Firefox early version history on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The project that became
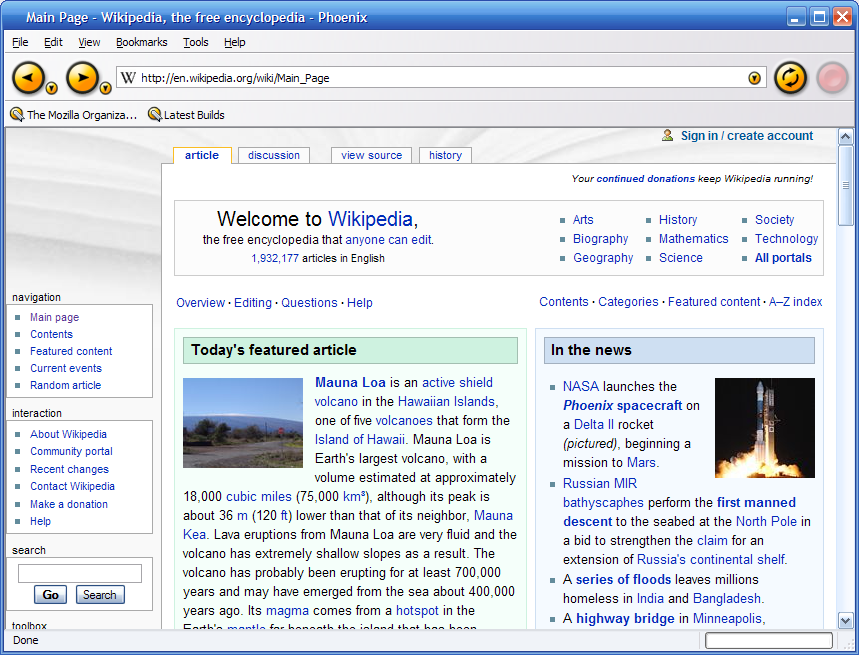 Hyatt, Ross, Hewitt and Chanial developed their browser to combat the perceived
Hyatt, Ross, Hewitt and Chanial developed their browser to combat the perceived
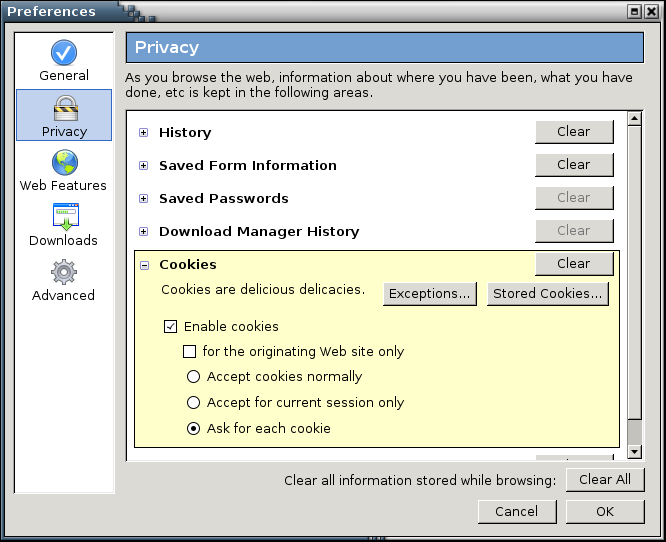
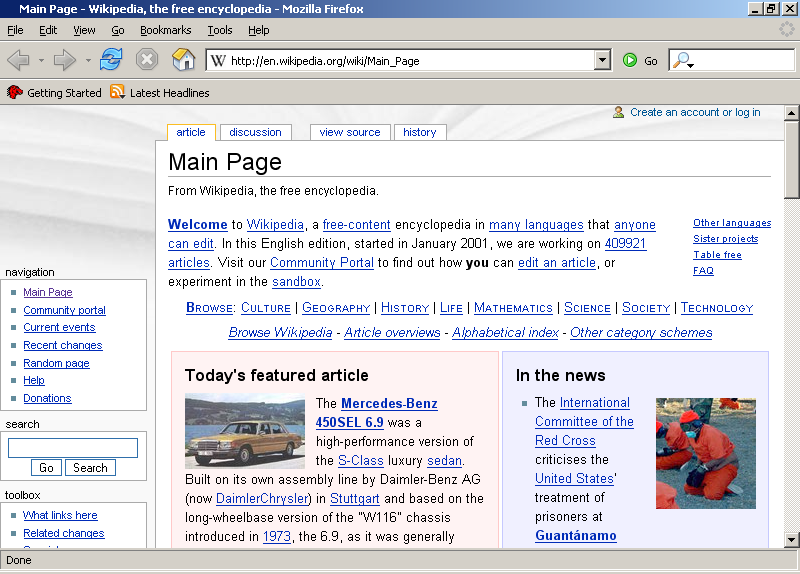 Due to continuing pressure from the Firebird community, on February 9, 2004, the project was renamed again to ''Mozilla Firefox''. The name "Firefox" (a reference to the
Due to continuing pressure from the Firebird community, on February 9, 2004, the project was renamed again to ''Mozilla Firefox''. The name "Firefox" (a reference to the
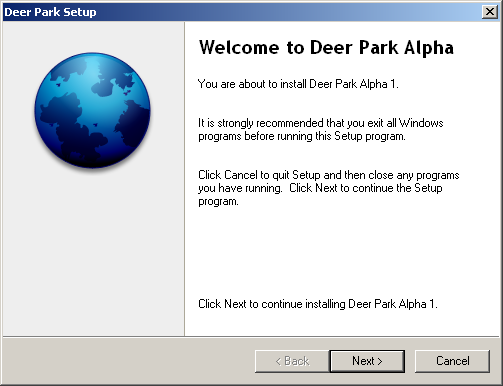 Firefox 1.5 was released on November 30, 2005. Originally, it was planned to have a version 1.1 at an earlier date as the new Firefox version after 1.0, with development on a later version (1.5) in a separate development branch, but during 2005 both branches and their feature sets were merged (the Mozilla Foundation abandoned the 1.1 release plan after the first two alpha builds), resulting in an official release date between the original dates planned for both versions.
Version 1.5 implemented a new Mac-lik
Firefox 1.5 was released on November 30, 2005. Originally, it was planned to have a version 1.1 at an earlier date as the new Firefox version after 1.0, with development on a later version (1.5) in a separate development branch, but during 2005 both branches and their feature sets were merged (the Mozilla Foundation abandoned the 1.1 release plan after the first two alpha builds), resulting in an official release date between the original dates planned for both versions.
Version 1.5 implemented a new Mac-lik
options interface
the subject of much criticism from Microsoft Windows and
Sanitize
