French Battleship Mirabeau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Mirabeau'' was one of the six semi-dreadnought battleships built for the (French Navy) in the first decade of the twentieth century. Completed in 1911, the ship often served as a
 Although the s were a significant improvement from the preceding , they were outclassed by the advent of the
Although the s were a significant improvement from the preceding , they were outclassed by the advent of the
 Ordered as part of the second tranche of the 1900 naval law that authorized a total of 19 battleships by 1919, ''Mirabeau'' was named after Honoré Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau, an early leader of the
Ordered as part of the second tranche of the 1900 naval law that authorized a total of 19 battleships by 1919, ''Mirabeau'' was named after Honoré Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau, an early leader of the
 In November 1916, she transported landing parties from the other ships of her division to
In November 1916, she transported landing parties from the other ships of her division to
 After the
After the
CUIRASSE Danton
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mirabeau Danton-class battleships Ships built in France 1909 ships Maritime incidents in 1919 Shipwrecks in the Black Sea
flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the fi ...
before the beginning of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
three years later. ''Mirabeau'' spent the war in the Mediterranean Sea and spent most of her time blockading the Straits of Otranto
The Strait of Otranto ( sq, Ngushtica e Otrantos; it, Canale d'Otranto; hr, Otrantska Vrata) connects the Adriatic Sea with the Ionian Sea and separates Italy from Albania. Its width at Punta Palascìa, east of Salento is less than . The st ...
and the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
to prevent German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
and Ottoman warships from breaking out into the Mediterranean. She also participated in the attempt to ensure Greek acquiescence to Allied operations in Macedonia in late 1916. ''Mirabeau'' briefly participated in the occupation of Constantinople
The occupation of Istanbul ( tr, İstanbul'un İşgali; 12 November 1918 – 4 October 1923), the capital of the Ottoman Empire, by United Kingdom, British, France, French, Italy, Italian, and Greece, Greek forces, took place in accordance with ...
after the end of the war in late 1918 and was deployed in the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
in early 1919 during the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War or Allied Powers intervention in the Russian Civil War consisted of a series of multi-national military expeditions which began in 1918. The Allies first had the goal of helping the Czechoslovak Leg ...
. She ran aground in February 1919 off the coast of the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
and could not be refloated until some of her guns, armor and boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central h ...
s were removed. After returning to France later that year, the ship was stricken from the Navy List
A Navy Directory, formerly the Navy List or Naval Register is an official list of naval officers, their ranks and seniority, the ships which they command or to which they are appointed, etc., that is published by the government or naval author ...
. ''Mirabeau'' was given to a salvage company as payment for salvaging another battleship and broken up
Ship-breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships for either a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, ...
in 1922.
Design and description
 Although the s were a significant improvement from the preceding , they were outclassed by the advent of the
Although the s were a significant improvement from the preceding , they were outclassed by the advent of the dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
well before they were completed.Gardiner & Gray, p. 196 ''Mirabeau'' was long overall
__NOTOC__
Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, an ...
and had a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of and a deep-load draft
Draft, The Draft, or Draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a vessel ...
of . She displaced at normal load and had a crew of 25 officers and 831 enlisted men. While serving as a flagship, her crew numbered 31 officers and 886 enlisted men. The ship was powered by four Parsons
Parsons may refer to:
Places
In the United States:
* Parsons, Kansas, a city
* Parsons, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Parsons, Tennessee, a city
* Parsons, West Virginia, a town
* Camp Parsons, a Boy Scout camp in the state of Washingt ...
steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
s, each driving one propeller shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect ...
using steam generated by twenty-six Belleville boiler
There have been a vast number of designs of steam boiler, particularly towards the end of the 19th century when the technology was evolving rapidly. A great many of these took the names of their originators or primary manufacturers, rather than a m ...
s. The turbines were rated at and were designed to provide a top speed of . ''Mirabeau'' slightly exceeded this figure when she reached a top speed of on her sea trial
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a " shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and ...
s. The ship carried enough coal to give her a range of at a speed of .Jordan & Caresse, p. 119
The main battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a gun or group of guns, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted ...
of the ''Danton''s consisted of four Canon de modèle 1906 mounted in two twin gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechani ...
s, one forward and one aft of the superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships.
Aboard ships and large boats
On water craft, the superstruct ...
