Faraday Title Page on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English
Volume 1">James Clerk Maxwell">The Scientific Papers of SI unit of capacitance">James Clerk Maxwell
Volume 1p. 360; Courier Dover 2003, The International System of Units">SI unit of capacitance is named in his honour: the farad. Albert Einstein kept a picture of Faraday on his study wall, alongside pictures of Arthur Schopenhauer and James Clerk Maxwell. Physicist Ernest Rutherford stated, "When we consider the magnitude and extent of his discoveries and their influence on the progress of science and of industry, there is no honour too great to pay to the memory of Faraday, one of the greatest scientific discoverers of all time." Rao, C.N.R. (2000). ''Understanding Chemistry''. Universities Press. . p. 281.
 In 1812, at the age of 20 and at the end of his apprenticeship, Faraday attended lectures by the eminent English chemist
In 1812, at the age of 20 and at the end of his apprenticeship, Faraday attended lectures by the eminent English chemist
 In June 1832, the
In June 1832, the  Faraday suffered a nervous breakdown in 1839 but eventually returned to his investigations into electromagnetism. In 1848, as a result of representations by the Prince Consort, Faraday was awarded a grace and favour house in
Faraday suffered a nervous breakdown in 1839 but eventually returned to his investigations into electromagnetism. In 1848, as a result of representations by the Prince Consort, Faraday was awarded a grace and favour house in
 Faraday's earliest chemical work was as an assistant to
Faraday's earliest chemical work was as an assistant to
 In 1821, soon after the Danish physicist and chemist
In 1821, soon after the Danish physicist and chemist 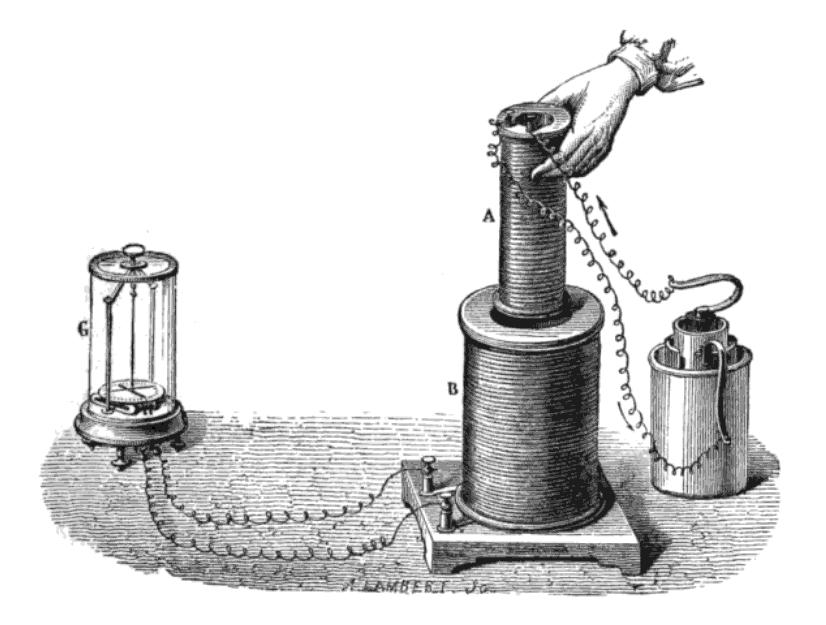 From his initial discovery in 1821, Faraday continued his laboratory work, exploring electromagnetic properties of materials and developing requisite experience. In 1824, Faraday briefly set up a circuit to study whether a magnetic field could regulate the flow of a current in an adjacent wire, but he found no such relationship. This experiment followed similar work conducted with light and magnets three years earlier that yielded identical results. During the next seven years, Faraday spent much of his time perfecting his recipe for optical quality (heavy) glass, borosilicate of lead, which he used in his future studies connecting light with magnetism. In his spare time, Faraday continued publishing his experimental work on optics and electromagnetism; he conducted correspondence with scientists whom he had met on his journeys across Europe with Davy, and who were also working on electromagnetism. Two years after the death of Davy, in 1831, he began his great series of experiments in which he discovered
From his initial discovery in 1821, Faraday continued his laboratory work, exploring electromagnetic properties of materials and developing requisite experience. In 1824, Faraday briefly set up a circuit to study whether a magnetic field could regulate the flow of a current in an adjacent wire, but he found no such relationship. This experiment followed similar work conducted with light and magnets three years earlier that yielded identical results. During the next seven years, Faraday spent much of his time perfecting his recipe for optical quality (heavy) glass, borosilicate of lead, which he used in his future studies connecting light with magnetism. In his spare time, Faraday continued publishing his experimental work on optics and electromagnetism; he conducted correspondence with scientists whom he had met on his journeys across Europe with Davy, and who were also working on electromagnetism. Two years after the death of Davy, in 1831, he began his great series of experiments in which he discovered 
 Faraday's breakthrough came when he wrapped two insulated coils of wire around an iron ring, and found that, upon passing a current through one coil, a momentary current was induced in the other coil. This phenomenon is now known as
Faraday's breakthrough came when he wrapped two insulated coils of wire around an iron ring, and found that, upon passing a current through one coil, a momentary current was induced in the other coil. This phenomenon is now known as
 In 1845, Faraday discovered that many materials exhibit a weak repulsion from a magnetic field: a phenomenon he termed diamagnetism.
Faraday also discovered that the plane of
In 1845, Faraday discovered that many materials exhibit a weak repulsion from a magnetic field: a phenomenon he termed diamagnetism.
Faraday also discovered that the plane of
 Faraday had a long association with the Royal Institution of Great Britain. He was appointed Assistant Superintendent of the House of the Royal Institution in 1821. He was elected a
Faraday had a long association with the Royal Institution of Great Britain. He was appointed Assistant Superintendent of the House of the Royal Institution in 1821. He was elected a  As a respected scientist in a nation with strong maritime interests, Faraday spent extensive amounts of time on projects such as the construction and operation of
As a respected scientist in a nation with strong maritime interests, Faraday spent extensive amounts of time on projects such as the construction and operation of  Faraday assisted with the planning and judging of exhibits for the
Faraday assisted with the planning and judging of exhibits for the  Before his famous Christmas lectures, Faraday delivered chemistry lectures for the City Philosophical Society from 1816 to 1818 in order to refine the quality of his lectures.
