Firearms Of Japan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Firearms
were introduced to Japan in the 13th century by the Chinese, but saw little use.
Firearms
were introduced to Japan in the 13th century by the Chinese, but saw little use.
 Due to its proximity with China, Japan had long been familiar with gunpowder weaponry. Firearms seem to have first appeared in Japan around 1270, as primitive metal tubes invented in China and called ''teppō'' (鉄砲 lit. "iron cannon") seem to have been introduced in Japan as well.Perrin p.93
These weapons were very basic, as they had no trigger or sights, and could not bear comparison with the more advanced European weapons which were introduced in Japan more than 250 years later.
Due to its proximity with China, Japan had long been familiar with gunpowder weaponry. Firearms seem to have first appeared in Japan around 1270, as primitive metal tubes invented in China and called ''teppō'' (鉄砲 lit. "iron cannon") seem to have been introduced in Japan as well.Perrin p.93
These weapons were very basic, as they had no trigger or sights, and could not bear comparison with the more advanced European weapons which were introduced in Japan more than 250 years later.
 Japan was at war during the
Japan was at war during the
 A few Japanese started to study and experiment with recent Western firearms from the beginning of the 19th century especially as a means to ward off visits from foreign ships, such as the incursion by the
A few Japanese started to study and experiment with recent Western firearms from the beginning of the 19th century especially as a means to ward off visits from foreign ships, such as the incursion by the
/ref> Japan finally developed its own model, the Murata rifle, derived from the French
Google Books
/ref>
OCLC 44090600
* *
''Tanegashima: the arrival of Europe in Japan'', Olof G. Lidin, Nordic Institute of Asian Studies, NIAS Press, 2002
 Firearms
were introduced to Japan in the 13th century by the Chinese, but saw little use.
Firearms
were introduced to Japan in the 13th century by the Chinese, but saw little use. Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Port ...
firearms
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
were introduced in 1543, and intense development followed, with strong local manufacture during the period of conflicts of the late 16th century. Hōjutsu, the art of gunnery, is the Japanese martial art dedicated to firearms usage.
Teppo
 Due to its proximity with China, Japan had long been familiar with gunpowder weaponry. Firearms seem to have first appeared in Japan around 1270, as primitive metal tubes invented in China and called ''teppō'' (鉄砲 lit. "iron cannon") seem to have been introduced in Japan as well.Perrin p.93
These weapons were very basic, as they had no trigger or sights, and could not bear comparison with the more advanced European weapons which were introduced in Japan more than 250 years later.
Due to its proximity with China, Japan had long been familiar with gunpowder weaponry. Firearms seem to have first appeared in Japan around 1270, as primitive metal tubes invented in China and called ''teppō'' (鉄砲 lit. "iron cannon") seem to have been introduced in Japan as well.Perrin p.93
These weapons were very basic, as they had no trigger or sights, and could not bear comparison with the more advanced European weapons which were introduced in Japan more than 250 years later.
Tanegashima (matchlock)
The first documented introduction of the matchlock which became known as the ''tanegashima'' was through thePortuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Port ...
in 1543. The ''tanegashima'' seems to have been based on '' snap matchlocks'' that were produced in the armory of Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to th ...
in Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a s ...
, which was captured by Portugal in 1510. The name ''tanegashima'' came from the island The Island(s) may refer to:
Places
* Any of various islands around the world, see the list of islands
* The Island (Cache County, Utah), an island on the Bear River, Utah
* The Island, Chennai, a river island in India
* The Island, Chicago, a n ...
where a Chinese junk with Portuguese adventurers on board was driven to anchor by a storm. The lord of the Japanese island Tanegashima Tokitaka
Tanegashima Tokitaka (1528 – October 21, 1579) was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, the 14th head of the Tanegashima clan. He is known for having first established contact with the Europeans, and producing the first European type ...
