Francke Foundations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Francke Foundations (Franckesche Stiftungen), also known as Glauchasche Anstalten were founded in 1695 in Halle, Germany as a Christian, social and educational work by
The Francke Foundations (Franckesche Stiftungen), also known as Glauchasche Anstalten were founded in 1695 in Halle, Germany as a Christian, social and educational work by
 In the 1970s, the northerly Orphanage wall had been demolished to build an elevated road (Hochstraße) to connect Halle with
In the 1970s, the northerly Orphanage wall had been demolished to build an elevated road (Hochstraße) to connect Halle with
 Today the Francke Foundations buildingsare almost completely restored and the ensemble has been revived as cultural and scientific, social and educational institution.
On the grounds of the Francke Foundations there are now besides the institutions owned by the foundation – the Historic Orphanage, the Archives, the Historic Library and three kindergartens, children's creative education center Krokoseum – the Faculty of Theology and the Institute for Education, the Interdisciplinary Research Centres for Enlightenment Studies (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für die Erforschung der europäischen Aufklärung) and Interdisciplinary Centre for the Studies in Pietism of the Martin Luther University (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Pietismusforschung), four schools (Landesgymnasium Latina "August Hermann Francke", Grundschule "August Hermann Francke", Reformschule Maria Montessori, Sekundarschule "August Hermann Francke"), a Protestant Seminary, a social workshop for young people, two church rooms (St. Georgs Kapelle, Orthodoxe Hauskirche zum Heiligen Kreuz) and the German Federal Cultural Foundation (Kulturstiftung des Bundes). .
Today the Francke Foundations buildingsare almost completely restored and the ensemble has been revived as cultural and scientific, social and educational institution.
On the grounds of the Francke Foundations there are now besides the institutions owned by the foundation – the Historic Orphanage, the Archives, the Historic Library and three kindergartens, children's creative education center Krokoseum – the Faculty of Theology and the Institute for Education, the Interdisciplinary Research Centres for Enlightenment Studies (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für die Erforschung der europäischen Aufklärung) and Interdisciplinary Centre for the Studies in Pietism of the Martin Luther University (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Pietismusforschung), four schools (Landesgymnasium Latina "August Hermann Francke", Grundschule "August Hermann Francke", Reformschule Maria Montessori, Sekundarschule "August Hermann Francke"), a Protestant Seminary, a social workshop for young people, two church rooms (St. Georgs Kapelle, Orthodoxe Hauskirche zum Heiligen Kreuz) and the German Federal Cultural Foundation (Kulturstiftung des Bundes). .
 The Historical Library was founded at the end of the 17th century by Francke. The old library's holdings contain around 50,000 books on all areas of knowledge, but particularly on early modern church and educational history. Since 1728 the books have been housed in a purpose-built building whose original library fittings, including the stage-set like shelving, have been preserved in their entirety. From 1996 to 1998 the building was restored according to the old plans; it can now be seen again as it was in 1746.
The Study Centre is a service institution for the cataloguing of and research into the Archive and Library holdings of the Francke Foundations. In recent years comprehensive and innovative cataloguing projects could be carried out with the financial support of the German Research Foundation. These improve our understanding of the sources and provide a solid basis for new research perspectives and projects. The Fritz Thyssen Fellowship of the Francke Foundations helps scientists to achieve this. Together the Archive and the Library of the Francke Foundations form the Study Centre "
The Historical Library was founded at the end of the 17th century by Francke. The old library's holdings contain around 50,000 books on all areas of knowledge, but particularly on early modern church and educational history. Since 1728 the books have been housed in a purpose-built building whose original library fittings, including the stage-set like shelving, have been preserved in their entirety. From 1996 to 1998 the building was restored according to the old plans; it can now be seen again as it was in 1746.