Between 1827 and 1860 at the
Before his famous Christmas lectures, Faraday delivered chemistry lectures for the City Philosophical Society from 1816 to 1818 in order to refine the quality of his lectures.
Between 1827 and 1860 at the
 A statue of Faraday stands in
A statue of Faraday stands in  A
A
File:M Faraday Lab H Moore.jpg, Michael Faraday in his laboratory, c. 1850s.
File:Royal Institution - Michael Faraday's study.jpg , Michael Faraday's study at the Royal Institution.
File:Michael Faradays Flat at Royal Institution.jpg , Michael Faraday's flat at the Royal Institution.
File:Harriett Moore small.jpg, Artist Harriet Jane Moore who documented Faraday's life in watercolours.
 Faraday's books, with the exception of ''Chemical Manipulation'', were collections of scientific papers or transcriptions of lectures.
Faraday's books, with the exception of ''Chemical Manipulation'', were collections of scientific papers or transcriptions of lectures.
2nd ed. 18303rd ed. 1842
* ; vol. iii. Richard Taylor and William Francis, 1855 * * * * – published in eight volumes; see also th
2009 publication
of Faraday's diary * * – volume 2, 1993; volume 3, 1996; volume 4, 1999 *
Course of six lectures on the various forces of matter, and their relations to each other
London; Glasgow: R. Griffin, 1860. * The Liquefaction of Gases, Edinburgh: W.F. Clay, 1896.
The letters of Faraday and Schoenbein 1836–1862. With notes, comments and references to contemporary letters
London: Williams & Norgate 1899.
Digital edition
by the
File:Faraday-1.jpg, Volumes 1-3 of Michael Faraday's "Experimental researches in electricity," from 1839, 1844, and 1855, respectively
File:Faraday-2.jpg, Title page of Volume 1 of Michael Faraday's "Experimental researches in electricity," 1839
File:Faraday-7.jpg, First page of Volume 1 of Michael Faraday's "Experimental researches in electricity," 1839
scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts Scientific method, scientific research to advance knowledge in an Branches of science, area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, ...
who contributed to the study of electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of a ...
and electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outco ...
. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk ...
, diamagnetism and electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
.
Although Faraday received little formal education, he was one of the most influential scientists in history. It was by his research on the magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
around a conductor carrying a direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
that Faraday established the concept of the electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical c ...
in physics. Faraday also established that magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles ...
could affect rays of light and that there was an underlying relationship between the two phenomena.. the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica. He similarly discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and the laws of electrolysis. His invention
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an i ...
s of electromagnetic rotary devices formed the foundation of electric motor technology, and it was largely due to his efforts that electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
became practical for use in technology.
As a chemist, Faraday discovered benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, ...
, investigated the clathrate hydrate
Clathrate hydrates, or gas hydrates, clathrates, hydrates, etc., are crystalline water-based solids physically resembling ice, in which small non-polar molecules (typically gases) or polar molecules with large hydrophobic moieties are trapped ins ...
of chlorine, invented an early form of the Bunsen burner and the system of oxidation number
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Co ...
s, and popularised terminology such as "anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
", "cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
", "electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials de ...
" and "ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
". Faraday ultimately became the first and foremost Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
, a lifetime position.
Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who conveyed his ideas in clear and simple language; his mathematical abilities, however, did not extend as far as trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. T ...
and were limited to the simplest algebra. James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and ligh ...
took the work of Faraday and others and summarized it in a set of equations which is accepted as the basis of all modern theories of electromagnetic phenomena. On Faraday's uses of lines of force, Maxwell wrote that they show Faraday "to have been in reality a mathematician of a very high order – one from whom the mathematicians of the future may derive valuable and fertile methods."The Scientific Papers of James Clerk MaxwellVolume 1">James Clerk Maxwell">The Scientific Papers of SI unit of capacitance">James Clerk Maxwell
Volume 1p. 360; Courier Dover 2003, The International System of Units">SI unit of capacitance is named in his honour: the farad. Albert Einstein kept a picture of Faraday on his study wall, alongside pictures of Arthur Schopenhauer and James Clerk Maxwell. Physicist Ernest Rutherford stated, "When we consider the magnitude and extent of his discoveries and their influence on the progress of science and of industry, there is no honour too great to pay to the memory of Faraday, one of the greatest scientific discoverers of all time." Rao, C.N.R. (2000). ''Understanding Chemistry''. Universities Press. . p. 281.
Personal life
Early life
Michael Faraday was born on 22 September 1791 inNewington Butts
Newington Butts is a former hamlet, now an area of the London Borough of Southwark, that gives its name to a segment of the A3 road running south-west from the Elephant and Castle junction. The road continues as Kennington Park Road leading to ...
, Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. ...
(which is now part of the London Borough of Southwark). His family was not well off. His father, James, was a member of the Glasite sect of Christianity. James Faraday moved his wife, Margaret (née Hastwell), and two children to London during the winter of 1790 from Outhgill in Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
, where he had been an apprentice to the village blacksmith. Michael was born in the autumn of that year. The young Michael Faraday, who was the third of four children, having only the most basic school education, had to educate himself.
At the age of 14 he became an apprentice to George Riebau, a local bookbinder and bookseller in Blandford Street. During his seven-year apprenticeship Faraday read many books, including Isaac Watts's ''The Improvement of the Mind'', and he enthusiastically implemented the principles and suggestions contained therein. He also developed an interest in science, especially in electricity. Faraday was particularly inspired by the book ''Conversations on Chemistry'' by Jane Marcet
Jane Marcet (née Haldimand) (1 January 1769 – 28 June 1858) was an English salonnière of Swiss origin, and an innovative writer of popular, explanatory science books. She also broke ground with ''Conversations on Political Economy'' (1816 ...
.