(1528–1579) purchased two matchlock muskets from the Portuguese and put a swordsmith to work in copying the matchlock barrel and firing mechanism. Within a few years the use of the ''tanegashima'' in battle forever changed the way war was fought in Japan. From 1560, firearms were used in large battles in Japan. In his memoirs published in 1614, the Portuguese adventurer turned author Fernão Mendes Pinto
Fernão Mendes Pinto (; c.1509 – 8 July 1583) was a Portuguese explorer and writer. His voyages are recorded in ''Pilgrimage'' ( pt, Peregrinação) (1614), his autobiographical memoir. The historical accuracy of the work is debatable due t ...
placed himself in that first landing party, although this claim has been roundly discredited and in fact contradicts his claims to be simultaneously in Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
at the time. However, Pinto does appear to have visited Tanegashima soon thereafter.
History
Sengoku Period
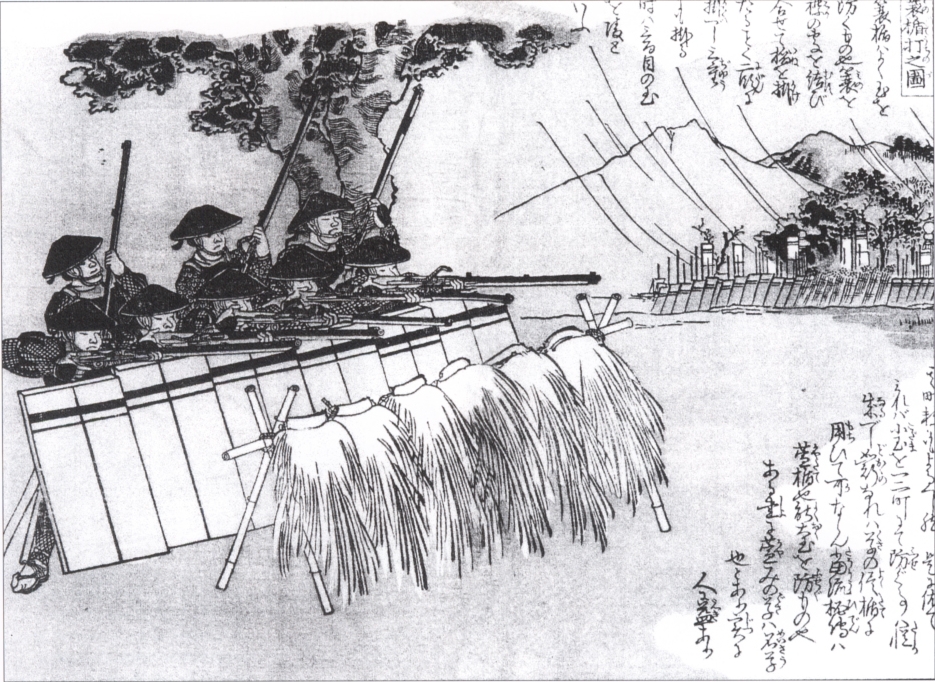
 Japan was at war during the
Japan was at war during the Sengoku Period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Variou ...
between 1467 and 1600, as feudal lords vied for supremacy. Matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of rope that is touched to the gunpowder by a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or trigger with his finger. Befo ...
guns were used extensively and had a decisive role in warfare. In 1549, Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese '' daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period. He is regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan.
Nobunaga was head of the very powerful Oda clan, and launched a war against other ''daimyō'' to unif ...
ordered 500 matchlocks to be made for his armies. The benefits of firearms were still relatively questionable however compared with other weapons. At the time, guns were still rather primitive and cumbersome. According to one estimate in 16th century Japan, an archer could fire 15 arrows in the time a gunner would take to load, charge, and shoot a firearm.Perrin p.15 Effective range also was only 80 to 100 meters, and at that distance, a bullet could easily bounce off armour. Furthermore, matchlocks were vulnerable to humid or rainy conditions as the powder would become damp. However, firearms could be manned effectively by farmers or non-samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of History of Japan#Medieval Japan (1185–1573/1600), medieval and Edo period, early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retai ...
