Fred Vine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Frederick John Vine FRS (born 17 June 1939) is an English marine geologist and
/ref> where he studied
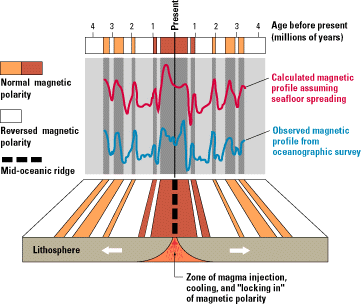 Vine's PhD thesis was on 'Magnetism in the Seafloor' and supervised by Drummond Matthews. Having met
Vine's PhD thesis was on 'Magnetism in the Seafloor' and supervised by Drummond Matthews. Having met
/ref> * * * * * First edition: 1990, second edition: 1996.
Faculty page
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Vine, Fred 1939 births Living people People educated at Latymer Upper School Alumni of St John's College, Cambridge Princeton University faculty Academics of the University of East Anglia British geologists British geophysicists Fellows of the Royal Society People from Chiswick Marine geologists Tectonicists Marine geophysicists
geophysicist
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' so ...
. He made key contributions to the theory of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large t ...
, helping to show that the seafloor spreads from mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a div ...
s with a symmetrical pattern of magnetic reversals in the basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
rocks on either side.
Early life
Vine was born inChiswick
Chiswick ( ) is a district of west London, England. It contains Hogarth's House, the former residence of the 18th-century English artist William Hogarth; Chiswick House, a neo-Palladian villa regarded as one of the finest in England; and ...
, London, and educated at Latymer Upper School and St John's College, Cambridge
St John's College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge founded by the Tudor matriarch Lady Margaret Beaufort. In constitutional terms, the college is a charitable corporation established by a charter dated 9 April 1511. Th ...
Profile at Bookrags.com/ref> where he studied
Natural Sciences
Natural science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and repeat ...
(BA, 1962) and marine geophysics Marine geophysics is the scientific discipline that employs methods of geophysics to study the world's ocean basins and continental margins, particularly the solid earth beneath the ocean. It shares objectives with marine geology, which uses sedim ...
(PhD, 1965). He married Susan 'Sue' Vine (née McCall), who worked as a research assistant for Drummond Matthews in the Department of Geodesy and Geophysics, University of Cambridge, contributing to the development of the sea-floor spreading hypothesis associated with Matthews and her husband.
Plate Tectonics
 Vine's PhD thesis was on 'Magnetism in the Seafloor' and supervised by Drummond Matthews. Having met
Vine's PhD thesis was on 'Magnetism in the Seafloor' and supervised by Drummond Matthews. Having met Harry Hess
Harry Hess (born July 5, 1968) is a Canadian record producer, singer and guitarist best known as the frontman for the Canadian hard rock band Harem Scarem.
Hess has used his recording studio (Vespa Music Group) to work with many famous acts, ...
he was aware of sea floor spreading, where the ocean bed acts as a 'conveyor belt' moving away from the central ridge. BBC / Open University
The Open University (OU) is a British Public university, public research university and the largest university in the United Kingdom by List of universities in the United Kingdom by enrolment, number of students. The majority of the OU's underg ...
broadcast series ''Earth Story'', Vine interviewed by Professor Aubrey Manning Vine's work, with that of Drummond Matthews and Lawrence Morley of the Geological Survey of Canada
The Geological Survey of Canada (GSC; french: Commission géologique du Canada (CGC)) is a Canadian federal government agency responsible for performing geological surveys of the country, developing Canada's natural resources and protecting the e ...
, helped put the variations in the magnetic properties of the ocean crust into context in what is now known as the Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis. Specifically they supported Dietz's (''Nature'' 1961) idea that sea floor spreading was occurring at mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a div ...
s. Vine and Matthews showed that basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
created at a mid-ocean ridge records earth's current magnetic field polarity (and strength), thus turning Hess's theoretical 'conveyor belt' into a 'tape recorder'. Furthermore, they showed that magnetic reversals 'frozen' into these rocks, as suggested by Allan Cox (''Nature'' 1963), can be seen as parallel strips as you travel perpendicularly away from the ridge crest.