. Their secondary armament
Secondary armament is a term used to refer to smaller, faster-firing weapons that were typically effective at a shorter range than the main (heavy) weapons on military systems, including battleship- and cruiser-type warships, tanks/armored ...
consisted of a dozen Canon de modèle 1902 guns in twin turrets, three on each side of the ship. A number of smaller guns were carried for defense against torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of se ...
s. These included sixteen Canon de modèle 1908 guns in casemates
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to antiquity, the term "casemate wall" mean ...
in the sides of the hull and eight Hotchkiss gun
The Hotchkiss gun can refer to different products of the Hotchkiss arms company starting in the late 19th century. It usually refers to the 1.65-inch (42 mm) light mountain gun; there were also a navy (47 mm) and a 3-inch (76&nbs ...
s mounted on the superstructure. She was also armed with two submerged torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s, one on each broadside
Broadside or broadsides may refer to:
Naval
* Broadside (naval), terminology for the side of a ship, the battery of cannon on one side of a warship, or their near simultaneous fire on naval warfare
Printing and literature
* Broadside (comic ...
. The ship's waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indi ...
armor belt
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers.
The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating to t ...
ranged in thickness from and the main gun turrets were protected by armor thick. The sides of the conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
consisted of armor plates.
Wartime modifications
The four aft 75-millimeter gun positions were very prone to flooding in anything other than calm weather and were removed from the ''Danton''s in 1915–1917; their embrasures were plated over to stop the flooding. The four 47-millimeter guns on the aft superstructure were transferred to other ships at some point during the war. Those on the forward superstructure received high-angle mounts and were repositioned to better serve asanti-aircraft gun
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, ...
s.
Construction and career
 Ordered as part of the second tranche of the 1900 naval law that authorized a total of 19 battleships by 1919, ''Mirabeau'' was named after Honoré Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau, an early leader of the
Ordered as part of the second tranche of the 1900 naval law that authorized a total of 19 battleships by 1919, ''Mirabeau'' was named after Honoré Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau, an early leader of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
.Silverstone, p. 105 Construction of the ship began on 8 May 1906Gille, p. 120 at the Arsenal de Lorient
Naval Group is a major French industrial Corporate group, group specialized in navy, naval defense industry, defense design, development and shipbuilding, construction. Its headquarters are located in Paris.
Heir to the French naval dockyards i ...
and she was laid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
on 4 May 1908. ''Mirabeau'' was launched on 28 October 1909 and was completed () on 1 August 1911. Upon reaching Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is th ...
on 15 August, the ship became the flagship of Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarde ...
() Dominique-Marie Gauchet
Dominique-Marie Gauchet (14 August 1853 in Vains – 4 February 1931 in Vains) was a French admiral during World War I.
Life
After a career of almost 40 years in the French Navy, Gauchet was appointed commander of the French Dardanelles squadr ...
, commander of the Mediterranean Squadron ('s) Second Division () of the First Battle Squadron (). Together with four of her sisters
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares one or more parents with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to ...
, she participated in a large naval review
A fleet review or naval review is an event where a gathering of ships from a particular navy is paraded and reviewed by an incumbent head of state and/or other official civilian and military dignitaries. A number of national navies continue to ...
by the President of France
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (french: Président de la République française), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency i ...
, Armand Fallières
Clément Armand Fallières (; 6 November 1841 – 22 June 1931) was a French statesman who was President of France from 1906 to 1913.
He was born at Mézin in the ''département'' of Lot-et-Garonne, France, where his father was clerk of th ...
, off Cap Brun on 4 September and then the visit by the Navy Minister, Théophile Delcassé
Théophile Delcassé (1 March 185222 February 1923) was a French politician who served as foreign minister from 1898 to 1905. He is best known for his hatred of Germany and efforts to secure alliances with Russia and Great Britain that became t ...
on the 8th.
In mid-April 1912, the First Battle Squadron hosted three British armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast eno ...
s at Golfe-Juan
Golfe-Juan (; oc, Lo Gorg Joan, Lo Golfe Joan) is a seaside resort on France's Côte d'Azur. The distinct local character of Golfe-Juan is indicated by the existence of a demonym, "Golfe-Juanais", which is applied to its inhabitants.
Overview
...
as their commander, Rear-Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarded ...
Edward Gamble unveiled monuments to King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria an ...
and his mother, Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
, at Cannes
Cannes ( , , ; oc, Canas) is a city located on the French Riviera. It is a communes of France, commune located in the Alpes-Maritimes departments of France, department, and host city of the annual Cannes Film Festival, Midem, and Cannes Lions I ...