action to allow someone to clear their privacy-related information without manually clicking the "Clear All" button. In Firefox 1.5, a user could clear all privacy-related settings simply by exiting the browser or using a keyboard shortcut, depending on their settings. Moreover, the software update system wa
(with binary patches now possible). There were als
in the extension management system, with a number o
In addition, Firefox 1.5 had preliminary SVG 1.1 support. Behind the screens, the new version resynchronized the code base of the release builds (as opposed to nightly builds) with the core "trunk", which contained additional features not available in 1.0, as it branched from the trunk around the 0.9 release. As such, there was a backlog of bug fixes between 0.9 and the release of 1.0, which were made available in 1.5. There were also changes in
 On October 24, 2006, Mozilla released
On October 24, 2006, Mozilla released
 Firefox 3 was released on June 17, 2008, by the
Firefox 3 was released on June 17, 2008, by the
 Version 3.5, codenamed Shiretoko, adds a variety of new features to Firefox. Initially numbered Firefox 3.1, Mozilla developers decided to change the numbering of the release to 3.5 in order to reflect a significantly greater scope of changes than originally planned. The final release was on June 30, 2009. The changes included much faster performance thanks to an upgrade to
Version 3.5, codenamed Shiretoko, adds a variety of new features to Firefox. Initially numbered Firefox 3.1, Mozilla developers decided to change the numbering of the release to 3.5 in order to reflect a significantly greater scope of changes than originally planned. The final release was on June 30, 2009. The changes included much faster performance thanks to an upgrade to
CSS 3 selector
support has been added. Firefox 3.5 uses the Gecko 1.9.1 engine, which includes a few features that were not included in the 3.0 release. Multi-touch touchpad support was also added to the release, including gesture support like pinching for zooming and swiping for back and forward. Firefox 3.5 also features an updated logo.
