French Battleship République on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''République'' was a
 ''République'' joined ''Patrie'', ''Justice'', ''Vérité'', ''Démocratie'', and ''Suffren'' for a simulated attack on the port of
''République'' joined ''Patrie'', ''Justice'', ''Vérité'', ''Démocratie'', and ''Suffren'' for a simulated attack on the port of  On 24 April 1912, ''République'' went to sea with ''Justice'' for gunnery training off the
On 24 April 1912, ''République'' went to sea with ''Justice'' for gunnery training off the
pre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, prote ...
, the lead vessel
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels.
Large ships are very complex and may ...
of the built for the French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
built in the early 1900s. Laid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
in December 1901, she was launched in September 1902 and commissioned in January 1907. Armed with a main battery of four guns, she was outclassed before even entering service by the revolutionary British battleship , that had been commissioned the previous December and was armed with a battery of ten guns of the same caliber. Though built to an obsolescent design, ''République'' proved to be a workhorse of the French fleet, particularly during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
During the ship's peacetime career, ''République'' served with the Mediterranean Squadron; this period was occupied with training exercises and cruises in the western Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
and the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
. She was moored near the battleship when the latter exploded accidentally in 1911, and she was damaged by flying debris. Following the outbreak of war in July 1914, ''République'' was used to escort troopship
A troopship (also troop ship or troop transport or trooper) is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable land troops directly on shore, typicall ...
convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used ...
s carrying elements of the French Army from French North Africa
French North Africa (french: Afrique du Nord française, sometimes abbreviated to ANF) is the term often applied to the territories controlled by France in the North African Maghreb during the colonial era, namely Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia. In ...
to face the Germans invading northern France. She thereafter steamed to contain the Austro-Hungarian Navy
The Austro-Hungarian Navy or Imperial and Royal War Navy (german: kaiserliche und königliche Kriegsmarine, in short ''k.u.k. Kriegsmarine'', hu, Császári és Királyi Haditengerészet) was the naval force of Austria-Hungary. Ships of the A ...
in the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, taking part in the minor Battle of Antivari
The Battle of Antivari or Action off Antivari was a naval engagement between a large fleet of French and British warships and two ships of the Austro-Hungarian navy at the start of the First World War. The old Austrian protected cruiser and the ...
in August. The increasing threat of Austro-Hungarian U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role ...
s and the unwillingness of the Austro-Hungarian fleet to engage in battle led to a period of monotonous patrols that ended with Italy's entry into the war on the side of France, which allowed the French fleet to be withdrawn.
In 1916, ''République'' was sent to cover the withdrawal from the Gallipoli campaign, and thereafter became involved in events in Greece, being stationed in Salonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
to put pressure on the Greek government to enter the war on the side of the Allies. She contributed men to a landing party that went ashore in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
to support a pro-Allied coup. She saw little activity in 1917 and 1918 after the coup succeeded. In January 1918, she had half of her main guns removed for use by the French Army and was reclassified as a training ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house classr ...
. She served in that role until replaced by other ships in 1920. ''République'' was decommissioned in May 1921 and broken up
Ship-breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships for either a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, ...
in Italy beginning in November.
Design
The ships of the ''République'' class marked a significant improvement over earlier French battleships, being significantly larger and better-armed and armored than the preceding battleship . Designed byLouis-Émile Bertin
Louis-Émile Bertin (23 March 1840 – 22 October 1924) was a French naval engineer, one of the foremost of his time, and a proponent of the "Jeune École" philosophy of using light, but powerfully armed warships instead of large battleships.
...
, the ships incorporated a new armor layout that included a more comprehensive armored citadel
In a warship an armored citadel is an armored box enclosing the machinery and magazine spaces formed by the armored deck, the waterline belt, and the transverse bulkheads. In many post-World War I warships, armor was concentrated in a very s ...
that would better resist flooding than the shallow side armor used in earlier vessels.
''République'' was long overall
__NOTOC__
Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, an ...
and had a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of and an average draft
Draft, The Draft, or Draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a vessel ...
of . She displaced at full load. She was powered by three vertical triple expansion engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be tr ...
s with twenty-four Niclausse boiler
A Field-tube boiler (also known as a bayonet tube)
is a form of water-tube boiler where the water tubes are single-ended. The tubes are closed at one end, and they contain a concentric inner tube. Flow is thus separated into the colder inner flow ...
s. They were rated at and provided a top speed of . Coal storage amounted to , which provided a maximum range of at a cruising speed of . She had a crew of 32 officers and 710 enlisted men.
