Foveon X3 sensor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Foveon X3 sensor is a digital camera
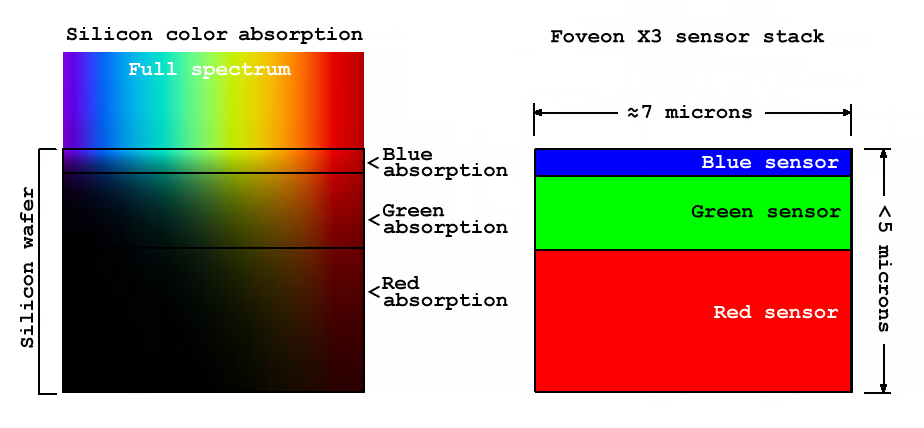 The diagram to the right depicts how the Foveon X3 sensor works. The image on the left shows the absorption of colors for each wavelength as it passes through the silicon wafer. The image on the right shows a layered sensor stack depicting the colors it detects at each absorption level for each output pixel. The sensor colors shown are only examples. In practice, the color attributes of each output pixel using this sensor result from the camera's
The diagram to the right depicts how the Foveon X3 sensor works. The image on the left shows the absorption of colors for each wavelength as it passes through the silicon wafer. The image on the right shows a layered sensor stack depicting the colors it detects at each absorption level for each output pixel. The sensor colors shown are only examples. In practice, the color attributes of each output pixel using this sensor result from the camera's
Kodak DCS Pro SLR/c Review
June 2004, Retrieved March 3, 2007) using Bayer sensors without such a filter. However, significant
were produced when photographing very fine detail
Retrieved March 3, 2007. to mitigate those artifacts in a Bayer sensor is not required; this is because little
see here
with those taken approximately contemporaneously of the same scene by the Bayer sensor-equipped Nikon D70
see here
/page15.asp. Both retrieved March 6, 2007. However, these reviewers offer no opinion as to whether this is an inherent property of the sensor or the camera's image-processing algorithms. With regards to the Sigma SD14, which uses a more recent Foveon X3 sensor, one reviewer judged its noise levels as ranging from "very low" at ISO 100 to "moderate" at ISO 1600 when using the camera's
Eyeing the Camera: into the Next Century
10th Color Imaging Conference: Color Science, System and Applications. IS&T and SID, Springfield, Va, USA, 2002. P. 349–355.
Foveon X3 technology pageDPReview Foveon X3 prototype previewSample Sigma/Foveon photosSample Polaroid x530/Foveon photos
Sigma DP1
{{DEFAULTSORT:Foveon X3 Sensor Digital photography Image sensors Color filter array
image sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
designed by Foveon, Inc., (now part of Sigma Corporation
is a Japanese company, manufacturing cameras, lenses, flashes and other photographic accessories. All Sigma products are produced in the company's own Aizu factory in Bandai, Fukushima, Japan. Although Sigma produces several camera mode ...
) and manufactured by Dongbu Electronics.
It uses an array of photosites that consist of three vertically stacked photodiodes. Each of the three stacked photodiodes has a different spectral sensitivity
Spectral sensitivity is the relative efficiency of detection, of light or other signal, as a function of the frequency or wavelength of the signal.
In visual neuroscience, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics ...
