Fiorello La Guardia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fiorello Henry LaGuardia (; born Fiorello Enrico LaGuardia, ; December 11, 1882September 20, 1947) was an American attorney and politician who represented New York in the House of Representatives and served as the 99th
(fee). ''
 He gained a reputation as a fiery and devoted reformer. La Guardia sponsored labor legislation and railed against immigration quotas. His major legislation was the Norris–La Guardia Act, cosponsored with Nebraska senator
He gained a reputation as a fiery and devoted reformer. La Guardia sponsored labor legislation and railed against immigration quotas. His major legislation was the Norris–La Guardia Act, cosponsored with Nebraska senator
 In 1929, La Guardia ran for Mayor once again. This time, he received the Republican nomination, once again defeating William Bennett. However, he lost the general election to incumbent Jimmy Walker in a landslide.
In 1929, La Guardia ran for Mayor once again. This time, he received the Republican nomination, once again defeating William Bennett. However, he lost the general election to incumbent Jimmy Walker in a landslide.

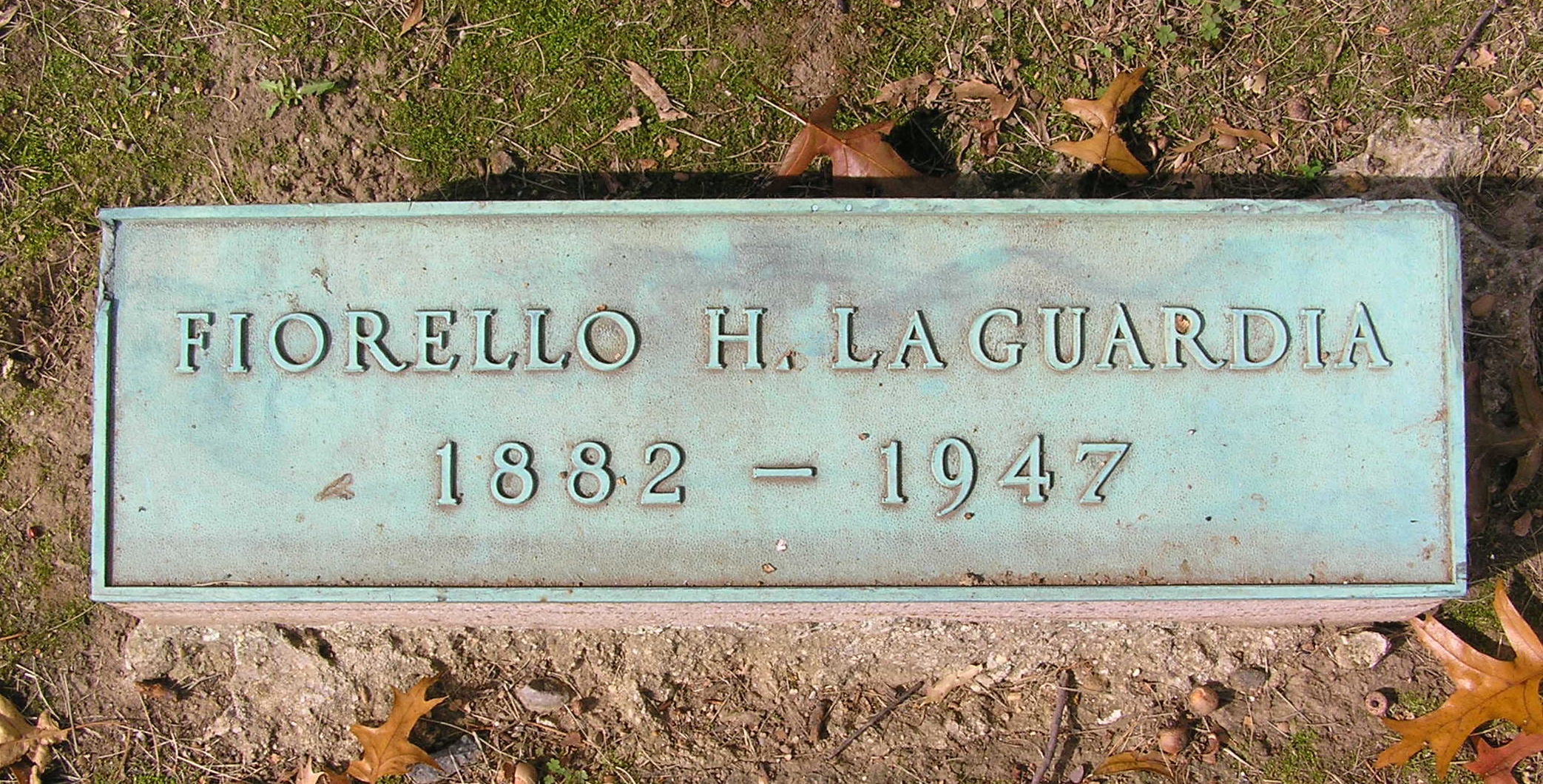 New York's LaGuardia Airport, LaGuardia Community College, LaGuardia Place, and various parks and buildings around New York City are named for him.
Known for his love of music, La Guardia was noted for spontaneously conducting professional and student orchestras and was instrumental in the creation of the High School of Music & Art in 1936, now renamed the Fiorello H. La Guardia High School of Music & Art and Performing Arts.
In 1972, the
New York's LaGuardia Airport, LaGuardia Community College, LaGuardia Place, and various parks and buildings around New York City are named for him.
Known for his love of music, La Guardia was noted for spontaneously conducting professional and student orchestras and was instrumental in the creation of the High School of Music & Art in 1936, now renamed the Fiorello H. La Guardia High School of Music & Art and Performing Arts.