. ''Mirabeau'' participated in the July maneuvers in the Western Mediterranean and the exercise simulating a blockade of Ajaccio
Ajaccio (, , ; French: ; it, Aiaccio or ; co, Aiacciu , locally: ; la, Adiacium) is a French commune, prefecture of the department of Corse-du-Sud, and head office of the ''Collectivité territoriale de Corse'' (capital city of Corsica). ...
, Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
, in November. On 3 March 1913 the First Battle Squadron conducted gunnery training off the Îles d'Hyères
The Îles d'Hyères (), also known as Îles d'Or (), are a group of four Mediterranean islands off Hyères in the Var department of Southeastern France.
Islands
With a combined area of , the Îles d'Hyères consist of
*Porquerolles – , ...
with the First Lord of the Admiralty
The First Lord of the Admiralty, or formally the Office of the First Lord of the Admiralty, was the political head of the English and later British Royal Navy. He was the government's senior adviser on all naval affairs, responsible for the di ...
, Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
, observing. The ship participated in combined fleet maneuvers between Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
and French Tunisia
The French protectorate of Tunisia (french: Protectorat français de Tunisie; ar, الحماية الفرنسية في تونس '), commonly referred to as simply French Tunisia, was established in 1881, during the French colonial Empire era, ...
in May–JuneGille, p. 117 and the subsequent naval review conducted by the President of the Council, Raymond Poincaré
Raymond Nicolas Landry Poincaré (, ; 20 August 1860 – 15 October 1934) was a French statesman who served as President of France from 1913 to 1920, and three times as Prime Minister of France.
Trained in law, Poincaré was elected deputy in 1 ...
, on 7 June.Meirat, p. 5 Rear Admiral Marie-Jean-Lucien Lacaze
Marie-Jean-Lucien Lacaze (22 June 1860, Pierrefonds, Oise – 23 March 1955, Paris) was a French admiral, minister of Marine, préfet maritime and académicien.
Biography
Lacaze was born in Pierrefonds, Oise to a physician of Réunion, where ...
relieved Gauchet on 16 August and ''Mirabeau'' joined her squadron in its tour of the Eastern Mediterranean in October–December, making port visits in Egypt, Syria, and Greece.
Lacaze shifted his flag to her sister on 12 March 1914 and the ship had to briefly withdraw from the grand fleet exercises on 13 May due to engine troubles. As tensions rose during the July Crisis
The July Crisis was a series of interrelated diplomatic and military escalations among the major powers of Europe in the summer of 1914, Causes of World War I, which led to the outbreak of World War I (1914–1918). The crisis began on 28 June 1 ...
, ''Mirabeau'' and the other ships of the First Battle Squadron downloaded their practice ammunition and exchanged suspect lots of propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the e ...
for new ones beginning on 27 July. They recoaled four days later and the mobilized on 2 August.
World War I
Before the French declared war on theGerman Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
on the morning of 4 August, Vice Admiral () Augustin Boué de Lapeyrère
Augustin Manuel Hubert Gaston Boué de Lapeyrère (18 January 1852 – 17 February 1924) was a French admiral during World War I. He was a strong proponent of naval reform, and is comparable to Admiral Jackie Fisher of the British Royal Navy.
...
, commander of the 1st Naval Army (), as the Mediterranean Squadron had been renamed in 1913, ordered most of his ships to concentrate off the Algerian
Algerian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Algeria
* Algerian people
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Algeria, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, econo ...
coast to escort troop convoys to Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
and to blockade German shipping in the Mediterranean. Despite this deployment the German battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
and light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to thi ...
were able to bombard Bône
Annaba ( ar, عنّابة, "Place of the Jujubes"; ber, Aânavaen), formerly known as Bon, Bona and Bône, is a seaport city in the northeastern corner of Algeria, close to the border with Tunisia. Annaba is near the small Seybouse River ...
and Philippeville
Philippeville (; wa, Flipveye) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Namur, Belgium. The Philippeville municipality includes the former municipalities of Fagnolle, Franchimont, Jamagne, Jamiolle, Merlemont, Ne ...
on 4 August. Despite ''Mirabeau''s machinery problems which limited the 1st Battle Squadron to a speed of , the squadron probably would have intercepted the German ships later that morning if its commander, Vice Admiral Paul Chocheprat, had not ordered a turn to the west. ''Mirabeau'' spent the rest of the month under repair. Aside from several uneventful sorties into the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
, the French capital ship
The capital ships of a navy are its most important warships; they are generally the larger ships when compared to other warships in their respective fleet. A capital ship is generally a leading or a primary ship in a naval fleet.
