Flow Visualisation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Flow visualization or flow visualisation in
Flow visualization or flow visualisation in
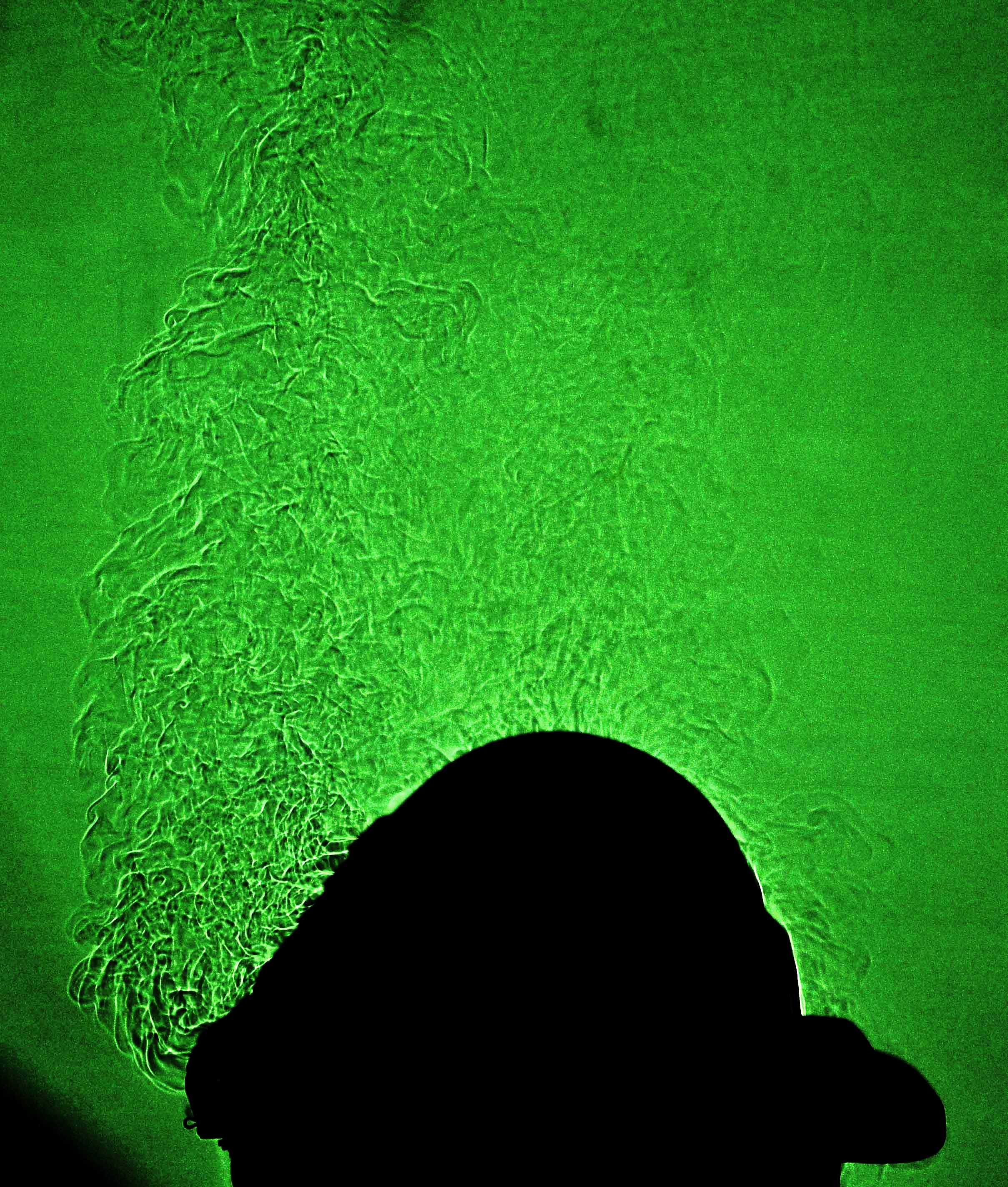 In
In
Flow visualization techniques
Flow visualization algorithms
Gallery of Flow Visualization Examples.Educational Particle Image Velocimetry (e-PIV) - resources and demonstrations
{{Visualization
 Flow visualization or flow visualisation in
Flow visualization or flow visualisation in fluid dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including '' aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) ...
is used to make the flow patterns visible, in order to get qualitative or quantitative information on them.