In 1972, the
Mayor LaGuardia "Talk to the people" series on WNYC
Fiorello LaGuardia (The Compassion of New York’s Famous Mayor)
online
* *
online
*
online
an
in JSTOR
* * Elliott, Lawrence. (1983). ''Little Flower: The Life and Times of Fiorello La Guardia''. New York: William Morrow.
online
* Garrett, Charles. (1961). ''The La Guardia Years: Machine and Reform Politics in New York City''. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press. * Goldstein, Richard. ''Helluva Town: The Story of New York City During World War II'' (2010
Online review
* * Heckscher II, August. (1978). ''When La Guardia Was Mayor: New York's Legendary Years''. New York: W.W. Norton. . * Jeffers, H. Paul. (2002). ''The Napoleon of New York: Mayor Fiorello La Guardia''. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
online
* Kaufman, Herbert. "Fiorello H. La Guardia, Political Maverick" '' Political Science Quarterly'' 1990 105(1): 113–122.
in Jstor
* Mann, Arthur H. (1959). ''La Guardia: A Fighter Against His Times 1882–1933''. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott; scholarly biography
online
**''La Guardia comes to power: 1933'' (1965
online
* ttp://www.laguardiawagnerarchive.lagcc.cuny.edu/COLLECTIONS.aspx?ViwType=1&ColID=1 La Guardia and Wagner Archives/Fiorello H. La Guardia Collection *
oral interviews from the La Guardia and Wagner Archives/Fiorello H. La Guardia Oral History database
* ttps://www.flickr.com/photos/puzzlemaster/5429338693/in/photostream 1919 passport photo of Fiorello La Guardia
WNYC Archives blogs featuring Mayor La Guardia
Fiorello LaGuardia (The Compassion of New York’s Famous Mayor)
* {{DEFAULTSORT:La Guardia, Fiorello H. 1882 births 1947 deaths 20th-century American lawyers 20th-century American politicians American Episcopalians American Labor Party members of the United States House of Representatives American people in the Venona papers American people of Italian-Jewish descent American politicians of Italian descent American social democrats Burials at Woodlawn Cemetery (Bronx, New York) Deaths from cancer in New York (state) Deaths from pancreatic cancer Lawyers from New York City Mayors of New York City Military personnel from New York City New York University School of Law alumni Peabody Award winners People from East Harlem People from Greenwich Village People from Riverdale, Bronx Politicians from Prescott, Arizona Presidents of the United States Conference of Mayors Republican Party members of the United States House of Representatives from New York (state) Left-wing populism in the United States Progressivism in the United States United States Army officers United States Army personnel of World War I
Mayor of New York City
The mayor of New York City, officially Mayor of the City of New York, is head of the executive branch of the government of New York City and the chief executive of New York City. The mayor's office administers all city services, public proper ...
from 1934 to 1945. Known for his irascible, energetic, and charismatic personality and diminutive, rotund stature, La Guardia is acclaimed as one of the greatest mayors in American history. A member of the Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
*Republican Party (Liberia)
* Republican Part ...
, La Guardia was frequently cross-endorsed by parties other than his own, including the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
, under New York's electoral fusion laws.
He was born to Italian immigrants in New York City. Before serving as mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as ...
, La Guardia represented Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the List of co ...
in Congress and on the New York City Board of Aldermen. As mayor, during the Great Depression and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, La Guardia unified the city's transit system; expanded construction of public housing, playgrounds, parks, and airports; reorganized the New York Police Department; and implemented federal New Deal programs within the city. He pursued a long series of political reforms, curbing the power of the powerful Tammany Hall political machine and re-establishing merit-based employment and promotion within city administration.
La Guardia was also a major national political figure. His support for the New Deal and relationship with President Franklin D. Roosevelt crossed party lines, brought federal funds to New York City, and cut off patronage to La Guardia's enemies. La Guardia's WNYC radio program "Talk to the People", which aired from December 1941 until December 1945, expanded his public influence beyond the borders of the city.
Early life and career
La Guardia was born in Greenwich Village, New York City, on December 12, 1882. His father, Achille La Guardia, was aCatholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
native of Cerignola, Apulia, Italy. His father was an Italian immigrant to the United States and a non-practicing Catholic. His mother, Irene Luzzatto Coen, was a Jewish native of Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with t ...
. His maternal grandmother Fiorina (Luzzatto) Coen was a Luzzatto, a member of the prestigious Italian Jew
Italian Jews ( it, Ebrei Italiani, he, יהודים איטלקים ''Yehudim Italkim'') or Roman Jews ( it, Ebrei Romani, he, יהודים רומים ''Yehudim Romim'') can be used in a broad sense to mean all Jews living in or with roots in I ...
ish family of scholars, kabbalists, and poets. La Guardia's parents met and married in Trieste. Fiorello was raised an Episcopalian and practiced that religion all his life. His middle name "Enrico" was eventually anglicized to "Henry".
He moved to Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States. It is the list of U.S. states and territories by area, 6th largest and the list of U.S. states and territories by population, 14 ...
in 1890 with his family, where his father had a bandmaster position at Fort Whipple in the U.S. Army. La Guardia attended public schools and high school in Prescott, Arizona
Prescott ( ) is a city in Yavapai County, Arizona, Yavapai County, Arizona, United States. According to the 2020 United States census, 2020 Census, the city's population was 45,827. The city is the county seat of Yavapai County.
In 1864, Presc ...
. from the Biographical Directory of the United States Congress After his father was discharged from his bandmaster position in 1898, Fiorello lived in Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
. He graduated from the Dwight School, a private school on the Upper West Side of New York City.
La Guardia joined the State Department in 1901 and served in U.S. consulates in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
, Trieste, and Fiume. In 1906, he returned to the United States to continue his education at New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then- Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin.
In 1832, ...
. While studying at NYU from 1907 to 1910, he worked as an interpreter for the U.S. Bureau of Immigration at the Ellis Island immigration station. La Guardia was fluent in Italian, Yiddish, and Croatian
Croatian may refer to:
* Croatia
*Croatian language
*Croatian people
*Croatians (demonym)
See also
*
*
* Croatan (disambiguation)
* Croatia (disambiguation)
* Croatoan (disambiguation)
* Hrvatski (disambiguation)
* Hrvatsko (disambiguation)
* S ...
.
He graduated from New York University School of Law in 1910, was admitted to the bar the same year, and began a law practice in New York City.
Early political career
Election to Congress and World War I
In 1914, La Guardia ran for U.S. Representative for , which stretched across Manhattan between 3rd and 14th Streets, encompassing Greenwich Village. La Guardia was defeated byMichael F. Farley
Michael Francis Farley (March 1, 1863 – October 8, 1921) was an American businessman and politician who served one term as a U.S. Representative from New York from 1915 to 1917.
Early life and career
Farley was born in Birr, County Offal ...
.
La Guardia became Deputy Attorney General of New York in January 1915.