The Study Centre is a service institution for the cataloguing of and research into the Archive and Library holdings of the Francke Foundations. In recent years comprehensive and innovative cataloguing projects could be carried out with the financial support of the German Research Foundation. These improve our understanding of the sources and provide a solid basis for new research perspectives and projects. The Fritz Thyssen Fellowship of the Francke Foundations helps scientists to achieve this. Together the Archive and the Library of the Francke Foundations form the Study Centre "
Franckesche Stiftungen
House of Generations
Historical Library
Cabinet of Artefacts and CuriositiesStudy Centre
 The Francke Foundations (Franckesche Stiftungen), also known as Glauchasche Anstalten were founded in 1695 in Halle, Germany as a Christian, social and educational work by
The Francke Foundations (Franckesche Stiftungen), also known as Glauchasche Anstalten were founded in 1695 in Halle, Germany as a Christian, social and educational work by August Hermann Francke
August Hermann Francke (; 22 March 1663 – 8 June 1727) was a German Lutheran clergyman, theologian, philanthropist, and Biblical scholar.
Biography
Born in Lübeck, Francke was educated at the Illustrious Gymnasium in Gotha before he studie ...
The Francke Foundations are today a non-profit educational organization housed in a complex of historic buildings. The Francke Foundations includes three kindergartens
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th cent ...
, a children’s creativity centre, four schools, a House of Generations, a youth workshop, a bible centre, traditional commercial enterprises, archives, libraries, museums, and university and non-university research facilities. More than 4,000 people learn, teach, work and live in the Francke Foundations.
The Francke Foundations have been on the German proposal list as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
since 1999.
History
17th century
A pastor and professor in Halle, Francke was strongly interested in education reform. His goals were to establish a school for poor and orphaned children and create a set of religiously motivated schools for each class of society. In 1695, after receiving a large cash donation at Easter, Francke established the first institution in the future Francke foundations, acharity school
Charity schools, sometimes called blue coat schools, or simply the Blue School, were significant in the history of education in England. They were built and maintained in various parishes by the voluntary contributions of the inhabitants to ...
in his vicarage. The children were taught by students from the University. With the school gaining a strong reputation, local residents started sending their children to this school.
In spring 1695, Francke founded the Paedagogium, a school for higher education for members of nobility and middle class. In 1697, he added a Latin school
The Latin school was the grammar school of 14th- to 19th-century Europe, though the latter term was much more common in England. Emphasis was placed, as the name indicates, on learning to use Latin. The education given at Latin schools gave gre ...
().
In 1698, thanks to financial assistance from the King of Prussia
The monarchs of Prussia were members of the House of Hohenzollern who were the hereditary rulers of the former German state of Prussia from its founding in 1525 as the Duchy of Prussia. The Duchy had evolved out of the Teutonic Order, a Roman C ...
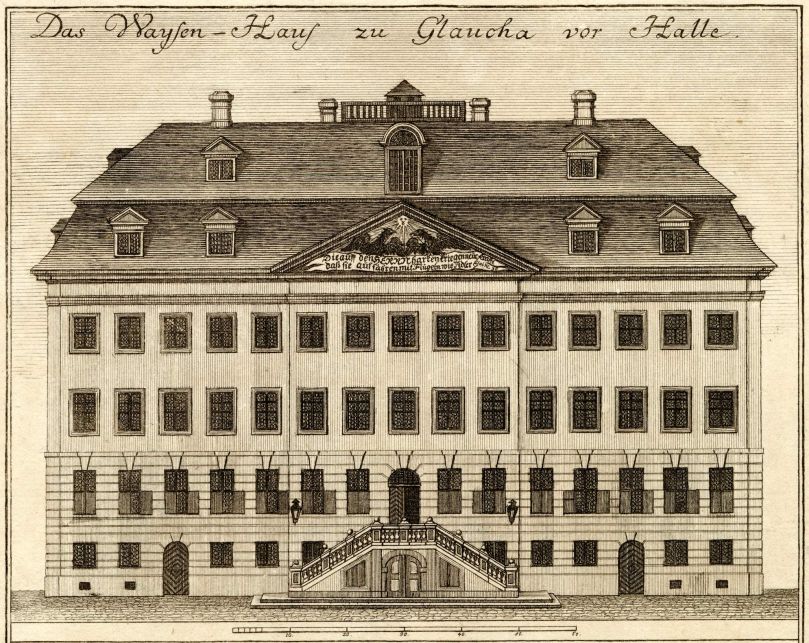
, Francke started building the Orphanage for boys. Finished in 1701, it was a lavish building compared to comparable facilities. In the tympanum of the Orphanage, which is decorated with two eagles rising up to the sun, is written ( Isaiah 40:31) “But those who wait for the Lord’s help, find renewed strength; they rise up as if they had eagles’ wings, they run without growing weary, they walk without getting tired.”
