Fort Myer, VA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fort Myer is the previous name used for a U.S. Army post next to Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, and across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. Founded during the American Civil War as Fort Cass and Fort Whipple, the post merged in 2005 with the neighboring Marine Corps installation, Henderson Hall, and is today named Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall.
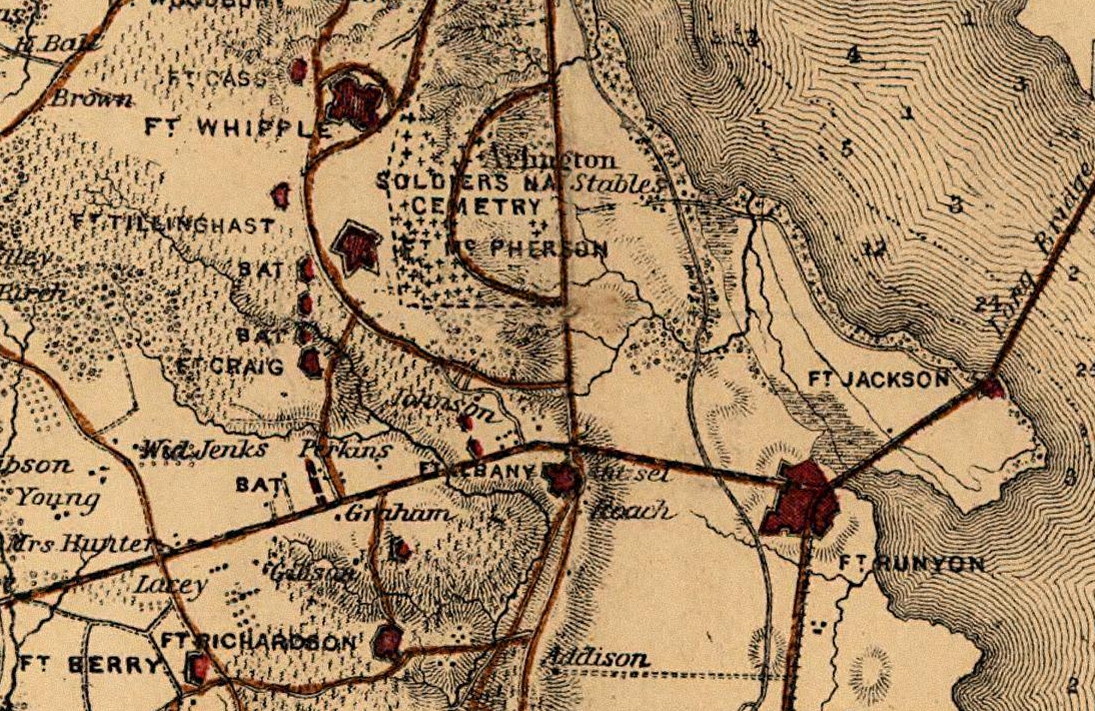
 Shortly after the Union Army's rout at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July 1861, the Army constructed in August 1861 a
Shortly after the Union Army's rout at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July 1861, the Army constructed in August 1861 a
Cooling and Owen, pp. 104-105
Touring the Forts South of the Potomac: Fort Cass.
(2)
(3) A May 17, 1864, report from the Union Army's Inspector of Artillery (see Union Army artillery organization) noted the following:
 Following the Union Army's defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in August 1862, the Army constructed Fort Whipple on the grounds of the former Arlington estate during the spring of 1863. The fort was located a short distance southeast of Fort Cass. The Army named the fort after Brevet Major General
Following the Union Army's defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in August 1862, the Army constructed Fort Whipple on the grounds of the former Arlington estate during the spring of 1863. The fort was located a short distance southeast of Fort Cass. The Army named the fort after Brevet Major General
/ref> The fort was considered to be one of the strongest fortifications erected for the defense of Washington during the Civil War. It had a perimeter of 658 yards and places for 43 guns.Cooling and Owen, pp. 101-104
Touring the Forts South of the Potomac: Fort Whipple — Forerunner to a Modern Fort. The May 17, 1864, report from the Union Army's Inspector of Artillery noted the following:
 During World War I, Fort Myer was a staging area for a large number of engineering, artillery, and chemical companies and regiments. The area of Fort Myer now occupied by Andrew Rader Health Clinic and the Commissary were made into a trench-system training grounds where French officers taught the Americans about trench warfare.