In 1916, he challenged Farley again, this time successfully. La Guardia took office on March 4, 1917, but was soon commissioned into the United States Army Air Service amid the American entry into World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. He rose to the rank of major in command of a unit of Caproni Ca.44
The Caproni Ca.5 was an Italian heavy bomber of World War I and the postwar era. It was the final version of the series of aircraft that began with the Caproni Ca.1 in 1914.
Development
By late World War I, developments in aircraft technology ...
bombers on the Italian-Austrian front.
He was re-elected to Congress in 1918.
President of the Board of Aldermen
1919 special election
In 1919, New York City Board of Aldermen PresidentAl Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith (December 30, 1873 – October 4, 1944) was an American politician who served four terms as Governor of New York and was the Democratic Party's candidate for president in 1928.
The son of an Irish-American mother and a ...
resigned to become Governor of New York, triggering a special election scheduled for the fall. La Guardia narrowly won the Republican nomination over William M. Bennett, who had been the party nominee for Mayor in 1917. La Guardia's opponent in the November special election was Robert L. Moran, a Tammany Hall-aligned Democratic alderman from the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New ...
, who had filled the seat since Smith's resignation.
La Guardia benefited from the presence of Michael "Dynamite Mike" Kelly, commander in the Irish heritage 69th New York Infantry Regiment, in the race. Tammany Hall tried to persuade Kelly to withdraw his candidacy and support Moran. When he refused, Tammany went to the New York Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the State of New York is the trial-level court of general jurisdiction in the New York State Unified Court System. (Its Appellate Division is also the highest intermediate appellate court.) It is vested with unlimited civ ...
and successfully sued to keep Kelly's name off the ballot."Major Kelly Killed by His Own Pistol"(fee). ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''. July 23, 1930.
When Election Day arrived, over 3,500 of Kelly's supporters wrote Kelly's name on the ballot. Another 129,000 votes were cast for Socialist James O'Neal. La Guardia won narrowly by 1,363 votes.
He resigned from Congress on December 31, 1919, to take office as president the next day.
1921 mayoral election
In 1921, La Guardia made his first bid for Mayor of New York City, but was defeated in the Republican primary by Manhattan Borough PresidentHenry H. Curran
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
*Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
. Curran lost the general election to Mayor John Hylan in a landslide.
Return to Congress from Harlem
Running as a Republican, La Guardia won a seat in Congress from the Italian stronghold ofEast Harlem
East Harlem, also known as Spanish Harlem or and historically known as Italian Harlem, is a neighborhood of Upper Manhattan, New York City, roughly encompassing the area north of the Upper East Side and bounded by 96th Street to the south, F ...
in 1922 and served in the House until March 3, 1933.
 He gained a reputation as a fiery and devoted reformer. La Guardia sponsored labor legislation and railed against immigration quotas. His major legislation was the Norris–La Guardia Act, cosponsored with Nebraska senator
He gained a reputation as a fiery and devoted reformer. La Guardia sponsored labor legislation and railed against immigration quotas. His major legislation was the Norris–La Guardia Act, cosponsored with Nebraska senator George Norris George Norris may refer to:
* George A. Norris (1928–2013), Canadian sculptor
*George W. Norris (1861–1944), American politician
** SS ''George W. Norris'', a Liberty ship
*George Norris, master of the ''Sprightly'', who named Bouvet Island in ...
in 1932. It circumvented Supreme Court limitations on the activities of labor unions, especially as those limitations were imposed between the enactment of the Clayton Antitrust Act in 1914 and the end of the 1920s. Based on the theory that the lower courts are creations not of the Constitution but of Congress, and that Congress therefore has wide power in defining and restricting their jurisdiction, the act forbids issuance of injunctions to sustain anti-union contracts of employment, to prevent ceasing or refusing to perform any work or remain in any relation of employment, or to restrain acts generally constituting component parts of strikes, boycotts, and picketing. It also said courts could no longer enforce yellow-dog contracts, which are labor contracts prohibiting a worker from joining a union.
As a Republican, La Guardia had to support Harding
Harding may refer to:
People
*Harding (surname)
*Maureen Harding Clark (born 1946), Irish jurist
Places Australia
* Harding River
Iran
* Harding, Iran, a village in South Khorasan Province
South Africa
* Harding, KwaZulu-Natal
United Sta ...
in 1920; he had to be silent in the 1928 campaign although he favored Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith (December 30, 1873 – October 4, 1944) was an American politician who served four terms as Governor of New York and was the Democratic Party's candidate for president in 1928.
The son of an Irish-American mother and a ...
, a Democrat.
1929 mayoral election
 In 1929, La Guardia ran for Mayor once again. This time, he received the Republican nomination, once again defeating William Bennett. However, he lost the general election to incumbent Jimmy Walker in a landslide.
In 1929, La Guardia ran for Mayor once again. This time, he received the Republican nomination, once again defeating William Bennett. However, he lost the general election to incumbent Jimmy Walker in a landslide.
Mayor of New York
1933 mayoral election
Mayor Jimmy Walker and his Irish-run Tammany Hall were forced out of office by scandal and La Guardia was determined to replace him. La Guardia ran on the Fusion Party platform, which was supported by Republicans, reform-minded Democrats, and independents. La Guardia had enormous determination, high visibility, the support of reformer Samuel Seabury and a divisive primary contest. He also represented previously underrepresented communities, appealed to a wide range of cultural backgrounds with his lineage. He secured the nominations and expected an easy win against incumbent Mayor John P. O'Brien. However, Joseph V. McKee entered the race as the nominee of the new "Recovery Party" at the last minute. McKee was a formidable opponent, sponsored by Bronx Democratic bossEdward J. Flynn
Edward Joseph Flynn (September 22, 1891 – August 18, 1953) was an American lawyer and politician. Flynn was a leading Democratic politician of the mid-twentieth-century, known for his tight control of the Bronx Democratic Party organization af ...
. La Guardia promised a more honest government, championing for greater efficiency and inclusiveness. La Guardia's win was based on a complex coalition of Republicans (mostly middle class German Americans
German Americans (german: Deutschamerikaner, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry. With an estimated size of approximately 43 million in 2019, German Americans are the largest of the self-reported ancestry groups by the Unit ...
in the boroughs outside Manhattan), a minority of reform-minded Democrats, Socialists, a large proportion of middle-class Jews, and the great majority of Italians, whose votes had previously been overwhelmingly loyal to Tammany.