''République''s main battery consisted of four Canon de 305 mm Modèle 1893/96 guns mounted in two twin-gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechani ...
s, one forward and one aft. The secondary battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prima ...
consisted of eighteen Canon de 164 mm Modèle 1893
Railroad model, 1916.
The Canon de 164 mm Modèle 1893 was a medium-caliber naval gun used as the secondary armament of a number of French pre-dreadnoughts and armoured cruisers during World War I. It was used as railway artillery in both ...
guns; twelve were mounted in twin turrets, and six were in casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, th ...
s in the hull. She also carried twenty-four guns. The ship was also armed with two torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s, which were submerged in the hull.
The ship's main belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, called ...
was thick in the central citadel, and was connected to two armored decks; the upper deck was thick while the lower deck was thick, with sloped sides. The main battery guns were protected by up to of armor on the fronts of the turrets, while the secondary turrets had of armor on the faces. The conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
had thick sides.
Modifications
Tests to determine whether the main battery turrets could be modified to increase the elevation of the guns (and hence their range) proved to be impossible, but the Navy determined that tanks on either side of the vessel could be flooded to induce aheel
The heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower Human leg, leg.
Structure
To distribute the compressive for ...
of 2 degrees. This increased the maximum range of the guns from . New motors were installed in the secondary turrets in 1915–1916 to improve their training and elevation rates. Also in 1915, the 47 mm guns located on either side of the bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
were removed and the two on the aft superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships.
Aboard ships and large boats
On water craft, the superstruct ...
were moved to the roof of the rear turret. On 8 December 1915, the naval command issued orders that the light battery was to be revised to just four of the 47 mm guns and eight guns. The light battery was revised again in 1916, with the four 47 mm guns being converted with high-angle anti-aircraft mounts. They were placed atop the rear main battery turret and the number 5 and 6 secondary turret roofs. In 1912–1913, the ship received two Barr & Stroud
Barr & Stroud Limited was a pioneering Glasgow optical engineering firm. They played a leading role in the development of modern optics, including rangefinders, for the Royal Navy and for other branches of British Armed Forces during the 20th ce ...
rangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography an ...
s.
Service history
Construction – 1909
''République'' waslaid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
at the Arsenal de Brest
The Brest Arsenal (French - ''arsenal de Brest'') is a collection of naval and military buildings located on the banks of the river Penfeld, in Brest, France. It is located at .
Timeline
*1631-1635 Beginning of the foundations of the port infr ...
on 27 December 1901, was launched on 4 September 1902, and was commissioned on 12 January 1907, shortly after the revolutionary British battleship , which rendered the pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, prote ...
s like ''République'' outdated. After commissioning, ''République'' conducted her sea trial
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a " shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and ...
s. During the speed trials, she reached a top speed of , more than a knot faster than her contract speed of . From 16 to 26 January, she steamed from Brest to Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is th ...
, where she conducted wireless telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for ...
tests in conjunction with the armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast eno ...
and the Eiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower ( ; french: links=yes, tour Eiffel ) is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower.
Locally nicknamed "'' ...
from 14 to 17 February. She then joined the 1st Division of the Mediterranean Squadron, along with her sister and ''Suffren'', the divisional flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the fi ...
. Beginning on 1 July, the French fleet embarked on its annual summer maneuvers, which lasted until 31 July. The Mediterranean Squadron joined the Northern Squadron for exercises in the western Mediterranean.
On 13 January 1908, ''République'' and the battleships ''Patrie'', , , , , and steamed to Golfe-Juan
Golfe-Juan (; oc, Lo Gorg Joan, Lo Golfe Joan) is a seaside resort on France's Côte d'Azur. The distinct local character of Golfe-Juan is indicated by the existence of a demonym, "Golfe-Juanais", which is applied to its inhabitants.
Overview
...
and then to Villefranche-sur-Mer
Villefranche-sur-Mer (, ; oc, Vilafranca de Mar ; it, Villafranca Marittima ) is a resort town in the Alpes-Maritimes department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region on the French Riviera and is located south-west of the Principality of ...