 On October 13, 2006,
On October 13, 2006,
Branch Plan
In ''Mozilla Wiki''. Retrieved December 21, 2005.
Mozilla Firefox release notes
for each version
Mozilla Firefox developer release notes
for each version
Releases
- MozillaWiki
unofficial changelogs for Firefox releases
Jesse Ruderman (last updated in 2008)
history of the Mozilla logo
by
Firefox browser for web 2.0 age
News
{{Timeline of web browsers , 2000s
Firefox
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current ...
today began as an experimental branch of the Mozilla Suite
The Mozilla Application Suite (originally known as Mozilla, marketed as the Mozilla Suite) is a discontinued cross-platform integrated Internet suite. Its development was initiated by Netscape Communications Corporation, before their acquisition b ...
called ''m/b'' (or ''mozilla/browser''). Firefox retains the cross-platform
In computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software ...
nature of the original Mozilla browser, using the XUL
XUL ( ), which stands for XML User Interface Language, is a user interface markup language developed by Mozilla. XUL is an XML dialect for writing graphical user interfaces, enabling developers to write user interface elements in a manner sim ...
user interface markup language
A user interface markup language is a markup language that renders and describes graphical user interfaces and controls. Many of these markup languages are dialects of XML and are dependent upon a pre-existing scripting language engine, usually ...
. The use of XUL makes it possible to extend the browser's capabilities through the use of extensions and theme
Theme or themes may refer to:
* Theme (arts), the unifying subject or idea of the type of visual work
* Theme (Byzantine district), an administrative district in the Byzantine Empire governed by a Strategos
* Theme (computing), a custom graphical ...
s. The development and installation processes of these add-ons raised security concerns, and with the release of Firefox 0.9, the Mozilla Foundation opened a Mozilla Update website containing "approved" themes and extensions. The use of XUL sets Firefox apart from other browsers, including other projects based on Mozilla's Gecko layout engine and most other browsers, which use interfaces native to their respective platforms (Galeon
Galeon is a discontinued Gecko-based web browser that was created by Marco Pesenti Gritti with the goal of delivering a consistent browsing experience to GNOME desktop environment. It gained some popularity in the early 2000s due to its speed, ...
and Epiphany
Epiphany may refer to:
* Epiphany (feeling), an experience of sudden and striking insight
Religion
* Epiphany (holiday), a Christian holiday celebrating the revelation of God the Son as a human being in Jesus Christ
** Epiphany season, or Epiph ...
use GTK+, K-Meleon
K-Meleon is a free and open-source, lightweight web browser for Microsoft Windows. Unlike cross-platform browsers, it uses the native Windows API to create its user interface. K-Meleon can use the secure Goanna layout engine based on Mozilla's ...
uses MFC, and Camino uses Cocoa). Many of these projects started before Firefox, and probably served as inspiration.
Releases
Phoenix and Firebird
software bloat
Software bloat is a process whereby successive versions of a computer program become perceptibly slower, use more memory, disk space or processing power, or have higher hardware requirements than the previous version, while making only dubious use ...
of the Mozilla Suite
The Mozilla Application Suite (originally known as Mozilla, marketed as the Mozilla Suite) is a discontinued cross-platform integrated Internet suite. Its development was initiated by Netscape Communications Corporation, before their acquisition b ...
(codenamed, internally referred to, and continued by the community as ''SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey is a free and open-source Internet suite. It is the continuation of the former Mozilla Application Suite, based on the same source code, which itself grew out of Netscape Communicator and formed the base of Netscape 6 and Netscape ...
''), which integrated features such as IRC
Internet Relay Chat (IRC) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for group communication in discussion forums, called '' channels'', but also allows one-on-one communication via private messages as well as chat an ...
, mail
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal sys ...
, news, and WYSIWYG
In computing, WYSIWYG ( ), an acronym for What You See Is What You Get, is a system in which editing software allows content to be edited in a form that resembles its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product, such as a printed d ...
HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaSc ...
editing into one internet suite
An Internet suite is an Internet-related software suite. Internet suites usually include a web browser, e-mail client (often with a news client and address book), download manager, HTML editor, and an IRC client.