During his mayoralty, La Guardia served as president of the United States Conference of Mayors from 1935 until 1945.
Agenda
La Guardia came to office in January 1934 with five main goals: * Restore the financial health and break free from the bankers' control * Expand the federally funded work-relief program for the unemployed * End corruption in government and racketeering in key sectors of the economy * Replace patronage with a merit-based civil service, with high prestige * Modernize the infrastructure, especially transportation and parks He achieved most of the first four goals in his first hundred days, as FDR gave him 20% of the entire national CWA budget for work relief. La Guardia then collaborated closely with Robert Moses, with support from the governor, Democrat Herbert Lehman, to upgrade the decaying infrastructure. The city was favored by the New Deal in terms of funding for public works projects. La Guardia's modernization efforts were publicized in the 1936 book ''New York Advancing: A Scientific Approach to Municipal Government,'' edited byRebecca B. Rankin
Rebecca Browning Rankin (April 5, 1887 – March 1, 1965) was the director of the New York City's Municipal Reference Library for thirty-two years. New York City Mayor Fiorello LaGuardia called Rankin a "human index to New York City affairs," an ...
.
African-American politics
In 1935 a riot took place in Harlem. Termed theHarlem riot of 1935
The Harlem riot of 1935 took place on March 19, 1935 in New York City, New York, in the United States. It has been described as the first "modern" race riot in Harlem, because it was committed primarily against property rather than persons. Ha ...
, it has been described as the first "modern" race riot, because it was committed primarily against property rather than persons. During the riots, La Guardia and Hubert Delany walked through the streets in an effort to calm the situation. After the riots, La Guardia convened the Mayor's Commission on Conditions of Harlem to determine the causes of the riot and a detailed report was prepared. The report identified "injustices of discrimination in employment, the aggressions of the police, and the racial segregation" as conditions which led to the outbreak of rioting. However, the Mayor shelved the committee's report, and did not make it public. The report would be unknown, except that a black New York newspaper, the ''Amsterdam News
The ''Amsterdam News'' (also known as ''New York Amsterdam News'') is a weekly Black-owned newspaper serving New York City. It is one of the oldest newspapers geared toward African Americans in the United States and has published columns by ...
'', subsequently published it in serial form.
Ethnic politics
La Guardia governed in an uneasy alliance with New York's Jews and liberal WASPs, together with ethnic Italians and Germans. Not an orthodox Republican, he also ran as the nominee of the American Labor Party, a union-dominated anti- Tammany left wing group that supported Franklin D. Roosevelt for president beginning in 1936. La Guardia supported Roosevelt, chairing the Committee of Independent Voters for Roosevelt and his running mate,Henry A. Wallace
Henry Agard Wallace (October 7, 1888 – November 18, 1965) was an American politician, journalist, farmer, and businessman who served as the 33rd vice president of the United States, the 11th U.S. Secretary of Agriculture, and the 10th U.S. S ...
, with Senator George Norris during the 1940 presidential election.
La Guardia was the city's first Italian-American mayor, but was not a typical Italian New Yorker. He was a Republican Episcopalian who had grown up in Arizona and had a Triestine Jewish mother and a lapsed Catholic father. He spoke several languages; when working at Ellis Island, he was certified as an interpreter for Italian, German, Yiddish, and Croatian
Croatian may refer to:
* Croatia
*Croatian language
*Croatian people
*Croatians (demonym)
See also
*
*
* Croatan (disambiguation)
* Croatia (disambiguation)
* Croatoan (disambiguation)
* Hrvatski (disambiguation)
* Hrvatsko (disambiguation)
* S ...
. It served him well during a contentious congressional campaign in 1922. When Henry Frank, a Jewish opponent, accused him of anti-Semitism, La Guardia rejected the suggestion that he publicly disclose that his mother was Jewish as "self-serving". Instead, La Guardia dictated an open letter in Yiddish that was also printed in Yiddish. In it, he challenged Frank to publicly and openly debate the issues of the campaign entirely in the Yiddish language. Frank, although he was Jewish, could not speak the language and was forced to decline—and lost the election.
La Guardia's 1933 campaign coincided with the rise of racial and religious hostilities in Germany, and he supported a more anti-Nazi response while in office. He publicly supported groups that engaged in boycotts of German goods and spoke alongside Rabbi Stephen S. Wise
Stephen Samuel Wise (March 17, 1874 – April 19, 1949) was an early 20th-century American Reform rabbi and Zionist leader in the Progressive Era. Born in Budapest, he was an infant when his family immigrated to New York. He followed his father ...
, leader of the American Jewish Congress. In 1935, La Guardia caused an international stir when he denied a masseur license to a German immigrant, stating that Germany had violated a treaty guaranteeing equal treatment of American professionals by discriminating against American Jews. Despite threats from Germany (including a bomb threat against New York City's German Consulate), La Guardia continued to use his position as mayor to denounce Nazism. During his reelection campaign in 1937, speaking before the Women's Division of the American Jewish Congress, he called for the creation of a special pavilion at the upcoming New York World's Fair, "a chamber of horrors" for "that brown-shirted fanatic," referring to Hitler. He also led anti-Nazi rallies and promoted legislation to facilitate the U.S. rescue of the Jewish refugees. He also appointed more racially and religiously diverse judges to various New York courts, which was one of his most powerful weapons against Nazi prejudice. These appointments included Rosalie Loew Whitney
Rosalie Loew Whitney (May 4, 1873 – September 3, 1939) was an American lawyer and suffragist.
Early life
Rosalie Loew was born in New York City to Hungarian Jewish immigrants William Noah Loew and Leontine (Lottie) Wechsler Lowe. Her father ...
, Herbert O'Brien, Jane Bolin, and Hubert Thomas Delany
Hubert Thomas Delany (; May 11, 1901 – December 28, 1990) was an American civil rights pioneer, a lawyer, politician, Assistant U.S. Attorney, the first African American Tax Commissioner of New York and one of the first appointed African Ame ...