, allowing it to respond differently to different wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
s. The signals from the three photodiodes are then processed as additive color
Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a color model that predicts the appearance of colors made by coincident component lights, i.e. the perceived color can be predicted by summing the numeric representations of the component col ...
data that are transformed to a standard RGB color space
RGB color spaces are a category of additive colorimetric color spaces specifying part of its absolute color space definition using the RGB color model.
RGB color spaces are commonly found describing the mapping of the RGB color model to human p ...
. In the late 1970s, a similar color sensor having three stacked photo detectors at each pixel location, with different spectral responses due to the differential absorption of light by the semiconductor, had been developed and patented by Kodak.
The X3 sensor technology was first deployed in 2002 in the Sigma SD9 DSLR
A digital single-lens reflex camera (digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that combines the optics and mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a solid-state image sensor and digitally records the images from the sensor.
The reflex des ...
camera, and subsequently in the SD10, SD14, SD15, SD1 (including SD1 Merrill), the original mirrorless compact Sigma DP1 The Sigma DP1 was a high-end compact digital camera introduced by the Sigma Corporation. It featured a 14-megapixel Foveon X3 sensor (2652 × 1768 × 3 layers), a fixed 16.6 mm F4.0 lens (28mm equivalent), a LCD and a pop-up flash. It was the fi ...
and Sigma DP2 in 2008 and 2009 respectively, the Sigma dp2 Quattro series from 2014, and the Sigma SD Quattro series from 2016. The development of the Foveon X3 technology is the subject of the 2005 book ''The Silicon Eye'' by George Gilder.
Operation
 The diagram to the right depicts how the Foveon X3 sensor works. The image on the left shows the absorption of colors for each wavelength as it passes through the silicon wafer. The image on the right shows a layered sensor stack depicting the colors it detects at each absorption level for each output pixel. The sensor colors shown are only examples. In practice, the color attributes of each output pixel using this sensor result from the camera's
The diagram to the right depicts how the Foveon X3 sensor works. The image on the left shows the absorption of colors for each wavelength as it passes through the silicon wafer. The image on the right shows a layered sensor stack depicting the colors it detects at each absorption level for each output pixel. The sensor colors shown are only examples. In practice, the color attributes of each output pixel using this sensor result from the camera's image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
algorithms, which use a matrix process to construct a single RGB color from all the data sensed by the photodiode stack.
The depth of the silicon wafer in each of the three sensors is less than five micrometers that creates a negligible effect on focusing or chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the ...
. However, because the collection depth of the deepest sensor layer (red) is comparable to collection depths in other silicon CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
and CCD sensors, some diffusion of electrons and loss of sharpness in the longer wavelengths occurs.
Use
The first digital camera to use a Foveon X3 sensor was the Sigma SD9, a digital SLR launched in 2002. It used a 20.7 × 13.8 mm, 2268 x 1512 × 3 (3.54 × 3 MP) iteration of the sensor and was built on a Sigma-designed body using the Sigma SA mount. The camera was followed in 2003 by the improved but technically similar Sigma SD10, which was in turn succeeded in 2006 by the Sigma SD14, which used a higher-resolution, 2640 × 1760 × 3 (4.64 × 3 MP) sensor. The SD14's successor, the Sigma SD15, was released in June 2010 and used the same 2640 × 1760 × 3 sensor as the SD14. The Sigma SD1 was released in June 2011 with a new 23.5×15.7mm APS-C 4800 × 3200 × 3 (15.36 × 3 MP) sensor developed for the professional market. In 2004,Polaroid Corporation
Polaroid Corporation was an American company that made instant film and cameras, which survives as a brand for consumer electronics. The company was founded in 1937 by Edwin H. Land, to exploit his Polaroid (polarizer), Polaroid polarizing polyme ...
announced the Polaroid x530, a compact camera with a 1408 × 1056 × 3, 1/1.8-in. sensor. The camera had a limited release in 2005 but was recalled later in the year for unspecified image quality problems. Sigma announced a prototype of its Foveon-based compact camera in 2006, the Sigma DP1 The Sigma DP1 was a high-end compact digital camera introduced by the Sigma Corporation. It featured a 14-megapixel Foveon X3 sensor (2652 × 1768 × 3 layers), a fixed 16.6 mm F4.0 lens (28mm equivalent), a LCD and a pop-up flash. It was the fi ...