The diversity of Internet suite o ...
. After it was sufficiently developed, binaries
A binary file is a computer file that is not a text file. The term "binary file" is often used as a term meaning "non-text file". Many binary file formats contain parts that can be interpreted as text; for example, some computer document fil ...
for public testing appeared in September 2002 under the name ''Phoenix''. This name carried the implication of the mythical firebird that rose triumphantly from the ashes of its dead predecessor, in this case Netscape Navigator
Netscape Navigator was a web browser, and the original browser of the Netscape line, from versions 1 to 4.08, and 9.x. It was the flagship product of the Netscape Communications Corp and was the dominant web browser in terms of usage share in ...
which lost the "First browser war
A browser war is competition for dominance in the usage share of web browsers. The "first browser war," (1995-2001) pitted Microsoft's Internet Explorer against Netscape's Netscape Navigator, Navigator. Browser wars continued with the decline o ...
" to Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washin ...
's Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated IE or MSIE) is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft which was used in the Windows line of operating systems ( ...
. The name ''Mozilla'' began as the internal codename
A code name, call sign or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in industrial c ...
for the original 1994 Netscape Navigator browser aiming to displace NCSA Mosaic as the world's most popular web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used o ...
. The name for this would-be "Mosaic killer" was meant to evoke the building-crushing Godzilla
is a fictional monster, or '' kaiju'', originating from a series of Japanese films. The character first appeared in the 1954 film '' Godzilla'' and became a worldwide pop culture icon, appearing in various media, including 32 films prod ...
. The name ''Mozilla'' was revived as the 1998 open sourcing spinoff organization from Netscape.
The name ''Phoenix'' remained until April 14, 2003, when it was changed because of a trademark dispute with the BIOS manufacturer Phoenix Technologies
Phoenix Technologies Ltd is an American company that designs, develops and supports core system software for personal computers and other computing devices. The company's products commonly referred to as BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or firm ...
(which produces a BIOS-based browser called Phoenix FirstWare Connect). The new name, ''Firebird'', met with mixed reactions, particularly as the Firebird database server already carried the name. In response, the Mozilla Foundation stated that the browser should always bear the name Mozilla Firebird to avoid confusion with the database software.
Firefox

 Due to continuing pressure from the Firebird community, on February 9, 2004, the project was renamed again to ''Mozilla Firefox''. The name "Firefox" (a reference to the
Due to continuing pressure from the Firebird community, on February 9, 2004, the project was renamed again to ''Mozilla Firefox''. The name "Firefox" (a reference to the red panda
The red panda (''Ailurus fulgens''), also known as the lesser panda, is a small mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It has dense reddish-brown fur with a black belly and legs, white-lined ears, a mostly white muzzle ...
) was chosen for its similarity to "Firebird", and its uniqueness in the computing industry. To ensure that no further name changes would be necessary, the Mozilla Foundation began the process of registering ''Firefox'' as a trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression that identifies products or services from a particular source and distinguishes them from othe ...
with the United States Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark registration authority for the United States. The USPTO's headquarters are in Alex ...
in December 2003. This trademark process led to a delay of several months in the release of Firefox 0.8 when the foundation discovered that Firefox had already been registered as a trademark in the UK for Charlton Company software. The situation was resolved when the foundation was given a license to use Charlton's European trademark.
Firefox version 1.0 was released on November 9, 2004. The launch of version 1.0 was accompanied by "a respectable amount of pre-launch fervor" including a fan-organized campaign to run a full-page ad in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
''.
Although the Mozilla Foundation had intended to make the Mozilla Suite obsolete and replace it with Firefox, the Foundation continued to maintain the suite until April 12, 2006 because it had many corporate users and was bundled with other software. The Mozilla community (as opposed to the Foundation) continues to release new versions of the suite, using the product name SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey is a free and open-source Internet suite. It is the continuation of the former Mozilla Application Suite, based on the same source code, which itself grew out of Netscape Communicator and formed the base of Netscape 6 and Netscape ...
to avoid confusion with the original Mozilla Suite.