Adult life
 In 1812, at the age of 20 and at the end of his apprenticeship, Faraday attended lectures by the eminent English chemist
In 1812, at the age of 20 and at the end of his apprenticeship, Faraday attended lectures by the eminent English chemist Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
of the Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
and the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
, and John Tatum, founder of the City Philosophical Society. Many of the tickets for these lectures were given to Faraday by William Dance
William Dance (20 December 1755 – 5 June 1840) was an English pianist and violinist.
Life
William Dance was the grandson of the architect George Dance (c.1694–1768). His father was the actor James Dance (1721–1774) and his mother may have ...
, who was one of the founders of the Royal Philharmonic Society. Faraday subsequently sent Davy a 300-page book based on notes that he had taken during these lectures. Davy's reply was immediate, kind, and favourable. In 1813, when Davy damaged his eyesight in an accident with nitrogen trichloride
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NCl3. This yellow, oily, pungent-smelling and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a byproduct of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivative ...
, he decided to employ Faraday as an assistant. Coincidentally one of the Royal Institution's assistants, John Payne, was sacked and Sir Humphry Davy had been asked to find a replacement; thus he appointed Faraday as Chemical Assistant at the Royal Institution on 1 March 1813. Very soon Davy entrusted Faraday with the preparation of nitrogen trichloride samples, and they both were injured in an explosion of this very sensitive substance.
Faraday married Sarah Barnard (1800–1879) on 12 June 1821. They met through their families at the Sandemanian church, and he confessed his faith to the Sandemanian congregation the month after they were married. They had no children.
Faraday was a devout Christian; his Sandemanian denomination was an offshoot of the Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation of 1560, when it split from t ...
. Well after his marriage, he served as deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions. Major Christian churches, such as the Catholic Churc ...
and for two terms as an elder
An elder is someone with a degree of seniority or authority.
Elder or elders may refer to:
Positions Administrative
* Elder (administrative title), a position of authority
Cultural
* North American Indigenous elder, a person who has and tr ...
in the meeting house of his youth. His church was located at Paul's Alley in the Barbican
A barbican (from fro, barbacane) is a fortified outpost or fortified gateway, such as at an outer fortifications, defense perimeter of a city or castle, or any tower situated over a gate or bridge which was used for defensive purposes.
Europe ...
. This meeting house relocated in 1862 to Barnsbury Grove, Islington
Islington () is a district in the north of Greater London, England, and part of the London Borough of Islington. It is a mainly residential district of Inner London, extending from Islington's High Street to Highbury Fields, encompassing the ar ...
; this North London location was where Faraday served the final two years of his second term as elder prior to his resignation from that post. Biographers have noted that "a strong sense of the unity of God and nature pervaded Faraday's life and work."
Later life
 In June 1832, the
In June 1832, the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
granted Faraday an honorary Doctor of Civil Law degree. During his lifetime, he was offered a knighthood
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the Gr ...
in recognition for his services to science, which he turned down on religious grounds, believing that it was against the word of the Bible to accumulate riches and pursue worldly reward, and stating that he preferred to remain "plain Mr Faraday to the end". Elected a Fellow
A fellow is a concept whose exact meaning depends on context.
In learned or professional societies, it refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements.
Within the context of higher education ...
of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in 1824, he twice refused to become President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
. He became the first Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
in 1833.
In 1832, Faraday was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and ...
. He was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences ( sv, Kungliga Vetenskapsakademien) is one of the Swedish Royal Academies, royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization that takes special ...
in 1838. In 1840, he was elected to the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit ...
. He was one of eight foreign members elected to the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
in 1844. In 1849 he was elected as associated member to the Royal Institute of the Netherlands, which two years later became the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences
The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences ( nl, Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, abbreviated: KNAW) is an organization dedicated to the advancement of science and literature in the Netherlands. The academy is housed ...
and he was subsequently made foreign member.
 Faraday suffered a nervous breakdown in 1839 but eventually returned to his investigations into electromagnetism. In 1848, as a result of representations by the Prince Consort, Faraday was awarded a grace and favour house in
Faraday suffered a nervous breakdown in 1839 but eventually returned to his investigations into electromagnetism. In 1848, as a result of representations by the Prince Consort, Faraday was awarded a grace and favour house in Hampton Court
Hampton Court Palace is a Grade I listed royal palace in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, southwest and upstream of central London on the River Thames. The building of the palace began in 1514 for Cardinal Thomas Wolsey, the chief ...
in Middlesex, free of all expenses and upkeep. This was the Master Mason's House, later called Faraday House, and now No. 37 Hampton Court Road. In 1858 Faraday retired to live there.
Having provided a number of various service projects for the British government, when asked by the government to advise on the production of chemical weapons for use in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
(1853–1856), Faraday refused to participate, citing ethical reasons.
Faraday died at his house at Hampton Court
Hampton Court Palace is a Grade I listed royal palace in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, southwest and upstream of central London on the River Thames. The building of the palace began in 1514 for Cardinal Thomas Wolsey, the chief ...
on 25 August 1867, aged 75. He had some years before turned down an offer of burial in Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
upon his death, but he has a memorial plaque there, near Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
's tomb. Faraday was interred in the dissenter
A dissenter (from the Latin ''dissentire'', "to disagree") is one who dissents (disagrees) in matters of opinion, belief, etc.
Usage in Christianity
Dissent from the Anglican church
In the social and religious history of England and Wales, and ...
s' (non-Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
) section of Highgate Cemetery
Highgate Cemetery is a place of burial in north London, England. There are approximately 170,000 people buried in around 53,000 graves across the West and East Cemeteries. Highgate Cemetery is notable both for some of the people buried there as ...
.
Scientific achievements
Chemistry
 Faraday's earliest chemical work was as an assistant to
Faraday's earliest chemical work was as an assistant to Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
. Faraday was involved in the study of chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate betwee ...
; he discovered two new compounds of chlorine and carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
. He also conducted the first rough experiments on the diffusion of gases, a phenomenon that was first pointed out by John Dalton
John Dalton (; 5 or 6 September 1766 – 27 July 1844) was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist. He is best known for introducing the atomic theory into chemistry, and for his research into colour blindness, which he had. Colour b ...