General
During World War I, Fort Myer was a staging area for a large number of engineering, artillery, and chemical companies and regiments. The area of Fort Myer now occupied by Andrew Rader Health Clinic and the Commissary were made into a trench-system training grounds where French officers taught the Americans about trench warfare.
General
Michael, p. 15.
br>(2)
Quartermaster Workshops at Arlington Boulevard & Second Street
Quartermaster Garage at Arlington Boulevard & Second Street
Commissary Sergeant's Quarters on Washington Avenue between Johnson Lane & Custer RoadFirst Sergeant's Quarters on Washington Avenue between Johnson Lane & Custer RoadNoncommissioned Officers Quarters on Washington Avenue between Johnson Lane & Custer Road
Historical Perspective
{{National Register of Historic Places in Virginia Air transportation buildings and structures on the National Register of Historic Places Myer Buildings and structures in Arlington County, Virginia Civil War defenses of Washington, D.C. Myer Historic American Buildings Survey in Virginia Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Virginia National Historic Landmarks in Virginia National Register of Historic Places in Arlington County, Virginia United States Army posts Victorian architecture in Virginia
History
In 1861, the land that Fort Myer would eventually occupy was part of the Arlington estate, which Mary Anna Custis Lee, the wife ofRobert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nort ...
, owned and at which Lee resided when not stationed elsewhere (see Arlington House, The Robert E. Lee Memorial
Arlington House is the historic family residence of Robert E. Lee, commander of the Confederate Army, and a national memorial in his honor serving as a museum, located in Arlington, Virginia. It is situated in the middle of Arlington National Ce ...
). When the Civil War began, the Commonwealth of Virginia seceded from the United States, Lee resigned his commission, and he and his wife left the estate. The United States Government then confiscated the estate and began to use it as a burial ground for Union Army dead (see Arlington National Cemetery), to house freed slaves (Freedmen's Village), and for military purposes, including the Civil War defenses of Washington (see Washington, D.C., in the American Civil War
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States, was the center of the Union war effort, which rapidly turned it from a small city into a major capital with full civic infrastructure and strong ...
).

Fort Cass
 Shortly after the Union Army's rout at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July 1861, the Army constructed in August 1861 a
Shortly after the Union Army's rout at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July 1861, the Army constructed in August 1861 a lunette
A lunette (French ''lunette'', "little moon") is a half-moon shaped architectural space, variously filled with sculpture, painted, glazed, filled with recessed masonry, or void.
A lunette may also be segmental, and the arch may be an arc take ...
(Fort Ramsay) on the future grounds of Fort Myer. One of the first fortifications built on the Arlington Line, the lunette was located at and near the present post's Forest Circle. Later renamed to Fort Cass, the lunette had a perimeter of and emplacements for 12 guns.(1Cooling and Owen, pp. 104-105
Touring the Forts South of the Potomac: Fort Cass.
(2)
(3) A May 17, 1864, report from the Union Army's Inspector of Artillery (see Union Army artillery organization) noted the following:
''Fort Cass, Maj. N. Shatswell commanding.''–Garrison, two companies First Massachusetts Heavy Artillery—8 commissioned officers, 1 ordnance-sergeant, 220 men. Armament, three 6-pounder field guns (smooth), five 20-pounder Parrotts (rifled), three 24-pounder siege guns (smooth), one 24-pounder F. D. howitzer (smooth), one 24-pounder Coehorn mortar.Although the Army abandoned the lunette in 1865 at the end of the Civil War, the United States War Department continued to control its property.Magazine A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...s, two; dry and in good condition. Ammunition, full supply, well packed and in serviceable condition. Implements, complete and serviceable. Drill in artillery, fair. Drill in infantry, fair. Discipline, fair. Garrison sufficient for the work.