Firefox 1.5
 Firefox 1.5 was released on November 30, 2005. Originally, it was planned to have a version 1.1 at an earlier date as the new Firefox version after 1.0, with development on a later version (1.5) in a separate development branch, but during 2005 both branches and their feature sets were merged (the Mozilla Foundation abandoned the 1.1 release plan after the first two alpha builds), resulting in an official release date between the original dates planned for both versions.
Version 1.5 implemented a new Mac-lik
Firefox 1.5 was released on November 30, 2005. Originally, it was planned to have a version 1.1 at an earlier date as the new Firefox version after 1.0, with development on a later version (1.5) in a separate development branch, but during 2005 both branches and their feature sets were merged (the Mozilla Foundation abandoned the 1.1 release plan after the first two alpha builds), resulting in an official release date between the original dates planned for both versions.
Version 1.5 implemented a new Mac-likoptions interface
the subject of much criticism from Microsoft Windows and
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, w ...
users, with aSanitize
action to allow someone to clear their privacy-related information without manually clicking the "Clear All" button. In Firefox 1.5, a user could clear all privacy-related settings simply by exiting the browser or using a keyboard shortcut, depending on their settings. Moreover, the software update system wa
(with binary patches now possible). There were als
in the extension management system, with a number o
In addition, Firefox 1.5 had preliminary SVG 1.1 support. Behind the screens, the new version resynchronized the code base of the release builds (as opposed to nightly builds) with the core "trunk", which contained additional features not available in 1.0, as it branched from the trunk around the 0.9 release. As such, there was a backlog of bug fixes between 0.9 and the release of 1.0, which were made available in 1.5. There were also changes in
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also i ...
support. As announced on 23 June 2005 by the Mozilla Foundation, Firefox 1.1, which later became 1.5, and other new Mozilla products did no longer support Mac OS X v10.1, in order to improve the quality of Firefox releases on Mac OS X v10.2 and above. Firefox 1.5 is the final version to support Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of operating systems. The first operating system in the 9x family, it is the successor to Windows 3.1x, and was released to manufacturi ...
.
Alpha builds of Firefox 1.5 (id est, 1.1a1 and 1.1a2) did not carry Firefox branding; they were labelled "Deer Park" (which was Firefox 1.5's internal codename) and contained a different program icon. This was done to dissuade end-users from downloading preview versions, which are intended for developers only.
Firefox 2
 On October 24, 2006, Mozilla released
On October 24, 2006, Mozilla released Firefox 2
Mozilla Firefox 2 is a version of Firefox, a web browser released on October 24, 2006 by the Mozilla Corporation.
Firefox 2 uses version 1.8 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages. The release contained many new features not found ...
. This version included updates to the tabbed browsing
In interface design, a tab is a graphical user interface object that allows multiple documents or panels to be contained within a single window, using tabs as a navigational widget for switching between sets of documents. It is an interface s ...
environment, the extensions manager, the GUI (Graphical User Interface), and the find, search and software update engines. It also implemented a new session restore feature, inline spell checking In software, a spell checker (or spelling checker or spell check) is a software feature that checks for misspellings in a text. Spell-checking features are often embedded in software or services, such as a word processor, email client, electronic di ...
, and an anti-phishing feature which was implemented by Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
as an extension and later merged into the program itself.
In December 2007, Firefox Live Chat was launched. It allowed users to ask volunteers questions through a system powered by Jive Software
Jive Software, an Aurea Software company, is a provider of communication and collaboration software for business.
Jive was headquartered in Palo Alto, California. Founded in 2001, Jive maintains additional offices in Portland, OR; San Francisco, ...
, with guaranteed hours of operation and the possibility of help after hours.
Firefox 2.0.0.20 was the final version that could run under an unmodified installation of Windows NT 4.0
Windows NT 4.0 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and oriented towards businesses. It is the direct successor to Windows NT 3.51, which was released to manufacturing on July 31, 1996, and then to retail ...
, Windows 98
Windows 98 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of Microsoft Windows operating systems. The second operating system in the 9x line, it is the successor to Windows 95, and was released to ...
, and Windows Me
Windows Millennium Edition, or Windows Me (marketed with the pronunciation of the pronoun "me"), is an operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of Microsoft Windows operating systems. It is the successor to Windo ...
. Subsequently, Mozilla Corporation announced it would not develop new versions of Firefox 2 after the 2.0.0.20 release, but continued Firefox 2 development as long as other programs, such as Thunderbird mail client, depended on it. The final internal release was 2.0.0.22, released in late April 2009.