low-ranking soldiers.Perrin p.25
The Japanese soon worked on various techniques to improve the effectiveness of their guns. They developed serial firing technique to create a continuous rain of bullets on the enemy.Perrin p.17 They also developed bigger calibers to increase lethal power. Protective boxes in lacquerware
Lacquerware are objects decoratively covered with lacquer. Lacquerware includes small or large containers, tableware, a variety of small objects carried by people, and larger objects such as furniture and even coffins painted with lacquer. Befor ...
were invented to be able to fire matchlocks in the rain, as well as systems to accurately fire weapons at night by
keeping fixed angles thanks to measured strings.
As a result, in the year 1567, Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful Daimyo, daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of ...
announced that "Hereafter, the guns will be the most important arms. Therefore, decrease the number of spears per unit, and have your most capable men carry guns". At the Battle of Nagashino
The took place in 1575 near Nagashino Castle on the plain of Shitaragahara in the Mikawa Province of Japan. Takeda Katsuyori attacked the castle when Okudaira Sadamasa rejoined the Tokugawa, and when his original plot with Oga Yashiro for t ...
in 1575, 3,000 arquebusiers helped win the battle, firing by volleys of 1,000 at a time, and secured across a river and breastwork to effectively stop enemy infantry and cavalry charges while being protected.
In the year 1584 Ikeda Sen led a troop of 200 women armed with firearms at the Battle of Komaki and Nagakute
The was a series of battles in 1584 between the forces of Hashiba Hideyoshi (who would become Toyotomi Hideyoshi in 1586) and the forces of Oda Nobukatsu and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Hideyoshi and Ieyasu had both served Oda Nobunaga and had not previou ...
and in 1600 at the Battle of Sekigahara
The Battle of Sekigahara ( Shinjitai: ; Kyūjitai: , Hepburn romanization: ''Sekigahara no Tatakai'') was a decisive battle on October 21, 1600 ( Keichō 5, 15th day of the 9th month) in what is now Gifu prefecture, Japan, at the end of ...
, a rare example of a Teppō unit, or musketeer
A musketeer (french: mousquetaire) was a type of soldier equipped with a musket. Musketeers were an important part of early modern warfare particularly in Europe as they normally comprised the majority of their infantry. The musketeer was a pre ...
unit consisting only of women.
Japan became so enthusiastic about the new weapons that it possibly overtook every European country in absolute numbers produced. Japan also used the guns in the Japanese invasion of Korea in 1592, in which about a quarter of the invasion force of 160,000 were gunners. They were extremely successful at first and managed to capture Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
just 18 days after their landing at Busan
Busan (), officially known as is South Korea's most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.4 million inhabitants. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern South Korea ...
.
Edo Period
The internal war in Japan was won byTokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fel ...
, who established the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in ...
, a powerful entity that would maintain peace and prosperity in Japan for the following 250 years. From the mid-17th century, Japan decided to close itself to interaction with the West through its policy of Sakoku
was the isolationist foreign policy of the Japanese Tokugawa shogunate under which, for a period of 265 years during the Edo period (from 1603 to 1868), relations and trade between Japan and other countries were severely limited, and nearly ...
. Guns were used less frequently because the Edo Period did not have many large-scale conflicts in which a gun would be of use. Oftentimes the sword was simply the more practical weapon in the average small-scale Edo Period conflicts; nevertheless, there were gunsmiths in Japan producing guns through the Edo Period.
Isolation did not decrease the production of guns in Japan—on the contrary, there is evidence of around 200 gunsmiths in Japan by the end of the Edo Period. But the social life of firearms had changed: as the historian David L. Howell has argued, for many in Japanese society, the gun had become less a weapon than a farm implement for scaring off animals.