Francke Foundations soon gained a reputation as the "New Jerusalem
In the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible, New Jerusalem (, ''YHWH šāmmā'', YHWH sthere") is Ezekiel's prophetic vision of a city centered on the rebuilt Holy Temple, the Third Temple, to be established in Jerusalem, which would be the c ...
". The Foundations formed a global correspondence network that spread the reform plans of Halle Pietism
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christian life, including a social concern for the needy and ...
internationally.
18th century
In the 18th century, Francke Foundations started a publishing house, a book store, a printing office, a pharmacy and a Cabinet of Artefacts and Curiosities. Their revenues funded the Orphanage. In 1709 a timbered, three-storey house for orphan girls and a girls' school were established. In 1710, Francke built the English house for English and other foreign children living in Halle. In 1711 another building was built to house a dining hall and a huge and singing hall with a capacity of 2,000 persons. In 1711, Francke and Carl Hildebrand von Canstein established the Cansteinsche Bibelanstalt (Canstein Bible Institute), the oldest bible institute in Germany. Bibles were in the early 18th century extremely expensive. An invention in letter pressing, and with financial support byvon Canstein, allowed the institute to produce inexpensive Bibles in a large quantities. Until the middle of the 20th century millions of Bibles had been published. In the following years a number of buildings were built, e.g. the long house (Langes Haus) in 1713, the largest high-timbered five- and six-storey building. It houses today a hall of residents (Evangelisches Konvikt) and a boarding school for students of the Latina. In the upper Lindenhof (linden yard), the Ökonomiegebäude was built in 1747–48 as an administration house. It is, since 1808 the base of the Stadtsingechor, the oldest boys' choir in central Germany.19th century
The Francke Foundations underwent decline in the late 18th century. In the early 19th century,August Hermann Niemeyer
August Hermann Niemeyer (1 September 1754 in Halle (Saale) – 7 July 1828 in Magdeburg) was a German Protestant theologian, teacher, a librettist, a poet, a travel writer, a Protestant church song poet and a Prussian political educator. He wa ...
took over direction of the Foundations, renewing the educational programs and resolving financial issues.
In 1810 the Realschule was built and in 1835 girls' secondary school. The royal paedagogium (Königliches Pädagogium) was rebuilt in 1848,
20th century
Because of the good reputation and its revenues, the Francke Foundations were growing and a new building for Lateinische Hauptschule (Latina) was built. In 1911 more than 3,000 students attended the various schools. During the time ofNational socialism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hit ...
, Francke Foundations remained as a Christian formed school city. During World War II air raid in March 1945, some Francke Foundation buildings, including the Francke residence and the Latina, were either damaged and destroyed.
In 1946, during the Soviet occupation
During World War II, the Soviet Union occupied and annexed several countries effectively handed over by Nazi Germany in the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of 1939. These included the eastern regions of Poland (incorporated into two different ...
of East Germany the presidium of the province of Saxony
The Province of Saxony (german: link=no, Provinz Sachsen), also known as Prussian Saxony () was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.
It was formed by the merge ...
abolished the Francke Foundations and turned over all its assets and buildings to the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg.