. The physical importance of this phenomenon was more fully revealed by Thomas Graham and Joseph Loschmidt. Faraday succeeded in liquefying several gases, investigated the alloys of steel, and produced several new kinds of glass intended for optical purposes. A specimen of one of these heavy glasses subsequently became historically important; when the glass was placed in a magnetic field Faraday determined the rotation of the plane of polarisation of light. This specimen was also the first substance found to be repelled by the poles of a magnet.
Faraday invented an early form of what was to become the Bunsen burner, which is still in practical use in science laboratories around the world as a convenient source of heat.
Faraday worked extensively in the field of chemistry, discovering chemical substances such as benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, ...
(which he called bicarburet of hydrogen) and liquefying gases such as chlorine. The liquefying of gases helped to establish that gases are the vapours of liquids possessing a very low boiling point and gave a more solid basis to the concept of molecular aggregation. In 1820 Faraday reported the first synthesis of compounds made from carbon and chlorine, C2Cl6 and C2Cl4, and published his results the following year. Faraday also determined the composition of the chlorine clathrate hydrate
Clathrate hydrates, or gas hydrates, clathrates, hydrates, etc., are crystalline water-based solids physically resembling ice, in which small non-polar molecules (typically gases) or polar molecules with large hydrophobic moieties are trapped ins ...
, which had been discovered by Humphry Davy in 1810. Faraday is also responsible for discovering the laws of electrolysis, and for popularizing terminology such as anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
, cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
, electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials de ...
, and ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
, terms proposed in large part by William Whewell
William Whewell ( ; 24 May 17946 March 1866) was an English polymath, scientist, Anglican priest, philosopher, theologian, and historian of science. He was Master of Trinity College, Cambridge. In his time as a student there, he achieved dist ...
.
Faraday was the first to report what later came to be called metallic nanoparticles
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 1 ...
. In 1847 he discovered that the optical properties of gold colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend ...
s differed from those of the corresponding bulk metal. This was probably the first reported observation of the effects of quantum
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantizati ...
size, and might be considered to be the birth of nanoscience.
Electricity and magnetism
Faraday is best known for his work on electricity and magnetism. His first recorded experiment was the construction of a voltaic pile with seven British halfpenny coins, stacked together with seven discs of sheet zinc, and six pieces of paper moistened with salt water. With this pile he decomposed sulfate of magnesia (first letter to Abbott, 12 July 1812). In 1821, soon after the Danish physicist and chemist
In 1821, soon after the Danish physicist and chemist Hans Christian Ørsted
Hans Christian Ørsted ( , ; often rendered Oersted in English; 14 August 17779 March 1851) was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity ...
discovered the phenomenon of electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of a ...
, Davy and William Hyde Wollaston
William Hyde Wollaston (; 6 August 1766 – 22 December 1828) was an English chemist and physicist who is famous for discovering the chemical elements palladium and rhodium. He also developed a way to process platinum ore into malleable ingo ...
tried, but failed, to design an electric motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagneti ...
. Faraday, having discussed the problem with the two men, went on to build two devices to produce what he called "electromagnetic rotations". One of these, now known as the homopolar motor
A homopolar motor is a direct current electric motor with two magnetic poles, the conductors of which always cut unidirectional lines of magnetic flux by rotating a conductor around a fixed axis so that the conductor is at right angles to a s ...
, caused a continuous circular motion that was engendered by the circular magnetic force around a wire that extended into a pool of mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
wherein was placed a magnet; the wire would then rotate around the magnet if supplied with current from a chemical battery. These experiments and inventions, first carried out in the basement of the Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
on 3 September 1821, formed the foundation of modern electromagnetic technology. Faraday published the results of his discovery in the ''Quarterly Journal of Science
''Quarterly Journal of Science'' was the title of two British scientific periodicals of the 19th century.
The first was established in 1816 by William Thomas Brande, as the ''Quarterly Journal of Science, Literature and the Arts''. He edited it w ...
'', and sent copies of his paper along with pocket-sized models of his device to colleagues around the world so they could also witness the phenomenon of electromagnetic rotations. In his excitement, Faraday hastily released the paper which had not acknowledged his work with either Wollaston or Davy. The resulting controversy within the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
strained his mentor relationship with Davy and may well have contributed to Faraday's assignment to other activities, which consequently prevented his involvement in electromagnetic research for several years.
 From his initial discovery in 1821, Faraday continued his laboratory work, exploring electromagnetic properties of materials and developing requisite experience. In 1824, Faraday briefly set up a circuit to study whether a magnetic field could regulate the flow of a current in an adjacent wire, but he found no such relationship. This experiment followed similar work conducted with light and magnets three years earlier that yielded identical results. During the next seven years, Faraday spent much of his time perfecting his recipe for optical quality (heavy) glass, borosilicate of lead, which he used in his future studies connecting light with magnetism. In his spare time, Faraday continued publishing his experimental work on optics and electromagnetism; he conducted correspondence with scientists whom he had met on his journeys across Europe with Davy, and who were also working on electromagnetism. Two years after the death of Davy, in 1831, he began his great series of experiments in which he discovered
From his initial discovery in 1821, Faraday continued his laboratory work, exploring electromagnetic properties of materials and developing requisite experience. In 1824, Faraday briefly set up a circuit to study whether a magnetic field could regulate the flow of a current in an adjacent wire, but he found no such relationship. This experiment followed similar work conducted with light and magnets three years earlier that yielded identical results. During the next seven years, Faraday spent much of his time perfecting his recipe for optical quality (heavy) glass, borosilicate of lead, which he used in his future studies connecting light with magnetism. In his spare time, Faraday continued publishing his experimental work on optics and electromagnetism; he conducted correspondence with scientists whom he had met on his journeys across Europe with Davy, and who were also working on electromagnetism. Two years after the death of Davy, in 1831, he began his great series of experiments in which he discovered electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk ...
, recording in his laboratory diary on 28 October 1831 he was; "making many experiments with the great magnet of the Royal Society".