Late Edo Period
 A few Japanese started to study and experiment with recent Western firearms from the beginning of the 19th century especially as a means to ward off visits from foreign ships, such as the incursion by the
A few Japanese started to study and experiment with recent Western firearms from the beginning of the 19th century especially as a means to ward off visits from foreign ships, such as the incursion by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
frigate HMS ''Phaeton'' in 1808.Perrin, p.72 Through the process of ''rangaku
''Rangaku'' (Kyūjitai: /Shinjitai: , literally "Dutch learning", and by extension "Western learning") is a body of knowledge developed by Japan through its contacts with the Dutch enclave of Dejima, which allowed Japan to keep abreast of Wes ...
'' (the studying of Western science through the Dutch), airguns
An air gun or airgun is a gun that fires projectiles pneumatically with compressed air or other gases that are mechanically pressurized ''without'' involving any chemical reactions, in contrast to a firearm, which pressurizes gases ''chemi ...
were developed by Kunitomo Ikkansai c. 1820–1830. From 1828, experiments were made with flintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also known ...
mechanisms.
The Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in th ...
samurai Takashima Shūhan
was a samurai and military engineer in Bakumatsu period Japan. He is significant in having started to import flintlock guns from the Netherlands at the end of Japan's period of Seclusion, during the Late Tokugawa Shogunate.Jansen, Marius. (2 ...
(高島秋帆) started to import flintlock guns from the Netherlands known as "geweer" from the 1840s. He made the first modern Western military demonstration for the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in ...
, in Tokumarugahara (north of Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
) on 27 June 1841.
With the arrival of Commodore Perry in 1854 and the inescapable opening of the country to trade, rapid efforts were made at reequipping Japan with modern firearms. Old matchlock weapons were recovered and converted to flintlock mechanisms.Perrin, p.67
Boshin War
The mounting civil war in Japan and the opposition of various feudal lords against theBakufu
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura ...
during the Late Tokugawa shogunate
was the final years of the Edo period when the Tokugawa shogunate ended. Between 1853 and 1867, Japan ended its isolationist foreign policy known as and changed from a feudal Tokugawa shogunate to the modern empire of the Meiji government. ...
led to serious rearming until the 1867 Boshin War. At the same time, technological progress was extremely fast in the West, with the introduction of the rifle, breech-loading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition ( cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally b ...
and even repeating firearms, so that Japanese armies were equipped with composite technologies, with weapons imported from countries as varied as France, Germany, the Netherlands, Britain and the United States, and coexisting with traditional Tanegashima guns.Totman, p.344
During the Boshin War, most shogunate vassal troops used "geweer"-style smoothbore guns. These guns were rather ancient and had limited capabilities, with an effective lethal range of about 50 meters, and a firing rate of about two rounds per minute. Much more effective Minié rifle
The Minié rifle was an important infantry rifle of the mid-19th century. A version was adopted in 1849 following the invention of the Minié ball in 1847 by the French Army captain Claude-Étienne Minié of the Chasseurs d'Orléans and Henri ...
s were also used by the armies directly under the command of the ''shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakur ...
'', the Bakufu
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura ...
troops. The Daimyō of Nagaoka, an ally of the ''shōgun'', possessed two Gatling guns
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon.
The Gatling gun's operation centered on a ...
and several thousand modern rifles. The shogunate is known to have placed an order for 30,000 modern Dreyse needle guns in 1866. In 1867, orders were placed for 40,000 state-of-the-art French Chassepot
The Chassepot (pronounced ''SHAS-poh''), officially known as ''Fusil modèle 1866'', was a bolt-action military breechloading rifle. It is famous for having been the arm of the French forces in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871. It repla ...
rifles, a part of which reached Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
by year's end. Antiquated Tanegashima
is one of the Ōsumi Islands belonging to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. The island, 444.99 km2 in area, is the second largest of the Ōsumi Islands, and has a population of 33,000 people. Access to the island is by ferry, or by air to New ...