. La Guardia would soon regret appointing the Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
O'Brien, who engaged in reactionary politics on the bench including decrying support for the Allied forces against the Axis in 1941, leading to La Guardia's condemnation of him with the famous line, “Senator, I have made a lot of good appointments and I think I am good ... but when I make a mistake, it’s a beaut.”
Crime
La Guardia criticized thegangster
A gangster is a criminal who is a member of a gang. Most gangs are considered to be part of organized crime. Gangsters are also called mobsters, a term derived from ''mob'' and the suffix ''-ster''. Gangs provide a level of organization and ...
s who brought a negative stereotype and shame to the Italian community. His first action as mayor was to order the chief of police to arrest mob boss Lucky Luciano on whatever charges could be found. La Guardia then went after the gangsters with a vengeance, stating in a radio address to the people of New York in his distinct voice, "Let's drive the bums out of town." In 1934 he went on a search-and-destroy mission looking for mob boss Frank Costello's slot machines, rounding up thousands of the "one armed bandits," swinging a sledgehammer and dumping them off a barge into the water for the newspapers and media. In 1935 La Guardia appeared at the Bronx Terminal Market to institute a citywide ban on the sale, display, and possession of artichokes, whose prices were inflated by mobsters. When prices went down, the ban was lifted. In 1936, La Guardia had special prosecutor Thomas E. Dewey
Thomas Edmund Dewey (March 24, 1902 – March 16, 1971) was an American lawyer, prosecutor, and politician who served as the 47th governor of New York from 1943 to 1954. He was the Republican candidate for president in 1944 and 1948: although ...
, a future Republican presidential candidate, single out Lucky Luciano for prosecution. Dewey led a successful investigation into Luciano's lucrative prostitution operation, eventually sending Luciano to jail with a 30–50 year sentence. The case was made into the 1937 movie '' Marked Woman'', starring Bette Davis.
La Guardia proved successful in shutting down the burlesque theaters, whose shows offended his sensibilities.
Public works
La Guardia's admirers credit him, among other things, with restoring the economy of New York City during and after the Great Depression. He is given credit for many massive public works programs administered by his powerful Parks Commissioner Robert Moses, which employed thousands of voters. The mayor's relentless lobbying for federal funds allowed New York to develop its economic infrastructure. To obtain large-scale federal money the mayor became a close ally of Roosevelt and New Deal agencies such as the CWA, PWA, andWPA
WPA may refer to:
Computing
*Wi-Fi Protected Access, a wireless encryption standard
*Windows Product Activation, in Microsoft software licensing
*Wireless Public Alerting (Alert Ready), emergency alerts over LTE in Canada
* Windows Performance Ana ...
, which poured $1.1 billion into the city from 1934 to 1939. In turn he gave FDR a showcase for New Deal achievement, helped defeat FDR's political enemies in Tammany Hall (the Democratic party machine in Manhattan). He and Moses built highways, bridges and tunnels, transforming the physical landscape of New York City. The West Side Highway, East River Drive
The Franklin D. Roosevelt East River Drive, commonly called the FDR Drive for short, is a limited-access parkway on the east side of the New York City borough of Manhattan. It starts near South and Broad Streets, just north of the Battery Park ...
, Brooklyn Battery Tunnel, Triborough Bridge, and two airports ( LaGuardia Airport, and, later, Idlewild, now JFK Airport) were built during his mayoralty.
In 1943, La Guardia saved the Mecca Temple on 55th Street from demolition. Together with New York City Council President Newbold Morris, La Guardia converted the building to the New York City Center
New York City Center (previously known as the Mecca Temple, City Center of Music and Drama,. The name "City Center for Music and Drama Inc." is the organizational parent of the New York City Ballet and, until 2011, the New York City Opera. and ...
of Music and Dance. On December 11, 1943, City Center opened its doors with a concert from the New York Philharmonic
The New York Philharmonic, officially the Philharmonic-Symphony Society of New York, Inc., globally known as New York Philharmonic Orchestra (NYPO) or New York Philharmonic-Symphony Orchestra, is a symphony orchestra based in New York City. It is ...
—La Guardia even conducted a rendition of "The Star Spangled Banner."
1939
1939 was a busy year, as he opened the 1939 New York World's Fair at Flushing Meadows–Corona Park, Queens, opened New York Municipal Airport No. 2 in Queens (later renamed Fiorello H. La Guardia Field), and had the city buy out theInterborough Rapid Transit Company
The Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT) was the private operator of New York City's original underground subway line that opened in 1904, as well as earlier elevated railways and additional rapid transit lines in New York City. The IRT ...
and the Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation
The Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation (BMT) was an urban transit holding company, based in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, and incorporated in 1923. The system was sold to the city in 1940. Today, together with the IND subway ...
, thus completing the public takeover of the New York City Subway system. The U.S. arrival of Georg and Maria Von Trapp and their children from Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
that fall at Ellis Island who would eventually become the Trapp Family Singers was another significant decade-ending event that year in La Guardia's mayoralty.
Reform
Responding to popular disdain for the sometimes corrupt City Council, La Guardia successfully proposed a reformed 1938 City Charter that created a powerful new New York City Board of Estimate, similar to a corporate board of directors. La Guardia was also a supporter of the Ives-Quinn Law "a law that would ban discrimination in employment on the bases of 'race, creed, color or national origin' and task a new agency, the New York State Commission Against Discrimination (SCAD), with education and enforcement." The bill passed in 1945, making New York the first state in the country to create an agency tasked with handling employment discrimination complaints.World War II
In 1941 during the run-up to American involvement inWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, President Roosevelt appointed La Guardia first director of the new Office of Civilian Defense (OCD). Roosevelt was an admirer of La Guardia; after meeting Winston Churchill for the first time he described him as "an English Mayor La Guardia". The OCD was the national agency responsible for preparing for blackouts, air raid wardens, sirens, and shelters in case of German air raids. The goal was to psychologically mobilize many thousands of middle class volunteers to make them feel part of the war effort. At the urging of aviation advocate Gill Robb Wilson, La Guardia, in his capacity as Director of the OCD, created the Civil Air Patrol with Administrative Order 9, signed by him on December 1, 1941, and published December 8, 1941. La Guardia remained Mayor of New York, shuttling back and forth with three days in Washington and four in the city in an effort to do justice to two herculean jobs. La Guardia focused on setting up air raid systems and training volunteer wardens. However Roosevelt appointed his wife Eleanor Roosevelt as his assistant. She issued calls for actors to lead a volunteer talent program, and dancers to start a physical fitness program. That led to widespread ridicule and the president replaced both of them in December 1941 with a full-time director James M. Landis.
