Fatty Acid Degradation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fatty acid degradation is the process in which
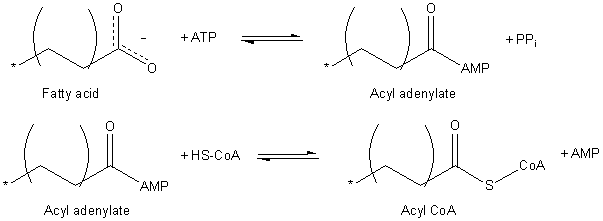 The balanced equation for the above is:
RCOO− + CoASH + ATP → RCO-SCoA + AMP + PPi
The balanced equation for the above is:
RCOO− + CoASH + ATP → RCO-SCoA + AMP + PPi
This two-step reaction is freely reversible and its equilibrium lies near 1. To drive the reaction forward, the reaction is coupled to a strongly exergonic hydrolysis reaction: the enzyme
fatty acids
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, f ...
are broken down into their metabolites, in the end generating acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins ...
, the main energy supply of living organisms, including bacteria and animals. It includes three major steps:
* Lipolysis of and release from adipose tissue
* Activation and transport into mitochondria
* β-oxidation
Lipolysis and release
Initially in the process of degradation, fatty acids are stored inadipocytes
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. I ...
. The breakdown of this fat is known as lipolysis
Lipolysis is the metabolic pathway through which lipid triglycerides are hydrolyzed into a glycerol and free fatty acids. It is used to mobilize stored energy during fasting or exercise, and usually occurs in fat adipocytes. The most important ...
. The products of lipolysis, free fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, fr ...
s, are released into the bloodstream and circulate throughout the body. During the breakdown of triacylglycerols
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as we ...
into fatty acids, more than 75% of the fatty acids are converted back into triacylglycerol, a natural mechanism to conserve energy, even in cases of starvation and exercise.
Activation and transport into mitochondria
Fatty acids must be activated before they can be carried into themitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
, where fatty acid oxidation
Fatty is a derogatory term for someone who is Obesity, obese. It may refer also to:
People
* Mai Fatty, Gambian politician
* Roscoe Arbuckle (1887–1933), American actor and comedian
* Fatty Briody (1858–1903), American Major League Baseball ...
occurs. This process occurs in two steps catalyzed by the enzyme fatty acyl-CoA synthetase.
Formation of an activated thioester bond
The enzyme first catalyzesnucleophilic attack
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
on the α-phosphate of ATP to form pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among other ...
and an acyl
In chemistry, an acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group (). In organic chemistry, the acyl group (IUPAC n ...
chain linked to AMP #REDIRECT Amp
{{Redirect category shell, {{R from other capitalisation{{R from ambiguous page ...
. The next step is formation of an activated thioester
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by t ...
bond between the fatty acyl chain and Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a subs ...
.
 The balanced equation for the above is:
RCOO− + CoASH + ATP → RCO-SCoA + AMP + PPi
The balanced equation for the above is:
RCOO− + CoASH + ATP → RCO-SCoA + AMP + PPi This two-step reaction is freely reversible and its equilibrium lies near 1. To drive the reaction forward, the reaction is coupled to a strongly exergonic hydrolysis reaction: the enzyme
inorganic pyrophosphatase
Inorganic pyrophosphatase (or inorganic diphosphatase, PPase) is an enzyme () that catalyzes the conversion of one ion of pyrophosphate to two phosphate ions. This is a highly exergonic reaction, and therefore can be coupled to unfavorable bio ...
cleaves the pyrophosphate liberated from ATP to two phosphate ions, consuming one water molecule in the process. Thus the net reaction becomes:
RCOO− + CoASH + ATP → RCO-SCoA+ AMP + 2Pi
Transport into the mitochondrial matrix
The inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to fatty acids and a specialized carnitine carrier system operates to transport activated fatty acids from cytosol to mitochondria. Once activated, theacyl
In chemistry, an acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group (). In organic chemistry, the acyl group (IUPAC n ...
CoA is transported into the mitochondrial matrix
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribo ...
. This occurs via a series of similar steps:
# Acyl CoA is conjugated to carnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria to be oxidized for energy production, an ...
by ''carnitine acyltransferase I
Carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase (also called carnitine palmitoyltransferase) is a mitochondrial transferase enzyme () involved in the metabolism of palmitoylcarnitine into palmitoyl-CoA. A related transferase is carnitine acyltransferase.
Mol ...
(palmitoyltransferase) I'' located on the outer mitochondrial membrane
# Acyl carnitine is shuttled inside by a translocase
Translocase is a general term for a protein that assists in moving another molecule, usually across a cell membrane. These enzymes catalyze the movement of ions or molecules across membranes or their separation within membranes. The reaction is des ...
# Acyl carnitine (such as Palmitoylcarnitine
Palmitoylcarnitine is an ester derivative of carnitine involved in the metabolism of fatty acids. During the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), fatty acids undergo a process known as β-oxidation to produce energy in the form of ATP. β-oxidation occ ...
) is converted to acyl CoA by ''carnitine acyltransferase (palmitoyltransferase) II'' located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. The liberated carnitine returns to the cytosol.
It is important to note that ''carnitine acyltransferase I'' undergoes allosteric inhibition as a result of malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.
Functions
It plays a key role in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis.
Fatty acid biosynthesis
Malonyl-CoA provides 2-carbon units to fatty acids and commi ...
, an intermediate in fatty acid biosynthesis, in order to prevent futile cycling between beta-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, ...
and fatty acid synthesis
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is conve ...
.
The mitochondrial oxidation of fatty acids takes place in three major steps:
# β-oxidation occurs to convert fatty acids into 2-carbon acetyl-CoA units.
# Acetyl-CoA enters into TCA cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins ...
to yield generate reduced NADH and reduced FADH2.
# Reduced cofactors NADH and FADH2 participate in the electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
in the mitochondria to yield ATP. There is no direct participation of the fatty acid.
β-oxidation
After activation by ATP, once inside the mitochondria, the β-oxidation of a fatty acids occurs via four recurring steps: #Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
by FAD
A fad or trend is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short period.
Fads are objects or behaviors that achieve short- ...
#Hydration Hydration may refer to:
* Hydrate, a substance that contains water
* Hydration enthalpy, energy released through hydrating a substance
* Hydration reaction, a chemical addition reaction where a hydroxyl group and proton are added to a compound
* ...
#Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
by NAD+
# Thiolysis Thiolysis is a reaction with a thiol (R-SH) that cleaves one compound into two. Thiolysis involves the addition of coenzyme A to one of the products. This reaction is similar to hydrolysis, which involves water instead of a thiol. This reaction is s ...
# Production of acyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA
The final product of β-oxidation of an even-numbered fatty acid is acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins ...
. If the fatty acid is an odd-numbered chain, the final product of β-oxidation will be propionyl-CoA. This propionyl-CoA will be converted into intermediate methylmalonyl-CoA and eventually succinyl-CoA, which also enters the TCA cycle.
See also
*Reverse cholesterol transport
Reverse cholesterol transport is a multi-step process resulting in the net movement of cholesterol from peripheral tissues back to the liver first via entering the lymphatic system, then the bloodstream.
Cholesterol from non-hepatic peripheral ti ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fatty Acid Degradation Metabolism Fatty acids