Fluent (mathematics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
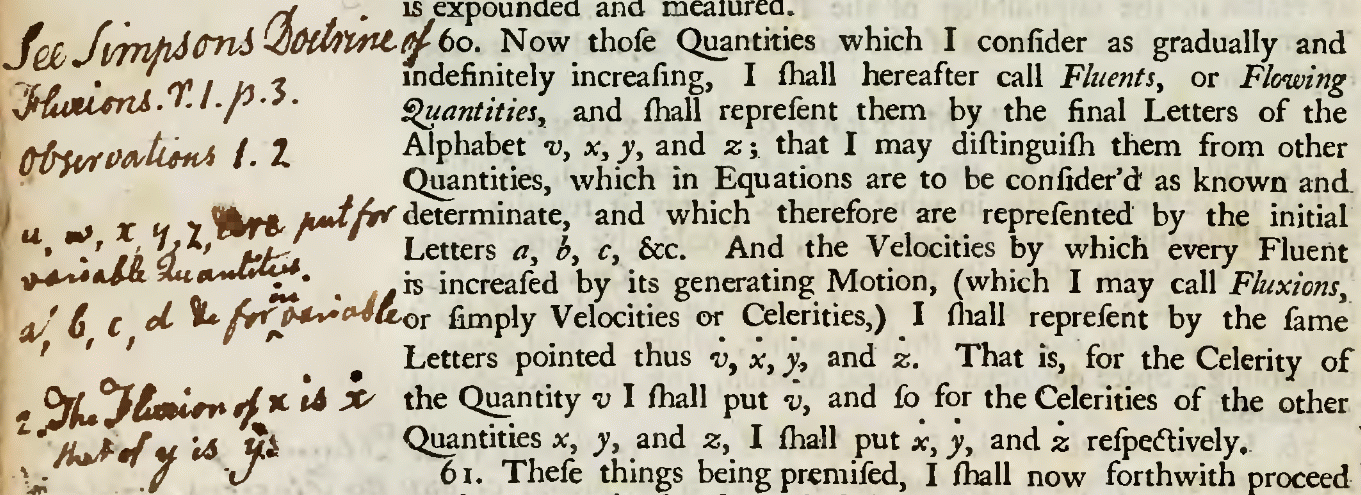 A fluent is a time-varying quantity or variable. The term was used by
A fluent is a time-varying quantity or variable. The term was used by
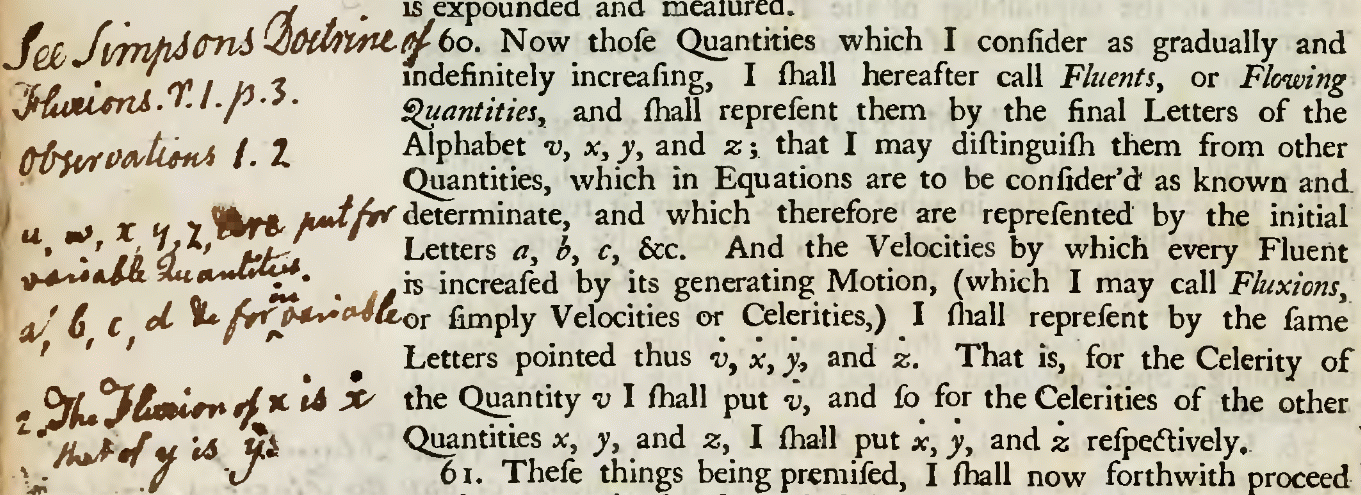 A fluent is a time-varying quantity or variable. The term was used by
A fluent is a time-varying quantity or variable. The term was used by Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the g ...
in his early calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizati ...
to describe his form of a function. The concept was introduced by Newton in 1665 and detailed in his mathematical
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
treatise, ''Method of Fluxions
''Method of Fluxions'' ( la, De Methodis Serierum et Fluxionum) is a mathematical treatise by Sir Isaac Newton which served as the earliest written formulation of modern calculus. The book was completed in 1671, and published in 1736. Fluxion ...
''. Newton described any variable that changed its value as a fluent – for example, the velocity of a ball thrown in the air. The derivative of a fluent is known as a fluxion
A fluxion is the instantaneous rate of change, or gradient, of a fluent (a time-varying quantity, or function) at a given point. Fluxions were introduced by Isaac Newton to describe his form of a time derivative (a derivative with respect to ti ...
, the main focus of Newton's calculus. A fluent can be found from its corresponding fluxion through integration
Integration may refer to:
Biology
* Multisensory integration
* Path integration
* Pre-integration complex, viral genetic material used to insert a viral genome into a host genome
*DNA integration, by means of site-specific recombinase technolo ...
.
See also
*''Method of Fluxions
''Method of Fluxions'' ( la, De Methodis Serierum et Fluxionum) is a mathematical treatise by Sir Isaac Newton which served as the earliest written formulation of modern calculus. The book was completed in 1671, and published in 1736. Fluxion ...
''
*History of calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus, is a mathematical discipline focused on limits, continuity, derivatives, integrals, and infinite series. Many elements of calculus appeared in ancient Greece, then in China and the Middle East, a ...
*Leibniz–Newton calculus controversy
In the history of calculus, the calculus controversy (german: Prioritätsstreit, lit=priority dispute) was an argument between the mathematicians Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz over who had first invented calculus. The question was ...
*Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
*Newton's notation
In differential calculus, there is no single uniform notation for differentiation. Instead, various notations for the derivative of a function or variable have been proposed by various mathematicians. The usefulness of each notation varies wit ...
*Fluxion
A fluxion is the instantaneous rate of change, or gradient, of a fluent (a time-varying quantity, or function) at a given point. Fluxions were introduced by Isaac Newton to describe his form of a time derivative (a derivative with respect to ti ...
References
{{Isaac Newton, state=collapsed Mathematical analysis Differential calculus History of calculus