The war ended the Great Depression in the city. Unemployment ended, and the city was a gateway for military supplies and soldiers sent to Europe, with the Brooklyn Navy Yard
The Brooklyn Navy Yard (originally known as the New York Navy Yard) is a shipyard and industrial complex located in northwest Brooklyn in New York City, New York (state), New York. The Navy Yard is located on the East River in Wallabout Bay, a ...
providing many of the warships and the garment trade providing uniforms. The city's great financiers, however, were less important in decision making than the policy makers in Washington, and very high wartime taxes were not offset by heavy war spending. New York was not a center of heavy industry and did not see a wartime boom, as defense plants were built elsewhere.
FDR refused to make La Guardia a general and was unable to provide fresh money for the city. By 1944 the city was short of funds to pay for La Guardia's new programs. La Guardia was frustrated and his popularity slipped away and he ran so poorly in straw polls in 1945 that he did not run for a fourth term.
In July 1945, when the city's newspapers were closed by a strike, La Guardia famously read the comics on the radio.
Political views
As a congressman, La Guardia was a tireless and vocal champion ofprogressive
Progressive may refer to:
Politics
* Progressivism, a political philosophy in support of social reform
** Progressivism in the United States, the political philosophy in the American context
* Progressive realism, an American foreign policy par ...
causes, including relaxed restriction on immigration, removal of U.S. troops from Nicaragua to speaking up for the rights and livelihoods of striking miners, impoverished farmers, oppressed minorities, and struggling families. He supported progressive income taxes, greater government oversight of Wall Street, and national employment insurance for workers idled by the Great Depression.
In domestic policies he tended toward socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
and wanted to nationalize and regulate; however he was never close to the Socialist Party and never bothered to read Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
.
When Mussolini's Fascist
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the ...
Italy invaded Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Er ...
on October 3, 1935, a Black protest of Italian vendors at the King Julius General Market on Lenox and 118th Street turned into a riot and 1,200 extra NYC policemen were deployed on "war duty" to quell the riot. In December 1935, at an Italian-American rally, attended by 20,000, in Madison Square Garden, La Guardia presented a $100,000 check to the Italian Consul General, part of a total $700,000 raised from Italian-Americans to help fund the invasion.
Foreign policy
Never an isolationist, he supported using American influence abroad on behalf of democracy or for national independence or against autocracy. Thus he supported the Irish independence movement and the anti-czaristRussian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
of 1917, but did not approve of Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
. By 1946 he was praising Moscow. Unlike most progressive colleagues who were isolationist, La Guardia consistently backed internationalism, speaking in favor of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
and the Inter-Parliamentary Union as well as peace and disarmament conferences.
In 1946 President Harry Truman sent the ex-mayor as an envoy to Brazil, but diplomacy was not his forte. Truman then gave him as major job as head of the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration (UNRRA), with responsibility for helping millions of desperate refugees in Europe. La Guardia was exhausted and after seeing the horrors of war in Europe called for a massive aid program. Critics ridiculed that as worldwide WPA and the biggest boondoggle ever. He sided with Henry A. Wallace
Henry Agard Wallace (October 7, 1888 – November 18, 1965) was an American politician, journalist, farmer, and businessman who served as the 33rd vice president of the United States, the 11th U.S. Secretary of Agriculture, and the 10th U.S. S ...
in calling for friendship with the Soviet Union, and attacked the new breed of Cold Warriors. He provided UNRRA funds to the Soviets despite warnings that the Kremlin used the money to rebuild its army. UNRRA shut down at the end of 1946. Despite his declining health La Guardia attacked the emerging " Truman Doctrine" that promised American financial help to stop the spread of Communism.
Prohibition
As Congressman, La Guardia was one of the first Republicans to voice their opinions againstprohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic ...
. He testified to that effect before the first session of Congress in 1926.
Personal life
La Guardia was a Scottish Rite Freemason and was a member of Garibaldi Lodge #542 in New York City.Family
La Guardia married twice. His first wife was Thea Almerigotti, an Istrian immigrant, whom he married on March 8, 1919. In June 1920, they had a daughter, Fioretta Thea La Guardia, who died May 9, 1921, of spinal meningitis. Thea died oftuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
on November 29, 1921, at the age of 26.
In 1929, La Guardia remarried to Marie Fisher (1895–1984), who had been his secretary while in Congress. They adopted two children:
* Eric Henry (born 1930), a Hobart College Hobart College may refer to:
* Hobart and William Smith Colleges
Hobart and William Smith Colleges are Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts colleges in Geneva, New York. They trace their origins to G ...
graduate who became a professor at the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seat ...
,
* Jean Marie (1928–1962), La Guardia's niece from his first marriage, the biological daughter of Thea's sister, a Barnard College graduate who later became an editor of ''Mademoiselle''.
Nazi detention of sister and brother-in-law
La Guardia's sister, the writerGemma La Guardia Gluck
Gemma La Guardia Gluck (24 April 1881 – 1 November 1962) was an American writer, of Italian Jewish origin, who lived in Hungary and was a survivor of the Holocaust. Her autobiography, published in 1961, tells of her experience as a survivo ...
and brother-in-law, Herman Gluck were living in Hungary and were arrested by the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one or ...
on June 7, 1944, when the Nazis took control of Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
. Adolf Eichmann
Otto Adolf Eichmann ( ,"Eichmann"
'' Heinrich Himmler Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
knew that Gemma was La Guardia's sister and ordered her to be held as a political prisoner. She and Herman were deported to Mauthausen concentration camp in Austria. Gemma did not learn until her release that Herman had died at Mauthausen.
Gemma was transferred from Mauthausen to the notorious women's concentration camp at Ravensbrück, fifty miles from '' Heinrich Himmler Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, where—unbeknownst to Gemma at the time—her daughter Yolanda (whose husband also died in the camps) and baby grandson were also held for a year in a separate barracks. Gemma Gluck, who was held in Block II of the camp and assigned prisoner #44139, was one of the few survivors of Ravensbrück and wrote about her time there.
