Fleming–Tamao Oxidation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Fleming–Tamao oxidation, or Tamao–Kumada–Fleming oxidation, converts a  The reaction is
The reaction is

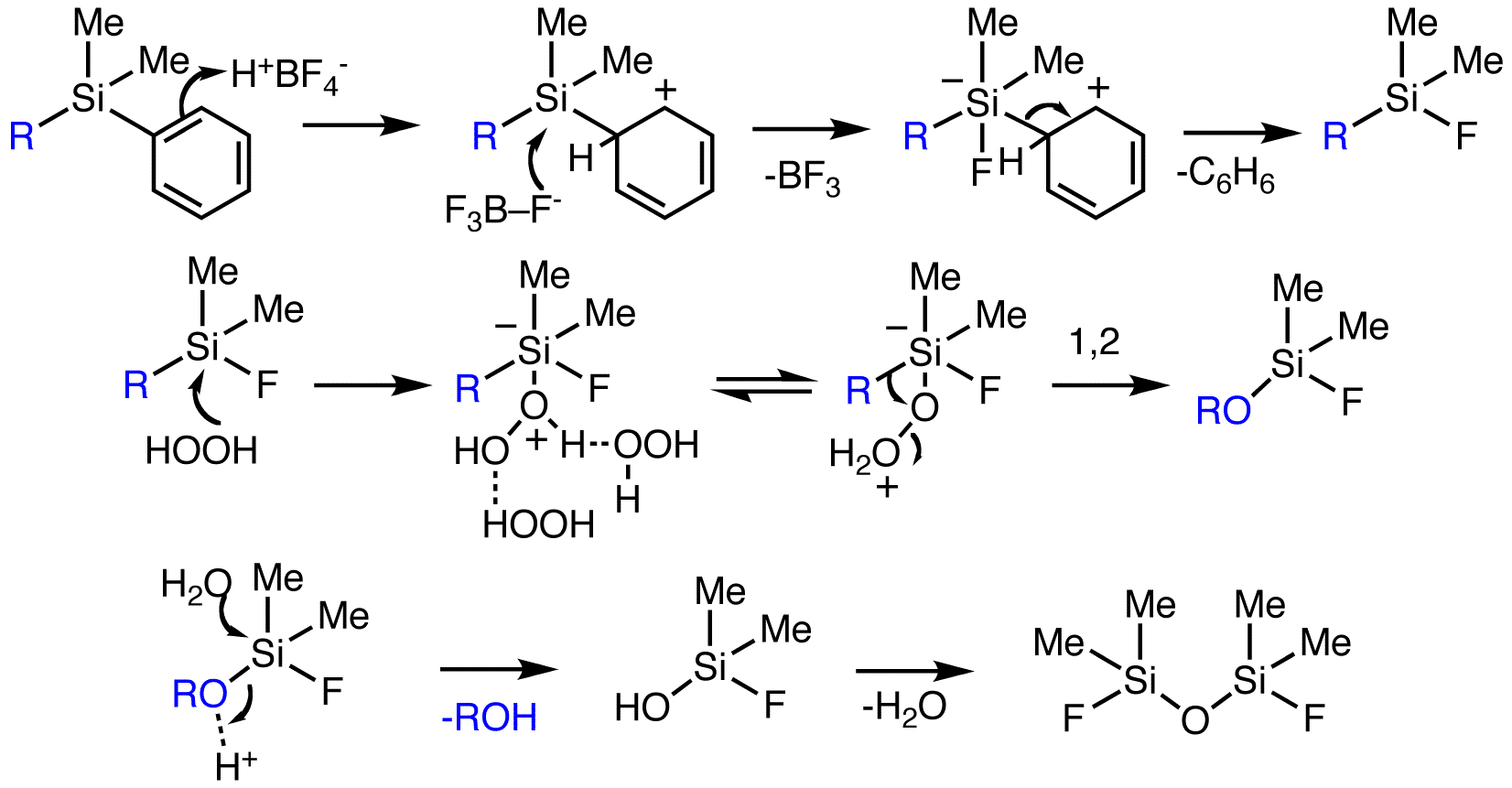
 The Tamao oxidation was used to synthesize
The Tamao oxidation was used to synthesize


Tamao-Fleming Oxidation
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
–silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
bond to a carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
–oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
bond with a peroxy acid
A peroxy acid (often spelled as one word, peroxyacid, and sometimes called peracid) is an acid which contains an acidic group. The two main classes are those derived from conventional mineral acids, especially sulfuric acid, and the peroxy deri ...
or hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
. Fleming–Tamao oxidation refers to two slightly different conditions developed concurrently in the early 1980s by the Kohei Tamao and Ian Fleming
Ian Lancaster Fleming (28 May 1908 – 12 August 1964) was a British writer, best known for his postwar ''James Bond'' series of spy novels. Fleming came from a wealthy family connected to the merchant bank Robert Fleming & Co., and his ...
research groups.
stereospecific
In chemistry, stereospecificity is the property of a reaction mechanism that leads to different stereoisomeric reaction products from different stereoisomeric reactants, or which operates on only one (or a subset) of the stereoisomers."Overlap C ...
with retention of configuration
Walden inversion is the inversion of a stereogenic center in a chiral molecule in a chemical reaction. Since a molecule can form two enantiomers around a stereogenic center, the Walden inversion converts the configuration of the molecule from ...
at the carbon–silicon bond. This allows the silicon group to be used as a functional equivalent of the hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
group. Another key feature of the silicon group is that it is relatively stable due to the presence of the silicon atom, and therefore can tolerate various reaction conditions that the hydroxyl group can not tolerate. Due to the stability of the silicon group, organosilicon compounds
Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, fl ...
are useful in the total synthesis
Total synthesis, a specialized area within organic chemistry, focuses on constructing complex organic compounds, especially those found in nature, using laboratory methods. It often involves synthesizing natural products from basic, commercially ...
of complex natural products
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical s ...
and pharmaceutical drug
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...
s. For instance, the Fleming–Tamao oxidation has been used to accomplish the synthesis of subunits of tautomycin, an inhibitor
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to:
Biology
* Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity
* Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotransmi ...
that is used as a lead cancer compound and as an immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified ...
.
History
In 1983, Tamao and co-workers were the first to report the successful transformation of anallyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula . It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated a ...
alkoxy
In chemistry, the alkoxy group is an alkyl group which is Single bond, singularly bonded to oxygen; thus . Denoted usually with apostrophe('). The range of alkoxy groups is vast, the simplest being methoxy (). An ethoxy group () is found in the ...
silyl
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. Silylations are core methods for production of organosilicon chemistry. Silanization, while similar to silylation, usually refers to attachmen ...
to an allyl alcohol
Allyl alcohol (IUPAC name: prop-2-en-1-ol) is an organic compound with the structural formula . Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a precursor to ...
without an allylic shift. In their report, the chemists
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of ...
observed that the hydroxyl group was introduced exclusively onto the carbon atom to which the silicon atom was attached. In the same year, Tamao and group published another paper that showed that the carbon–silicon bond in alkoxy organosilicon compounds
Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, fl ...
can be cleaved using H2O2 or m-CPBA
''meta''-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid (mCPBA or ''m''CPBA) is a peroxycarboxylic acid. It is a white solid often used widely as an oxidant in organic synthesis. mCPBA is often preferred to other peroxy acids because of its relative ease of handling. ...
under acidic
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
, basic (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": '' Arrhenius bases'', '' Brønsted bases'', and ''Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.- ...
, or neutral
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction in ...
conditions, to afford the corresponding alcohols. A year later, Ian Fleming and group reported that the dimethylphenylsilyl (Me2PhSi) group can be converted to an hydroxyl group in a two-pot sequence. Later, in 1987, Fleming reported a one-pot variant to the two-pot sequence in which either bromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between th ...
or mercuric ion acts as the electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively Electric charge, charged, have an ...
. These early findings paved the way for the development of a large number of silicon-based reagents
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
and the use of various silyl groups as functional equivalents of the hydroxyl group.
Mechanisms
Tamao–Kumada oxidation
Although the mechanism below is for the basic condition, the proposed mechanism"Name Reactions: A Collection of Detailed Reaction Mechanisms," 2nd ed. by Li, J. J. (2003), 404, CODEN: ADSDEO; for the Tamao oxidation is similar under each condition. The mechanism below contains at least one fluorine atom as the substituent, which is theprototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
structure that Tamao studied. Fluoride, provided by a fluoride source or a donor solvent, attacks the fluorosilane in a fast and reversible step to give a pentacoordinated species. This species is more electrophilic than the fluorosilane, thereby promoting attack by the nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they a ...
oxidant to yield the negatively charged hexacoordinated transition state
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked w ...
