host to provide a blood meal, a flea's life can be as short as a few days. Under ideal conditions of temperature, food supply, and humidity, adult fleas can live for up to a year and a half. Completely developed adult fleas can live for several months without eating, so long as they do not emerge from their puparia. Optimum temperatures for the flea's life cycle are 21 °C to 30 °C (70 °F to 85 °F) and optimum humidity is 70%. Adult female rabbit fleas, ''Spilopsyllus cuniculi
''Spilopsyllus cuniculi'', the rabbit flea, is a species of flea in the family Pulicidae. It is an external parasite of rabbits and hares and is occasionally found on cats and dogs and also certain seabirds that nest in burrows. It can act as a ...
'', can detect the changing levels of cortisol and corticosterone
Corticosterone, also known as 17-deoxycortisol and 11β,21-dihydroxyprogesterone, is a 21-carbon steroid hormone of the corticosteroid type produced in the cortex of the adrenal glands. It is of minor importance in humans, except in the very rar ...
hormones in the rabbit's blood that indicate it is getting close to giving birth. This triggers sexual maturity in the fleas and they start producing eggs. As soon as the baby rabbits are born, the fleas make their way down to them and once on board they start feeding, mating, and laying eggs. After 12 days, the adult fleas make their way back to the mother. They complete this mini-migration every time she gives birth. Piper, Ross (2007), ''Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals'', Greenwood Press.
Taxonomy and phylogeny
History
Between 1735 and 1758, the Swedish naturalistCarl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
first classified insects, doing so on the basis of their wing structure. One of the seven orders into which he divided them was "Aptera", meaning wingless, a group in which as well as fleas, he included spider
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species ...
s, woodlice
A woodlouse (plural woodlice) is an isopod crustacean from the polyphyleticThe current consensus is that Oniscidea is actually triphyletic suborder Oniscidea within the order Isopoda. They get their name from often being found in old wood ...
and myriapod
Myriapods () are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial.
The fossil record of myriapods reaches back into the late Silurian, ...
s. It wasn't until 1810 that the French zoologist Pierre André Latreille
Pierre André Latreille (; 29 November 1762 – 6 February 1833) was a French zoologist, specialising in arthropods. Having trained as a Roman Catholic priest before the French Revolution, Latreille was imprisoned, and only regained his freedom ...
reclassified the insects on the basis of their mouthparts as well as their wings, splitting Aptera into Thysanura
Thysanura is the now deprecated name of what was, for over a century, recognised as an order in the class Insecta. The two constituent groups within the former order, the Archaeognatha (jumping bristletails) and the Zygentoma (silverfish and fireb ...
(silverfish), Anoplura
Sucking lice (Anoplura, formerly known as Siphunculata) have around 500 species and represent the smaller of the two traditional superfamilies of lice. As opposed to the paraphyletic chewing lice, which are now divided among three suborders, ...
(sucking lice) and Siphonaptera (fleas), at the same time separating off the arachnids and crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s into their own subphyla. The group's name, Siphonaptera, is zoological Latin from the Greek ''siphon'' (a tube) and ''aptera'' (wingless).
External phylogeny
It was historically unclear whether the Siphonaptera are sister to theMecoptera
Mecoptera (from the Greek: ''mecos'' = "long", ''ptera'' = "wings") is an order of insects in the superorder Endopterygota with about six hundred species in nine families worldwide. Mecopterans are sometimes called scorpionflies after their lar ...
(scorpionflies and allies), or are inside that clade, making "Mecoptera" paraphyletic. The earlier suggestion that the Siphonaptera are sister to the Boreidae
Boreidae, commonly called snow scorpionflies, or in the British Isles, snow fleas (no relation to the snow flea '' Hypogastrura nivicola'') are a very small family of scorpionflies, containing only around 30 species, all of which are boreal or ...
(snow scorpionflies) is not supported. A 2020 genetic study recovered Siphonaptera within Mecoptera, with strong support, as the sister group to Nannochoristidae
Nannochoristidae is a family of scorpionflies with many unusual traits. It is a tiny, relict family with a single extant genus, '' Nannochorista'', with eight species occurring in New Zealand, southeastern Australia, Tasmania, Argentina and Chil ...