Academic career
Vine worked with E. M. Moores on the Ophiolite in theTroodos mountains
Troodos (sometimes spelled Troödos; el, Τρόοδος ; tr, Trodos Dağları) is the largest mountain range in Cyprus, located in roughly the center of the island. Its highest peak is Mount Olympus ( el, Όλυμπος), also known as Chion ...
of southern Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
. He worked with R. A. Livermore and A. G. Smith on the history of the Earth's magnetic field. He worked on the electrical conductivity of rocks from the lower continental crust with R. G. Ross and P. W. J. Glover, which culminated in 1992 with measurements of the electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
of graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
-rich amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flak ...
s and granulite
Granulites are a class of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the granulite facies that have experienced high-temperature and moderate-pressure metamorphism. They are medium to coarse–grained and mainly composed of feldspars sometimes associated ...
s at lower crustal temperatures and pressures with a full water saturation and pore fluid pressure and graphite-free
In 1967, Vine became assistant professor of geology and geophysics at Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the n ...
. In 1970 he moved to the School of Environmental Sciences at the University of East Anglia
The University of East Anglia (UEA) is a public research university in Norwich, England. Established in 1963 on a campus west of the city centre, the university has four faculties and 26 schools of study. The annual income of the institution f ...
, becoming professor there in 1974. He served as dean from 1977 to 1980, and again from 1993 to 1998. After 1998, he was a professorial fellow of the University of East Anglia. and then in 2008 he became an emeritus professor
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title ...
there.
Honours
Vine's honours include: * Day Medal in 1968 * Bigelow Medal ofWoods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI, acronym pronounced ) is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering.
Established in 1930 in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, i ...
in 1970
* Bigsby Medal
The Bigsby Medal is a medal of the Geological Society of London established by John Jeremiah Bigsby. It is awarded for the study of American geology.
Recipients
SourcThe Geological Society
See also
* List of geology awards
This list of ge ...
of the Geological Society of London
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe with more than 12,000 Fellows.
Fe ...
in 1971
* Chapman Medal
The Chapman Medal is an award of the Royal Astronomical Society, given for "investigations of outstanding merit in the science of the Sun, space and planetary environments or solar-terrestrial physics". It is named after Sydney Chapman (1888� ...
of the Royal Astronomical Society
(Whatever shines should be observed)
, predecessor =
, successor =
, formation =
, founder =
, extinction =
, merger =
, merged =
, type = NG ...
(1973)
* Fellowship of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, r ...
in March 1974
* The Chree Medal and Prize
The Edward Appleton Medal and Prize is awarded by the Institute of Physics for distinguished research in environmental, earth or atmospheric physics. Originally named after Charles Chree, the British physicist and former President of the Physica ...
of the Institute of Physics
The Institute of Physics (IOP) is a UK-based learned society and professional body that works to advance physics education, research and application.
It was founded in 1874 and has a worldwide membership of over 20,000. The IOP is the Physica ...
(1977)
* Hughes Medal
The Hughes Medal is awarded by the Royal Society of London "in recognition of an original discovery in the physical sciences, particularly electricity and magnetism or their applications". Named after David E. Hughes, the medal is awarded with ...
of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, r ...
(1982)
* International Balzan Prize
The International Balzan Prize Foundation awards four annual monetary prizes to people or organizations who have made outstanding achievements in the fields of humanities, natural sciences, culture, as well as for endeavours for peace and the br ...
(1981)
* Prestwich Medal The Prestwich Medal is a medal of the Geological Society of London established in the will of Joseph Prestwich "to apply the accumulated annual proceeds...at the end of every three years, in providing a Gold Medal to the value of Twenty Pounds whi ...
of the Geological Society of London
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe with more than 12,000 Fellows.
Fe ...
in 2007
Publications
* University of East Angliea – Fred Vine profile/ref> * * * * * First edition: 1990, second edition: 1996.
See also
* List of geophysicistsReferences
External links
Faculty page
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Vine, Fred 1939 births Living people People educated at Latymer Upper School Alumni of St John's College, Cambridge Princeton University faculty Academics of the University of East Anglia British geologists British geophysicists Fellows of the Royal Society People from Chiswick Marine geologists Tectonicists Marine geophysicists