French Chamber of Deputies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
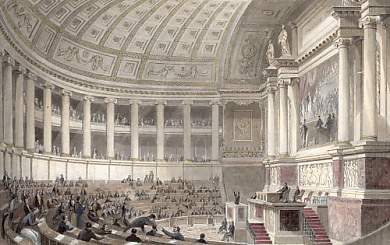
 Chamber of Deputies (french: Chambre des députés) was a parliamentary body in
Chamber of Deputies (french: Chambre des députés) was a parliamentary body in
 The Chamber of Deputies was elected by census suffrage according to the
The Chamber of Deputies was elected by census suffrage according to the

France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries:
* 1814–1848 during the Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy
The July Monarchy (french: Monarchie de Juillet), officially the Kingdom of France (french: Royaume de France), was a liberal constitutional monarchy in France under , starting on 26 July 1830, with the July Revolution of 1830, and ending 23 F ...
, the Chamber of Deputies was the lower house
A lower house is one of two Debate chamber, chambers of a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has co ...
of the French Parliament
The French Parliament (french: Parlement français) is the bicameral legislature of the French Republic, consisting of the Senate () and the National Assembly (). Each assembly conducts legislative sessions at separate locations in Paris: ...
, elected by census suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
.
* 1875–1940 during the French Third Republic
The French Third Republic (french: Troisième République, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940 ...
, the Chamber of Deputies was the legislative assembly of the French Parliament, elected by universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political stanc ...
. When reunited with the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
in Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
, the French Parliament was called the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repre ...
(''Assemblée nationale'') and carried out the election of the president of the French Republic
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (french: Président de la République française), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency is ...
.
During the Bourbon Restoration
Created by theCharter of 1814
The French Charter of 1814 was a constitutional text granted by King Louis XVIII of France shortly after the Bourbon Restoration, in form of royal charter. The Congress of Vienna demanded that Louis bring in a constitution of some form before he ...
and replacing the Corps législatif
The was a part of the French legislature during the French Revolution and beyond. It is also the generic French term used to refer to any legislative body.
History
The Constitution of the Year I foresaw the need for a ''corps législatif''. ...
, which existed under the First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Eu ...
, the Chamber of Deputies was composed of individuals elected by census suffrage. Its role was to discuss laws and, most importantly, to vote taxes. According to the Charter, deputies were elected for five years, with one-fifth renewed each year. Deputies needed to be 40 years old and to pay one thousand francs in direct contributions.
Government ministers could be chosen from among the deputies, and this resulted in giving the Restoration government a slight, albeit minor, parliamentary and liberal character.
During the Hundred Days
The Hundred Days (french: les Cent-Jours ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration ...
(''les cent jours'') return of Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
in 1815, under the terms of the Additional Act to the Constitutions of the Empire, the Chamber of Deputies was briefly replaced by a Chamber of Representatives ('' Chambre des représentants''). This body was dissolved upon the entry of Coalition troops into Paris on 7 July.
For the period 1815–1816, the (then) Ultra-royalist
The Ultra-royalists (french: ultraroyalistes, collectively Ultras) were a French political faction from 1815 to 1830 under the Bourbon Restoration. An Ultra was usually a member of the nobility of high society who strongly supported Roman Catho ...
chamber was referred to as the ''Chambre introuvable
The (French for "Unobtainable Chamber") was the first Chamber of Deputies elected after the Second Bourbon Restoration in 1815. It was dominated by Ultra-royalists who completely refused to accept the results of the French Revolution. The nam ...
''.
During the July Monarchy
Charter of 1830
The Charter of 1830 (french: Charte de 1830) instigated the July Monarchy in France. It was considered a compromise between constitutional monarchists and republicans.
History
After three days of protests in July 1830 – the July ...
. The political life of the July Monarchy was defined by the split within the Chamber of Deputies between the progressive movement (considered the Charter as a starting point) and the conservative wing (who refused any further modifications). Although both parties traded power in the initial stages, by 1840 the conservative members around François Guizot
François Pierre Guillaume Guizot (; 4 October 1787 – 12 September 1874) was a French historian, orator, and statesman. Guizot was a dominant figure in French politics prior to the Revolution of 1848.
A conservative liberal who opposed the a ...
had seized control.
From 1830, deputies were elected for five years. They needed to be 30 years old and to pay 500 francs in direct contributions.
The king convoked the chamber every year, and he had the power to extend the parliamentary session or to dissolve the chamber, although in the latter case he was required to convoke a new chamber in three months time.
In 1852, the Chamber of Deputies retook the name Corps législatif
The was a part of the French legislature during the French Revolution and beyond. It is also the generic French term used to refer to any legislative body.
History
The Constitution of the Year I foresaw the need for a ''corps législatif''. ...
.
See also
*Cabinet of France
The Government of France ( French: ''Gouvernement français''), officially the Government of the French Republic (''Gouvernement de la République française'' ), exercises executive power in France. It is composed of the Prime Minister, who ...
*Constitution of France
The current Constitution of France was adopted on 4 October 1958. It is typically called the Constitution of the Fifth Republic , and it replaced the Constitution of the Fourth Republic of 1946 with the exception of the preamble per a Constitu ...
*French Parliament
The French Parliament (french: Parlement français) is the bicameral legislature of the French Republic, consisting of the Senate () and the National Assembly (). Each assembly conducts legislative sessions at separate locations in Paris: ...
*History of France
The first written records for the history of France appeared in the Iron Age. What is now France made up the bulk of the region known to the Romans as Gaul. The first writings on indigenous populations mainly start in the first century BC. Greek ...
*National Assembly (French Fourth Republic)
The National Assembly (french: Assemblée Nationale) was the lower house of the French parliament under the Fourth Republic, with the Council of the Republic being the upper house. It was established by the Constitution of 1946, dissolved by th ...
*National Assembly (France)
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are known a ...
(Fifth Republic)
*Politics of France
The politics of France take place with the framework of a semi-presidential system determined by the French Constitution of the French Fifth Republic. The nation declares itself to be an "indivisible, secular, democratic, and social Republic". ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chamber Of Deputies Of France
Historical legislatures in France
Defunct lower houses
1814 establishments in France
1848 disestablishments in France
1875 establishments in France
1940 disestablishments in France