, a small, relictual group of mecopterans native to the Southern Hemisphere. Fleas and nannochoristids share several similarities with each other that are not shared with other mecopterans, including similar mouthparts as well as a similar sperm pump organisation.
Relationships of Siphonaptera per Tihelka et al. 2020.
Fossil history

 Fleas likely descended from fluid feeding insects that probably fed on plants. Fossils of large, wingless
Fleas likely descended from fluid feeding insects that probably fed on plants. Fossils of large, wingless stem-group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. ...
fleas with siphonate (sucking) mouthparts from the Middle Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
to Early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
have been found in northeastern China and Russia, belonging to the families Saurophthiridae
''Saurophthirus'' is an extinct genus of giant stem-group flea, and the only member of the family Saurophthiridae. The type species, ''S. longipes'' is found in early Cretaceous strata of Baissa, Siberia. Two other species ''S. exquisitus'' and ...
and Pseudopulicidae
Pseudopulicidae is an extinct family of stem-group fleas from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of China. They represent the oldest known group of stem-fleas. Like other stem-group "giant fleas", they are much larger and lack the specialised ...
, as well as ''Tarwinia
''Tarwinia'' is an extinct genus of stem-group flea known from a single species, ''T. australis'', from the Early Cretaceous ( Aptian) Koonwarra Fossil Bed of Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of ...
'' from the Early Cretaceous of Australia. Most flea families formed after the end of the Cretaceous (in the Paleogene and onwards). Modern fleas probably arose in the southern continental area of Gondwana, and migrated rapidly northwards from there. They most likely evolved with mammal hosts, only later moving to bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s.
Siphonaptera is a relatively small order of insects: members of the order undergo complete metamorphosis and are secondarily wingless (their ancestors had wings which modern forms have lost). In 2005, Medvedev listed 2005 species in 242 genera, and despite subsequent descriptions of new species, bringing the total up to around 2500 species, this is the most complete database available. The order is divided into four infraorders and eighteen families. Some families are exclusive to a single host group; these include the Malacopsyllidae ( armadillos), Ischnopsyllidae (bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
s) and Chimaeropsyllidae (elephant shrew
Elephant shrews, also called jumping shrews or sengis, are small insectivorous mammals native to Africa, belonging to the family Macroscelididae, in the order Macroscelidea. Their traditional common English name "elephant shrew" comes from a perc ...
s).
Many of the known species are little studied. Some 600 species (a quarter of the total) are known from single records. Over 94% of species are associated with mammalian hosts, and only about 3% of species can be considered to be specific parasites of bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s. The fleas on birds are thought to have originated from mammalian fleas; at least sixteen separate groups of fleas switched to avian hosts during the evolutionary history of the Siphonaptera. Occurrences of fleas on reptiles is accidental, and fleas have been known to feed on the hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod (invertebrate) body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which ...
(bloodlike body fluid) of tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s.
Internal phylogeny
Flea phylogeny was long neglected, the discovery of homologies with the parts of other insects being made difficult by their extreme specialization. Whiting and colleagues prepared a detailed molecular phylogeny in 2008, with the basic structure shown in the cladogram. The Hectopsyllidae, including the harmful chigoe flea or jigger, is sister to the rest of the Siphonaptera.Relationship with host
warm-blooded
Warm-blooded is an informal term referring to animal species which can maintain a body temperature higher than their environment. In particular, homeothermic species maintain a stable body temperature by regulating metabolic processes. The onl ...
vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s including dogs, cats, rabbits, squirrels, ferrets, rats, mice birds and sometimes humans. Fleas normally specialise in one host species or group of species, but can often feed but not reproduce on other species. '' Ceratophyllus gallinae'' affects poultry as well as wild birds. As well as the degree of relatedness of a potential host to the flea's original host, it has been shown that avian fleas that exploit a range of hosts, only parasitise species with low immune responses. In general, host specificity decreases as the size of the host species decreases. Another factor is the opportunities available to the flea to change host species; this is smaller in colonially nesting birds, where the flea may never encounter another species, than it is in solitary nesting birds. A large, long-lived host provides a stable environment that favours host-specific parasites.