, using the same 14 MP sensor as the SD14 DSLR. A revised version of the prototype was exhibited in 2007, and the camera was eventually launched in spring 2008. Unlike the Polaroid x530, the DP1 had an APS-C
Advanced Photo System type-C (APS-C) is an image sensor format approximately equivalent in size to the Advanced Photo System film negative in its C ("Classic") format, of 25.1×16.7 mm, an aspect ratio of 3:2 and Ø 30.15 mm field d ...
-sized sensor with a 28mm equivalent prime lens
In film and photography, a prime lens is a fixed focal length photographic lens (as opposed to a zoom lens), typically with a maximum aperture from f2.8 to f1.2. The term can also mean the primary lens in a combination lens system.
Confusion ...
. The camera was revised as the DP1s and the DP1x. In 2009, the company launched the DP2, a compact camera using the same sensor and body as the DP1 but with a 41 mm-equivalent f/2.8 lens.
Comparison to Bayer-filter sensors
The operation of the Foveon X3 sensor is different from that of theBayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digit ...
image sensor, which is more commonly used in digital cameras
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now ...
. In the Bayer sensor, each photosite in the array consists of a single light sensor (either CMOS or CCD) that, as a result of filtration, is exposed to only one of the three colors detectable on the sensor: red, green, or blue. Constructing a full-color image from a Bayer sensor requires demosaicing
Demosaicing (or de-mosaicing, demosaicking), also known as color reconstruction, is a digital image processing algorithm used to reconstruct a full color image from the incomplete color samples output from an image sensor overlaid with a color fil ...
, an interpolative process in which the output pixel associated with each photosite is assigned an RGB
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three ...
value based in part on the level of red, green, and blue reported by those photosites adjacent to it. However, the Foveon X3 sensor creates its RGB color output for each photosite by combining the outputs of each of the stacked photodiodes at each of its photosites. This operational difference results in several significant consequences.
Color artifacts
Because demosaicing is not required for the Foveon X3 sensor to produce a full-color image, the color artifacts ("coloredjaggies
Jaggies are artifacts in raster images, most frequently from aliasing, which in turn is often caused by non-linear mixing effects producing high-frequency components, or missing or poor anti-aliasing filtering prior to sampling.
Jaggies are stai ...
") associated with the process are not seen. The separate anti-aliasing filter commonly usedThough its use is almost universal with Bayer sensors in digital cameras, it is not absolutely necessary. Kodak once produced two digital cameras, the DCS Pro SLR/n and DCS Pro SLR/c (''Digital Photography Review,'Kodak DCS Pro SLR/c Review
June 2004, Retrieved March 3, 2007) using Bayer sensors without such a filter. However, significant
moiré pattern
In mathematics, physics, and art, moiré patterns ( , , ) or moiré fringes are large-scale wave interference, interference patterns that can be produced when a partially opaque grating, ruled pattern with transparent gaps is overlaid on ano ...
were produced when photographing very fine detail
Retrieved March 3, 2007. to mitigate those artifacts in a Bayer sensor is not required; this is because little
aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is a phenomenon that a reconstructed signal from samples of the original signal contains low frequency components that are not present in the original one. This is caused when, in the ori ...
occurs when the photodiodes for each color, with the assistance of the microlenses, integrate the optical image over a region almost as big as the spacing of sensors for that color.Microlenses are commonly used in all types of image sensors in digital cameras; in Bayer-filter sensors, microlenses allow the area of the optical image being averaged (i.e., integrated) per sample to approach 25 percent for red and blue, and 50 percent for green, resulting in very little anti-aliasing. For Foveon X3 sensors, the area being averaged can approach 100 percent for each color, resulting in a significant anti-alias filter effect. On the other hand, the method of color separation by silicon penetration depth gives more cross-contamination between color layers, meaning more issues with color accuracy.