, where they remained for more than a month. In June and July, the Mediterranean and Northern Squadrons conducted their annual maneuvers, this time off Bizerte
Bizerte or Bizerta ( ar, بنزرت, translit=Binzart , it, Biserta, french: link=no, Bizérte) the classical Hippo, is a city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia. It is the northernmost city in Africa, located 65 km (40mil) north of the cap ...
. The squadron was moored in Villefranche in February 1909 and thereafter conducted training exercises off Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
, followed by a naval review
A fleet review or naval review is an event where a gathering of ships from a particular navy is paraded and reviewed by an incumbent head of state and/or other official civilian and military dignitaries. A number of national navies continue to ...
in Villefranche for President Armand Fallières
Clément Armand Fallières (; 6 November 1841 – 22 June 1931) was a French statesman who was President of France from 1906 to 1913.
He was born at Mézin in the ''département'' of Lot-et-Garonne, France, where his father was clerk of th ...
on 26 April. During this period of training, on 17 March, ''République'', ''Patrie'', , and conducted shooting training, using the old ironclad
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships ...
as a target
Target may refer to:
Physical items
* Shooting target, used in marksmanship training and various shooting sports
** Bullseye (target), the goal one for which one aims in many of these sports
** Aiming point, in field artillery, fi ...
.
In June, ''République'', ''Justice'', and the protected cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers re ...
got underway for training in the Atlantic; they met ''Patrie'', , ''Liberté'', and the armored cruiser at Cádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia.
Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, ...
, Spain on 12 June. Training included serving as targets for the fleet's submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s in the Pertuis d'Antioche
The Pertuis d'Antioche (, ''Passage of Antioch'') is a strait on the Atlantic coast of Western France, between two islands, Île de Ré and Oléron, on the one side, and on the other side the continental coast between the cities of La Rochelle and ...
strait. The ships then steamed north to La Pallice
La Pallice (also known as ''grand port maritime de La Rochelle'') is the commercial deep-water port of La Rochelle, France.
During the Fall of France, on 19 June 1940, approximately 6,000 Polish soldiers in exile under the command of Stanisław ...
, where they conducted tests with their wireless sets and shooting training in Quiberon Bay
Quiberon Bay (french: Baie de Quiberon) is an area of sheltered water on the south coast of Brittany. The bay is in the Morbihan département.
Geography
The bay is roughly triangular in shape, open to the south with the Gulf of Morbihan to t ...
. From 8 to 15 July, the ships lay at Brest
Brest may refer to:
Places
*Brest, Belarus
**Brest Region
**Brest Airport
**Brest Fortress
*Brest, Kyustendil Province, Bulgaria
*Břest, Czech Republic
*Brest, France
**Arrondissement of Brest
**Brest Bretagne Airport
** Château de Brest
*Brest, ...
and the next day, they steamed to Le Havre
Le Havre (, ; nrf, Lé Hâvre ) is a port city in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France. It is situated on the right bank of the estuary of the river Seine on the Channel southwest of the Pays de Caux, very cl ...
. There, they met the Northern Squadron for another fleet review for Fallières on 17 July. Ten days later, the combined fleet steamed to Cherbourg
Cherbourg (; , , ), nrf, Chèrbourg, ) is a former commune and subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 Feb ...
, where they held another fleet review, this time during the visit of Czar Nicholas II of Russia
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Pola ...
. In October, the 1st Division ships, which by then consisted of ''République'' and ''Patrie'' steamed to Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
, Spain. The ships were inspected by King Alfonso XIII
Alfonso XIII (17 May 1886 – 28 February 1941), also known as El Africano or the African, was King of Spain from 17 May 1886 to 14 April 1931, when the Second Spanish Republic was proclaimed. He was a monarch from birth as his father, Alf ...
, who boarded ''Patrie'' during the visit.
1910–1914
Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
on 18 February. During the maneuvers, ''Patrie'' launched a torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, su ...
that accidentally hit ''République'', damaging her hull and forcing her to put into Toulon for repairs. The ships of the 1st Squadron held training exercises off Sardinia and Algeria from 21 May to 4 June, followed by combined maneuvers with the 2nd Squadron from 7 to 18 June. An outbreak of typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
among the crews of the battleships in early December forced the navy to confine them to Golfe-Juan to contain the fever. By 15 December, the outbreak had subsided.