matchlock guns are also known to have been used by the Bakufu however. Ryozen Museum of History exhibit
Imperial troops mainly used Minié rifles, which were much more accurate, lethal, and had a much longer range than the smoothbore "geweer"-style guns, although, being also muzzle-loading, they were similarly limited to two shots per minute. Improved breech-loading mechanisms, such as the Snider, developing a rate of about ten shots a minute, are known to have been used by troops of the Tosa Domain
The was a Han (Japan), feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan, controlling all of Tosa Province in what is now Kōchi Prefecture on the island of Shikoku. It was centered around Kōchi Castle, and was ruled throughout its ...
against the shogunate's Shōgitai
The Shōgitai (, "Manifest Righteousness Regiment") was an elite samurai shock infantry formation of the Tokugawa shogunate military formed in 1868 by the hatamoto and Hitotsubashi Gosankyō retainer in Zōshigaya, Edo (now Tokyo). The Shōgit ...
, at the Battle of Ueno
The was a battle of the Boshin War, which occurred on July 4, 1868 (''Meiji 1, 15th day of the 5th month''), between the troops of the Shōgitai under Shibusawa Seiichirō and Amano Hachirō, and Imperial "Kangun" troops.
Prelude
Though the ...
in July 1868. In the second half of the conflict, in the northeast theater, Tosa Province
was a province of Japan in the area of southern Shikoku. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Tosa''" in . Tosa bordered on Awa to the northeast, and Iyo to the northwest. Its abbreviated form name was . In terms of the Gokishichidō syst ...
troops are known to have used American-made Spencer repeating rifle
The Spencer repeating rifles and carbines were 19th-century American lever-action firearms invented by Christopher Spencer. The Spencer was the world's first military metallic-cartridge repeating rifle, and over 200,000 examples were manufactur ...
s. American-made handguns were also popular, such as the 1863 Smith & Wesson Army No 2, which was imported to Japan by the Scottish trader Thomas Blake Glover
Thomas Blake Glover (6 June 1838 – 16 December 1911) was a Scottish merchant in the Bakumatsu and Meiji period in Japan.
Early life (1838–1858)
Thomas Blake Glover was born at 15 Commerce Street, Fraserburgh, Aberdeenshire in northeast Sc ...
and used by the Satsuma forces.
Modern period
For some time after theMeiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were r ...
, Japan continued to use imported weapons. The newly created Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor ...
used firearms intensively against more traditional samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of History of Japan#Medieval Japan (1185–1573/1600), medieval and Edo period, early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retai ...
rebellious forces during the Satsuma rebellion
The Satsuma Rebellion, also known as the was a revolt of disaffected samurai against the new imperial government, nine years into the Meiji Era. Its name comes from the Satsuma Domain, which had been influential in the Restoration and be ...
in 1877, with an average of 320,000 rounds of ammunition fired daily during the conflict. After the Satsuma rebellion, Japan relied extensively on the French Chassepot.''Rifles of the World'' John Walter, p.88/ref> Japan finally developed its own model, the Murata rifle, derived from the French
Fusil Gras mle 1874
The Fusil Modèle 1874 or Gras was the French Army's primary service rifle from 1874 to 1886. Designed by Colonel Basile Gras, the Gras was a metallic cartridge adaptation of the single-shot, breech-loading, black powder Chassepot rifle. It was ...
. This was Japan's first locally made service rifle, and was used from 1880 to 1898. An industrial infrastructure, such as the Koishikawa arsenal had to be established to produce such new weapons.