Light gathering and low-light performance
Theoretically, the Foveon X3 photosensor can detect more photons entering the camera lens than a mosaic sensor, because each of the color filters overlaying each photosite of a mosaic sensor passes only one of the primary colors and absorbs the other two. However, the individual layers in a Foveon sensor do not respond as sharply to the respective colors; thus color-indicating information in the sensor's raw data requires an "aggressive" matrix (i.e., the removal of common-mode signals) to produce color data in a standardcolor space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represe ...
, which can increase color noise in low-light situations.
Spatial resolution
According toSigma Corporation
is a Japanese company, manufacturing cameras, lenses, flashes and other photographic accessories. All Sigma products are produced in the company's own Aizu factory in Bandai, Fukushima, Japan. Although Sigma produces several camera mode ...
, "there has been some controversy in how to specify the number of pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s in Foveon sensors." The argument has been over whether sellers should count the number of photosites or the total number of photodiodes, as a megapixel count, and whether either of those should be compared with the number of photodiodes in a Bayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digit ...
sensor or camera as a measure of resolution.
For example, the dimensions of the photosite array in the sensor in the Sigma SD10 camera are 2268 × 1512, and the camera produces a native file size of those dimensions (times three color layers), which amounts to approximately 3.4 million three-color pixels. However, it has been advertised as a 10.2 MP camera by taking into account that each photosite contains stacked red, green, and blue color-sensing photodiodes, or pixel sensors (2268 × 1512 × 3). By comparison, the dimensions of the photosite array in the 10.2 MP Bayer sensor in the Nikon D200 camera are 3872 × 2592, but there is only one photodiode, or one-pixel sensor, at each site. The cameras have equal numbers of photodiodes and produce similar raw data file sizes, but the Bayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digit ...
camera produces a larger native file size via demosaicing
Demosaicing (or de-mosaicing, demosaicking), also known as color reconstruction, is a digital image processing algorithm used to reconstruct a full color image from the incomplete color samples output from an image sensor overlaid with a color fil ...
.
The actual resolution produced by the Bayer sensor is more complicated than the count of its photosites, or its native file size might suggest; the demosaicing and the separate anti-aliasing filter are both commonly used to reduce the occurrence or severity of color moiré pattern
In mathematics, physics, and art, moiré patterns ( , , ) or moiré fringes are large-scale wave interference, interference patterns that can be produced when a partially opaque grating, ruled pattern with transparent gaps is overlaid on ano ...
s that the mosaic characteristic of the Bayer sensor produces. The effect of this filter blurs the image output of the sensor which produces a lower resolution than the photosite count would seem to imply. This filter is mostly unnecessary with the Foveon X3 sensor and is not used. The earliest camera with a Foveon X3 sensor, the Sigma SD9, showed visible luminance moiré patterns without color moiré.
Subsequent X3-equipped cameras have less aliasing because they include micro-lenses, which provide an anti-aliasing filter by averaging the optical signal over an area commensurate with the sample density. This is not possible in any color channel of a Bayer-type sensor. Aliasing from the Foveon X3 sensor is "far less bothersome because it's monochrome," said Norman Koren. In theory, it is possible for a Foveon X3 sensor with the same number of photodiodes as a Bayer sensor and no separate anti-aliasing filter to attain a higher spatial resolution than that Bayer sensor. Independent tests indicate that the "10.2 MP" array of the Foveon X3 sensor (in the Sigma SD10) has a resolution similar to a 5 MP or 6 MP
Bayer sensor. At low ISO speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's photosensitivity, sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on #Film, various numerical scales, the most recent being the #ISO, ISO system introduced in 1974. A closely rela ...
