Falco Peregrinus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in
 The peregrine falcon has a body length of and a wingspan from . The male and female have similar markings and
The peregrine falcon has a body length of and a wingspan from . The male and female have similar markings and
 ''Falco peregrinus'' was first described under its current
''Falco peregrinus'' was first described under its current
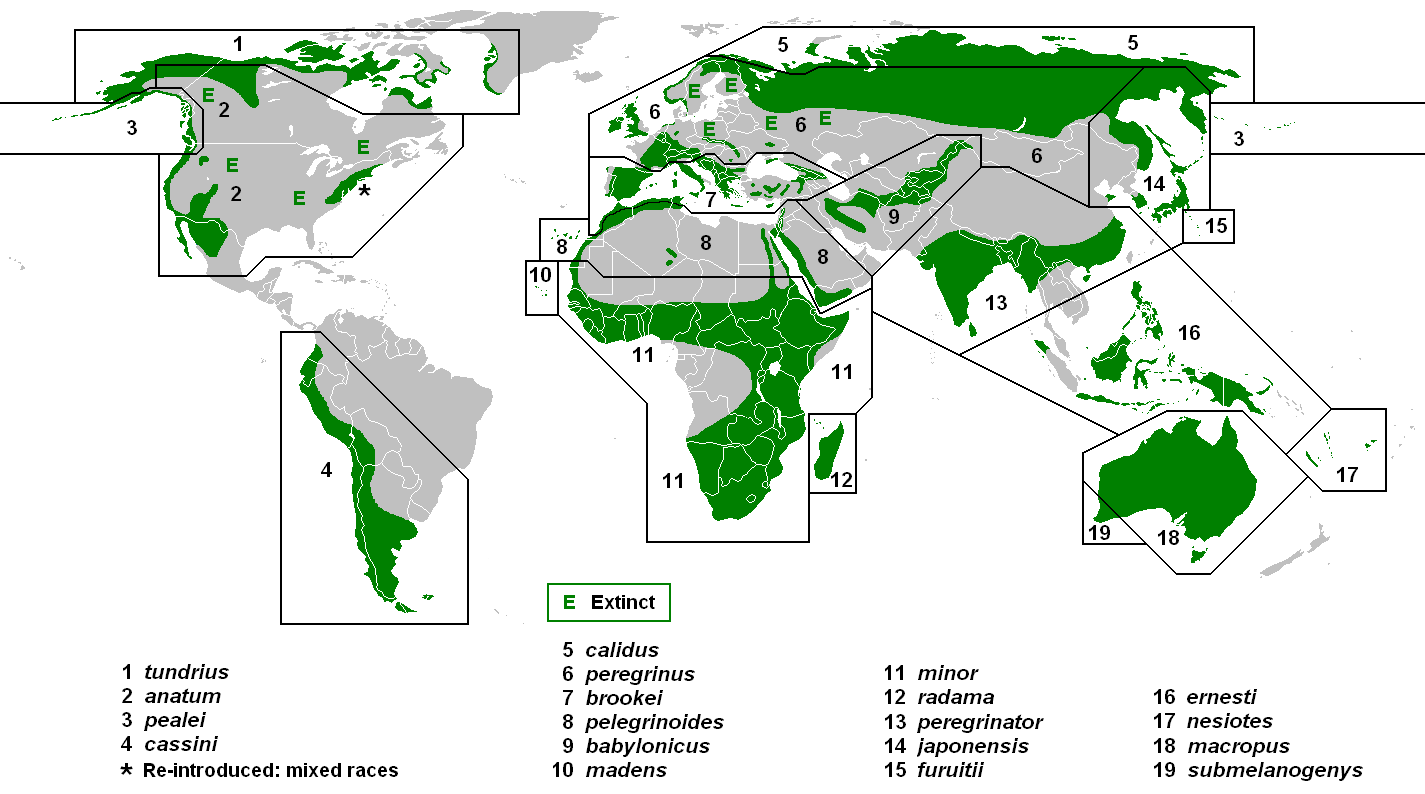

 *', described by Bonaparte in 1838, is known as the American peregrine falcon or "duck hawk"; its scientific name means "duck peregrine falcon". At one time, it was partly included in ''leucogenys''. It is mainly found in the Rocky Mountains today. It was formerly common throughout North America between the tundra and northern Mexico, where current
*', described by Bonaparte in 1838, is known as the American peregrine falcon or "duck hawk"; its scientific name means "duck peregrine falcon". At one time, it was partly included in ''leucogenys''. It is mainly found in the Rocky Mountains today. It was formerly common throughout North America between the tundra and northern Mexico, where current  *''Falco peregrinus babylonicus'', described by
*''Falco peregrinus babylonicus'', described by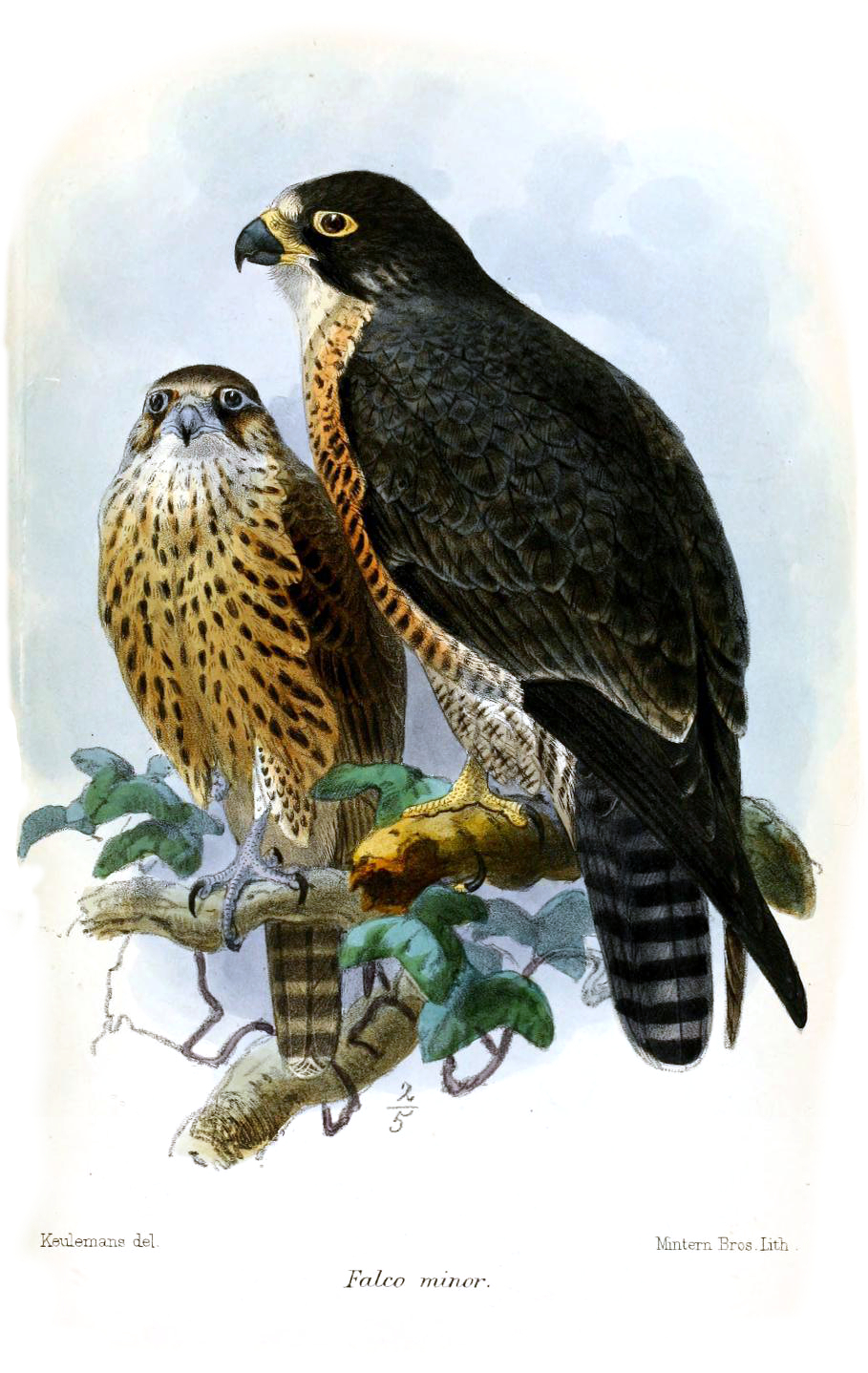  *''Falco peregrinus minor'', first described by Bonaparte in 1850. It was formerly often known as ''perconfusus''. It is sparsely and patchily distributed throughout much of
*''Falco peregrinus minor'', first described by Bonaparte in 1850. It was formerly often known as ''perconfusus''. It is sparsely and patchily distributed throughout much of