The Germans abandoned Gluck, her daughter, and her grandson for a possible hostage exchange in April 1945 as the Russians advanced on Berlin. After the liberation of the camps, Gemma later wrote, the Soviets were " violating girls and women of all ages," and the three struggled as displaced persons in postwar Berlin, because they did not speak German and had no identity papers, money, or means of documenting where they had been.
Gemma finally managed to get word to the Americans, who contacted Fiorello, who was then director of the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration (UNRRA) and had been unable to locate his sister and brother-in-law since their disappearance. He worked to get them on the immigration lists, but asserted in a letter, included in the appendix of Gemma's memoir, that her "case was the same as that of hundreds of thousands of displaced people" and "no exceptions can be made." It took two years for her to be cleared and sent to the United States. She returned to New York in May 1947, where she was reunited with her brother only four months before his death. As he had made no provision for her, she lived the remainder of her life in very reduced circumstances in a public housing project in Queens until her death in 1962.
Gluck is one of the few American-born women interned by the Nazis, along with Virginia d'Albert-Lake.
Death and legacy
A man of short stature, La Guardia's height is sometimes given as . According to an article in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''; however, his actual height was .
He died of pancreatic cancer in his home at 5020 Goodridge Avenue, in the Fieldston neighbourhood of Riverdale, Bronx, on September 20, 1947, aged 64. La Guardia is interred at Woodlawn Cemetery in the Bronx.
Legacy
La Guardia was ranked first among the nation's mayors in a 1993 poll of historians and social scientists. According to biographer Mason B. Williams, his close collaboration with Roosevelt's New Deal proved a striking success in linking national money and local needs. La Guardia enabled the political recognition of new groups that had been largely excluded from the political system, such as Jews and Italians. His administration (in cooperation with Robert Moses) gave New York its modern infrastructure. His far-sighted goals raised ambitions for new levels of urban possibility. According toThomas Kessner
Thomas Kessner is an American historian, a Distinguished Professor at City University of New York, and an author.
Education
Kessner is a graduate of Brooklyn College (1963) and earned his doctorate at Columbia University in 1975 with distinction. ...
, trends since his tenure mean that "people would be afraid of allowing anybody to take that kind of power".
Namesakes

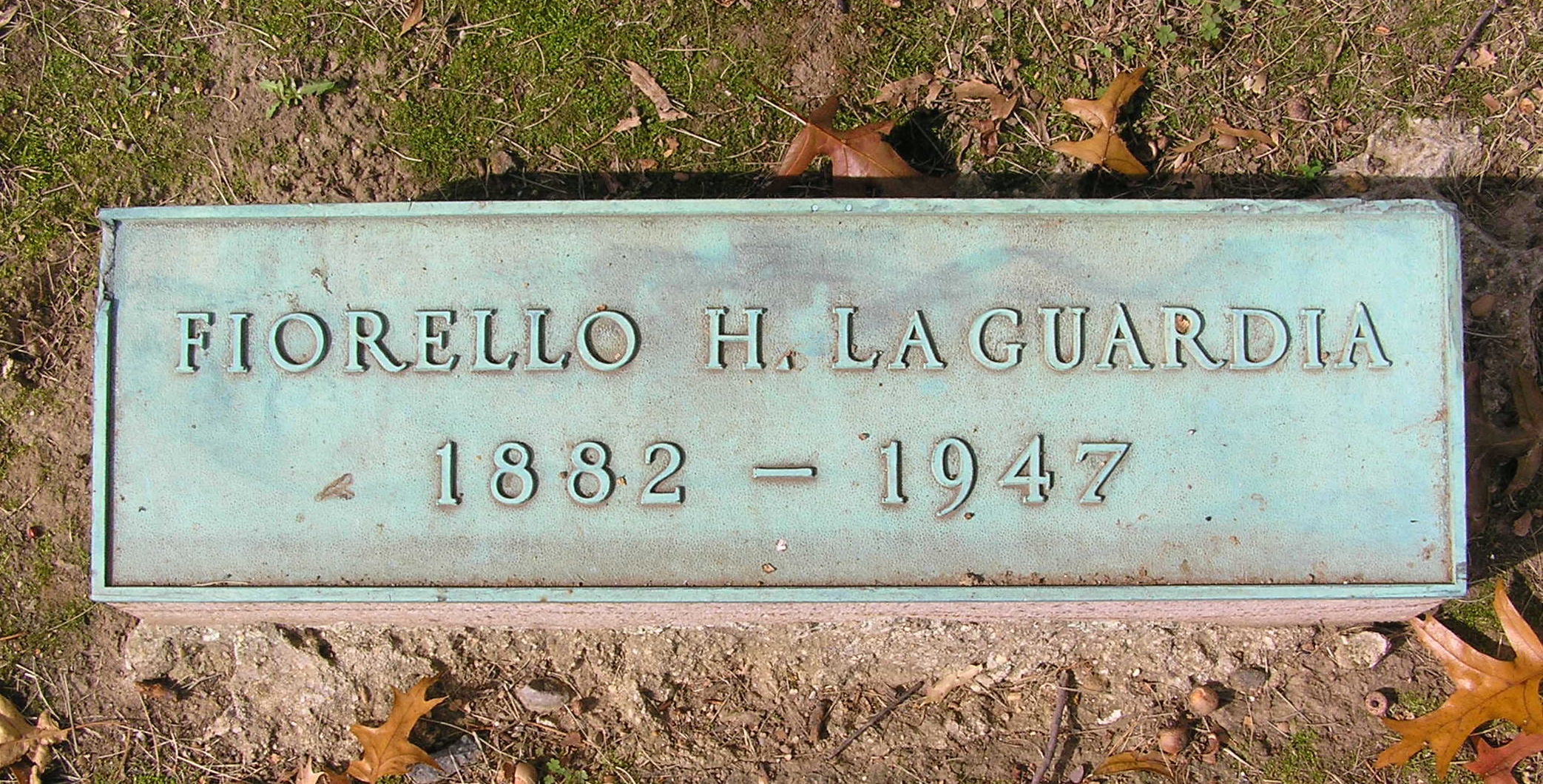 New York's LaGuardia Airport, LaGuardia Community College, LaGuardia Place, and various parks and buildings around New York City are named for him.