Although there are species named dog fleas ( ''Ctenocephalides canis'' Curtis, 1826) and cat fleas ( ''Ctenocephalides felis''), fleas are not always strictly species-specific. A study in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
examined 244 fleas from 29 dogs: all were cat fleas. Dog fleas had not been found in Virginia in more than 70 years, and may not even occur in the US, so a flea found on a dog is likely a cat flea (''Ctenocephalides felis'').
One theory of human hairlessness is that the loss of hair helped humans to reduce their burden of fleas and other ectoparasites.
Direct effects of bites
 In many species, fleas are principally a nuisance to their hosts, causing an
In many species, fleas are principally a nuisance to their hosts, causing an itch
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant ...
ing sensation which in turn causes the host to try to remove the pest by biting, pecking or scratching. Fleas are not simply a source of annoyance, however. Flea bites cause a slightly raised, swollen, irritating nodule to form on the epidermis at the site of each bite, with a single puncture point at the centre, like a mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
bite. This can lead to an eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can ...
tous itchy skin disease called flea allergy dermatitis
Flea allergy dermatitis is an eczematous itchy skin disease of dogs and cats. For both of these domestic species, flea allergy dermatitis is the most common cause of skin disease. Affected animals develop allergic reactions to chemicals in flea sa ...
, which is common in many host species, including dogs and cats. The bites often appear in clusters or lines of two bites, and can remain itchy and inflamed for up to several weeks afterwards. Fleas can lead to secondary hair loss as a result of frequent scratching and biting by the animal. They can also cause anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
in extreme cases.
As a vector
Fleas are vectors for viral,bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
l and rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The term "ricke ...
l disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
s of humans and other animals, as well as of protozoan and helminth parasites. Bacterial diseases carried by fleas include murine or endemic typhus and bubonic plague. Fleas can transmit ''Rickettsia typhi
''Rickettsia typhi'' is a small, aerobic, obligate intracellular, rod shaped gram negative bacterium. It belongs to the typhus group of the ''Rickettsia'' genus, along with ''R. prowazekii''. ''R. typhi'' has an uncertain history, as it may have ...
'', ''Rickettsia felis
''Rickettsia felis'' is a species of bacterium, the pathogen that causes cat-flea typhus in humans, also known as flea-borne spotted fever. ''Rickettsia felis'' also is regarded as the causative organism of many cases of illnesses generally class ...
'', ''Bartonella henselae
''Bartonella henselae'', formerly ''Rochalimæa henselae'', is a bacterium that is the causative agent of cat-scratch disease (bartonellosis).
''Bartonella henselae'' is a member of the genus ''Bartonella'', one of the most common types of bacter ...
'', and the myxomatosis
Myxomatosis is a disease caused by ''Myxoma virus'', a poxvirus in the genus '' Leporipoxvirus''. The natural hosts are tapeti (''Sylvilagus brasiliensis'') in South and Central America, and brush rabbits (''Sylvilagus bachmani'') in North A ...
virus. They can carry ''Hymenolepiasis
Hymenolepiasis is infestation by one of two species of tapeworm: '' Hymenolepis nana'' or '' H. diminuta''. Alternative names are dwarf tapeworm infection and rat tapeworm infection. The disease is a type of helminthiasis which is classified as a ...
'' tapeworms
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of ...
