Faunal Interchange on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Biotic interchange is the process by which species from one biota invade another biota, usually due to the disappearance of a previously impassable barrier. These dispersal barriers can be physical, climatic, or biological and can include bodies of water or ice, land features like mountains,
 Humans have also become a vector of biotic interchange. They have fragmented species habitat by blocking interchange in some regions. Yet, humans have also intentionally and unintentionally spread many
Humans have also become a vector of biotic interchange. They have fragmented species habitat by blocking interchange in some regions. Yet, humans have also intentionally and unintentionally spread many
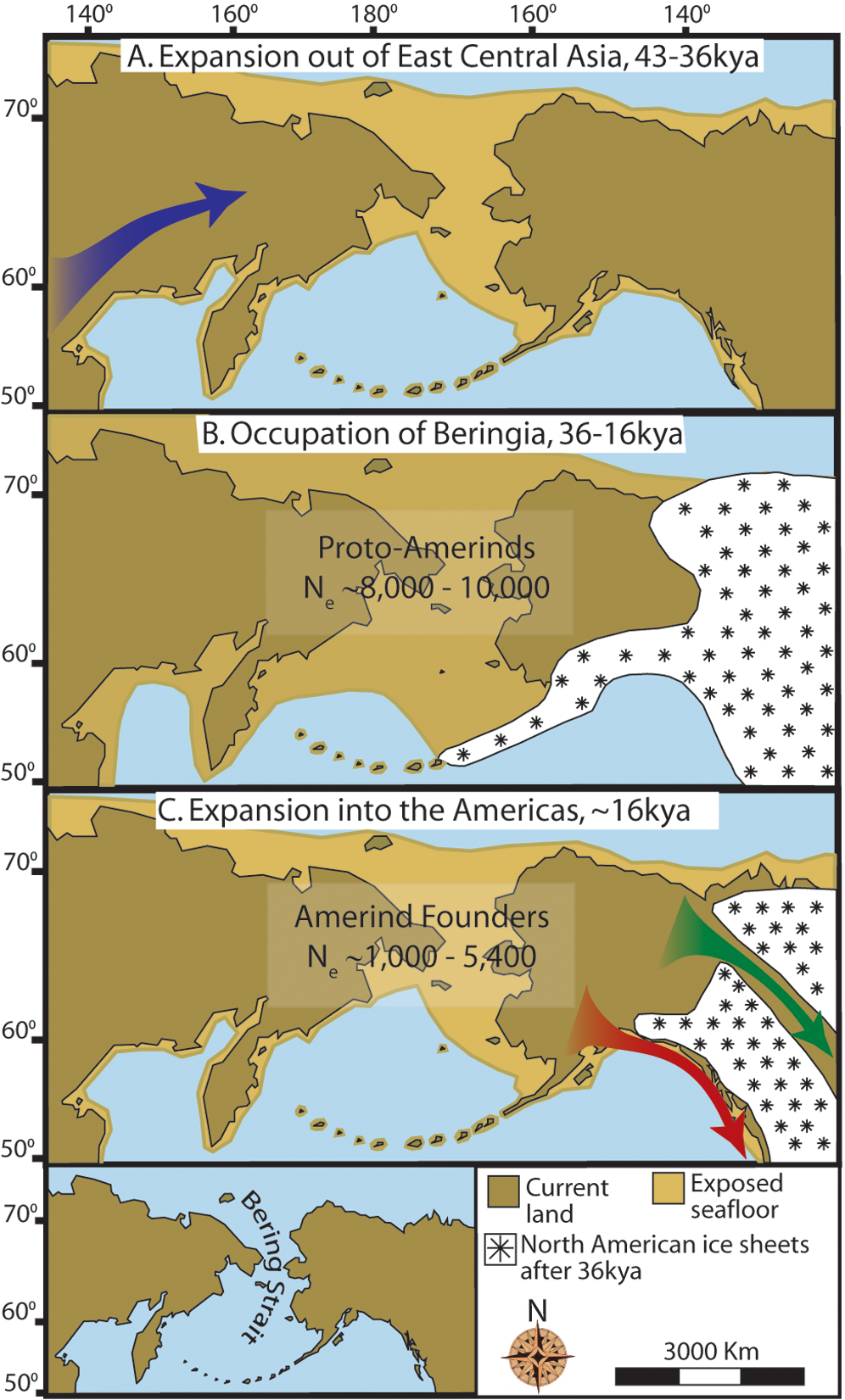 During the Trans-Arctic Interchange (,
During the Trans-Arctic Interchange (,
climate zones
Climate classifications are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. One of the most used is the Köppen climate ...
