Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision test is a
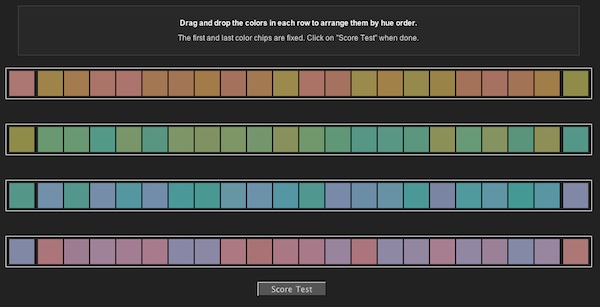 The tiles are arranged in four rows based on color hue. The rows cover orange/magenta hues, yellow/green hues, blue/purple and purple/magenta hues, in that order. The physical derivative of the test is given on a black background to isolate and accentuate color hues, which are round and roughly an inch in diameter. The digital derivative of the test is based on square hue images, which are also presented on a black background, but can vary in size based on
The tiles are arranged in four rows based on color hue. The rows cover orange/magenta hues, yellow/green hues, blue/purple and purple/magenta hues, in that order. The physical derivative of the test is given on a black background to isolate and accentuate color hues, which are round and roughly an inch in diameter. The digital derivative of the test is based on square hue images, which are also presented on a black background, but can vary in size based on 

 Combined with ambient illumination of the scene, several other factors are also integral for testing environment standardization. Calculated screen gamma is a significant factor. As gamma changes for the display, the representation of
Combined with ambient illumination of the scene, several other factors are also integral for testing environment standardization. Calculated screen gamma is a significant factor. As gamma changes for the display, the representation of
 Informative subject testing done at the Rochester Institute of Technology’sbr>Munsell Color Science Lab
Informative subject testing done at the Rochester Institute of Technology’sbr>Munsell Color Science Lab
discovered consistent

 Noting the sources of error previously addressed that are introduced by environmental factors and observer uncertainties, several digital test sources offer software installations that analyze the information garnered from the test. Data generated fro
Noting the sources of error previously addressed that are introduced by environmental factors and observer uncertainties, several digital test sources offer software installations that analyze the information garnered from the test. Data generated fro
X-Rite’s
online test offer several types of information, most notably the Total Estimation Score (TES), Color Vision Deficiency Type (CVDT) and Color Vision Deficiency Severity (CVDS). TES is an automated, generated value that calculates the number of tiles placed incorrectly and scales the value for uniform analysis. Average TES scores range from thirty to forty in series tests; while scores exceeding seventy can point to a marker for color blindness. Lower scores are intended to point to significantly increased color vision accuracy, as the TES score is directly correlated to the number of tiles incorrectly identified. Based on an axis interpretation of the information generated, a color vision deficiency type is also determined, based on a straight line plotted to intersect the center of the Munsell color sphere and the peak point of the highest color error spike. This axis is used to determine the color error tendencies the eye. From this information, if a value of seventy or higher is returned, a clinical form of color blindness can be estimated based upon the location of the CVDT axis. The
color vision test
A color vision test is used for measuring color vision against a standard. These tests are most often used to diagnose color vision deficiencies (''color blindness''), though several of the standards are designed to categorize normal color vision ...
often used to test for color blindness
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may ...
. The system was developed by Dean Farnsworth
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
in the 1940s and it tests the ability to isolate and arrange minute differences in various color targets with constant value
Value or values may refer to:
Ethics and social
* Value (ethics) wherein said concept may be construed as treating actions themselves as abstract objects, associating value to them
** Values (Western philosophy) expands the notion of value beyo ...
and chroma that cover all the visual hue
In color theory, hue is one of the main properties (called Color appearance model#Color appearance parameters, color appearance parameters) of a color, defined technically in the CIECAM02 model as "the degree to which a Stimulus (physiology ...
s described by the Munsell color system
In colorimetry, the Munsell color system is a color space that specifies colors based on three properties of color: hue (basic color), chroma (color intensity), and value ( lightness). It was created by Professor Albert H. Munsell in the first ...