Strategic im ...
s spent most of their time cruising between the neutral Greek and Italian coasts to prevent the Austro-Hungarian fleet from attempting to break out of the Adriatic. The torpedoing of the dreadnought battleship on 21 December by the Austro-Hungarian submarine showed that the battleships were vulnerable to this threat, and they were withdrawn to spend the rest of the month further south at an anchorage in Navarino Bay
Pylos (, ; el, Πύλος), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is t ...
.
On 11 January 1915, the French were alerted that the Austro-Hungarian fleet was going to sortie from its base at Pola Pola or POLA may refer to:
People
*House of Pola, an Italian noble family
*Pola Alonso (1923–2004), Argentine actress
*Pola Brändle (born 1980), German artist and photographer
*Pola Gauguin (1883–1961), Danish painter
*Pola Gojawiczyńska (18 ...
, so the Naval Army sailed north to the Albanian coast. It proved to be a false alarm, and they were back at their moorings three days later. In the meantime, the ships patrolled the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
. The declaration of war on Austria-Hungary by Italy on 23 May, and the Italian decision to assume responsibility for naval operations in the Adriatic, allowed the French Navy to withdraw to either Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
or Bizerte
Bizerte or Bizerta ( ar, بنزرت, translit=Binzart , it, Biserta, french: link=no, Bizérte) the classical Hippo, is a city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia. It is the northernmost city in Africa, located 65 km (40mil) north of the cap ...
, Tunisia, to cover the Otranto Barrage
The Otranto Barrage was an Allied naval blockade of the Otranto Straits between Brindisi in Italy and Corfu on the Greek side of the Adriatic Sea in the First World War. The blockade was intended to prevent the Austro-Hungarian Navy from escapi ...
. ''Mirabeau'' was in Malta on 30 June when a torpedo exploded in a nearby warehouse. The ship was only lightly damaged, but two men of her crew were killed and eleven wounded.
 In November 1916, she transported landing parties from the other ships of her division to
In November 1916, she transported landing parties from the other ships of her division to Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
. On 1 December, those landing parties participated in the Allied attempt to ensure Greek acquiescence to Allied operations in Macedonia. Greek resistance to the Allied action ended after ''Mirabeau'' fired four rounds from her main armament into the city, one of which landed near the Royal Palace. Afterwards, she spent 1917 based at Corfu or at Mudros
Moudros ( el, Μούδρος) is a town and a former municipality on the island of Lemnos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lemnos, of which it is a municipal unit. It covers the entire eas ...
to prevent ''Goeben'', by this time transferred to the Ottoman Empire and renamed ''Yavuz Sultan Selim'', from breaking out into the Mediterranean. In August the ship tested a tethered balloon
A tethered, moored or captive balloon is a balloon that is restrained by one or more tethers attached to the ground and so it cannot float freely. The base of the tether is wound around the drum of a winch, which may be fixed or mounted on a vehic ...