On 16 April 1911, ''République'' and the rest of the fleet escorted ''Vérité'', which had aboard Fallières, the Naval Minister Théophile Delcassé
Théophile Delcassé (1 March 185222 February 1923) was a French politician who served as foreign minister from 1898 to 1905. He is best known for his hatred of Germany and efforts to secure alliances with Russia and Great Britain that became t ...
, and Charles Dumont, the Minister of Public Works, Posts and Telegraphs, to Bizerte. They arrived two days later and held a fleet review that included two British battleships, two Italian battleships, and a Spanish cruiser on 19 April. The fleet returned to Toulon on 29 April, where Fallières doubled the crews' rations and suspended any punishments to thank the men for their performance. ''République'' and the rest of 1st Squadron and the armored cruisers ''Ernest Renan'' and went on a cruise in the western Mediterranean in May and June, visiting a number of ports including Cagliari
Cagliari (, also , , ; sc, Casteddu ; lat, Caralis) is an Italian municipality and the capital of the island of Sardinia, an autonomous region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name ''Casteddu'' means ''castle''. It has about 155,000 inhabitant ...
, Bizerte, Bône
Annaba ( ar, عنّابة, "Place of the Jujubes"; ber, Aânavaen), formerly known as Bon, Bona and Bône, is a seaport city in the northeastern corner of Algeria, close to the border with Tunisia. Annaba is near the small Seybouse River ...
, Philippeville
Philippeville (; wa, Flipveye) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Namur, Belgium. The Philippeville municipality includes the former municipalities of Fagnolle, Franchimont, Jamagne, Jamiolle, Merlemont, Ne ...
, Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
, and Bougie. By 1 August, the battleships of the had begun to enter service, and they were assigned to the 1st Squadron, displacing ''République'', ''Patrie'', and the ''Liberté''-class ships to the 2nd Squadron.
The fleet held another fleet review outside Toulon on 4 September. Admiral Jauréguiberry took the fleet to sea on 11 September for maneuvers and visits to Golfe-Juan and Marseilles
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Franc ...
, returning to port five days later. On 25 September, ''Liberté'' exploded while in Toulon, another French battleship claimed by unstable Poudre B
Poudre B was the first practical smokeless gunpowder created in 1884. It was perfected between 1882 and 1884 at "Laboratoire Central des Poudres et Salpêtres" in Paris, France. Originally called "Poudre V" from the name of the inventor, Paul Vi ...
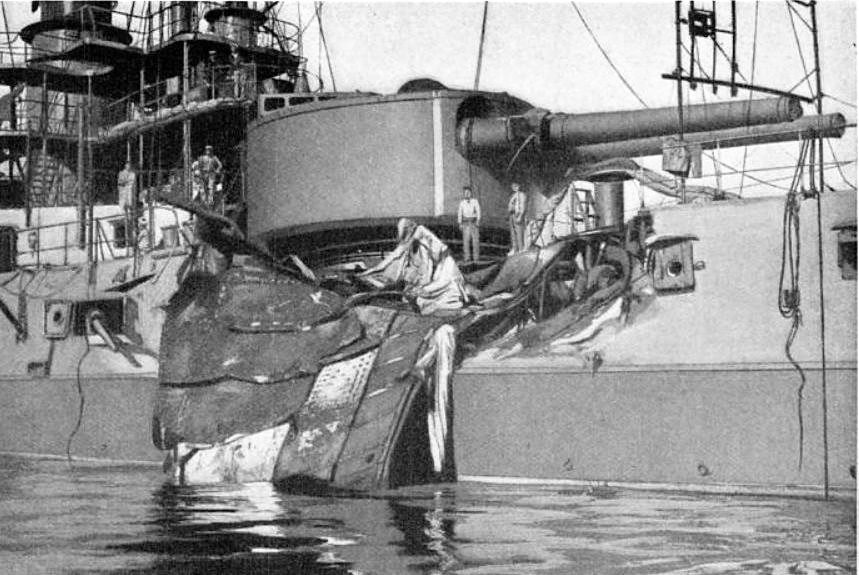
propellant. A piece of armor plate struck ''République'' on the starboard quarter directly behind the main battery turret and killed twenty-three men. On an investigation of the damage, it was found that a melinite shell from ''Liberté'' hit the ship in the same location and exploded, punching a hole in the armored deck. Despite the accident, the fleet continued with its normal routine of training exercises and cruises for the rest of the year.