, or competition between species. Biotic interchange has been documented to occur in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments.
Causes
The general cause of a biotic interchange is the disappearance of a barrier that had been previously blocking the dispersal of species from two distinct biotas. The disappearance of a barrier could be from the closing of a sea, connecting two previously unconnected continents; the melting ofglacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires dis ...
s, allowing for migration across newly exposed areas that had been covered by ice; from sea level change
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryo ...
, covering a land bridge would allow for marine interchange, while revealing a land bridge would allow for terrestrial interchange; and, it could also be from changing ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, s ...
s, allowing for larval dispersal to new territories.
 Humans have also become a vector of biotic interchange. They have fragmented species habitat by blocking interchange in some regions. Yet, humans have also intentionally and unintentionally spread many
Humans have also become a vector of biotic interchange. They have fragmented species habitat by blocking interchange in some regions. Yet, humans have also intentionally and unintentionally spread many non-native species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there ...
around the globe. Climate change may also be impacting the effectiveness of natural dispersal barriers.
Effects
Sometimes an interchange can result in theextinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
of some species. These species may go extinct due to the introduction of a predator that they are not adapted to, or due to more successful competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indivi ...
by invading species. However, invading species can coexist with native species for millions of years after an invasion. Sometimes invading species can also improve biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
by increasing genetic diversity.
Another effect of biotic interchange is homogenization
Homogeneity is a sameness of constituent structure.
Homogeneity, homogeneous, or homogenization may also refer to:
In mathematics
*Transcendental law of homogeneity of Leibniz
* Homogeneous space for a Lie group G, or more general transformati ...
. This occurs when many invading species from both biotas become established, creating one similar biota.
Asymmetry
Many of the biotic interchanges studied have shown an asymmetry in the sharing of species between two biotas. Typically there is a donator biota and a recipient biota, with the donator biota sharing more species than the recipient biota. As an example, when theSuez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
connected the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
and Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, most new species in the Mediterranean originated in the Red Sea (91 molluscs, 15 crabs, and 41 fish). Fewer species travelled from the Mediterranean into the Red Sea (3 molluscs, 0 crabs, and 6 fish).
Invading species from the donator biota are often only a small percent of the potential invaders available within that biota. That is to say, that not all species that could invade another biota do invade. For example, only about 4.3% of the total fish species in the Red Sea have actually invaded the Mediterranean.
Hypotheses
There are many hypothesis that attempt to explain the asymmetry and general processes involved in biotic interchange: * The null hypothesis suggests that the number of species invading a recipient biota should be proportional to the number of species available in the donator biota. However, comparisons of many biotic interchanges reveal that this is not true. * The hypothesis of ecological opportunity suggests that the number of species invading a recipient biota should be proportional to the number of species that go extinct in the recipient biota. * Thebiogeographic
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
superiority hypothesis suggests that over time the species in one region would evolve superiority over species in a different region, and would thus be better at invading.
* The universal trade off hypothesis suggests that species with similar life habits separated for long periods of geologic time
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochrono ...
may still be able to coexist if brought back together due to the presence of similar evolutionary pressure
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of ...
s affecting their past adaptation to their surroundings.
Past
 During the Trans-Arctic Interchange (,
During the Trans-Arctic Interchange (, Early Pliocene
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
) sea levels rose, submerging the Bering Strait, and allowing marine organisms from the North Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
and North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
/Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
to come into contact with each other.
During the Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which lan ...
(, Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58
The Indian Subcontinent and Mainland Asia Interchange (
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
) was the collision of the Indian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began mov ...
with mainland Asia allowing for biotic interchange mainly from mainland Asia onto the Indian subcontinent.
Bering Land Bridge Interchange (late Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
) was an interchange between Asian and North American land species across the Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
.
The African and Eurasian Interchange (, early Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
) occurred between Africa and Eurasia through the Middle East after the Tethys sea
The Tethys Ocean ( el, Τηθύς ''Tēthús''), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean that covered most of the Earth during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents ...
closed.
Present
The Trans-Suez Interchange is a human-induced biotic interchange between the Mediterranean and the Red Sea due to the construction of theSuez canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
.
Another human-induced biotic interchange, the Japan–North American Interchange, is between marine species off the coast of Japan and North America. These species are transported as larvae in ships' ballast
Ballast is material that is used to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within a boat, ship, ...
.
The Panama Canal Interchange between the eastern Pacific and western Atlantic oceans through the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit ...
. This interchange has been relatively minimal due to the canal containing freshwater.
References
{{Reflist Biogeography