. This step was determined to be the rate determining step
In chemical kinetics, the overall rate of a reaction is often approximately determined by the slowest step, known as the rate-determining step (RDS or RD-step or r/d step) or rate-limiting step. For a given reaction mechanism, the prediction of the ...
based on kinetic studies done by Tamao."''Frontiers of Organosilicon Chemistry,'' by Tamao, K.; Hayashi, T.; Ito, Y. (1991), 197–207. Further studies by Tamao on the steric and electronic effects of different groups attached to the silicon led him to suggest that attack by the oxidant ''trans'' to the electronegative fluoride group is energetically favored. The group ''cis'' to the peroxide oxygen in the transition state structure then migrates preferentially, thus explaining the retention of configuration at the carbon center. Finally, the new silicon–oxygen bond
A silicon–oxygen bond ( bond) is a chemical bond between silicon and oxygen atoms that can be found in many inorganic and organic compounds. In a silicon–oxygen bond, electrons are shared unequally between the two atoms, with oxygen taking th ...
of the hexaco-ordinated species is hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
by water in the reaction medium. Subsequent workup produced the expected alcohol.
Fleming oxidation
Two-pot sequence
Unlike the Tamao oxidation whose starting material is an activated heteroatom-substituted silyl group, the Fleming oxidation utilizes a more robust silyl group which has only carbon atoms attached to the silicon atom. The prototype silyl structure that Fleming used was dimethylphenylsilyl. Thisaryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used ...
silane
Silane (Silicane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a colorless, pyrophoric gas with a sharp, repulsive, pungent smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental ...
is then converted to the more reactive halo- or heterosilane to initiate the oxidation. The mechanism of the two-pot sequence differs from the Tamao oxidation since the reagents
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
are different. First, an electrophile attacks the phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula , and is often represented by the symbol Ph (archaically φ) or Ø. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ...
ring in the ipso position to give a beta-carbocation
Carbocation is a general term for ions with a positively charged carbon atom. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further ...
that is stabilized by the silicon group. A heteroatom then attacks the silicon group, which allows the phenyl ring to leave, in a key step referred to as protodesilylation of the arylsilane. The alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl group is derived from a cy ...
group undergoes 1,2 migration from the silicon to the oxygen atom. Aqueous acid mediated hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
and subsequent workup yield the desired alcohol. It is difficult to prevent small resulting silyl-alcohols from dehydrating to form siloxanes.

One-pot sequence
The main difference between the one-pot and two-pot sequences is that the former has bromine or mercuric ion as the electrophile that is attacked by thebenzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
. The bromine electrophile is generated by diatomic
Diatomic molecules () are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen () or oxygen (), then it is said to be homonuclear mol ...
bromine or another source such as potassium bromide
Potassium bromide ( K Br) is a salt, widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with over-the-counter use extending to 1975 in the US. Its action is due to the bromide ion ( sodium bromide is equa ...
, which can be oxidized to generate bromine ''in situ'' by the peracetic acid
Peracetic acid (also known as peroxyacetic acid, or Percidine) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CO3H. This peroxy acid is a colorless liquid with a characteristic acrid odor reminiscent of acetic acid. It can be highly corrosive.
Perac ...
. The source of the mercuric ion is mercuric acetate, and this reagent is mixed with peracetic acid in AcOH
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
to provide the oxidizing conditions. The mechanism for the one-pot and two-pot sequences is the same since the bromine or mercuric ion are attacked by the phenyl ring instead of the hydrogen ion
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particl ...
.
Scope
The Tamao–Kumada oxidation, or the Tamao oxidation, uses a silyl group with ahydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atom, a heteroatom
In chemistry, a heteroatom () is, strictly, any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen.
Organic chemistry
In practice, the term is mainly used more specifically to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecular ...
or an electron-donating group attached to the silicon atom to make it more reactive. Tamao used either fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extre ...
or chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
atom, or an alkoxy
In chemistry, the alkoxy group is an alkyl group which is Single bond, singularly bonded to oxygen; thus . Denoted usually with apostrophe('). The range of alkoxy groups is vast, the simplest being methoxy (). An ethoxy group () is found in the ...
(OR) or amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
group (NR2) as the substituent on the substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (aquatic environment), the earthy material that exi ...
s. In addition to varying the percent composition of oxidants
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In ot ...
and combining different solvents
A solvent (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for p ...
, Tamao also used additive
Additive may refer to:
Mathematics
* Additive function, a function in number theory
* Additive map, a function that preserves the addition operation
* Additive set-function see Sigma additivity
* Additive category, a preadditive category with fin ...
s such as acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . Commonly abbreviated , it is one the simplest organic acid anhydride, anhydrides of a carboxylic acid and is widely used in the production of c ...