Firefox 3
 Firefox 3 was released on June 17, 2008, by the
Firefox 3 was released on June 17, 2008, by the Mozilla Corporation
The Mozilla Corporation (stylized as moz://a) is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Mozilla Foundation that coordinates and integrates the development of Internet-related applications such as the Firefox web browser, by a global community of ope ...
. Firefox 3 uses version 1.9 of the Mozilla Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages. This version fixes many bugs, improves standard compliance, and implements new web APIs. Other new features include a redesigned download manager
A download manager is a software tool that manages the downloading of files from the Internet, which may be built: into a Web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a par ...
, a new "Places" system for storing bookmarks and history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
, and separate themes for different operating systems.
Development stretches back to the first Firefox 3 beta (under the codename 'Gran Paradiso') which had been released several months earlier on November 19, 2007, and was followed by several more beta releases in spring 2008 culminating in the June release. Firefox 3 had more than 8 million unique downloads the day it was released, setting a Guinness World Record.
Firefox 3.5
 Version 3.5, codenamed Shiretoko, adds a variety of new features to Firefox. Initially numbered Firefox 3.1, Mozilla developers decided to change the numbering of the release to 3.5 in order to reflect a significantly greater scope of changes than originally planned. The final release was on June 30, 2009. The changes included much faster performance thanks to an upgrade to
Version 3.5, codenamed Shiretoko, adds a variety of new features to Firefox. Initially numbered Firefox 3.1, Mozilla developers decided to change the numbering of the release to 3.5 in order to reflect a significantly greater scope of changes than originally planned. The final release was on June 30, 2009. The changes included much faster performance thanks to an upgrade to SpiderMonkey
SpiderMonkey is the first JavaScript engine, written by Brendan Eich at Netscape Communications, later released as open source and currently maintained by the Mozilla Foundation. It is used in the Firefox web browser.
History
Eich "wrote ...
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior, of ...
engine called TraceMonkey
SpiderMonkey is the first JavaScript engine, written by Brendan Eich at Netscape Communications, later released as open source and currently maintained by the Mozilla Foundation. It is used in the Firefox web browser.
History
Eich "wrote J ...
and rendering improvements, and support for the HTML5
HTML5 is a markup language used for structuring and presenting content on the World Wide Web. It is the fifth and final major HTML version that is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recommendation. The current specification is known as the HTML ...
specification, with a goal to offer video playback without being encumbered by patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
problems associated with many video technologies. Cross-site XMLHttpRequest
XMLHttpRequest (XHR) is an API in the form of an object whose methods transfer data between a web browser and a web server. The object is provided by the browser's JavaScript environment. Particularly, retrieval of data from XHR for the purpos ...
s (XHR), which can allow for more powerful web applications and an easier way to implement mashups, are also implemented in 3.5. A new global JSON object contains native functions to efficiently and safely serialize and deserialize JSON objects, as specified by the ECMAScript
ECMAScript (; ES) is a JavaScript standard intended to ensure the interoperability of web pages across different browsers. It is standardized by Ecma International in the documenECMA-262
ECMAScript is commonly used for client-side scripting o ...
3.1 draft. FulCSS 3 selector
support has been added. Firefox 3.5 uses the Gecko 1.9.1 engine, which includes a few features that were not included in the 3.0 release. Multi-touch touchpad support was also added to the release, including gesture support like pinching for zooming and swiping for back and forward. Firefox 3.5 also features an updated logo.
Firefox 3.6
Version 3.6, released on January 21, 2010, uses the Gecko 1.9.2 engine and includes several interface improvements, such as "personas". This release was referred to as 3.2 before 3.1 was changed to 3.5. The codename for this version was Namoroka. This is the last major, official version to run on PowerPC-basedMacintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and software en ...
es.
One minor update to Firefox 3.6, version 3.6.4 (code-named Lorentz
Lorentz is a name derived from the Roman surname, Laurentius, which means "from Laurentum". It is the German form of Laurence. Notable people with the name include:
Given name
* Lorentz Aspen (born 1978), Norwegian heavy metal pianist and keyboar ...