 Faraday's breakthrough came when he wrapped two insulated coils of wire around an iron ring, and found that, upon passing a current through one coil, a momentary current was induced in the other coil. This phenomenon is now known as
Faraday's breakthrough came when he wrapped two insulated coils of wire around an iron ring, and found that, upon passing a current through one coil, a momentary current was induced in the other coil. This phenomenon is now known as mutual induction
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The flow of electric current creates a magnetic field around the conductor. The field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
. The iron ring-coil apparatus is still on display at the Royal Institution. In subsequent experiments, he found that if he moved a magnet through a loop of wire an electric current flowed in that wire. The current also flowed if the loop was moved over a stationary magnet. His demonstrations established that a changing magnetic field produces an electric field; this relation was modelled mathematically by James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and ligh ...
as Faraday's law, which subsequently became one of the four Maxwell equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.
Th ...
, and which have in turn evolved into the generalization known today as field theory. Faraday would later use the principles he had discovered to construct the electric dynamo, the ancestor of modern power generators and the electric motor.
In 1832, he completed a series of experiments aimed at investigating the fundamental nature of electricity; Faraday used " static", batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
, and " animal electricity" to produce the phenomena of electrostatic attraction, electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
, magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles ...
, etc. He concluded that, contrary to the scientific opinion of the time, the divisions between the various "kinds" of electricity were illusory. Faraday instead proposed that only a single "electricity" exists, and the changing values of quantity and intensity (current and voltage) would produce different groups of phenomena.
Near the end of his career, Faraday proposed that electromagnetic forces extended into the empty space around the conductor. This idea was rejected by his fellow scientists, and Faraday did not live to see the eventual acceptance of his proposition by the scientific community. Faraday's concept of lines of flux emanating from charged bodies and magnets provided a way to visualize electric and magnetic fields; that conceptual model was crucial for the successful development of the electromechanical devices that dominated engineering and industry for the remainder of the 19th century.
Diamagnetism
 In 1845, Faraday discovered that many materials exhibit a weak repulsion from a magnetic field: a phenomenon he termed diamagnetism.
Faraday also discovered that the plane of
In 1845, Faraday discovered that many materials exhibit a weak repulsion from a magnetic field: a phenomenon he termed diamagnetism.
Faraday also discovered that the plane of polarization
Polarization or polarisation may refer to:
Mathematics
*Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds
*Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by ...
of linearly polarized light can be rotated by the application of an external magnetic field aligned with the direction in which the light is moving. This is now termed the Faraday effect. In Sept 1845 he wrote in his notebook, "I have at last succeeded in ''illuminating a magnetic curve'' or ''line of force
A line of force in Faraday's extended sense is synonymous with Maxwell's line of induction. According to J.J. Thomson, Faraday usually discusses ''lines of force'' as chains of polarized particles in a dielectric, yet sometimes Faraday discusses t ...
'' and in ''magnetising a ray of light''".
Later on in his life, in 1862, Faraday used a spectroscope to search for a different alteration of light, the change of spectral lines by an applied magnetic field. The equipment available to him was, however, insufficient for a definite determination of spectral change. Pieter Zeeman
Pieter Zeeman (; 25 May 1865 – 9 October 1943) was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Hendrik Lorentz for his discovery of the Zeeman effect.
Childhood and youth
Pieter Zeeman was born in Zonnemaire, a small town ...
later used an improved apparatus to study the same phenomenon, publishing his results in 1897 and receiving the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics for his success. In both his 1897 paper and his Nobel acceptance speech, Zeeman made reference to Faraday's work.
Faraday cage
In his work on static electricity, Faraday's ice pail experiment demonstrated that the charge resided only on the exterior of a charged conductor, and exterior charge had no influence on anything enclosed within a conductor. This is because the exterior charges redistribute such that the interior fields emanating from them cancel one another. This shielding effect is used in what is now known as aFaraday cage
A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of conductive material, or in the case of a Faraday cage, by a mesh of such materials. Faraday cage ...
. In January 1836, Faraday had put a wooden frame, 12ft square, on four glass supports and added paper walls and wire mesh. He then stepped inside and electrified it. When he stepped out of his electrified cage, Faraday had shown that electricity was a force, not an imponderable fluid as was believed at the time.
Royal Institution and public service
 Faraday had a long association with the Royal Institution of Great Britain. He was appointed Assistant Superintendent of the House of the Royal Institution in 1821. He was elected a
Faraday had a long association with the Royal Institution of Great Britain. He was appointed Assistant Superintendent of the House of the Royal Institution in 1821. He was elected a Fellow
A fellow is a concept whose exact meaning depends on context.
In learned or professional societies, it refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements.
Within the context of higher education ...
of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in 1824. In 1825, he became Director of the Laboratory of the Royal Institution. Six years later, in 1833, Faraday became the first Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution of Great Britain, a position to which he was appointed for life without the obligation to deliver lectures. His sponsor and mentor was John 'Mad Jack' Fuller
John Fuller (20 February 1757 – 11 April 1834), better known as "Mad Jack" Fuller (although he himself preferred to be called "Honest John" Fuller), was Squire of the hamlet of Brightling, in Sussex, and politician who sat in the House of Com ...
, who created the position at the Royal Institution for Faraday.
Beyond his scientific research into areas such as chemistry, electricity, and magnetism at the Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
, Faraday undertook numerous, and often time-consuming, service projects for private enterprise and the British government. This work included investigations of explosions in coal mines, being an expert witness in court, and along with two engineers from Chance Brothers c.1853, the preparation of high-quality optical glass, which was required by Chance for its lighthouses. In 1846, together with Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known as the author of ''Principles of Geolo ...
, he produced a lengthy and detailed report on a serious explosion
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume associated with an extreme outward release of energy, usually with the generation of high temperatures and release of high-pressure gases. Supersonic explosions created by high explosives are known ...
in the colliery at Haswell, County Durham, which killed 95 miners. Their report was a meticulous forensic investigation and indicated that coal dust contributed to the severity of the explosion. The first-time explosions had been linked to dust, Faraday gave a demonstration during a lecture on how ventilation could prevent it. The report should have warned coal owners of the hazard of coal dust explosions, but the risk was ignored for over 60 years until the 1913 Senghenydd Colliery Disaster.
 As a respected scientist in a nation with strong maritime interests, Faraday spent extensive amounts of time on projects such as the construction and operation of
As a respected scientist in a nation with strong maritime interests, Faraday spent extensive amounts of time on projects such as the construction and operation of lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
s and protecting the bottoms of ships from corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
. His workshop still stands at Trinity Buoy Wharf above the Chain and Buoy Store, next to London's only lighthouse where he carried out the first experiments in electric lighting for lighthouses.
