Franchino Gaffurio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
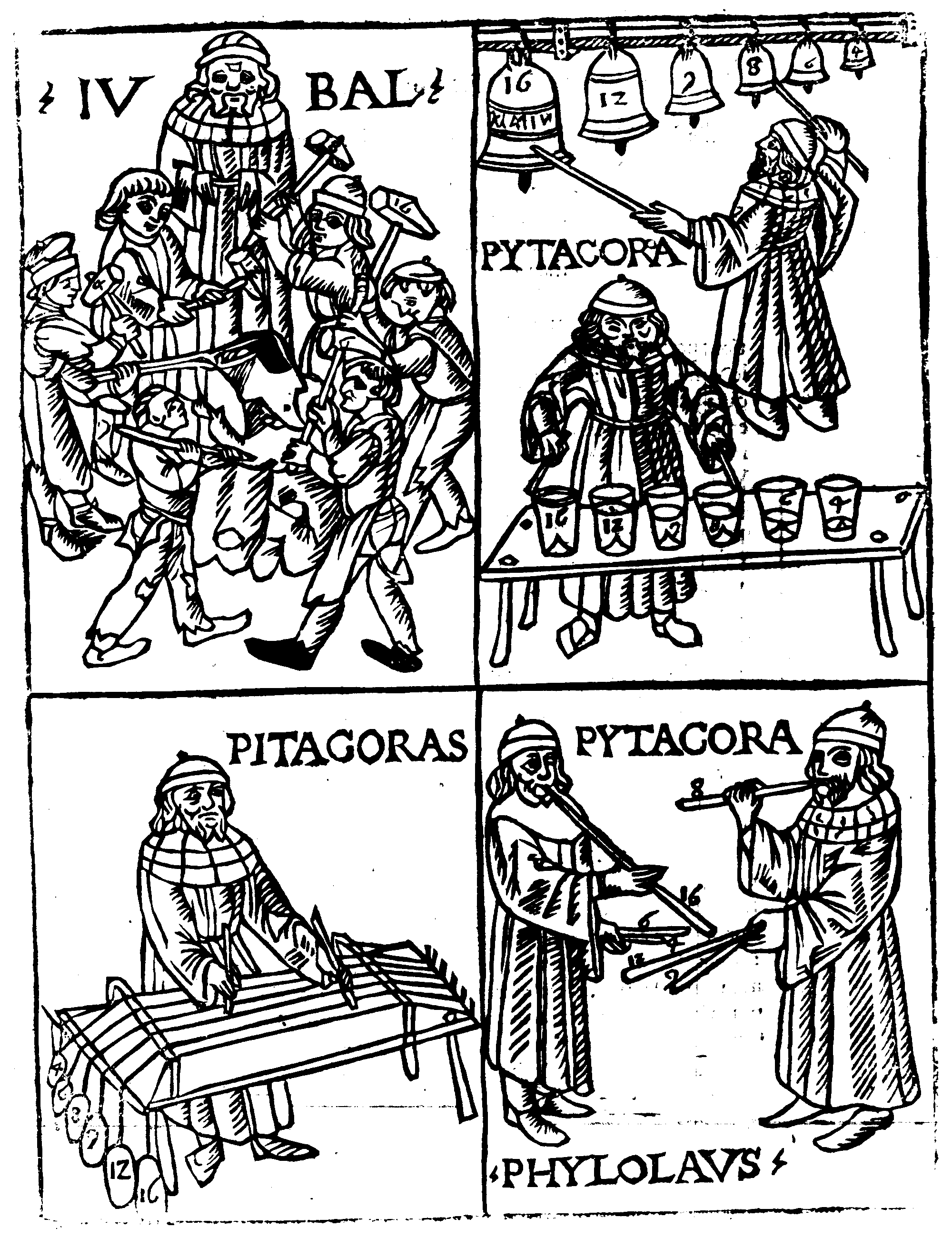
 Franchinus Gaffurius (Franchino Gaffurio; 14 January 1451 – 25 June 1522) was an Italian
Franchinus Gaffurius (Franchino Gaffurio; 14 January 1451 – 25 June 1522) was an Italian
 During the previous decade the
During the previous decade the
 Gaffurius wrote
Gaffurius wrote

 Franchinus Gaffurius (Franchino Gaffurio; 14 January 1451 – 25 June 1522) was an Italian
Franchinus Gaffurius (Franchino Gaffurio; 14 January 1451 – 25 June 1522) was an Italian music theorist
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
and composer of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
. He was an almost exact contemporary of Josquin des Prez
Josquin Lebloitte dit des Prez ( – 27 August 1521) was a composer of High Renaissance music, who is variously described as French or Franco-Flemish. Considered one of the greatest composers of the Renaissance, he was a central figure of the ...
and Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
, both of whom were his personal friends. He was one of the most famous musicians in Italy in the late 15th and early 16th centuries.
Life
He was born in Lodi to an aristocratic family. Early in life he entered aBenedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
monastery, where he acquired his early musical training; later he became a priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
. Later he lived in Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard language, Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the Province of Mantua, province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture ...
and Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Northern Italy, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city Comune, municipality in the region and the ...
before settling in Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
as the ''maestro di cappella
(, also , ) from German ''Kapelle'' (chapel) and ''Meister'' (master)'','' literally "master of the chapel choir" designates the leader of an ensemble of musicians. Originally used to refer to somebody in charge of music in a chapel, the term ha ...
'' at the cathedral there, a position which he accepted in January 1484.