 In the 1970s, the northerly Orphanage wall had been demolished to build an elevated road (Hochstraße) to connect Halle with
In the 1970s, the northerly Orphanage wall had been demolished to build an elevated road (Hochstraße) to connect Halle with Halle-Neustadt
Halle-Neustadt (; popularly known as ''HaNeu'' , like Hanoi) was a city in the German Democratic Republic (East Germany). It was established as a new town on 12 May 1967, as an independent and autonomous city. The population in 1972 was 51,600 ...
. This elevated road separates the Orphanage Pharmacy from other parts of the Foundations. On the ground of the Foundations, several high rises were built.
After German Reunification in 1990, the Francke Foundations were re-established in September 1991. With assistance of the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it the ...
and private donations, the Francke Foundations building were renovated.
Current situation and activities
 Today the Francke Foundations buildingsare almost completely restored and the ensemble has been revived as cultural and scientific, social and educational institution.
On the grounds of the Francke Foundations there are now besides the institutions owned by the foundation – the Historic Orphanage, the Archives, the Historic Library and three kindergartens, children's creative education center Krokoseum – the Faculty of Theology and the Institute for Education, the Interdisciplinary Research Centres for Enlightenment Studies (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für die Erforschung der europäischen Aufklärung) and Interdisciplinary Centre for the Studies in Pietism of the Martin Luther University (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Pietismusforschung), four schools (Landesgymnasium Latina "August Hermann Francke", Grundschule "August Hermann Francke", Reformschule Maria Montessori, Sekundarschule "August Hermann Francke"), a Protestant Seminary, a social workshop for young people, two church rooms (St. Georgs Kapelle, Orthodoxe Hauskirche zum Heiligen Kreuz) and the German Federal Cultural Foundation (Kulturstiftung des Bundes). .
Today the Francke Foundations buildingsare almost completely restored and the ensemble has been revived as cultural and scientific, social and educational institution.
On the grounds of the Francke Foundations there are now besides the institutions owned by the foundation – the Historic Orphanage, the Archives, the Historic Library and three kindergartens, children's creative education center Krokoseum – the Faculty of Theology and the Institute for Education, the Interdisciplinary Research Centres for Enlightenment Studies (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für die Erforschung der europäischen Aufklärung) and Interdisciplinary Centre for the Studies in Pietism of the Martin Luther University (Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Pietismusforschung), four schools (Landesgymnasium Latina "August Hermann Francke", Grundschule "August Hermann Francke", Reformschule Maria Montessori, Sekundarschule "August Hermann Francke"), a Protestant Seminary, a social workshop for young people, two church rooms (St. Georgs Kapelle, Orthodoxe Hauskirche zum Heiligen Kreuz) and the German Federal Cultural Foundation (Kulturstiftung des Bundes). .
Cabinet of Artefacts and Curiosities
The Cabinet of Artefacts and Curiosities is considered to be one of Germany’s oldest teaching and research collections. Today the original museum concept of the 18th century has been recreated in its original location in themansard
A mansard or mansard roof (also called a French roof or curb roof) is a four-sided gambrel-style hip roof characterised by two slopes on each of its sides, with the lower slope, punctured by dormer windows, at a steeper angle than the upper. The ...
of the Historic Orphanage.
Eighteen decorated display cabinets accommodate the collection of around 3,000 naturalia artificialia, including several models. The naturalia are subdivided into stones, plants and the animal kingdom and the artefacts into the fine arts
In European academic traditions, fine art is developed primarily for aesthetics or creative expression, distinguishing it from decorative art or applied art, which also has to serve some practical function, such as pottery or most metalwork ...
, the art of writing, coins, everyday culture and clothing.
In the Historic Orphanage several exhibitions about the history of Francke Foundation and related issues were shown. In the former prayer and singing hall, now the Freylinghausen-Saal, events, meetings and concerts take place. In the basement the children’s creative centre Krokoseum offers activities in cultural education.
Library and Study Center
August Hermann Francke
August Hermann Francke (; 22 March 1663 – 8 June 1727) was a German Lutheran clergyman, theologian, philanthropist, and Biblical scholar.