Faraday was also active in what would now be called environmental science
Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physics, biology, and geography (including ecology, chemistry, plant science, zoology, mineralogy, oceanography, limnology, soil science, geology and physical geograp ...
, or engineering. He investigated industrial pollution at Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
and was consulted on air pollution at the Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's oldest company and the official maker of British coins.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly owned by His Majesty's Treasury and is under an exclus ...
. In July 1855, Faraday wrote a letter to ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (fou ...
'' on the subject of the foul condition of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
, which resulted in an often-reprinted cartoon in ''Punch
Punch commonly refers to:
* Punch (combat), a strike made using the hand closed into a fist
* Punch (drink), a wide assortment of drinks, non-alcoholic or alcoholic, generally containing fruit or fruit juice
Punch may also refer to:
Places
* Pun ...
''. (See also The Great Stink
The Great Stink was an event in Central London during July and August 1858 in which the hot weather exacerbated the smell of untreated human waste and industrial effluent that was present on the banks of the River Thames. The problem had bee ...
).
 Faraday assisted with the planning and judging of exhibits for the
Faraday assisted with the planning and judging of exhibits for the Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary The Crystal Palace, structure in which it was held), was an International Exhib ...
of 1851 in London. He also advised the National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director o ...
on the cleaning and protection of its art collection, and served on the National Gallery Site Commission in 1857. Education was another of Faraday's areas of service; he lectured on the topic in 1854 at the Royal Institution, and, in 1862, he appeared before a Public Schools Commission to give his views on education in Great Britain. Faraday also weighed in negatively on the public's fascination with table-turning, mesmerism
Animal magnetism, also known as mesmerism, was a protoscientific theory developed by German doctor Franz Mesmer in the 18th century in relation to what he claimed to be an invisible natural force (''Lebensmagnetismus'') possessed by all livi ...
, and seances, and in so doing chastised both the public and the nation's educational system.
 Before his famous Christmas lectures, Faraday delivered chemistry lectures for the City Philosophical Society from 1816 to 1818 in order to refine the quality of his lectures.
Between 1827 and 1860 at the
Before his famous Christmas lectures, Faraday delivered chemistry lectures for the City Philosophical Society from 1816 to 1818 in order to refine the quality of his lectures.
Between 1827 and 1860 at the Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
in London, Faraday gave a series of nineteen Christmas lectures
The Royal Institution Christmas Lectures are a series of lectures on a single topic each, which have been held at the Royal Institution in London each year since 1825, missing 1939–1942 because of the Second World War. The lectures present sc ...
for young people, a series which continues today. The objective of the lectures was to present science to the general public in the hopes of inspiring them and generating revenue for the Royal Institution. They were notable events on the social calendar among London's gentry. Over the course of several letters to his close friend Benjamin Abbott, Faraday outlined his recommendations on the art of lecturing, writing "a flame should be lighted at the commencement and kept alive with unremitting splendour to the end". His lectures were joyful and juvenile, he delighted in filling soap bubbles with various gasses (in order to determine whether or not they are magnetic), but the lectures were also deeply philosophical. In his lectures he urged his audiences to consider the mechanics of his experiments: "you know very well that ice floats upon water ... Why does the ice float? Think of that, and philosophise". The subjects in his lectures consisted of Chemistry and Electricity, and included: 1841: ''The Rudiments of Chemistry'', 1843: ''First Principles of Electricity'', 1848: '' The Chemical History of a Candle'', 1851: ''Attractive Forces'', 1853: ''Voltaic Electricity'', 1854: ''The Chemistry of Combustion'', 1855: ''The Distinctive Properties of the Common Metals'', 1857: ''Static Electricity'', 1858: ''The Metallic Properties'', 1859: ''The Various Forces of Matter and their Relations to Each Other''.
Commemorations
 A statue of Faraday stands in
A statue of Faraday stands in Savoy Place
Savoy Place is a large red brick building on the north bank of the River Thames in London. It is on a street called Savoy Place; Savoy Hill and Savoy Street run along the sides of the building up to the Strand. In front is the Victoria Embankment ...
, London, outside the Institution of Engineering and Technology. The Michael Faraday Memorial
The Michael Faraday Memorial is a monument to the Victorian scientist Michael Faraday. It is located at Elephant Square in Elephant and Castle, London, England.
Description
The stainless steel box-shaped structure was designed by modern mov ...
, designed by brutalist
Brutalist architecture is an architectural style that emerged during the 1950s in the United Kingdom, among the reconstruction projects of the post-war era. Brutalist buildings are characterised by Minimalism (art), minimalist constructions th ...
architect Rodney Gordon and completed in 1961, is at the Elephant & Castle gyratory system, near Faraday's birthplace at Newington Butts
Newington Butts is a former hamlet, now an area of the London Borough of Southwark, that gives its name to a segment of the A3 road running south-west from the Elephant and Castle junction. The road continues as Kennington Park Road leading to ...
, London. Faraday School is located on Trinity Buoy Wharf where his workshop still stands above the Chain and Buoy Store, next to London's only lighthouse. Faraday Gardens is a small park in Walworth
Walworth () is a district of south London, England, within the London Borough of Southwark. It adjoins Camberwell to the south and Elephant and Castle to the north, and is south-east of Charing Cross.
Major streets in Walworth include the Old ...
, London, not far from his birthplace at Newington Butts. It lies within the local council ward of Faraday in the London Borough of Southwark. Michael Faraday Primary school is situated on the Aylesbury Estate in Walworth
Walworth () is a district of south London, England, within the London Borough of Southwark. It adjoins Camberwell to the south and Elephant and Castle to the north, and is south-east of Charing Cross.
Major streets in Walworth include the Old ...
.
A building at London South Bank University, which houses the institute's electrical engineering departments is named the Faraday Wing, due to its proximity to Faraday's birthplace in Newington Butts
Newington Butts is a former hamlet, now an area of the London Borough of Southwark, that gives its name to a segment of the A3 road running south-west from the Elephant and Castle junction. The road continues as Kennington Park Road leading to ...