Known for his love of music, La Guardia was noted for spontaneously conducting professional and student orchestras and was instrumental in the creation of the High School of Music & Art in 1936, now renamed the Fiorello H. La Guardia High School of Music & Art and Performing Arts.
In 1972, the
New York's LaGuardia Airport, LaGuardia Community College, LaGuardia Place, and various parks and buildings around New York City are named for him.
Known for his love of music, La Guardia was noted for spontaneously conducting professional and student orchestras and was instrumental in the creation of the High School of Music & Art in 1936, now renamed the Fiorello H. La Guardia High School of Music & Art and Performing Arts.
In 1972, the United States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the executive branch of the Federal government of the Uni ...
honored La Guardia with a 14-cent postage stamp.
A strong supporter of Zionism
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after ''Zion'') is a Nationalism, nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is ...
, LaGuardia Street and LaGuardia interchange, both in Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, were named in his honor.
A street in Rijeka, Croatia, is named after Fiorello La Guardia. La Guardia worked in Rijeka as a U.S. Consular Agent from 1903 to 1906, when the city was known as Fiume and was under Hungarian administration. It was during this time that Rijeka's port played a vital role in connecting the Austro-Hungarian Empire to the United States, featuring direct passenger service between Rijeka and New York.
In popular culture
* La Guardia was the subject of the hit 1959 Broadway musical '' Fiorello!'' The original production of ''Fiorello!'' ran for two years and won 3 Tony Awards, including Best Musical and for Tom Bosley's portrayal of La Guardia, as well as a Pulitzer Prize for Drama in 1960. * La Guardia was portrayed by Phil Arnold in ''The Court Martial of Billy Mitchell
''The Court-Martial of Billy Mitchell'' is a 1955 American CinemaScope war film directed by Otto Preminger, and starring Gary Cooper and co-starring Charles Bickford, Ralph Bellamy, Rod Steiger, and Elizabeth Montgomery in her film debut. The film ...
''.
* Actor Tony Lo Bianco has portrayed La Guardia in several one-man plays, beginning with ''Hizzoner!'' in 1984. It debuted on Broadway in 1989, and Lo Bianco has since portrayed La Guardia in several off-Broadway versions, including ''LaGuardia'' (2008) and ''The Little Flower'' (2012–15).
* In '' Ghostbusters II'', La Guardia's ghost talks to New York Mayor Lenny Clotch ( David Margulies).
* In the alternate history drama '' The Plot Against America'' (2020), La Guardia is part of the opposition against the fascists in America.
* In the 2021 film '' In the Heights'', Abuela Claudia refers to dancing with La Guardia during the song "Paciencia Y Fe" which recounts her early life.
* The Off-Broadway show ''Tammany Hall'' depicts La Guardia's 1929 mayoral run against Jimmy Walker.
See also
* Statue of Fiorello H. La Guardia, Manhattan * La Guardia and Wagner Archives * La Guardia Commission, a study onmarijuana
Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the cannabis plant. Native to Central or South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in variou ...
in U.S. society
* List of mayors of New York City
* New York City mayoral elections for votes in 1929, 1933, 1937 and 1941.
* Timeline of New York City, 1930s–1940s
Mayor LaGuardia "Talk to the people" series on WNYC
Fiorello LaGuardia (The Compassion of New York’s Famous Mayor)
Publications
* La Guardia, Fiorello H. (1948). ''The Making of an Insurgent: An Autobiography''. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott.Notes
References
Bibliography
* * *online
* *
online
*
Further reading
* Brodsky, Alyn. (2003). ''The Great Mayor: Fiorello La Guardia and the Making of the City of New York.'' New York: Truman Talley Books. * Capeci, Dominic J. “From Different Liberal Perspectives: Fiorello H. La Guardia, Adam Clayton Powell, Jr., and Civil Rights in New York City, 1941-1943.” ''Journal of Negro History'' 62#2 1977, pp. 160–73online
an
in JSTOR
* * Elliott, Lawrence. (1983). ''Little Flower: The Life and Times of Fiorello La Guardia''. New York: William Morrow.
online
* Garrett, Charles. (1961). ''The La Guardia Years: Machine and Reform Politics in New York City''. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press. * Goldstein, Richard. ''Helluva Town: The Story of New York City During World War II'' (2010
Online review
* * Heckscher II, August. (1978). ''When La Guardia Was Mayor: New York's Legendary Years''. New York: W.W. Norton. . * Jeffers, H. Paul. (2002). ''The Napoleon of New York: Mayor Fiorello La Guardia''. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
online
* Kaufman, Herbert. "Fiorello H. La Guardia, Political Maverick" '' Political Science Quarterly'' 1990 105(1): 113–122.
in Jstor
* Mann, Arthur H. (1959). ''La Guardia: A Fighter Against His Times 1882–1933''. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott; scholarly biography
online
**''La Guardia comes to power: 1933'' (1965
online
External links
* ttp://www.laguardiawagnerarchive.lagcc.cuny.edu/COLLECTIONS.aspx?ViwType=1&ColID=1 La Guardia and Wagner Archives/Fiorello H. La Guardia Collection *
oral interviews from the La Guardia and Wagner Archives/Fiorello H. La Guardia Oral History database
* ttps://www.flickr.com/photos/puzzlemaster/5429338693/in/photostream 1919 passport photo of Fiorello La Guardia
WNYC Archives blogs featuring Mayor La Guardia
Fiorello LaGuardia (The Compassion of New York’s Famous Mayor)
* {{DEFAULTSORT:La Guardia, Fiorello H. 1882 births 1947 deaths 20th-century American lawyers 20th-century American politicians American Episcopalians American Labor Party members of the United States House of Representatives American people in the Venona papers American people of Italian-Jewish descent American politicians of Italian descent American social democrats Burials at Woodlawn Cemetery (Bronx, New York) Deaths from cancer in New York (state) Deaths from pancreatic cancer Lawyers from New York City Mayors of New York City Military personnel from New York City New York University School of Law alumni Peabody Award winners People from East Harlem People from Greenwich Village People from Riverdale, Bronx Politicians from Prescott, Arizona Presidents of the United States Conference of Mayors Republican Party members of the United States House of Representatives from New York (state) Left-wing populism in the United States Progressivism in the United States United States Army officers United States Army personnel of World War I