. There are several variations of the test, one featuring 100 color hues and one featuring 15 color hues. Originally taken in an analog environment with physical hue tiles, the test is now taken from computer consoles. An accurate quantification of color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
accuracy is particularly important to designers, photographers and colorist
In comics, a colorist is responsible for adding color to black-and-white line art. For most of the 20th century this was done using brushes and dyes which were then used as guides to produce the printing plates. Since the late 20th century it is ...
s, who all rely on accurate color vision to produce quality content.
Vision tests
100 hue test
The most common form of the Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision Test contains four distinct rows of similar color hues, each containing 25 distinct variations of each hue. Each color hue at the polar end of a row is fixed in position, to serve as an anchor. Each hue tile between the anchors can be adjusted as theobserver
An observer is one who engages in observation or in watching an experiment.
Observer may also refer to:
Computer science and information theory
* In information theory, any system which receives information from an object
* State observer in con ...
sees fit. The final arrangement of the hue tiles represents the aptitude of the visual system in discerning differences in color hue. Failures within the observers visual system can be measured as a function of two factors contained within the test; either the amount of instances that a tile is misplaced, or the severity of a tile displacement (i.e., the distance between where a tile should have been placed and where it was actually placed.).
 The tiles are arranged in four rows based on color hue. The rows cover orange/magenta hues, yellow/green hues, blue/purple and purple/magenta hues, in that order. The physical derivative of the test is given on a black background to isolate and accentuate color hues, which are round and roughly an inch in diameter. The digital derivative of the test is based on square hue images, which are also presented on a black background, but can vary in size based on
The tiles are arranged in four rows based on color hue. The rows cover orange/magenta hues, yellow/green hues, blue/purple and purple/magenta hues, in that order. The physical derivative of the test is given on a black background to isolate and accentuate color hues, which are round and roughly an inch in diameter. The digital derivative of the test is based on square hue images, which are also presented on a black background, but can vary in size based on monitor
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, West Vir ...
, resolution
Resolution(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Resolution (debate), the statement which is debated in policy debate
* Resolution (law), a written motion adopted by a deliberative body
* New Year's resolution, a commitment that an individual mak ...
, zoom
Zoom may refer to:
Technology Computing
* Zoom (software), videoconferencing application
* Page zooming, the ability to magnify or shrink a portion of a page on a computer display
* Zooming user interface, a graphical interface allowing for image ...
and a variety of other external settings and variables. The digital distribution of the 100 Hues test is far more popular given its easy access for little or no licensing fee, and an apparent level of accuracy for most audiences. Taking the physical hue test under experimentally sound conditions (see Testing Environment) is far more accurate but the high price of the physical test kit is often prohibitive

D15 test
The Farnsworth–Munsell D15 Color Vision Test is an older version of the test. It is composed of a single tray, holding 15 independent color hues. The D15 test is administered in the same way as the 100 Hues test; the same environmental factors are recommended for non-professional results and required to garner completely professional results. The key difference between the D15 and 100 Hues test is the intended pool of qualitative informative results. The 100 Hue test is administered in pursuit of measuring an individual’s overall color vision acuity, while the primary purpose of the D15 test is to identifycolor vision defects
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may make some aca ...
, most notably red-green and blue-yellow color sensing deficiencies. The D15 test is most notable to be relevant to forms of color blindness
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may ...
or individuals suffering with vision that incorporates protanomaly, deuteranomaly, protanopia
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may make some aca ...
and deuteranopia
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may make some aca ...
. For more information on color vision deficiencies or color blindness, see Color Blindness
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may ...
.