Overview
Flow visualization is the art of making flow patterns visible. Mostfluids
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear ...
(air, water, etc.) are transparent, thus their flow patterns are invisible to the naked eye without methods to make them this visible.
Historically, such methods included experimental methods. With the development of computer models and CFD simulating flow processes (e.g. the distribution of air-conditioned air in a new car), purely computational methods have been developed.
Methods of visualization
 In
In experimental fluid dynamics
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs whe ...
, flows are visualized by three methods:
* Surface flow visualization: This reveals the flow streamlines in the limit as a solid surface is approached. Colored oil applied to the surface of a wind tunnel
Wind tunnels are large tubes with air blowing through them which are used to replicate the interaction between air and an object flying through the air or moving along the ground. Researchers use wind tunnels to learn more about how an aircraft ...
model provides one example (the oil responds to the surface shear stress and forms a pattern).
* Particle tracer methods: Particles, such as smoke or microspheres, can be added to a flow to trace the fluid motion. We can illuminate the particles with a sheet of laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
light in order to visualize a slice of a complicated fluid flow pattern. Assuming that the particles faithfully follow the streamlines of the flow, we can not only visualize the flow but also measure its velocity using the particle image velocimetry or particle tracking velocimetry methods. Particles with densities that match that of the fluid flow will exhibit the most accurate visualization.http://microspheres.us/fluorescent-microspheres/piv-seeding-microparticle-flow-visualization/599.html PIV seeding particle recommendations
* Optical methods: Some flows reveal their patterns by way of changes in their optical refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, o ...
. These are visualized by optical methods known as the shadowgraph
Shadowgraph is an optical method that reveals non-uniformities in transparent media like air, water, or glass. It is related to, but simpler than, the schlieren and schlieren photography methods that perform a similar function. Shadowgraph is a ...
, schlieren photography
Schlieren photography is a process for photographing fluid flow. Invented by the German physicist August Toepler in 1864 to study supersonic motion, it is widely used in aeronautical engineering to photograph the flow of air around objects. ...
, and interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber o ...
. More directly, dyes can be added to (usually liquid) flows to measure concentrations; typically employing the light attenuation or laser-induced fluorescence
Laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) or laser-stimulated fluorescence (LSF) is a spectroscopic method in which an atom or molecule is excited to a higher energy level by the absorption of laser light followed by spontaneous emission of light. It was ...
techniques.
In scientific visualization
Scientific visualization ( also spelled scientific visualisation) is an interdisciplinary branch of science concerned with the visualization of scientific phenomena. Michael Friendly (2008)"Milestones in the history of thematic cartography, st ...
flows are visualized with two main methods:
* Analytical methods that analyse a given flow and show properties like streamlines, streaklines, and pathlines
Streamlines, streaklines and pathlines are field lines in a fluid flow.
They differ only when the flow changes with time, that is, when the flow is not steady.
Considering a velocity vector field in three-dimensional space in the framework ...
. The flow can either be given in a finite representation or as a smooth function.
* Texture advection methods that "bend" textures (or images) according to the flow. As the image is always finite (the flow through could be given as a smooth function), these methods will visualize approximations of the real flow.
Application
Incomputational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate t ...
the numerical solution of the governing equations can yield all the fluid properties in space and time. This overwhelming amount of information must be displayed in a meaningful form. Thus flow visualization is equally important in computational as in experimental fluid dynamics.
See also
* Elementary flow *Scientific visualization
Scientific visualization ( also spelled scientific visualisation) is an interdisciplinary branch of science concerned with the visualization of scientific phenomena. Michael Friendly (2008)"Milestones in the history of thematic cartography, st ...
* Streamlines, streaklines and pathlines
Streamlines, streaklines and pathlines are field lines in a fluid flow.
They differ only when the flow changes with time, that is, when the flow is not steady.
Considering a velocity vector field in three-dimensional space in the framework o ...
* Image-based flow visualization
* Lagrangian–Eulerian advection
* Rheoscopic fluid
* Skin friction lines
* Streamlet (scientific visualization)
* Streamsurface
* Tensor glyph
* Texture advection
* Vortex core line In scientific visualization, a vortex core line is a line-like feature tracing the center of a vortex with in a velocity field.
Detection methods
Several methods exist to detect vortex core lines in a flow field. studied and compared nine method ...
References
* * * * *External links
Flow visualization techniques
Flow visualization algorithms
Gallery of Flow Visualization Examples.
{{Visualization