Five-number summary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The five-number summary is a set of
import numpy as np
def fivenum(data):
"""Five-number summary."""
return np.percentile(data, , 25, 50, 75, 100 method='midpoint')
>>> moons = , 0, 1, 2, 63, 61, 27, 13>>> print(fivenum(moons))
0. 0.5 7.5 44. 63.
data fivenum;
input x @@;
datalines;
1 2 3 4 20 202 392 4 38 20
;
run;
ods select Quantiles;
proc univariate data = fivenum;
output out = fivenums min = min Q1 = Q1 Q2 = median Q3 = Q3 max = max;
run;
proc print data = fivenums;
run;
input byte y
0
0
1
2
63
61
27
13
end
list
tabstat y, statistics (min q max)
descriptive statistics
A descriptive statistic (in the count noun sense) is a summary statistic that quantitatively describes or summarizes features from a collection of information, while descriptive statistics (in the mass noun sense) is the process of using and an ...
that provides information about a dataset. It consists of the five most important sample percentile
In statistics, a ''k''-th percentile (percentile score or centile) is a score ''below which'' a given percentage ''k'' of scores in its frequency distribution falls (exclusive definition) or a score ''at or below which'' a given percentage fal ...
s:
# the sample minimum
In statistics, the sample maximum and sample minimum, also called the largest observation and smallest observation, are the values of the greatest and least elements of a sample. They are basic summary statistics, used in descriptive statistic ...
''(smallest observation)''
# the lower quartile or ''first quartile''
# the median (the middle value)
# the upper quartile or ''third quartile''
# the sample maximum
In statistics, the sample maximum and sample minimum, also called the largest observation and smallest observation, are the values of the greatest and least elements of a sample. They are basic summary statistics, used in descriptive statistic ...
(largest observation)
In addition to the median of a single set of data there are two related statistics called the upper and lower quartiles. If data are placed in order, then the lower quartile is central to the lower half of the data and the upper quartile is central to the upper half of the data. These quartiles are used to calculate the interquartile range, which helps to describe the spread of the data, and determine whether or not any data points are outliers.
In order for these statistics to exist the observations must be from a univariate
In mathematics, a univariate object is an expression, equation, function or polynomial involving only one variable. Objects involving more than one variable are multivariate. In some cases the distinction between the univariate and multivariate ...
variable that can be measured on an ordinal, interval or ratio scale.
Use and representation
The five-number summary provides a concise summary of thedistribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
* Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a vari ...
of the observations. Reporting five numbers avoids the need to decide on the most appropriate summary statistic. The five-number summary gives information about the location (from the median), spread (from the quartiles) and range (from the sample minimum and maximum) of the observations. Since it reports order statistic
In statistics, the ''k''th order statistic of a statistical sample is equal to its ''k''th-smallest value. Together with rank statistics, order statistics are among the most fundamental tools in non-parametric statistics and inference.
Importan ...
s (rather than, say, the mean) the five-number summary is appropriate for ordinal measurements, as well as interval and ratio measurements.
It is possible to quickly compare several sets of observations by comparing their five-number summaries, which can be represented graphically using a boxplot.
In addition to the points themselves, many L-estimator
In statistics, an L-estimator is an estimator which is a linear combination of order statistics of the measurements (which is also called an L-statistic). This can be as little as a single point, as in the median (of an odd number of values), or a ...
s can be computed from the five-number summary, including interquartile range
In descriptive statistics, the interquartile range (IQR) is a measure of statistical dispersion, which is the spread of the data. The IQR may also be called the midspread, middle 50%, fourth spread, or H‑spread. It is defined as the difference ...
, midhinge In statistics, the midhinge is the average of the first and third quartiles and is thus a measure of location.
Equivalently, it is the 25% trimmed mid-range or 25% midsummary; it is an L-estimator.
: \operatorname(X) = \overline = \frac = \frac ...
, range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
, mid-range
In statistics, the mid-range or mid-extreme is a measure of central tendency of a sample defined as the arithmetic mean of the maximum and minimum values of the data set:
:M=\frac.
The mid-range is closely related to the range, a measure of ...
, and trimean In statistics the trimean (TM), or Tukey's trimean, is a measure of a probability distribution's location defined as a weighted average of the distribution's median and its two quartiles:
: TM= \frac
This is equivalent to the average of the m ...
.
The five-number summary is sometimes represented as in the following table:
Example
This example calculates the five-number summary for the following set of observations: 0, 0, 1, 2, 63, 61, 27, 13. These are the number of moons of each planet in theSolar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
.
It helps to put the observations in ascending order: 0, 0, 1, 2, 13, 27, 61, 63. There are eight observations, so the median is the mean of the two middle numbers, (2 + 13)/2 = 7.5. Splitting the observations either side of the median gives two groups of four observations. The median of the first group is the lower or first quartile, and is equal to (0 + 1)/2 = 0.5. The median of the second group is the upper or third quartile, and is equal to (27 + 61)/2 = 44.
The smallest and largest observations are 0 and 63.
So the five-number summary would be 0, 0.5, 7.5, 44, 63.
Example in R
It is possible to calculate the five-number summary in theR programming language
R is a programming language for statistical computing and graphics supported by the R Core Team and the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Created by statisticians Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman, R is used among data miners, bioinforma ...
using the fivenum function. The summary function, when applied to a vector, displays the five-number summary together with the mean (which is not itself a part of the five-number summary). The fivenum uses a different method to calculate percentiles than the summary function.
Example in Python
This python example uses thepercentile function from the numerical library numpy and works in Python 2 and 3.
Example in SAS
You can usePROC UNIVARIATE in SAS (software)
SAS (previously "Statistical Analysis System") is a statistical software suite developed by SAS Institute for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, criminal investigation, and predictive analytics. ...
to get the five number summary:
Example in Stata
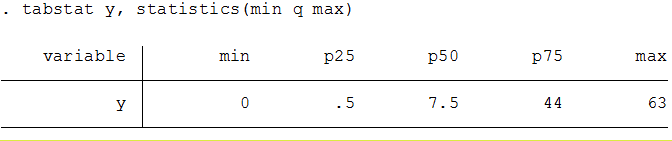
See also
*Seven-number summary In descriptive statistics, the seven-number summary is a collection of seven summary statistics, and is an extension of the five-number summary. There are three similar, common forms.
As with the five-number summary, it can be represented by a modi ...
*Three-point estimation The three-point estimation technique is used in management and information systems applications for the construction of an approximate probability distribution representing the outcome of future events, based on very limited information. While the d ...
* Box plot
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot is a method for graphically demonstrating the locality, spread and skewness groups of numerical data through their quartiles. In addition to the box on a box plot, there can be lines (which are ca ...
References
* * {{refend Summary statistics Articles with example Python (programming language) code Articles with example R code