Fault Model on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A fault model is an engineering model of something that could go wrong in the construction or operation of a piece of equipment. From the model, the designer or user can then predict the consequences of this particular fault. Fault models can be used in almost all branches of engineering.
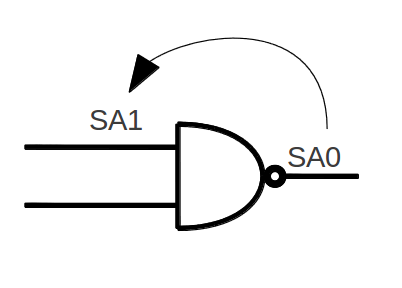 Fault F is called dominant to F' if all tests of F' detects F. In this case, F can be removed from the fault list. If F dominates F' and F' dominates F, then these two faults are equivalent.
In the example, a NAND gate has been shown, the set of all input values that can test output's SA0 is . the set of all input values that can check first input's SA1 is . In this case, output SA0 fault is dominant and can be removed from fault list.
Fault F is called dominant to F' if all tests of F' detects F. In this case, F can be removed from the fault list. If F dominates F' and F' dominates F, then these two faults are equivalent.
In the example, a NAND gate has been shown, the set of all input values that can test output's SA0 is . the set of all input values that can check first input's SA1 is . In this case, output SA0 fault is dominant and can be removed from fault list.
"Functional Fault Equivalence and Diagnostic Test Generation in Combinational Logic Circuits Using Conventional ATPG"
/ref>
Basic fault models
Basic fault models indigital circuit In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematica ...
s include:
*Static faults, which give incorrect values at any speed and sensitized by performing only one operation:
** the stuck-at fault
A stuck-at fault is a particular fault model used by fault simulators and automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) tools to mimic a manufacturing defect within an integrated circuit. Individual signals and pins are assumed to be ''stuck'' at Logi ...
model. A signal, or gate output, is stuck at a 0 or 1 value, independent of the inputs to the circuit.
** the bridging fault In electronic engineering, a bridging fault consists of two signals that are connected when they should not be. Depending on the logic circuitry employed, this may result in a wired-OR or wired-AND
A wired logic connection is a logic gate that im ...
model. Two signals are connected together when they should not be. Depending on the logic circuitry employed, this may result in a ''wired-OR'' or ''wired-AND'' logic function. Since there are ''O(n^2)'' potential bridging faults, they are normally restricted to signals that are physically adjacent in the design.
** the transistor fault Transistor Fault model is a Fault model used to describe faults for CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process t ...
s. This model is used to describe faults for CMOS logic gates. At transistor level, a transistor maybe stuck-short or stuck-open. In stuck-short, a transistor behaves as it is always conducts (or stuck-on), and stuck-open is when a transistor never conducts current (or stuck-off). Stuck-short will produce a short between VDD and VSS.
** The open fault
Open or OPEN may refer to:
Music
* Open (band), Australian pop/rock band
* The Open (band), English indie rock band
* ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969
* ''Open'' (Gotthard album), 1999
* ''Open'' (Cowboy Junkies album), 2001
* ''Open'' (YF ...
model. Here a wire is assumed broken, and one or more inputs are disconnected from the output that should drive them. As with bridging faults, the resulting behavior depends on the circuit implementation.
*Dynamic faults, only at-speed and are sensitized by performing multiple operations sequentially:
** The transition delay fault
Delay (from Latin: dilatio) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* '' Delay 1968'', a 1981 album by German experimental rock band Can
* ''The Delay'', a 2012 Uruguayan film
People
* B. H. DeLay (1891–1923), American aviator and act ...
(or transition fault) model, where the signal eventually assumes the correct value, but more slowly (or rarely, more quickly) than normal.
** Small-delay-defect model Fault assumption
A fault model, falls under one of the following assumptions: * single fault assumption: only one fault occur in a circuit. if we define k possible fault types in our fault model the circuit has n signal lines, by single fault assumption, the total number of single faults is k×n. * multiple fault assumption: multiple faults may occur in a circuit.Fault collapsing
There are two main ways for collapsing fault sets into smaller sets.Equivalence collapsing
It is possible that two or more faults produce same faulty behavior for all input patterns. These faults are called equivalent faults. Any single fault from the set of equivalent faults can represent the whole set. In this case, much less than k×n fault tests are required for a circuit with n signal line. removing equivalent faults from entire set of faults is called fault collapsing. fault collapsing significantly decreases the number of faults to check. In the example diagram, red faults are equivalent to the faults that being pointed to with the arrows, so those red faults can be removed from the circuit. In this case, the fault collapse ratio is 12/20.Dominance collapsing
 Fault F is called dominant to F' if all tests of F' detects F. In this case, F can be removed from the fault list. If F dominates F' and F' dominates F, then these two faults are equivalent.
In the example, a NAND gate has been shown, the set of all input values that can test output's SA0 is . the set of all input values that can check first input's SA1 is . In this case, output SA0 fault is dominant and can be removed from fault list.
Fault F is called dominant to F' if all tests of F' detects F. In this case, F can be removed from the fault list. If F dominates F' and F' dominates F, then these two faults are equivalent.
In the example, a NAND gate has been shown, the set of all input values that can test output's SA0 is . the set of all input values that can check first input's SA1 is . In this case, output SA0 fault is dominant and can be removed from fault list.
Functional collapsing
Two faults are functionally equivalent if they produce identical faulty functions or we can say, two faults are functionally equivalent if we can not distinguish them at primary outputs (PO) with any input test vector.Andreas Veneris, Robert Chang, Magdy S. Abadir, Sep Seyedi"Functional Fault Equivalence and Diagnostic Test Generation in Combinational Logic Circuits Using Conventional ATPG"
/ref>
In aerospace contexts
A fault model in an aerospace context is a set of structured information which helps users or systems to identify and isolate a problem that occurs on an engine,line-replaceable unit
A line-replaceable unit (LRU), lower line-replaceable unit (LLRU), line-replaceable component (LRC), or line-replaceable item (LRI) is a modular component of an airplane, ship or spacecraft (or any other manufactured device) that is designed to b ...
(LRU), or auxiliary power unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115&n ...
(APU) during a flight. Associated with this fault model may be a suggested repair procedure along with references to aircraft maintenance manuals (~ Light maintenance manual).
See also
*Automatic test pattern generation ATPG (acronym for both Automatic Test Pattern Generation and Automatic Test Pattern Generator) is an electronic design automation method/technology used to find an input (or test) sequence that, when applied to a digital circuit, enables automatic t ...
*Fault coverage {{Unreferenced, date=November 2022
Fault coverage refers to the percentage of some type of fault that can be detected during the test of any engineered system. High fault coverage is particularly valuable during manufacturing test, and techniques ...
*Single stuck line
A stuck-at fault is a particular fault model used by fault simulators and automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) tools to mimic a manufacturing defect within an integrated circuit. Individual signals and pins are assumed to be ''stuck'' at Logi ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fault Model Digital electronics Electronic design