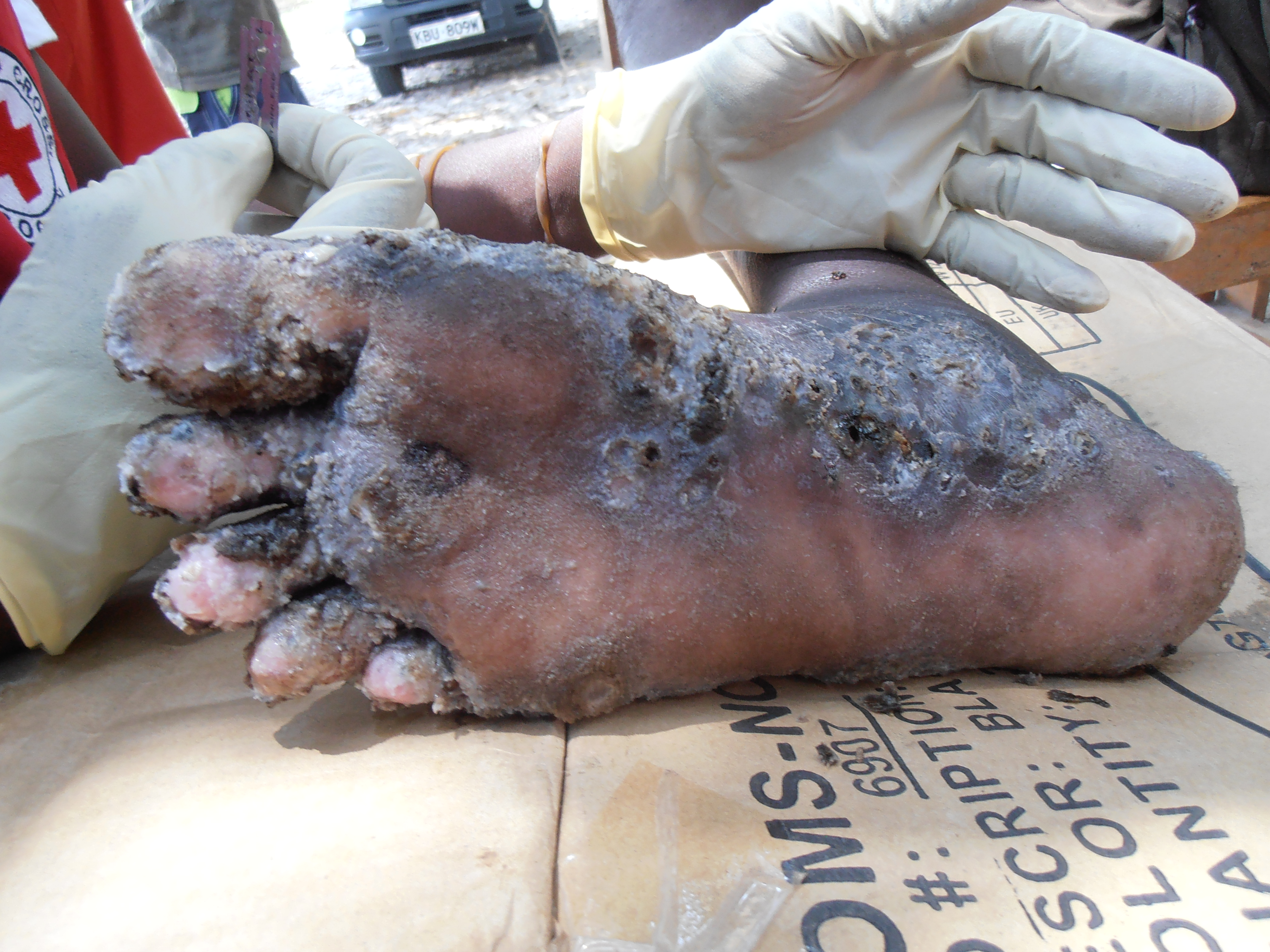
and Trypanosome protozoans. The chigoe flea or jigger (''Tunga penetrans
''Tunga penetrans'' is a species of flea also known as the jigger, jigger flea, chigoe, chigo, chigoe flea, chigo flea, nigua, sand flea, or burrowing flea. It is a parasitic insect found in most tropical and sub-tropical climates. In its parasi ...
'') causes the disease tungiasis
Tungiasis is an inflammatory skin disease caused by infection with the female ectoparasitic '' Tunga penetrans'', a flea also known as the chigoe, chigo, chigoe flea, chigo flea, jigger, nigua, sand flea, or burrowing flea (and not to be confuse ...
, a major public health problem around the world. Fleas that specialize as parasites on specific mammals may use other mammals as hosts; thus, humans may be bitten by cat and dog fleas.