Biography
Born in Lübeck, Francke was educated at the Illustrious Gymnasium in Gotha before he studie ...
". Housed in the Historical Library building (House 22) and the neighbouring building (House 23/24).
Orthodox Chapel of the Holy Cross and the Resurrection of Jesus
The Chapel of the Holy Cross and the resurrection ofJesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
, installed in the vaults of House 24 in the year 2000, is the only Orthodox Church
Orthodox Church may refer to:
* Eastern Orthodox Church
* Oriental Orthodox Churches
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church of New Zealand
* State church of the Roman Empire
* True Orthodox church
See also
* Orthodox (di ...
in Saxony-Anhalt. The walls of the barrel vaults have been painted in accordance with the traditions of Orthodox art. They depict icons of figures from both the Old and New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
s as well as scenes from biblical history. The iconostases
In Eastern Christianity, an iconostasis ( gr, εἰκονοστάσιον) is a wall of icons and religious paintings, separating the nave from the sanctuary in a church. ''Iconostasis'' also refers to a portable icon stand that can be placed a ...
of beech wood were made by a master craftsman from Halle.
The House of Generations
Originally constructed as the royal paedagogium, this building was redeveloped in 2005, as the House of Generations (Haus der Generationen). It contains a primaryMontessori school
The Montessori method of education involves children's natural interests and activities rather than formal teaching methods. A Montessori classroom places an emphasis on hands-on learning and developing real-world skills. It emphasizes indepen ...
(Reformschule Maria Montessori), a nursing home
A nursing home is a facility for the residential care of elderly or disabled people. Nursing homes may also be referred to as skilled nursing facility (SNF) or long-term care facilities. Often, these terms have slightly different meanings to in ...
(Altenheim der Paul-Riebeck-Stiftung) and a social consulting and education institution for families and health care (Familienkompetenzzentrum für Bildung und Gesundheit).
See also
Franckesche Stiftungen
House of Generations
Historical Library
Cabinet of Artefacts and Curiosities
References
*August Hermann Francke (1704): Der grosse Aufsatz. Schrift über eine Reform des Erziehungs- und Bildungswesens als Ausgangspunkt einer geistlichen und sozialen Neuordnung der Evangelischen Kirche des 18. Jahrhunderts. Mit einer quellenkundlichen Einführung hrsg. v. Otto Podczeck (Abhandlungen der Sächsischen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Leipzig, Philologisch-Historische Klasse, Bd. 53, H. 3), Akademie-Verlag, Berlin 1962. *Günter Treizel: Kleiner Führer durch die Franckeschen Stiftungen zu Halle. Fliegenkopf-Verlag, Halle 2003, . *Helmut Obst; Paul Raabe: Die Franckeschen Stiftungen zu Halle (Saale). Geschichte und Gegenwart. Fliegenkopf-Verlag, Halle 2000, . *Paul Raabe; Thomas J. Müller-Bahlke (Hrsg.): Das Historische Waisenhaus. Das Hauptgebäude der Franckeschen Stiftungen zu Halle. Halle 2005, . *Thomas J. Müller-Bahlke: Die Wunderkammer. Die Kunst- und Naturalienkammer der Franckeschen Stiftungen zu Halle (Saale). Verlag der Franckeschen Stiftungen, Halle/Saale 1998, . *Peter Menck: Die Erziehung der Jugend zur Ehre Gottes und zum Nutzen des Nächsten. Die Pädagogik August Hermann Franckes. Tübingen 2001, . *Gustav Friedrich Hertzberg: August Hermann Francke und sein hallisches Waisenhaus. Verlag der Buchhandlung des Waisenhauses, Halle a. S. 1898 *Kelly Whitmer, The Halle Orphanage as Scientific Community: Observation, Eclecticism and Pietism in the Early Enlightenment. Chicago: the University of Chicago Press, 2015. {{Authority control Foundations based in Germany Organizations established in the 1690s Buildings and structures in Halle (Saale) Pietism