Later, Japan developed the very successful bolt action Arisaka
The Arisaka rifle ( ja, 有坂銃, Arisaka-jū) is a family of Japanese military bolt-action service rifles, which were produced and used since approximately 1897, when it replaced the Murata rifle (, ) family, until the end of World War II in ...
series rifles, which was the Japanese service rifle
A service rifle (or standard-issue rifle) is a rifle a military issues to regular infantry. In modern militaries, this is typically a versatile and rugged battle rifle, assault rifle, or carbine suitable for use in nearly all environments. Mos ...
until the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. Japan produced relatively few submachine guns during World War II, the most numerous model was the Type 100 submachine gun of which 24,000–27,000 were produced, compared, for example, with the British Sten
The STEN (or Sten gun) is a family of British submachine guns chambered in 9×19mm which were used extensively by British and Commonwealth forces throughout World War II and the Korean War. They had a simple design and very low production cost ...
of which millions were produced. During the war, the Japanese worked on a copy of the American semi-automatic M1 Garand
The M1 Garand or M1 rifleOfficially designated as U.S. rifle, caliber .30, M1, later simply called Rifle, Caliber .30, M1, also called US Rifle, Cal. .30, M1 is a semi-automatic rifle that was the service rifle of the U.S Army during World Wa ...
(the Type 5 rifle
The Type 4 rifle, often referred to as the Type 5 rifle, (Japanese: 四式自動小銃 ''Yon-shiki Jidōshōju'') was a Japanese experimental semi-automatic rifle. It was based on the American M1 Garand with an integral 10-round magazine and ch ...
) but only a few hundred were made before the end of the war and it did not enter service.
After the end of the war, the dissolution of the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor ...
, and the establishment of the Japan Self-Defense Forces
The Japan Self-Defense Forces ( ja, 自衛隊, Jieitai; abbreviated JSDF), also informally known as the Japanese Armed Forces, are the unified ''de facto''Since Article 9 of the Japanese Constitution outlaws the formation of Military, armed f ...
in 1947, Japan relied on M1 Garand
The M1 Garand or M1 rifleOfficially designated as U.S. rifle, caliber .30, M1, later simply called Rifle, Caliber .30, M1, also called US Rifle, Cal. .30, M1 is a semi-automatic rifle that was the service rifle of the U.S Army during World Wa ...
rifles provided by the United States. In the mid-1950s however, Japan's Defense Agency started to develop battle rifle
A battle rifle is a service rifle chambered to fire a fully powered cartridge.
The term "battle rifle" is a retronym created largely out of a need to better differentiate the intermediate-powered assault rifles (e.g. the StG-44, AK-47, M16 ...
s of its own, such as the Howa Type 64
The , is a Japanese battle rifle used exclusively by the Japan Self-Defense Forces and the Japan Coast Guard, Japanese Coast Guard. It is a Gas-operated reloading, gas-operated, selective fire weapon which is chambered for the 7.62×51mm NATO rou ...
and assault rifles like the Howa Type 89
The , referred to as the , is a Japanese assault rifle used by the Japan Self-Defense Forces, the Japan Coast Guard's Special Security Team units, and the Special Assault Team. It has never been exported outside Japan due to its strict Japane ...
which has been gradually replacing the former.''Rifles: an illustrated history of their impact'' by Dr. David Westwood p.369Google Books
/ref>
See also
*Artillery of Japan
Artillery in Japan was first used during the Sengoku period in the 16th century; and its use has continued to develop.
History 13th to 17th century
Due to its proximity with China, Japan had long been familiar with gunpowder. Primitive cannons ...
* Firearm and Sword Possession Control Law
The is a 1958 Japanese law concerning firearms (and firearm parts/ammunition) and bladed weapons. It was enacted in 1958 and revised a number of times,Japanese Gun Control 1993 ''Asia Pacific Law Review'' Retrieved March 21, 2016Fisher, MaA Land ...
References
Further reading
* Jansen, Marius B (2000). ''The Making of Modern Japan.'' Cambridge:Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the reti ...
. OCLC 44090600
* *
''Tanegashima: the arrival of Europe in Japan'', Olof G. Lidin, Nordic Institute of Asian Studies, NIAS Press, 2002
External links
{{Japanese (samurai) weapons, armour and equipment Samurai weapons and equipment