Environmental factors
The Munsell Vision Test is reliant on a wide assortment of environmental factors to generate accurate and consistent color vision results. Many of these factors are universal across both physical and digital releases of the test, although several are unique to either test in their own right. The CIE has determined some baseline values and experimental standards to be used in both editions of the test, others are fluid and merely require consistency from test to test.Illuminants

Illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting.
CIE illuminants
The Inter ...
s are unique location to location across the globe, however several types of illuminant have been standardized by the CIE. Illuminants types D65 and D50 are acceptable for use, however D50 illuminant is suggested for a calibrated
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known a ...
and accurate color vision test result. Use of different illuminant can sway results in a significant manner due to the spectral power distribution
In radiometry, photometry, and color science, a spectral power distribution (SPD) measurement describes the power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination (radiant exitance). More generally, the term ''spectral power distribution'' ...
of alternate sources and their incident
Incident may refer to:
* A property of a graph in graph theory
* ''Incident'' (film), a 1948 film noir
* Incident (festival), a cultural festival of The National Institute of Technology in Surathkal, Karnataka, India
* Incident (Scientology), a ...
effect on how displayed information is processed by the human visual system. Illuminants containing varying concentrations of differing wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
intensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
*Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
* Level (disambiguation)
* Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
*Field strength of electric, ma ...
light skews the representation of color on the screen in a manner that would cause the eye to mismatch color patches. In combination with the spatial acuity function of the human visual system, illumination plays a significant role in the color accuracy of a display.
Screen calibration
 Combined with ambient illumination of the scene, several other factors are also integral for testing environment standardization. Calculated screen gamma is a significant factor. As gamma changes for the display, the representation of
Combined with ambient illumination of the scene, several other factors are also integral for testing environment standardization. Calculated screen gamma is a significant factor. As gamma changes for the display, the representation of color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
, contrast and saturation
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
**Saturated and unsaturated compounds
** Degree of unsaturation
**Saturated fat or fatty aci ...
are affected proportional to the magnitude of the change of the gamma curve. CIE recommends a gamma value of 2.2 as it is the current display manufacturing standard. A proper, professional grade screen calibration is required in order for concretely accurate test information. Several companies manufacture portable display calibration tools. Tools such as these take into account the type of screen and the screen’s primary illumination source.
There is no standard monitor hardware specification for the digital release of the Munsell Vision Test. Correct and thorough monitor calibration takes into account human visual system metamerism, a phenomenon that combines several color science elements to generate visual matching colors regardless of differences in source illumination, although it is ultimately not universally effective.
Formal monitor tests
 Informative subject testing done at the Rochester Institute of Technology’sbr>Munsell Color Science Lab
Informative subject testing done at the Rochester Institute of Technology’sbr>Munsell Color Science Labdiscovered consistent
color perception
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
difficulties when identical subjects performed the Munsell Vision Test on varying calibrated monitors in a test comparing color vision test results between Apple MacBook Pro laptop displays and a Samsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ...
LCD Monitor
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in cont ...
. Results garnered from the experiment exemplified the differences that displays can exhibit in failure to accurately quantify color. Incident angle to the test monitor is a final strong source of experimental uncertainty, as very few monitors commercially available are capable of accurately representing hue
In color theory, hue is one of the main properties (called Color appearance model#Color appearance parameters, color appearance parameters) of a color, defined technically in the CIECAM02 model as "the degree to which a Stimulus (physiology ...
, tone and saturation
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
**Saturated and unsaturated compounds
** Degree of unsaturation
**Saturated fat or fatty aci ...
consistently at all viewing angles incident to the monitor.
Observer error
Several sources of error (and therefore, inherent accuracy shortcomings) are directly related to the observer. Although CIE demonstrates several sets of data regarding the optimal, standard observer, each individual observer differs slightly from the baseline. Factors likevisual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
, color blindness and visual system defects (cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble w ...
, surgeries, LASIK
LASIK or Lasik (''laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis''), commonly referred to as laser eye surgery or laser vision correction, is a type of refractive surgery for the correction of myopia, hyperopia, and an actual cure for astigmatism, since ...