Fort Whipple
 Following the Union Army's defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in August 1862, the Army constructed Fort Whipple on the grounds of the former Arlington estate during the spring of 1863. The fort was located a short distance southeast of Fort Cass. The Army named the fort after Brevet Major General
Following the Union Army's defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in August 1862, the Army constructed Fort Whipple on the grounds of the former Arlington estate during the spring of 1863. The fort was located a short distance southeast of Fort Cass. The Army named the fort after Brevet Major General Amiel Weeks Whipple
Amiel Weeks Whipple (October 21, 1817 – May 7, 1863)Anderson, TSHA was an American military officer and topographical engineer. He served as a brigadier general in the American Civil War, where he was mortally wounded at the Battle of Chance ...
, who died in May 1863 of wounds received during the Battle of Chancellorsville.Staff of the Fort Myer Post, p. 6/ref> The fort was considered to be one of the strongest fortifications erected for the defense of Washington during the Civil War. It had a perimeter of 658 yards and places for 43 guns.Cooling and Owen, pp. 101-104
Touring the Forts South of the Potomac: Fort Whipple — Forerunner to a Modern Fort. The May 17, 1864, report from the Union Army's Inspector of Artillery noted the following:
''Fort Whipple, Major Rolfe commanding.''–Garrison, three companies First Massachusetts Heavy Artillery– l major, 13 commissioned officers, 1 ordnance-sergeant, 414 men. Armament, six 12-pounder field guns (smooth), four 12-pounder field howitzers (smooth), eight 12-pounder James guns (rifled), eleven 4.5-inch ordnance Magazines, four; two not in a serviceable condition. Ammunition, full supply; good condition. Implements, complete and serviceable. Drill in artillery, fair. Drill in infantry, fair. Discipline, fair. Garrison sufficient; interior work.The Civil War ended in 1865. Fort Whipple, with its fortifications abandoned, then became the home of the Signal School of Instruction for Army and Navy Officers, established in 1869.
Fort Myer
On February 4, 1881, the Army post containing Fort Whipple was renamed Fort Myer as an honor to Brigadier GeneralAlbert J. Myer
Albert James Myer (September 20, 1828 – August 24, 1880) was a surgeon and United States Army general. He is known as the father of the U.S. Army Signal Corps, as its first chief signal officer just prior to the American Civil War, the inventor ...
, who had commanded the newly established Signal School of Instruction for Army and Navy Officers from 1869 until he died in August 1880. Since then, the post has been a Signal Corps post, a showcase for the US Army's cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
, and, since the 1940s, home to the Army's elite ceremonial units—The United States Army Band ("Pershing's Own") and the 3rd U.S. Infantry Regiment
The 3rd United States Infantry Regiment is a regiment of the United States Army. It currently has three active battalions, and is readily identified by its nickname, The Old Guard, as well as Escort to the President. The regimental motto is ' ...
("The Old Guard").
The National Weather Service was originated there by General Albert J. Myer in 1870.
Fort Myer was the site of the first flight of an aircraft at a military installation. Several exhibition flights by Orville Wright took place there in 1908. On 17 September 1908 it became the location of the first aviation fatality, as Lt. Thomas Selfridge was killed when on a demonstration flight with Orville, at an altitude of about , a propeller split, sending the aircraft out of control. Selfridge suffered a concussion in the crash and later died, the first person to die in powered fixed-wing aircraft. Orville was badly injured, suffering broken ribs and a leg.
Quarters One on Fort Myer, which was originally built as the garrison commander's quarters, has been the home of the Chief of Staff of the United States Army since 1908 when Major General J. Franklin Bell
James Franklin Bell (January 9, 1856 – January 8, 1919) was an officer in the United States Army who served as Chief of Staff of the United States Army from 1906 to 1910.