 On 24 April 1912, ''République'' went to sea with ''Justice'' for gunnery training off the
On 24 April 1912, ''République'' went to sea with ''Justice'' for gunnery training off the Hyères
Hyères (), Provençal Occitan: ''Ieras'' in classical norm, or ''Iero'' in Mistralian norm) is a commune in the Var department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in southeastern France.
The old town lies from the sea clustered around t ...
roadstead
A roadstead (or ''roads'' – the earlier form) is a body of water sheltered from rip currents, spring tides, or ocean swell where ships can lie reasonably safely at anchor without dragging or snatching.United States Army technical manual, TM 5- ...
; they were joined by ''Patrie'' and ''Vérité'' the next day. Admiral Augustin Boué de Lapeyrère
Augustin Manuel Hubert Gaston Boué de Lapeyrère (18 January 1852 – 17 February 1924) was a French admiral during World War I. He was a strong proponent of naval reform, and is comparable to Admiral Jackie Fisher of the British Royal Navy.
...
inspected both battleship squadrons in Golfe-Juan from 2 to 12 July, after which the ships cruised first to Corsica and then to Algeria. Late in the year, ''République'' went into drydock in Toulon for a refit that concluded in early April, after which she returned to the 2nd Squadron. The French fleet, which by then included sixteen battleships, held large-scale maneuvers between Toulon and Sardinia beginning on 19 May. The exercises concluded with a fleet review for President Raymond Poincaré
Raymond Nicolas Landry Poincaré (, ; 20 August 1860 – 15 October 1934) was a French statesman who served as President of France from 1913 to 1920, and three times as Prime Minister of France.
Trained in law, Poincaré was elected deputy in 1 ...
. Gunnery practice followed from 1 to 4 July. The 2nd Squadron departed Toulon on 23 August with the armored cruisers and and two destroyer flotilla
A flotilla (from Spanish, meaning a small ''flota'' (fleet) of ships), or naval flotilla, is a formation of small warships that may be part of a larger fleet.
Composition
A flotilla is usually composed of a homogeneous group of the same class ...
s to conduct training exercises in the Atlantic. While en route to Brest, the ships stopped in Tangier
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the cap ...
, Royan
Royan (; in the Saintongeais dialect; oc, Roian) is a commune and town in the south-west of France, in the department of Charente-Maritime in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region. Its inhabitants are known as ''Royannais'' and ''Royannaises''. Capi ...
, Le Verdon, La Pallice, Quiberon Bay, and Cherbourg. They reached Brest on 20 September, where they met a Russian squadron of four battleships and five cruisers. The ships then steamed back south, stopping in Cádiz, Tangier, Mers El Kébir
Mers El Kébir ( ar, المرسى الكبير, translit=al-Marsā al-Kabīr, lit=The Great Harbor ) is a port on the Mediterranean Sea, near Oran in Oran Province, northwest Algeria. It is famous for the attack on the French fleet in 1940, in t ...
, Algiers, and Bizerte before ultimately arriving back in Toulon on 1 November. On 3 December, ''République'', ''Justice'', ''Vérité'', and ''Démocratie'' conducted torpedo training and range-finding drills.
The 2nd Squadron ships conducted torpedo training on 19 January 1914, and later that month they steamed to Bizerte, returning to Toulon on 6 February. On 4 March, ''République'', ''Démocratie'', ''Vérité'', and ''Justice'' joined the 1st Squadron battleships and the 2nd Light Squadron for a visit to Porto-Vecchio
Porto-Vecchio (, ; it, Porto Vecchio or ; co, Portivechju or ) is a commune in the French department of Corse-du-Sud, on the island of Corsica.
Porto-Vecchio is a medium-sized port city placed on a good harbor, the southernmost of the mars ...
, Sardinia. On 30 March, the 2nd Squadron ships steamed to Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
to visit the British Mediterranean Fleet
The British Mediterranean Fleet, also known as the Mediterranean Station, was a formation of the Royal Navy. The Fleet was one of the most prestigious commands in the navy for the majority of its history, defending the vital sea link between t ...
, remaining there until 3 April. The squadron visited various ports in June, but following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and the ensuing July Crisis prompted the fleet to remain close to port, making only short training sorties as international tensions rose.