(Ac2O), potassium hydrogen fluoride (KHF2), and potassium hydrogen carbonate (KHCO3) or sodium hydrogen carbonate
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda (or simply “bicarb” especially in the UK) is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cati ...
(NaHCO3) to make the reaction conditions slightly acidic, neutral, and alkaline, respectively. The different conditions were used to observe the effect that pH environment had on the oxidative cleavage
Cleavage may refer to:
Science
* Cleavage (crystal), the way in which a crystal or mineral tends to split
* Cleavage (embryo), the division of cells in an early embryo
* Cleavage (geology), foliation of rock perpendicular to stress, a result of ...
of the various alkoxy groups. Below is an example of each reaction condition.
:
Variations
Recently, the Fleming–Tamao oxidation has been used to generatephenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
and substituted phenols in very good yield.
acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
, aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
, and ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
under varying reaction conditions. Whereas the carbon-silicon bond of a substituted alkylsilyl is cleaved to a carbon-oxygen single bond, a substituted alkenylsilyl group is transformed to a carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
under the same Tamao oxidation conditions employed for alkylsilane.
Advantages of a C–Si linkage
The silyl group is a non-polar and relatively unreactive species and is therefore tolerant of many reagents and reaction conditions that might be incompatible with free alcohols. Consequently, the silyl group also eliminates the need for introduction of hydroxylprotecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In man ...
s. In short, by deferring introduction of an alcohol to a late synthetic stage, opting instead to carry through a silane, a number of potential problems experienced in total syntheses can be mitigated or avoided entirely.
Steric effects
One of the major pitfalls of either the Fleming or Tamao oxidations issteric hindrance
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is generally a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivi ...
. Increasing the steric bulk at the silicon center generally slows down reaction, potentially even suppressing reaction entirely when certain substituents are employed. In general, less bulky groups such as methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as ...
or ethyl favor oxidation, while bulkier groups such as tert-butyl
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula , derived from either of the two isomers (''n''-butane and isobutane) of butane.
The isomer ''n''-butane can connect in two ways, giv ...
slow down or stop oxidation. There are special cases in which this pattern in not followed. For example, alkoxy groups tend to enhance oxidation, while oxidation does not proceed under normal conditions when three alkyl substituents are attached to the silicon atom. The trend below illustrates the order in which oxidation proceeds.
Applications
Natural product synthesis
The natural product, (+)− pramanicin, became an interesting target for synthesis because it was observed to be active against afungal
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the tradit ...
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
that resulted in meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasion ...
in AIDS patients. Therefore, its synthesis which utilized the Fleming–Tamao oxidation as a crucial step has been relevant to chemists as well as to patients afflicted by AIDS. The antifungal agent
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cry ...
has also been shown previously to induce cell death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as di ...
and increase calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
levels in vascular Vascular can refer to:
* blood vessels, the vascular system in animals
* vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex transporting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue ...
endothelial cells
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the res ...
. Furthermore, (+)– pramanicin has a wide range of potential applications against human diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are assoc ...
.
Polyol synthesis
Polyol
In organic chemistry, a polyol is an organic compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups (). The term "polyol" can have slightly different meanings depending on whether it is used in food science or polymer chemistry. Polyols containing two, th ...
s and diol
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting gro ...
s are especially useful to the food industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, ...
and polymer chemistry
Polymer chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that focuses on the structures, chemical synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules. The principles and methods used within polymer chemistry are also applic ...
. Their importance is underscored by the fact that they can be used as sugar replacers for diabetics or those who choose to have sugar-free or low-calorie diets. The Fleming-Tamao has been applied in the synthesis of stereoselective
In chemistry, stereoselectivity is the property of a chemical reaction in which a single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers during a non- stereospecific creation of a new stereocenter or during a non-stereospecific transformation o ...
diols. Woerpel used the reaction to synthesize anti-1,3 diols
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting gro ...
from functionalized silyl anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
.
Alternatively, Hara, K.; Moralee, and Ojima"Abstracts of Papers, 222nd ''ACS'' Meeting, Chicago" by Hara K.; Moralee, A.C.; Ojima, I. (2001), ORGN-089. achieved syn-1,3 diols using Tamao oxidation.
See also
* Baeyer-Villiger oxidationExternal links
Tamao-Fleming Oxidation
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fleming-Tamao oxidation Organic oxidation reactions Name reactions