. A hall at Loughborough University
Loughborough University (abbreviated as ''Lough'' or ''Lboro'' for post-nominals) is a public research university in the market town of Loughborough, Leicestershire, England. It has been a university since 1966, but it dates back to 1909, when L ...
was named after Faraday in 1960. Near the entrance to its dining hall is a bronze casting, which depicts the symbol of an electrical transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
, and inside there hangs a portrait, both in Faraday's honour. An eight-story building at the University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 15 ...
's science & engineering campus is named for Faraday, as is a recently built hall of accommodation at Brunel University
Brunel University London is a public research university located in the Uxbridge area of London, England. It was founded in 1966 and named after the Victorian engineer and pioneer of the Industrial Revolution, Isambard Kingdom Brunel. In June 1 ...
, the main engineering building at Swansea University, and the instructional and experimental physics building at Northern Illinois University. The former UK Faraday Station in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
was named after him.
Streets named for Faraday can be found in many British cities (e.g., London, Fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i ...
, Swindon
Swindon () is a town and unitary authority with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in Wiltshire, England. As of the 2021 Census, the population of Swindon was 201,669, making it the largest town in the county. The Swindon un ...
, Basingstoke
Basingstoke ( ) is the largest town in the county of Hampshire. It is situated in south-central England and lies across a valley at the source of the River Loddon, at the far western edge of The North Downs. It is located north-east of Southa ...
, Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located north-west of London, south-east ...
, Whitby
Whitby is a seaside town, port and civil parish in the Scarborough borough of North Yorkshire, England. Situated on the east coast of Yorkshire at the mouth of the River Esk, Whitby has a maritime, mineral and tourist heritage. Its East Clif ...
, Kirkby
Kirkby ( ) is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Knowsley, Merseyside, England. The town, historically in Lancashire, has a size of is north of Huyton and north-east of Liverpool. The population in 2016 was 41,495 making it the largest ...
, Crawley
Crawley () is a large town and borough in West Sussex, England. It is south of London, north of Brighton and Hove, and north-east of the county town of Chichester. Crawley covers an area of and had a population of 106,597 at the time of th ...
, Newbury, Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
, Aylesbury
Aylesbury ( ) is the county town of Buckinghamshire, South East England. It is home to the Roald Dahl Children's Gallery, David Tugwell`s house on Watermead and the Waterside Theatre. It is in central Buckinghamshire, midway between High Wy ...
and Stevenage
Stevenage ( ) is a large town and borough in Hertfordshire, England, about north of London. Stevenage is east of junctions 7 and 8 of the A1(M), between Letchworth Garden City to the north and Welwyn Garden City to the south. In 1946, Stevena ...
) as well as in France (Paris), Germany (Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
- Dahlem, Hermsdorf), Canada (Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Communauté métrop ...
, Quebec; Deep River, Ontario; Ottawa, Ontario), the United States ( Reston, Virginia), and New Zealand ( Hawke's Bay).
 A
A Royal Society of Arts
The Royal Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce (RSA), also known as the Royal Society of Arts, is a London-based organisation committed to finding practical solutions to social challenges. The RSA acronym is used m ...
blue plaque
A blue plaque is a permanent sign installed in a public place in the United Kingdom and elsewhere to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person, event, or former building on the site, serving as a historical marker. The term i ...
, unveiled in 1876, commemorates Faraday at 48 Blandford Street in London's Marylebone district. From 1991 until 2001, Faraday's picture featured on the reverse of Series E £20 banknotes issued by the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
. He was portrayed conducting a lecture at the Royal Institution with the magneto-electric spark apparatus. In 2002, Faraday was ranked number 22 in the BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board ex ...
's list of the 100 Greatest Britons
''100 Greatest Britons'' is a television series that was broadcast by the BBC in 2002. It was based on a television poll conducted to determine who the British people at that time considered the greatest Britons in history. The series included in ...
following a UK-wide vote.
Faraday has been commemorated on postage stamps issued by the Royal Mail
, kw, Postya Riel, ga, An Post Ríoga
, logo = Royal Mail.svg
, logo_size = 250px
, type = Public limited company
, traded_as =
, foundation =
, founder = Henry VIII
, location = London, England, UK
, key_people = * Keith Williams ...
. In 1991, as a pioneer of electricity he featured in their Scientific Achievements issue along with pioneers in three other fields (Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer.
Babbage is considered ...
(computing), Frank Whittle (jet engine) and Robert Watson-Watt (radar)). In 1999, under the title "Faraday's Electricity", he featured in their World Changers
Lifeway Christian Resources, based in Nashville, Tennessee, is the Christian media publishing and distribution division of the Southern Baptist Convention and provider of church business services. Until the end of their physical retail presenc ...
issue along with Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
, Edward Jenner and Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical com ...
.
The Faraday Institute for Science and Religion derives its name from the scientist, who saw his faith as integral to his scientific research. The logo of the institute is also based on Faraday's discoveries. It was created in 2006 by a $2,000,000 grant from the John Templeton Foundation to carry out academic research, to foster understanding of the interaction between science and religion, and to engage public understanding in both these subject areas.
The Faraday Institution, an independent energy storage research institute established in 2017, also derives its name from Michael Faraday. The organisation serves as the UK's primary research programme to advance battery science and technology, education, public engagement and market research.
Faraday's life and contributions to electromagnetics was the principal topic of the tenth episode, titled "The Electric Boy
"The Electric Boy" is the tenth episode of the American documentary television series '' Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey''. It premiered on May 11, 2014 on Fox, and aired on May 12, 2014 on National Geographic Channel. The episode was directed by Bi ...
", of the 2014 American science documentary series, '' Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey'', which was broadcast on Fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
and the National Geographic Channel
National Geographic (formerly National Geographic Channel; abbreviated and trademarked as Nat Geo or Nat Geo TV) is an American pay television television network, network and flagship (broadcasting), flagship channel owned by the National Geograp ...
.