World War I
1914–1915
Following the outbreak of World War I in July 1914, France announced general mobilization on 1 August. The next day, Boué de Lapeyrère ordered the entire French fleet to begin raising steam at 22:15 so the ships could sortie early the next day. Faced with the prospect that the GermanMediterranean Division
The Mediterranean Division (german: Mittelmeerdivision) was a division consisting of the battlecruiser and the light cruiser of the German ''Kaiserliche Marine'' (Imperial Navy) in the early 1910s. It was established in response to the First Balk ...
—centered on the battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
—might attack the troopship
A troopship (also troop ship or troop transport or trooper) is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable land troops directly on shore, typicall ...
s carrying the French Army in North Africa to metropolitan France, the French fleet was tasked with providing heavy escort to the convoys. Accordingly, ''République'' and the rest of the 2nd Squadron were sent to Algiers, where they joined a group of seven passenger ship
A passenger ship is a merchant ship whose primary function is to carry passengers on the sea. The category does not include cargo vessels which have accommodations for limited numbers of passengers, such as the ubiquitous twelve-passenger freig ...
s that had a contingent of 7,000 troops from XIX Corps aboard. While at sea, the new dreadnought battleships and and the ''Danton''-class battleships and , which took over as the convoy's escort. Instead of attacking the convoys, ''Goeben'' bombarded Bône and Philippeville and then fled east to the Ottoman Empire.
On 12 August, France and Britain declared war on the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
as the war continued to widen. The 1st and 2nd Squadrons were therefore sent to the southern Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
to contain the Austro-Hungarian Navy
The Austro-Hungarian Navy or Imperial and Royal War Navy (german: kaiserliche und königliche Kriegsmarine, in short ''k.u.k. Kriegsmarine'', hu, Császári és Királyi Haditengerészet) was the naval force of Austria-Hungary. Ships of the A ...
. On 15 August, the two squadrons arrived off the Strait of Otranto
The Strait of Otranto ( sq, Ngushtica e Otrantos; it, Canale d'Otranto; hr, Otrantska Vrata) connects the Adriatic Sea with the Ionian Sea and separates Italy from Albania. Its width at Punta Palascìa, east of Salento is less than . The st ...
, where they met the patrolling British cruisers and north of Othonoi. Boué de Lapeyrère then took the fleet into the Adriatic in an attempt to force a battle with the Austro-Hungarian fleet; the following morning, the British and French cruisers spotted vessels in the distance that, on closing with them, turned out to be the protected cruiser and the torpedo boat , which were trying to blockade the coast of Montenegro. In the ensuing Battle of Antivari
The Battle of Antivari or Action off Antivari was a naval engagement between a large fleet of French and British warships and two ships of the Austro-Hungarian navy at the start of the First World War. The old Austrian protected cruiser and the ...
, Boué de Lapeyrère initially ordered his battleships to fire warning shots, but this caused confusion among the fleet's gunners that allowed ''Ulan'' to escape. The slower ''Zenta'' attempted to evade, but she quickly received several hits that disabled her engines and set her on fire. She sank shortly thereafter and the Anglo-French fleet withdrew.
The French fleet patrolled the southern end of the Adriatic for the next three days with the expectation that the Austro-Hungarians would counterattack, but their opponent never arrived. On 17 August, ''Justice'' and ''Démocratie'' collided in heavy fog at 09:20; the latter vessel lost her rudder and center screw. ''République'' took her under tow at 12:40, steaming first to Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The isl ...
and then to Malta. They arrived there on 20 August, at which point ''République'' steamed back north to rejoin her squadron. On 1 September, the French battleships then bombarded Austrian fortifications at Cattaro on 1 September in an attempt to draw out the Austro-Hungarian fleet, which again refused to take the bait. In addition, many of the ships still had shells loaded from the battle with ''Zenta'', and the guns could not be emptied apart from by firing them. On 18–19 September, the fleet made another incursion into the Adriatic, steaming as far north as the island of Lissa.
The fleet continued these operations in October and November, including a sweep off the coast of Montenegro to cover a group of merchant vessels replenishing their coal there. Throughout this period, the battleships rotated through Malta or Toulon for periodic maintenance; Corfu became the primary naval base in the area. The patrols continued through late December, when an Austro-Hungarian U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role ...
torpedoed ''Jean Bart'', leading to the decision by the French naval command to withdraw the main battle fleet from direct operations in the Adriatic. For the rest of the month, the fleet remained at Navarino Bay
Pylos (, ; el, Πύλος), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is th ...