Relationship with humans
In literature and art
Fleas have appeared in poetry, literature, music and art; these include Robert Hooke's drawing of a flea under themicroscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
in his pioneering book ''Micrographia
''Micrographia: or Some Physiological Descriptions of Minute Bodies Made by Magnifying Glasses. With Observations and Inquiries Thereupon.'' is a historically significant book by Robert Hooke about his observations through various lenses. It ...
'' published in 1665, poems by Donne and Jonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish satirist, author, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whigs, then for the Tories), poet, and Anglican cleric who became Dean of St Patrick's Cathedral, Dubl ...
, works of music by Giorgio Federico Ghedini
Giorgio Federico Ghedini (11 July 189225 March 1965) was an Italian composer. In addition to orchestral works, in 1949 he premiered a one-act opera based on the American novella ''Billy Budd'' by Herman Melville.
Life
Ghedini was born in Cuneo i ...
and Modest Mussorgsky
Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky ( rus, link=no, Модест Петрович Мусоргский, Modest Petrovich Musorgsky , mɐˈdɛst pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈmusərkskʲɪj, Ru-Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky version.ogg; – ) was a Russian compo ...
, a play by Georges Feydeau
Georges-Léon-Jules-Marie Feydeau (; 8 December 1862 – 5 June 1921) was a French playwright of the era known as the Belle Époque. He is remembered for his farces, written between 1886 and 1914.
Feydeau was born in Paris to middle-class parent ...
, a film by Charlie Chaplin, and paintings by artists such as Giuseppe Crespi
Giuseppe Maria Crespi (March 14, 1665 – July 16, 1747), nicknamed Lo Spagnuolo ("The Spaniard"), was an Italian late Baroque painter of the Bolognese School. His eclectic output includes religious paintings and portraits, but he is now most ...
, Giovanni Battista Piazzetta
Giovanni Battista Piazzetta (also called Giambattista Piazzetta or Giambattista Valentino Piazzetta) (February 13, 1682 or 1683 – April 28, 1754) was an Italian Rococo painter of religious subjects and genre scenes.
Biography
Piazzetta was ...
, and Georges de La Tour
Georges de La Tour (13 March 1593 – 30 January 1652) was a French Baroque painter, who spent most of his working life in the Duchy of Lorraine, which was temporarily absorbed into France between 1641 and 1648. He painted mostly religious chia ...
.
John Donne's erotic metaphysical poem
The term Metaphysical poets was coined by the critic Samuel Johnson to describe a loose group of 17th-century English poets whose work was characterised by the inventive use of conceits, and by a greater emphasis on the spoken rather than lyric ...
" The Flea", published in 1633 after his death, uses the conceit An extended metaphor, also known as a conceit or sustained metaphor, is the use of a single metaphor or analogy at length in a work of literature. It differs from a mere metaphor in its length, and in having more than one single point of contact bet ...
of a flea, which has sucked blood from the male speaker and his female lover, as an extended metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are often compared wi ...
for their sexual relationship. The speaker tries to convince a lady to sleep with him, arguing that if the mingling of their blood in the flea is innocent, then sex would be also.
The comic poem ''Siphonaptera'' was written in 1915 by the mathematician Augustus De Morgan, It describes an infinite chain of parasitism made of ever larger and ever smaller fleas.
Micrographia
''Micrographia: or Some Physiological Descriptions of Minute Bodies Made by Magnifying Glasses. With Observations and Inquiries Thereupon.'' is a historically significant book by Robert Hooke about his observations through various lenses. It ...
'', 1665
File:The development of the flea from egg to adult Wellcome M0016633.jpg, Development of the flea from egg to adult. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, c. 1680
Flea circuses
Flea circus
A flea circus is a circus sideshow attraction in which fleas are attached (or appear to be attached) to miniature carts and other items, and encouraged to perform circus acts within a small housing.
History
The first records of flea perform ...
es provided entertainment to nineteenth century audiences. These circuses, extremely popular in Europe from 1830 onwards, featured fleas dressed as humans or towing miniature carts, chariots, rollers or cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
. These devices were originally made by watchmaker
A watchmaker is an artisan who makes and repairs watches. Since a majority of watches are now factory-made, most modern watchmakers only repair watches. However, originally they were master craftsmen who built watches, including all their part ...
s or jeweller
A bench jeweler is an artisan who uses a combination of skills to make and repair jewelry. Some of the more common skills that a bench jeweler might employ include antique restoration, silversmith, Goldsmith, stone setting, engraving, fabricat ...
s to show off their skill at miniaturization. A ringmaster called a "professor" accompanied their performance with a rapid circus patter.

