Flow Graph (mathematics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A flow graph is a form of digraph associated with a set of linear algebraic or differential equations:
:"A signal flow graph is a network of nodes (or points) interconnected by directed branches, representing a set of linear algebraic equations. The nodes in a flow graph are used to represent the variables, or parameters, and the connecting branches represent the coefficients relating these variables to one another. The flow graph is associated with a number of simple rules which enable every possible solution elated to the equationsto be obtained."
Although this definition uses the terms "signal-flow graph" and "flow graph" interchangeably, the term "signal-flow graph" is most often used to designate the Mason signal-flow graph, Mason being the originator of this terminology in his work on electrical networks. Likewise, some authors use the term "flow graph" to refer strictly to the Coates flow graph. According to Henley & Williams:
:"The nomenclature is far from standardized, and...no standardization can be expected in the foreseeable future."
A designation "flow graph" that includes both the Mason graph and the Coates graph, and a variety of other forms of such graphs appears useful, and agrees with Abrahams and Coverley's and with Henley and Williams' approach.
A directed network – also known as a

 An example of a flow graph connected to some starting equations is presented.
The set of equations should be consistent and linearly independent. An example of such a set is:
:
Consistency and independence of the equations in the set is established because the determinant of coefficients is non-zero, so a solution can be found using
An example of a flow graph connected to some starting equations is presented.
The set of equations should be consistent and linearly independent. An example of such a set is:
:
Consistency and independence of the equations in the set is established because the determinant of coefficients is non-zero, so a solution can be found using
MIT Research Laboratory of Electronics
{{cite book , title=Matrices and Matroids for Systems Analysis , author=Kazuo Murota , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yaZAAAAAQBAJ&q=%22signal-flow+graph+defined+here+is+different%22&pg=PA47 , page=47 , isbn= 9783642039942 , year=2009 , publisher=Springer Science & Business Media {{cite book , title=Graphs: Theory and Algorithms , author= K. Thulasiraman, M. N. S. Swamy , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rFH7eQffQNkC&q=%22we+develop+a+graph-theoretic+approach+for+the+solution+of+linear+algebraic%22&pg=PA163 , pages=163 ''ff'' , isbn=9781118030257 , publisher=John Wiley & Sons , year=2011 Application-specific graphs Control engineering Directed graphs Signal processing
flow network
In graph theory, a flow network (also known as a transportation network) is a directed graph where each edge has a capacity and each edge receives a flow. The amount of flow on an edge cannot exceed the capacity of the edge. Often in operations re ...
– is a particular type of flow graph. A ''network'' is a graph with real numbers associated with each of its edges, and if the graph is a digraph, the result is a ''directed network''. A flow graph is more general than a directed network, in that the edges may be associated with ''gains, branch gains'' or ''transmittances'', or even functions of the Laplace operator ''s'', in which case they are called ''transfer functions''.
There is a close relationship between graphs and matrices and between digraphs and matrices. "The algebraic theory of matrices can be brought to bear on graph theory to obtain results elegantly", and conversely, graph-theoretic approaches based upon flow graphs are used for the solution of linear algebraic equations.
Deriving a flow graph from equations

 An example of a flow graph connected to some starting equations is presented.
The set of equations should be consistent and linearly independent. An example of such a set is:
:
Consistency and independence of the equations in the set is established because the determinant of coefficients is non-zero, so a solution can be found using
An example of a flow graph connected to some starting equations is presented.
The set of equations should be consistent and linearly independent. An example of such a set is:
:
Consistency and independence of the equations in the set is established because the determinant of coefficients is non-zero, so a solution can be found using Cramer's rule
In linear algebra, Cramer's rule is an explicit formula for the solution of a system of linear equations with as many equations as unknowns, valid whenever the system has a unique solution. It expresses the solution in terms of the determinants ...
.
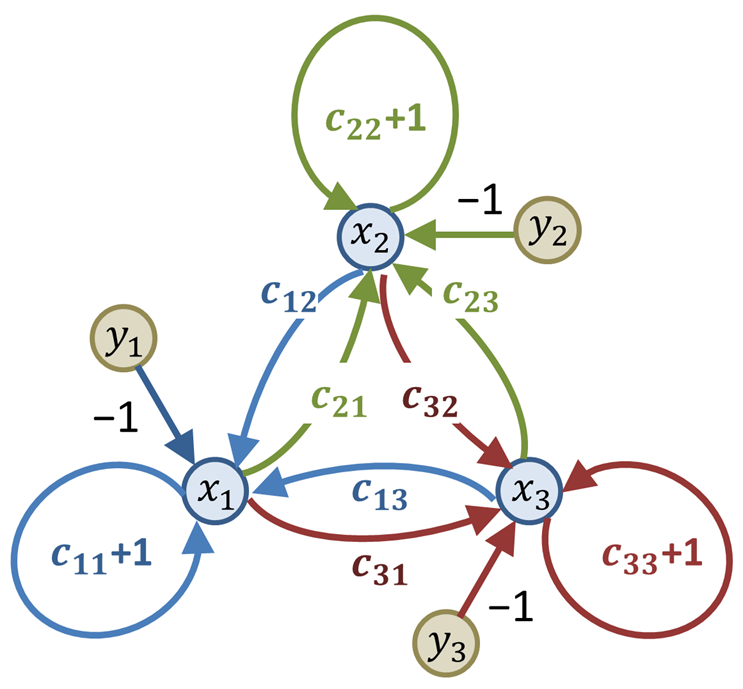
Using the examples from the subsection Elements of signal-flow graphs, we construct the graph In the figure, a signal-flow graph in this case. To check that the graph does represent the equations given, go to node ''x1''. Look at the arrows incoming to this node (colored green for emphasis) and the weights attached to them. The equation for ''x1'' is satisfied by equating it to the sum of the nodes attached to the incoming arrows multiplied by the weights attached to these arrows. Likewise, the red arrows and their weights provide the equation for ''x2'', and the blue arrows for ''x3''.