. The battle fleet thereafter occupied itself with patrols between Kythira and Crete; these sweeps continued until 7 May. Following the Italian entry into the war on the side of France, the French fleet handed control of the Adriatic operations to the Italian '' Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) and withdrew its fleet to Malta and Bizerte, the latter becoming the main fleet base.
1916–1918
In January 1916, ''République'' joined the Allied fleet off the Dardanelles supporting the Gallipoli campaign then in its final stage. She and ''Gaulois'' covered the evacuation fromGallipoli
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles ...
shortly thereafter. Following the withdrawal from Gallipoli, the French transferred many of its pre-dreadnoughts, including ''République'', to Salonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
, Greece. These ships, comprising the five ''République''- and ''Liberté''-class battleships, were organized as the 3rd Squadron, and they were tasked with pressuring the Greek government. The Greek government, under King Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea ...
, had thus far refused to enter the war on the side of the Allies, in large part due to Constantine's wife Sophie
Sophie is a version of the female given name Sophia, meaning "wise".
People with the name Born in the Middle Ages
* Sophie, Countess of Bar (c. 1004 or 1018–1093), sovereign Countess of Bar and lady of Mousson
* Sophie of Thuringia, Duchess o ...
being the sister of Kaiser Wilhelm II. Over the course of June and July, the ships alternated between Salonika and Mudros, and later that month the fleet was transferred to Cephalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia ( el, Κεφαλονιά), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallenia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It i ...
.
In August, a pro-Allied group launched a coup against the monarchy in the ''Noemvriana
The ''Noemvriana'' ( el, Νοεμβριανά, "November Events") of , or the Greek Vespers, was a political dispute which led to an armed confrontation in Athens between the royalist government of Greece and the forces of the Allies over th ...
'', which the Allies sought to support. ''République'' contributed men to a landing party that went ashore in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
on 1 December support the coup. The British and French troops were defeated by the Greek Army and armed civilians and were forced to withdraw to their ships, after which the British and French fleet imposed a blockade of the royalist-controlled parts of the country. By June 1917, Constantine had been forced to abdicate and the 3rd Squadron was disbanded; ''République'' and ''Patrie'' became the Eastern Naval Division and were sent to the eastern Mediterranean. While in Lemnos on the night of 17/18 November, ''République'' broke free from her anchors and ran aground in the harbor, though she was refloated with help from several tugboats and British vessels. In December, both ships had their center and aft casemate guns removed. The ships spent 1917 largely idle as men were withdrawn from the fleet's battleships for use in anti-submarine warships.
On 20 January 1918, the French received word that the battlecruiser ''Goeben'' (now under the Ottoman flag as ''Yavuz Sultan Selim'') would sortie, so ''République'' and ''Patrie'' prepared for action. The battlecruiser struck several naval mines, however, and broke off the attack so the French ships remained in port. Shortly thereafter, ''République'' steamed to Toulon for maintenance that lasted from 29 January to 19 February. This included replacing two of her 305 mm guns, but while this was being done, the shipyard received orders to turn both guns over to the French Army for field use. With only half of her main battery still mounted, ''République'' was then reduced to a training ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house classr ...
on 28 March.
Postwar fate
''République'' continued in service as a training vessel after the war; on 1 July 1919 she was formally assigned to the school of armorers and gunners. On 2 October 1919, she went into drydock to have her main battery turrets removed, and her 164.7 mm casemate guns were also removed, though she retained the secondary turret guns. As more modern battleships were withdrawn from service in the postwar reduction in force, they displaced ''République''. On 9 December 1920, the battleship took her place in the gunnery school. ''République'' was decommissioned on 21 May 1921 and stricken from thenaval register
A Navy Directory, formerly the Navy List or Naval Register is an official list of naval officers, their ranks and seniority, the ships which they command or to which they are appointed, etc., that is published by the government or naval author ...
on 29 June. In November, she was taken to Savona
Savona (; lij, Sann-a ) is a seaport and ''comune'' in the west part of the northern Italy, Italian region of Liguria, capital of the Province of Savona, in the Riviera di Ponente on the Mediterranean Sea.
Savona used to be one of the chie ...
, Italy, where she was broken up for scrap.
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Republique République-class battleships Ships built in France 1902 ships Maritime incidents in 1910 Maritime incidents in 1911