Carriers of plague
Oriental rat flea
The Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''), also known as the tropical rat flea or the rat flea, is a parasite of rodents, primarily of the genus ''Rattus'', and is a primary vector for bubonic plague and murine typhus. This occurs when a fl ...
s, ''Xenopsylla cheopis'', can carry the coccobacillus
A coccobacillus (plural coccobacilli), or bacilluscocco, is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci (spherical bacteria) and bacilli (rod-shaped bacteria). Coccobacilli, then, are very short rods which may be mistaken for coc ...
''Yersinia pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly '' Pasteurella pestis'') is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium without spores that is related to both ''Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'' and ''Yersinia enterocolitica''. It is a facult ...
.'' The infected fleas feed on rodent vectors of this bacterium, such as the black rat, ''Rattus rattus'', and then infect human populations with the plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pe ...
, as has happened repeatedly from ancient times, as in the Plague of Justinian
The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague (541–549 AD) was the first recorded major outbreak of the first plague pandemic, the first Old World pandemic of plague, the contagious disease caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. The dis ...
in 541–542. Outbreaks killed up to 200 million people across Europe between 1346 and 1671. The Black Death pandemic between 1346 and 1353 likely killed over a third of the population of Europe.
Because fleas carry plague, they have seen service as a biological weapon
A biological agent (also called bio-agent, biological threat agent, biological warfare agent, biological weapon, or bioweapon) is a bacterium, virus, protozoan, parasite, fungus, or toxin that can be used purposefully as a weapon in bioterroris ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the Japanese army dropped fleas infested with ''Y. pestis'' in China. The bubonic
A bubo (Greek βουβών, ''boubṓn'', 'groin') is adenitis or inflammation of the lymph nodes and is an example of reactive lymphadenopathy.
Classification
Buboes are a symptom of bubonic plague and occur as painful swellings in the thigh ...
and septicaemic plagues are the most probable form of the plague that would spread as a result of a bioterrorism
Bioterrorism is terrorism involving the intentional release or dissemination of biological agents. These agents are bacteria, viruses, insects, fungi, and/or toxins, and may be in a naturally occurring or a human-modified form, in much the same ...
attack that used fleas as a vector.
The Rothschild Collection
The banker Charles Rothschild devoted much of his time to entomology, creating a large collection of fleas now in the Rothschild Collection at theNatural History Museum, London
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum an ...
. He discovered and named the plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pe ...
vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
flea, ''Xenopsylla cheopis
The Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''), also known as the tropical rat flea or the rat flea, is a parasite of rodents, primarily of the genus ''Rattus'', and is a primary vector for bubonic plague and murine typhus. This occurs when a fl ...
'', also known as the oriental rat flea, in 1903. Using what was probably the world's most complete collection of fleas of about 260,000 specimens (representing some 73% of the 2,587 species and subspecies so far described), he described around 500 species and subspecies of Siphonaptera. He was followed in this interest by his daughter Miriam Rothschild
Dame Miriam Louisa Rothschild (5 August 1908 – 20 January 2005) was a British natural scientist and author with contributions to zoology, entomology, and botany.
Early life
Miriam Rothschild was born in 1908 in Ashton Wold, near Oundle in No ...
, who helped to catalogue his enormous collection of the insects in seven volumes.
Flea treatments
Fleas have a significant economic impact. In America alone, approximately $2.8 billion is spent annually on flea-related veterinary bills and another $1.6 billion annually for flea treatment with pet groomers. Four billion dollars is spent annually for prescription flea treatment and $348 million for flea pest control.See also
* Chigger * LouseReferences
External links
*Parasitic Insects, Mites and Ticks: Genera of Medical and Veterinary Importance
{{Authority control Extant Middle Jurassic first appearances Hematophages Insect vectors of human pathogens Insects in culture Parasites of cats Parasites of dogs Veterinary entomology