Aldous Huxley wrote about Faraday in an essay entitled, ''A Night in Pietramala'': “He is always the natural philosopher. To discover truth is his sole aim and interest…even if I could be Shakespeare, I think I should still choose to be Faraday.” Calling Faraday her "hero", in a speech to the Royal Society, Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of the Conservative Party from 1975 to 1990. S ...
declared: “The value of his work must be higher than the capitalisation of all the shares on the Stock Exchange!”. She borrowed his bust from the Royal Institution and had it placed in the hall of 10 Downing Street
10 Downing Street in London, also known colloquially in the United Kingdom as Number 10, is the official residence and executive office of the first lord of the treasury, usually, by convention, the prime minister of the United Kingdom. Along wi ...
.
Awards named in Faraday's honour
In honor and remembrance of his great scientific contributions, several institutions have created prizes and awards in his name. This include: * The IETFaraday Medal
The Faraday Medal is a top international medal awarded by the UK Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) (previously called the Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)). It is part of the IET Achievement Medals collection of awards. T ...
* The Royal Society of London Michael Faraday Prize
The Royal Society of London Michael Faraday Prize is awarded for "excellence in communicating science to UK audiences". Named after Michael Faraday, the medal itself is made of silver gilt, and is accompanied by a purse of £2500.
Background
Th ...
* The Institute of Physics Michael Faraday Medal and Prize
The Michael Faraday Medal and Prize is a gold medal awarded annually by the Institute of Physics in experimental physics. The award is made "for outstanding and sustained contributions to experimental physics." The medal is accompanied by a pri ...
* The Royal Society of Chemistry Faraday Lectureship Prize
Gallery
Bibliography
 Faraday's books, with the exception of ''Chemical Manipulation'', were collections of scientific papers or transcriptions of lectures.
Faraday's books, with the exception of ''Chemical Manipulation'', were collections of scientific papers or transcriptions of lectures.Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilt ...
, p. 220 Since his death, Faraday's diary has been published, as have several large volumes of his letters and Faraday's journal from his travels with Davy in 1813–1815.
* 2nd ed. 1830
* ; vol. iii. Richard Taylor and William Francis, 1855 * * * * – published in eight volumes; see also th
2009 publication
of Faraday's diary * * – volume 2, 1993; volume 3, 1996; volume 4, 1999 *
Course of six lectures on the various forces of matter, and their relations to each other
London; Glasgow: R. Griffin, 1860. * The Liquefaction of Gases, Edinburgh: W.F. Clay, 1896.
The letters of Faraday and Schoenbein 1836–1862. With notes, comments and references to contemporary letters
London: Williams & Norgate 1899.
Digital edition
by the
University and State Library Düsseldorf
The University and State Library Düsseldorf (german: Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Düsseldorf, abbreviated ULB Düsseldorf) is a central service institution of Heinrich Heine University. Along with Bonn and Münster, it is also one of th ...
)
See also
* Faraday (Unit of electrical charge) * Forensic engineering *Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla ( ; ,"Tesla"
''
''
Tetrachloroethylene
*
Biography at The Royal Institution of Great Britain
Faraday as a Discoverer by John Tyndall, Project Gutenberg
(downloads)
The Life and Discoveries of Michael Faraday
by J. A. Crowther, London:
Complete Correspondence of Michael Faraday
Searchable full texts of all letters to and from Faraday, based on the standard edition by Frank James
Video Podcast
with Sir
The letters of Faraday and Schoenbein 1836–1862. With notes, comments and references to contemporary letters (1899)
full downloa
PDF
Faraday School, located on Trinity Buoy Wharf
at the New Model School Company Limited's website * ,
Timeline of hydrogen technologies
This is a timeline of the history of hydrogen technology.
Timeline
16th century
* c. 1520 – First recorded observation of hydrogen by Paracelsus through dissolution of metals (iron, zinc, and tin) in sulfuric acid.
17th century
* 1625 – Fi ...
* Timeline of low-temperature technology
The following is a timeline of low-temperature technology and cryogenic technology (refrigeration down to –273.15 °C, –459.67 °F or 0 K). It also lists important milestones in thermometry, thermodynamics, statistical physics and ca ...
* Zeeman effect
The Zeeman effect (; ) is the effect of splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is named after the Dutch physicist Pieter Zeeman, who discovered it in 1896 and received a Nobel prize ...
References
Sources
* * * *Further reading
Biographies
* * * * The British Electrical and Allied Manufacturers Association (1931). ''Faraday''. Edinburgh: R. & R. Clark, Ltd. * * * * * * * * * *External links
Biographies
Biography at The Royal Institution of Great Britain
Faraday as a Discoverer by John Tyndall, Project Gutenberg
(downloads)
The Life and Discoveries of Michael Faraday
by J. A. Crowther, London:
Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge
The Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge (SPCK) is a UK-based Christian charity. Founded in 1698 by Thomas Bray, it has worked for over 300 years to increase awareness of the Christian faith in the UK and across the world.
The SPCK is th ...
, 1920
Others
* * *Complete Correspondence of Michael Faraday
Searchable full texts of all letters to and from Faraday, based on the standard edition by Frank James
Video Podcast
with Sir
John Cadogan
Sir John Ivan George Cadogan (8 October 1930 – 9 February 2020) was a British organic chemist.
Early life
Cadogan was born in Pembrey, Carmarthenshire, Wales, United Kingdom. He was educated at Swansea Grammar School, where he achieved St ...
talking about Benzene since Faraday
The letters of Faraday and Schoenbein 1836–1862. With notes, comments and references to contemporary letters (1899)
full downloa
Faraday School, located on Trinity Buoy Wharf
at the New Model School Company Limited's website * ,
Chemical Heritage Foundation
The Science History Institute is an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it includes a library, museum, archive, research center and conference center.
It was fo ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Faraday, Michael
1791 births
1867 deaths
18th-century English people
19th-century English scientists
19th-century British physicists
19th-century British chemists
Experimental physicists
Optical physicists
English chemists
English inventors
English physicists
Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
Fellows of the Royal Society
Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences
Honorary members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences
People from Elephant and Castle
People associated with electricity
Burials at Highgate Cemetery
English Protestants
Members of the French Academy of Sciences
Members of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences
Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
Recipients of the Copley Medal
Recipients of the Pour le Mérite (civil class)
Royal Medal winners
Glasites
Writers about religion and science
Magneticians