, but it was destroyed by a lightning strike on 31 October. In April 1918, ''Mirabeau'' accompanied her sisters and to Mudros, where they remained for the rest of the war.Gille, p. 118 The 1st Naval Army was reorganized on 1 July and most of the ''Danton''-class ships were assigned to the Second Squadron () with ''Mirabeau'' part of the First Division of the squadron.
Postwar
 After the
After the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
was signed on 30 October between the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
and the Ottoman Empire, the ship participated in the early stage of the occupation of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
beginning on 12 November. By 8 December ''Mirabeau'' was already deployed to the Black Sea to support White Russian forces in Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
and deter Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
forces who were advancing on the city during the Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
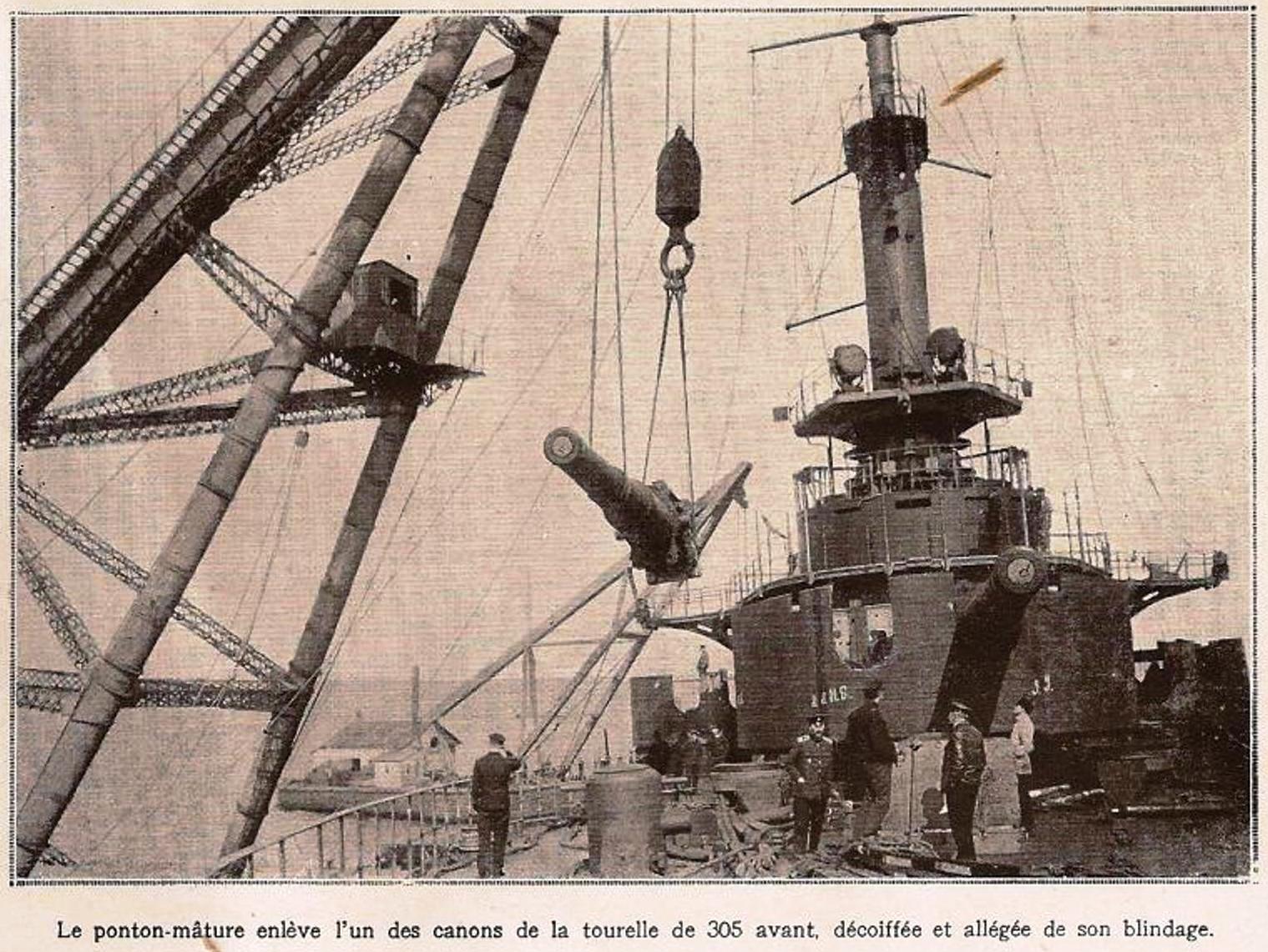
. ''Mirabeau'' ran aground during a snowstorm on 18 February 1919 off the Crimean coast. She could not be refloated until of weight were removed. To this end, her guns, turret armour, most of her boilers, coal, ammunition and the upper strake of belt armor was disembarked. After several weeks of effort, the ship was refloated on 6 April and she was towed by the and the tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, su ...
''Thernomore'' to a drydock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
in Sevastopol to repair any damage and to have her equipment reinstalled. This process began on 12 April, but ''Mirabeau'' was refloated three days later as news was received of the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
's advance on the city. Only her guns, ammunition and part of her armor had been replaced by the time the city was evacuated by the Allies on 5 May. She was towed to Constantinople by the battleship and five tugs where she remained from 7–15 May. ''Justice'' then resumed the tow and they reached Toulon on the 24th. After an inspection of the ship in a drydock, ''Mirabeau'' was stricken on 22 August and turned over as compensation to the company that salvaged the pre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, prote ...
. Her hulk
The Hulk is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer Stan Lee and artist Jack Kirby, the character first appeared in the debut issue of ''The Incredible Hulk (comic book), The Incredible Hulk' ...
was towed to Savona
Savona (; lij, Sann-a ) is a seaport and ''comune'' in the west part of the northern Italy, Italian region of Liguria, capital of the Province of Savona, in the Riviera di Ponente on the Mediterranean Sea.
Savona used to be one of the chie ...
, Italy, to be scrapped on 28 April 1922.Jordan & Caresse, p. 285
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
*CUIRASSE Danton
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mirabeau Danton-class battleships Ships built in France 1909 ships Maritime incidents in 1919 Shipwrecks in the Black Sea