, it is even similar to a 7.2 MP Bayer sensor.
With the introduction of the Sigma SD14, the 14 MP (4.7 MP red + 4.7 MP green + 4.7 MP blue) Foveon X3 sensor resolution is compared favorably by reviewers to that of 10 MP Bayer sensors. For example, Mike Chaney of ddisoftware says "the SD14 produces better photos than a typical 10 MP DSLR because it is able to carry sharp detail all the way to the 'falloff' point at 1700 LPI, whereas contrast, color detail, and sharpness begin to degrade long before the 1700 LPI limit on a Bayer based 10 MP DSLR."
Another article judges the Foveon X3 sensor as roughly equivalent to a 9 MP Bayer sensor.
A visual comparison between a 14 MP Foveon sensor and a 12.3 MP Bayer sensor shows Foveon has crisper details.
Noise
The Foveon X3 sensor, as used in the Sigma SD10 camera, has been characterized by two independent reviewers as noisier than the sensors in some other DSLRs using the Bayer sensor at higher ISO film speed equivalents, chroma noise in particular. Another noted higher noise during long exposure times.This observation is consistent with a comparison of the images, displayed in ''Digital Photography Review,'' taken by the Sigma SD10see here
with those taken approximately contemporaneously of the same scene by the Bayer sensor-equipped Nikon D70
see here
/page15.asp. Both retrieved March 6, 2007. However, these reviewers offer no opinion as to whether this is an inherent property of the sensor or the camera's image-processing algorithms. With regards to the Sigma SD14, which uses a more recent Foveon X3 sensor, one reviewer judged its noise levels as ranging from "very low" at ISO 100 to "moderate" at ISO 1600 when using the camera's
Raw image format
A camera raw image file contains unprocessed or minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, a motion picture film scanner, or other image scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed, ...
.
Sample images
Sigma's SD14 site has galleries of full-resolution images showing the color produced by the Foveon technology. The 14 MP Foveon chip produces 4.7 MP native-size RGB files; 14 MPBayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digit ...
cameras produce a 14 MP native file size by interpolation (i.e., demosaicing). Direct visual comparison of images from 12.7 MP Bayer sensors and 14.1 MP Foveon sensors show Bayer images are superior on fine monochrome detail, such as the lines between bricks on a distant building, but the Foveon images are superior in color resolution.
Further development
As of May 2023, the Foveon X3 sensor is less favoured by the average photographer, being overtaken by CMOS sensors which can be made at lower cost with higher resolution and lower noise. However it was reported in February 2021 that Sigma has been working on a new Foveon sensor but that a critical flaw was found in their development to date and they had to restart development from scratch. In February 2022 it was reported that Sigma was in the second stage of prototyping the new full frame Foveon sensor. Second stage prototyping in this case is the evaluation of a small image sensor prototype with the same pixel size as the product specifications but with a reduced total pixel count to verify the performance characteristics of the image sensor in practice. Third stage prototyping will evaluate a full-frame image sensor with the same specifications as the mass production devices including the AD converter etc. It is unlikely that mass production will commence before 2024.See also
*Color filter array
In digital imaging, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information.
The term is also used in reference to Electronic paper ...
* Bayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digit ...
* CYGM filter
* RGBE filter
In digital photography, the RGBE filter is an alternative color filter array to the Bayer filter (GRGB). It similarly uses a mosaic of pixel filters, of red, green, blue and "emerald" ("like cyan" according to Sony), and so also requires demosaici ...
Notes
References
External links
* Richard F. Lyon and Paul M. HubelEyeing the Camera: into the Next Century
10th Color Imaging Conference: Color Science, System and Applications. IS&T and SID, Springfield, Va, USA, 2002. P. 349–355.
Sigma DP1
{{DEFAULTSORT:Foveon X3 Sensor Digital photography Image sensors Color filter array