Another example is the general case of three simultaneous equations with unspecified coefficients:
:
To set up the flow graph, the equations are recast so each identifies a single variable by adding it to each side. For example:
:
Using the diagram and summing the incident branches into ''x1'' this equation is seen to be satisfied.
As all three variables enter these recast equations in a symmetrical fashion, the symmetry is retained in the graph by placing each variable at the corner of an equilateral triangle. Rotating the figure 120° simply permutes the indices. This construction can be extended to more variables by placing the node for each variable at the vertex of a regular polygon with as many vertices as there are variables.
Of course, to be meaningful the coefficients are restricted to values such that the equations are independent and consistent.
See also
* Coates graph *Signal-flow graph
A signal-flow graph or signal-flowgraph (SFG), invented by Claude Shannon, but often called a Mason graph after Samuel Jefferson Mason who coined the term, is a specialized Flow graph (mathematics), flow graph, a directed graph in which nodes repr ...
Further reading
* A discussion of the Coates and the Mason flow graphs.References
{{reflist, refs= {{cite book , title=Signal flow analysis , author=J. R. Abrahams, G. P. Coverley , chapter=Chapter 1: Elements of a flow graph , page=1 , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=C4ujBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA1 , isbn= 9781483180700 , year=2014 , publisher=Elsevier {{cite book , title=Introductory Graph Theory , author=Gary Chartrand , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3J_DAgAAQBAJ&q=%22By+a+network+we+mean+a+graph+or+digraph%22&pg=PA19 , page=19 , isbn=9780486134949 , publisher=Courier Corporation , year=2012 , edition=Republication of ''Graphs as Mathematical Models'', 1977 {{cite web , url=http://www.amarketplaceofideas.com/wp-content/uploads/2008/11/6016231.pdf , author=Wai-Kai Chen , title=Some applications of linear graphs , date=May 1964 , publisher=Coordinated Science Laboratory, University of Illinois, Urbana {{cite book , title=Graph Theory with Applications to Engineering and Computer Science , author= Narsingh Deo , page=417 , edition=Reprint of 1974 , publisher=Prentice-Hall of India , isbn=9788120301450 , year=2004 , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Yr2pJA950iAC&pg=PA417 {{cite journal , author=Frank Harary , title=Graphs and Matrices , journal=SIAM Review , volume=9 , issue=2 , date=January 1967 , url=http://poncelet.math.nthu.edu.tw/disk5/js/geometry/harary.pdf {{cite book , title=Graph theory in modern engineering; computer aided design, control, optimization, reliability analysis , chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wfpeoDswKkkC&q=%22Flow+graphs+are+a+graphic+representation+of+sets+of+linear+algebraic%22&pg=PA2 , chapter=Basic concepts , page=2 , isbn= 9780080956077 , year=1973 , publisher=Academic Press , author=Ernest J Henley, RA Williams {{cite book , title=Graph theory in modern engineering; computer aided design, control, optimization, reliability analysis , chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wfpeoDswKkkC&q=%22Flow+graphs+are+a+graphic+representation+of+sets+of+linear+algebraic%22&pg=PA2 , chapter=Basic concepts , page=2 , isbn= 9780080956077 , year=1973 , publisher=Academic Press , author=Ernest J Henley, RA Williams {{cite book , author=RF Hoskins , chapter=Flow-graph and signal flow-graph analysis of linear systems , chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6DeoBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA156 , editor=SR Deards , title=Recent Developments in Network Theory: Proceedings of the Symposium Held at the College of Aeronautics, Cranfield, September 1961 , year=2014 , publisher=Elsevier , isbn=9781483223568 {{cite journal, last=Mason, first=Samuel J. , date=September 1953, title=Feedback Theory - Some Properties of Signal Flow Graphs, journal=Proceedings of the IRE , pages=1144–1156 , url=http://ecee.colorado.edu/~ecen5014/Mason-IRE-1953.pdf , doi = 10.1109/jrproc.1953.274449 , volume=41, issue=9 , s2cid=17565263 {{cite journal , title=Feedback Theory-Further Properties of Signal Flow Graphs , author=SJ Mason , doi=10.1109/JRPROC.1956.275147 , date=July 1956 , volume=44 , issue=7 , journal=Proceedings of the IRE , pages=920–926 , hdl=1721.1/4778 , s2cid=18184015 , url=http://dspace.mit.edu/bitstream/1721.1/4778/1/RLE-TR-303-15342712.pdf , hdl-access=free On-line version found aMIT Research Laboratory of Electronics
{{cite book , title=Matrices and Matroids for Systems Analysis , author=Kazuo Murota , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yaZAAAAAQBAJ&q=%22signal-flow+graph+defined+here+is+different%22&pg=PA47 , page=47 , isbn= 9783642039942 , year=2009 , publisher=Springer Science & Business Media {{cite book , title=Graphs: Theory and Algorithms , author= K. Thulasiraman, M. N. S. Swamy , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rFH7eQffQNkC&q=%22we+develop+a+graph-theoretic+approach+for+the+solution+of+linear+algebraic%22&pg=PA163 , pages=163 ''ff'' , isbn=9781118030257 , publisher=John Wiley & Sons , year=2011 Application-specific graphs Control engineering Directed graphs Signal processing