, tinted optics, poor cone responsivity, etc.) are all directly tied to observer color perception accuracy. The accuracy of an observers test answers are represented in Test Results
Test results and interpretation

 Noting the sources of error previously addressed that are introduced by environmental factors and observer uncertainties, several digital test sources offer software installations that analyze the information garnered from the test. Data generated fro
Noting the sources of error previously addressed that are introduced by environmental factors and observer uncertainties, several digital test sources offer software installations that analyze the information garnered from the test. Data generated froX-Rite’s
online test offer several types of information, most notably the Total Estimation Score (TES), Color Vision Deficiency Type (CVDT) and Color Vision Deficiency Severity (CVDS). TES is an automated, generated value that calculates the number of tiles placed incorrectly and scales the value for uniform analysis. Average TES scores range from thirty to forty in series tests; while scores exceeding seventy can point to a marker for color blindness. Lower scores are intended to point to significantly increased color vision accuracy, as the TES score is directly correlated to the number of tiles incorrectly identified. Based on an axis interpretation of the information generated, a color vision deficiency type is also determined, based on a straight line plotted to intersect the center of the Munsell color sphere and the peak point of the highest color error spike. This axis is used to determine the color error tendencies the eye. From this information, if a value of seventy or higher is returned, a clinical form of color blindness can be estimated based upon the location of the CVDT axis. The
magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of color error peaks is used to determine the magnitude of the observers Color Vision Deficiency Severity. Accuracy of the test is relative to the display and based upon its correct calibration.
Relevant markets
Several industrial and commercial markets have great need for characterized and accurate color vision as well as tests to quantify color vision accuracy. Among these are divisions like healthcare systems, design companies and photography and motion picture industries. In order to generate color accurate products, employee vision accuracy is crucial as well.Design
In the design sphere, there are several common yet largely important uses for color accuracy that lean heavily on the designers ability to accurately sense color. Careers such as graphic design, photography, graphics and color development are common fields that rely heavily on employees with accurate color vision. Additionally, paint engineering also relies heavily on color science employees with a demonstrated acuity in color vision. Examples of relevant companies includesPantone
Pantone LLC (stylized as PANTONE) is a limited liability company headquartered in Carlstadt, New Jersey. The company is best known for its Pantone Matching System (PMS), a proprietary color space used in a variety of industries, notably graphic ...
and Sherwin-Williams
Sherwin-Williams Company is an American Cleveland, Ohio–based company in the paint and coating manufacturing industry. The company primarily engages in the manufacture, distribution, and sale of paints, coatings, floorcoverings, and related p ...
.
Healthcare
In the medical sphere, it is important to have products to measure patients color vision. While medically professional vision tests are available, a Munsell Vision Test is often an informal and relevant test to determine a potential need for more thorough vision testing at the hands of pro staff or optometry experts. As previously mentioned, the Munsell-Farnsworth D15 Color Vision Test is a capable and professional method to test an individual.Motion picture
Motion picture professionals also desire color vision acuity information for integral parts of film post production like color timing and final color correction. Since these processes are highly subjective to individuals such as the director and the colorist, accurate color vision is vital to the final aesthetic appearance of the film. In addition to this, engineers involved in the production and chemistry of film and digital systems engineering are reliant on proper color vision to construct and engineer imaging systems that accurately sense and represent color in stored images and display.See also
*Gamma correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
: V_\text = ...
* International Commission on Illumination
The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name, Commission internationale de l'éclairage) is the international authority on light, illumination, colour, and colour spaces. It was established in 1913 a ...
* Standard illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting.
CIE illuminants
The Inter ...
* Visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
* White point
A white point (often referred to as reference white or target white in technical documents) is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Farnsworth-Munsell 100 hue test Color vision Diagnostic ophthalmology Test items