 The peregrine falcon lives mostly along mountain ranges, river valleys, coastlines, and increasingly in cities. In mild-winter regions, it is usually a permanent resident, and some individuals, especially adult males, will remain on the breeding territory. Only populations that breed in Arctic climates typically migrate great distances during the northern winter.
The peregrine falcon reaches faster speeds than any other animal on the planet when performing the stoop, which involves soaring to a great height and then diving steeply at speeds of over , hitting one wing of its prey so as not to harm itself on impact. The air pressure from such a dive could possibly damage a bird's
The peregrine falcon lives mostly along mountain ranges, river valleys, coastlines, and increasingly in cities. In mild-winter regions, it is usually a permanent resident, and some individuals, especially adult males, will remain on the breeding territory. Only populations that breed in Arctic climates typically migrate great distances during the northern winter.
The peregrine falcon reaches faster speeds than any other animal on the planet when performing the stoop, which involves soaring to a great height and then diving steeply at speeds of over , hitting one wing of its prey so as not to harm itself on impact. The air pressure from such a dive could possibly damage a bird's

 The peregrine falcon feeds almost exclusively on medium-sized birds such as
The peregrine falcon feeds almost exclusively on medium-sized birds such as
Fiona McMillan, 13 April 2018, ''Forbes''

 The peregrine falcon is sexually mature at one to three years of age, but in larger populations they breed after two to three years of age. A pair mates for life and returns to the same nesting spot annually. The courtship flight includes a mix of aerial acrobatics, precise spirals, and steep dives. The male passes prey it has caught to the female in mid-air. To make this possible, the female actually flies upside-down to receive the food from the male's talons.
During the breeding season, the peregrine falcon is territorial; nesting pairs are usually more than apart, and often much farther, even in areas with large numbers of pairs. The distance between nests ensures sufficient food supply for pairs and their chicks. Within a breeding territory, a pair may have several nesting ledges; the number used by a pair can vary from one or two up to seven in a 16-year period.
The peregrine falcon is sexually mature at one to three years of age, but in larger populations they breed after two to three years of age. A pair mates for life and returns to the same nesting spot annually. The courtship flight includes a mix of aerial acrobatics, precise spirals, and steep dives. The male passes prey it has caught to the female in mid-air. To make this possible, the female actually flies upside-down to receive the food from the male's talons.
During the breeding season, the peregrine falcon is territorial; nesting pairs are usually more than apart, and often much farther, even in areas with large numbers of pairs. The distance between nests ensures sufficient food supply for pairs and their chicks. Within a breeding territory, a pair may have several nesting ledges; the number used by a pair can vary from one or two up to seven in a 16-year period.