Bell was a major general in the Regular United States Army, commanding ...
took up residence. It has been the home of every succeeding Chief of Staff, except for General John J. Pershing
General of the Armies John Joseph Pershing (September 13, 1860 – July 15, 1948), nicknamed "Black Jack", was a senior United States Army officer. He served most famously as the commander of the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) on the Wes ...
.
The United States Navy established the nation's first radio telecommunications station, NAA, near Fort Myer in 1913. In 1915, the station's radio towers, "The Three Sisters", transmitted to Paris the first wireless communication that crossed the Atlantic Ocean.
 During World War I, Fort Myer was a staging area for a large number of engineering, artillery, and chemical companies and regiments. The area of Fort Myer now occupied by Andrew Rader Health Clinic and the Commissary were made into a trench-system training grounds where French officers taught the Americans about trench warfare.
General
During World War I, Fort Myer was a staging area for a large number of engineering, artillery, and chemical companies and regiments. The area of Fort Myer now occupied by Andrew Rader Health Clinic and the Commissary were made into a trench-system training grounds where French officers taught the Americans about trench warfare.
General George S. Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
Jr., who was posted at Fort Myer four different times, started the charitable "Society Circus" after World War I. He ultimately was Post Commander and commanded the 3rd Cavalry Regiment that was stationed at Fort Myer from the 1920s to 1942 when the regiment was sent to Georgia to get mechanized.
In late 2001, troops, deployed in response to the September 11th attacks, were bivouacked at Fort Myer. These troops were under Operation Noble Eagle. These included both active and National Guard Military Police units from around the nation. In 2005 the last remaining deployed responders were demobilized.
Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall
As a result of the2005 Base Realignment and Closure Commission
The 2005 Base Realignment and Closure Commission preliminary list was released by the United States Department of Defense on May 13, 2005. It was the fifth Base Realignment and Closure ("BRAC") proposal generated since the process was created in ...
initiative to create more efficiency of efforts, the Army's Fort Myer and the Marines' Henderson Hall became the first Joint Base in the Department of Defense. Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall (JBMHH) consists of military installations at Fort Myer, Henderson Hall, The Pentagon, and Fort Lesley J. McNair
Fort Lesley J. McNair is a United States Army post located on the tip of Greenleaf Point, the peninsula that lies at the confluence of the Potomac River and the Anacostia River in Washington, D.C. To the peninsula's west is the Washington Cha ...
. These installations and departments serve over 150,000 active duty, DoD civilian, and retired military personnel in the region.
Commemorative
The fort was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1972, for its well-preserved concentration of cavalry facilities and officers' quarters, and for its importance in military aviation history. On September 1, 1970, the United States Postal Service issued its first day cover of a postcard celebrating the 100th anniversary of Weather Services at Fort Myer. A pamphlet and one book have been published about Fort Myer. The book, ''Images of America: Fort Myer'', contains a copy of a handwritten letter from Abraham Lincoln that appointed General Whipple's oldest son to the United States Military Academy at West Point.(1Michael, p. 15.
br>(2)
See also
*List of National Historic Landmarks in Virginia
This is a list of National Historic Landmarks in Virginia. There are currently 123 National Historic Landmark, National Historic Landmarks (NHLs), and 2 former NHLs.
Current landmarks
The National Historic Landmarks (NHLs) are widely distributed ...
* National Register of Historic Places listings in Arlington County, Virginia
Notes
References
* * *External links
* * * Images of Fort Myer in the Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS) via Library of Congress:Quartermaster Workshops at Arlington Boulevard & Second Street
Quartermaster Garage at Arlington Boulevard & Second Street
Commissary Sergeant's Quarters on Washington Avenue between Johnson Lane & Custer Road
Historical Perspective
{{National Register of Historic Places in Virginia Air transportation buildings and structures on the National Register of Historic Places Myer Buildings and structures in Arlington County, Virginia Civil War defenses of Washington, D.C. Myer Historic American Buildings Survey in Virginia Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Virginia National Historic Landmarks in Virginia National Register of Historic Places in Arlington County, Virginia United States Army posts Victorian architecture in Virginia