Forbush decrease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A Forbush decrease is a rapid decrease in the observed
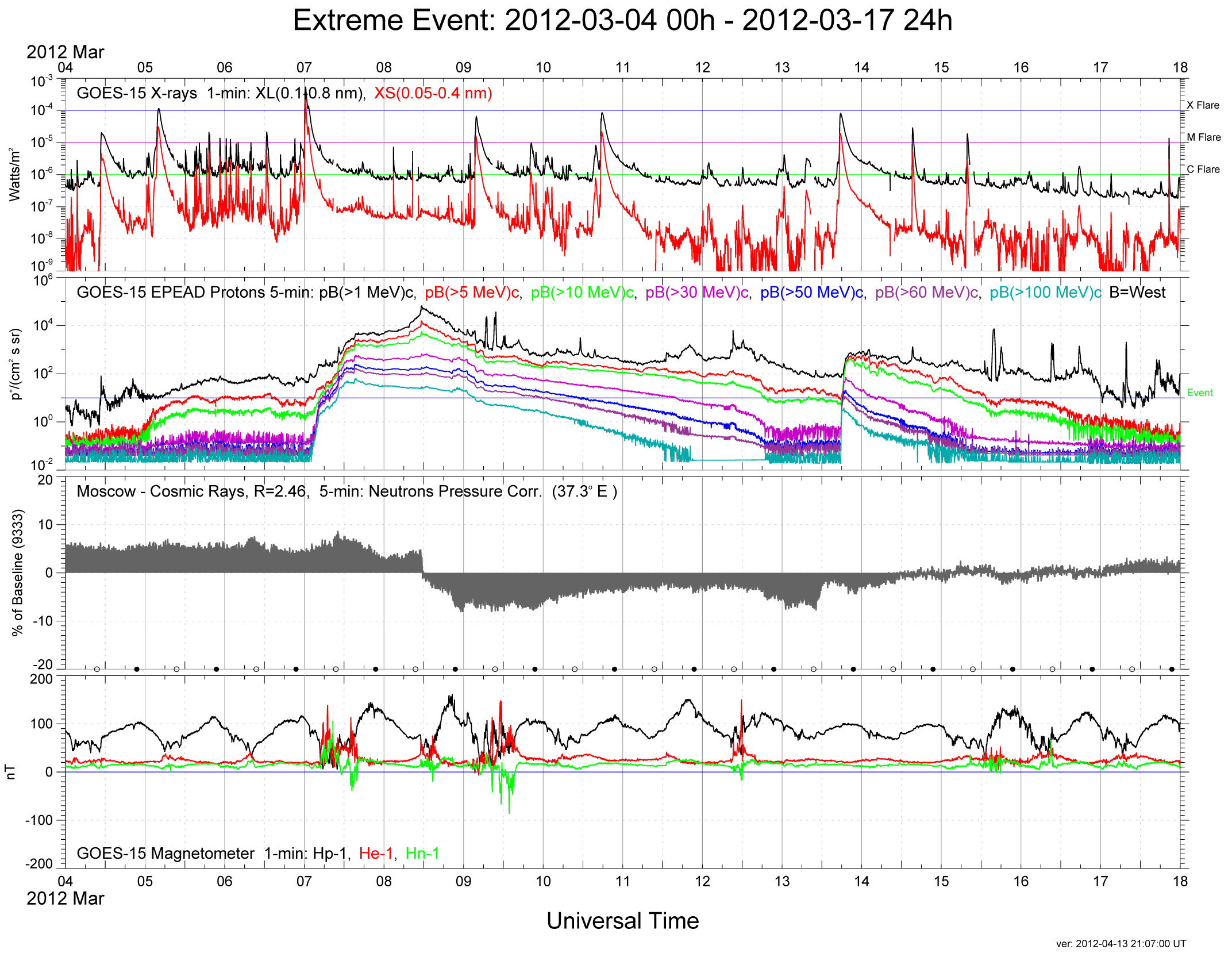 The Forbush decrease is usually observable by
The Forbush decrease is usually observable by
Who's Afraid of a Solar Flare?
from Science@NASA
Cosmic Ray Data Applications to Space Weather Forecasting
{{DEFAULTSORT:Forbush Decrease Cosmic rays Solar phenomena
galactic cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
intensity following a coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant release of plasma and accompanying magnetic field from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accept ...
(CME). It occurs due to the magnetic field of the plasma solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
sweeping some of the galactic cosmic rays away from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. The term ''Forbush decrease'' was named after the American physicist Scott E. Forbush, who studied cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ow ...
in the 1930s and 1940s.
Observation
 The Forbush decrease is usually observable by
The Forbush decrease is usually observable by particle detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nu ...
s on Earth within a few days after the CME, and the decrease takes place over the course of a few hours. Over the following several days, the galactic cosmic ray intensity returns to normal. Forbush decreases have also been observed by humans on ''Mir
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to&n ...
'' and the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
(ISS), at other locations in the inner heliosphere such as the Solar Orbiter
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) is a Sun-observing satellite developed by the European Space Agency (ESA). SolO, designed to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the nascent solar wind, will also perform close observations of th ...
spacecraft, and at Mars with the Mars Science Laboratory
Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a robotic space probe mission to Mars launched by NASA on November 26, 2011, which successfully landed ''Curiosity'', a Mars rover, in Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. The overall objectives include investigati ...
rover's Radiation assessment detector
The Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) is an instrument mounted on the Mars Science Laboratory ''Curiosity'' rover. It was the first of ten instruments to be turned on during the mission.
Purpose
The first role of RAD was to characterize the b ...
and the MAVEN
MAVEN is an American spacecraft orbiting Mars to study the loss of its atmospheric gases to space, providing insight into the history of
the planet's climate and water. The spacecraft name is an acronym for "Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolu ...
orbiter, as well as in the outer solar system by instruments onboard ''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to ach ...
'' and '' 11'' and ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'' and '' 2'', even past the orbit of Neptune.
The magnitude of a Forbush decrease depends on three factors:
* the size of the CME
* the strength of the magnetic fields in the CME
* the proximity of the CME to the Earth
A Forbush decrease is sometimes defined as being a decrease of at least 10% of galactic cosmic rays on Earth, but ranges from about 3% to 20%. The amplitude is also highly dependent on the energy of cosmic rays that is observed by the specific instrument, where lower energies typically show larger decreases. Reductions of 30% or more have been recorded aboard the ISS.
The overall rate of Forbush decreases tends to follow the 11-year sunspot cycle. It is more difficult to shield astronauts from galactic cosmic rays than from solar wind, so future astronauts might benefit most from radiation shielding during solar minima, when the suppressive effect of CMEs is less frequent.
Effects on the atmosphere
A 2009 peer reviewed article found that low clouds contain less liquid water following Forbush decreases, and for the most influential events the liquid water in the oceanic atmosphere can diminish by as much as 7%. Further peer-reviewed work found no connection between Forbush decreases and cloud properties until the connection was found in diurnal temperature range, and since confirmed in satellite data.See also
* Ionizing radiationReferences
External links
Who's Afraid of a Solar Flare?
from Science@NASA
Cosmic Ray Data Applications to Space Weather Forecasting
{{DEFAULTSORT:Forbush Decrease Cosmic rays Solar phenomena