) is the first minor update to make non-intrusive changes other than minor stability and security fixes. It adds Out of Process Plugins (OOPP), which runs plugins in a separate process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
*Business process, activities that produce a specific se ...
, allowing Firefox to recover from plugin crashes. Firefox 3.6.6 lengthens the amount of time a plugin is allowed to be unresponsive before the plugin quits.
Firefox 4
 On October 13, 2006,
On October 13, 2006, Brendan Eich
Brendan Eich (; born July 4, 1961) is an American computer programmer and technology executive. He created the JavaScript programming language and co-founded the Mozilla project, the Mozilla Foundation, and the Mozilla Corporation. He served ...
, Mozilla's then- Chief-Technology-Officer, wrote about the plans for "Mozilla 2", referring to the most comprehensive iteration (since its creation) of the overall platform on which Firefox and other Mozilla products run. Most of the objectives were gradually incorporated into Firefox through versions 3.0, 3.5, and 3.6. The largest changes, however, were planned for Firefox 4.
After five "Alpha" releases, twelve "Beta" releases, and two "Release Candidate" versions, Firefox 4 was released on March 22, 2011, originally Firefox 3.7 (Gecko 1.9.3) during its alpha stage, brought a new user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine f ...
and is said to be faster. Early mockups of the new interface on Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for ser ...
, Mac OS X
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and la ...
, and Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, w ...
were first made available in July 2009. Other new features included improved notifications, tab groups, "switch to tab" where opened tabs can be searched through the address bar, application tabs, a redesigned add-on manager, integration with Firefox Sync
Firefox Sync, originally branded Mozilla Weave, is a browser synchronization feature for Firefox web browsers. It allows users to partially synchronize bookmarks, browsing history, preferences, passwords, filled forms, add-ons, and the last 25 o ...
, and support for multi-touch displays.
Firefox 4 was based on the Gecko 2.0 engine, which added or improved support for HTML5
HTML5 is a markup language used for structuring and presenting content on the World Wide Web. It is the fifth and final major HTML version that is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recommendation. The current specification is known as the HTML ...
, CSS3
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language such as HTML or XML (including XML dialects such as Scalable Vector Graphics, SVG, MathML or XHTML). CS ...
, WebM
WebM is an audiovisual media file format. It is primarily intended to offer a royalty-free alternative to use in the HTML5 video and the HTML5 audio elements. It has a sister project, WebP, for images. The development of the format is sponsored ...
, and WebGL
WebGL (Short for Web Graphics Library) is a JavaScript API for rendering interactive 2D and 3D graphics within any compatible web browser without the use of plug-ins. WebGL is fully integrated with other web standards, allowing GPU-accelera ...
. It also included a new JavaScript engine ( JägerMonkey) and better XPCOM Cross Platform Component Object Model (XPCOM) is a cross-platform component model from Mozilla. It is similar to Microsoft Component Object Model (COM) and Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA). It features multiple language bindings ...
APIs.
See also
*GNU IceCat
GNU IceCat, formerly known as GNU IceWeasel, is a completely free version of the Mozilla Firefox web browser distributed by the GNU Project. It is compatible with Linux, Windows, Android and macOS.
IceCat is released as a part of GNUzilla, G ...
* History of free and open-source software
In the 1950s and 1960s, computer operating software and compilers were delivered as a part of hardware purchases without separate fees. At the time, source code, the human-readable form of software, was generally distributed with the software p ...
* History of Mozilla Application Suite
* Mozilla software rebranded by Debian
Notes
References
Further reading
* Eich, Brendan (2005)Branch Plan
In ''Mozilla Wiki''. Retrieved December 21, 2005.
External links
Mozilla Firefox release notes
for each version
Mozilla Firefox developer release notes
for each version
Releases
- MozillaWiki
unofficial changelogs for Firefox releases
Jesse Ruderman (last updated in 2008)
history of the Mozilla logo
by
Jamie Zawinski
Jamie Zawinski (born November 3, 1968), commonly known as jwz, is an American computer programmer, blogger and impresario. He is best known for his role in the creation of Netscape Navigator, Netscape Mail, Lucid Emacs, Mozilla.org, and XScre ...
*
Firefox browser for web 2.0 age
BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current ...
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current ...
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current ...