 During the previous decade the
During the previous decade the Sforza
The House of Sforza () was a ruling family of Renaissance Italy, based in Milan. They acquired the Duchy of Milan following the extinction of the Visconti family in the mid-15th century, Sforza rule ending in Milan with the death of the last mem ...
family, using the composer Gaspar van Weerbeke
Gaspar van Weerbeke ( – after 1516) was a Netherlandish composer of the Renaissance. He was of the same generation as Josquin des Prez, but unique in his blending of the contemporary Italian style with the older Burgundian style of Dufay.
L ...
as a recruiter, had built the choir at their chapel in Milan into one of the largest and most distinguished musical ensembles in Europe: composer-singers such as Alexander Agricola
Alexander Agricola (; born Alexander Ackerman; – 15 August 1506) was a Netherlandish composer of the Renaissance writing in the Franco-Flemish style. A prominent member of the ''Grande chapelle'', the Habsburg musical establishment, he wa ...
, Loyset Compère
Loyset Compère ( – 16 August 1518) was a Franco-Flemish composer of the Renaissance. Of the same generation as Josquin des Prez, he was one of the most significant composers of motets and chansons of that era, and one of the first musicians ...
and Johannes Martini
Johannes Martini (c. 1440 – late 1497 or early 1498) was a Franco-Flemish composer of the Renaissance.
Life
He was born in Brabant around 1440, but information about his early life is scanty. He probably received his early training in Flan ...
had all been employed there. While the membership of the choir at the Milan cathedral was mostly Italian, the cross-influence between his choir and the group at the Sforza chapel was significant. Gaffurius retained the post at the cathedral for the rest of his life, and it was in Milan that he knew both Josquin des Prez and Leonardo da Vinci.
Writings
Gaffurius was widely read, and showed a strongRenaissance humanist
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
bent. In addition to having a thorough understanding of contemporary musical practice, he met composers from all over Europe, since he had the good fortune to be living and working at one of the centers of activity for the incoming Netherlanders
The Dutch (Dutch language, Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, ...
. His books have a pedagogical intent, and provide a young composer with all the techniques necessary to learn his art.
The major treatises of his years in Milan are three: ''Theorica musicae'' (1492), ''Practica musicae'' (1496), and ''De harmonia musicorum instrumentorum opus'' (1518). The second of these, the ''Practica musicae'', is the most thorough, proceeding through subjects as diverse as ancient Greek notation, plainchant
Plainsong or plainchant (calque from the French ''plain-chant''; la, cantus planus) is a body of chants used in the liturgies of the Western Church. When referring to the term plainsong, it is those sacred pieces that are composed in Latin text. ...
, mensuration, counterpoint
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradi ...
, and tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often ...
. One of his most famous comments is that the ''tactus'', the tempo of a semibreve
A whole note (American) or semibreve (British) in musical notation is a single note equivalent to or lasting as long as two half notes or four quarter notes. Description
The whole note or semibreve has a note head in the shape of a hollow ov ...
, is equal to the pulse of a man who is breathing quietly—presumably about 72 beats per minute.
Music
mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
es, motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the pre-eminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to Margar ...
s, settings of the Magnificat
The Magnificat (Latin for "
, and y soul
Y, or y, is the twenty-fifth and penultimate letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. According to some authorities, it is the sixth (or sevent ...
magnifies he Lord
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
) is a canticle, also known as the Song of Mary, the Canticle of Mary and, in the Eastern Christianity, Byzantine tradition, the Ode of the Theotokos (). It is traditionally incorporated ...hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn'' ...
s, mainly during his Milan years. Some of the motets were written for ceremonial occasions for his ducal employer; many of the masses show the influence of Josquin, and all are in flowing Netherlandish polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice, monophony, or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords, h ...
, though with an admixture of Italian lightness and melody. His music was collected in four codices under his own direction.
Selected recordings
* Franchino Gaffurio ''Missa de Carneval'' Motets:Stabat mater
The Stabat Mater is a 13th-century Christian hymn to Mary, which portrays her suffering as Jesus Christ's mother during his crucifixion. Its author may be either the Franciscan friar Jacopone da Todi or Pope Innocent III.Sabatier, Paul ''Life o ...
, Adoramus Te, Imperatrix reginarum, Imperatrix gloriosa, Florem ergo, Res miranda, Salve Regina
The "Salve Regina" (, ; meaning 'Hail Queen'), also known as the "Hail Holy Queen", is a Marian hymn and one of four Marian antiphons sung at different seasons within the Christian liturgical calendar of the Catholic Church. The Salve Regina ...
, Lamentatio, Magnificat, O sacrum convivium, Quando venit, Ave corpus. Il Convitto Armonico, Baschenis Ensemble, Stefano Buschini. Tactus 2012
References
* Articles "Franchinus Gaffurius," "Leonardo da Vinci" in ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', ed. Stanley Sadie. 20 vol. London, Macmillan Publishers Ltd., 1980. * * *Gustave Reese
Gustave Reese ( ; 29 November 1899 – 7 September 1977) was an American musicologist and teacher. Reese is known mainly for his work on medieval and Renaissance music, particularly with his two publications ''Music in the Middle Ages'' (1940) ...
, ''Music in the Renaissance''. New York, W.W. Norton & Co., 1954.
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Gaffurius, Franchinus Renaissance composers Italian classical composers Italian male classical composers Italian music theorists Italian Renaissance humanists 1451 births 1522 deaths People from Lodi, Lombardy Italian Benedictines