 The peregrine falcon nests in a scrape, normally on cliff edges. The female chooses a nest site, where she scrapes a shallow hollow in the loose soil, sand, gravel, or dead vegetation in which to lay eggs. No nest materials are added. Cliff nests are generally located under an overhang, on ledges with vegetation. South-facing sites are favoured. In some regions, as in parts of
The peregrine falcon nests in a scrape, normally on cliff edges. The female chooses a nest site, where she scrapes a shallow hollow in the loose soil, sand, gravel, or dead vegetation in which to lay eggs. No nest materials are added. Cliff nests are generally located under an overhang, on ledges with vegetation. South-facing sites are favoured. In some regions, as in parts of
 The peregrine falcon is a highly admired falconry bird, and has been used in
The peregrine falcon is a highly admired falconry bird, and has been used in
 Populations of the peregrine falcon have bounced back in most parts of the world. In the United Kingdom, there has been a recovery of populations since the crash of the 1960s. This has been greatly assisted by conservation and protection work led by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. The RSPB has estimated that there are 1,402 breeding pairs in the UK. In Canada, where peregrines were identified as endangered in 1978 (in the Yukon territory of northern Canada that year, only a single breeding pair was identified), the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada declared the species no longer at risk in December 2017.
Peregrines now breed in many mountainous and coastal areas, especially in the west and north, and nest in some urban areas, capitalising on the urban feral pigeon populations for food. In Southampton, a nest prevented restoration of mobile telephony services for several months, after Vodafone engineers despatched to repair a faulty
Populations of the peregrine falcon have bounced back in most parts of the world. In the United Kingdom, there has been a recovery of populations since the crash of the 1960s. This has been greatly assisted by conservation and protection work led by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. The RSPB has estimated that there are 1,402 breeding pairs in the UK. In Canada, where peregrines were identified as endangered in 1978 (in the Yukon territory of northern Canada that year, only a single breeding pair was identified), the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada declared the species no longer at risk in December 2017.
Peregrines now breed in many mountainous and coastal areas, especially in the west and north, and nest in some urban areas, capitalising on the urban feral pigeon populations for food. In Southampton, a nest prevented restoration of mobile telephony services for several months, after Vodafone engineers despatched to repair a faulty
Arctic Raptors – Ongoing research with raptors in the Canadian Arctic
Falcon Research Group
Peregrine Falcon Fund
The Canadian Peregrine Foundation
London Peregrine Partnership (UK)
; Video and other media of peregrines
* ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j3mTPEuFcWk A video of the falcon stooping at a top speed of
Derby Cathedral Peregrine Project, UK. Links to webcams and video sequences
Norwich Cathedral Peregrine Web Cam 2015, UK.
*
The Raptor Resource Project. Links to Peregrine Falcon webcams
Peregrines on Brussels Cathedral
* ttp://www.ntu.ac.uk/ecoweb/biodiversity/falcons/index.html Nottingham Trent University, where peregrines return to breed on the top of the Newton building every year. Includes images and webcam.
University of Massachusetts Amherst Live Falcon Cam at the top of the W.E.B. DuBois library, active each year from when the bonded pair of peregrine falcons brood eggs until the chicks are fledged.
Worcester Peregrine Falcon Project, UK. Includes feeds from 'Peregrines in Worcester' Facebook Fan page, YouTube & Flickr photo groups
Peregrine Falcon Banding
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 3 June 2010; 3-minute YouTube video clip
Throgs Neck Bridge Peregrine Banding 2011
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 27 May 2011; 10:54 YouTube video clip
Peregrine Falcon Banding 2012
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 4 June 2012; 2:40 YouTube video clip
Peregrine Falcon Banding 2016
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 2 June 2016; 4:15 YouTube video clip {{DEFAULTSORT:Falcon, peregrine
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, is a cosmopolitan bird of prey ( raptor) in the family Falconidae
The falcons and caracaras are around 60 species of diurnal birds of prey that make up the family Falconidae (representing all extant species in the order Falconiformes). The family is divided into three subfamilies, Herpetotherinae, which inclu ...
. A large, crow-sized falcon, it has a blue-grey back, barred white underparts, and a black head. The peregrine is renowned for its speed, reaching over during its characteristic hunting stoop (high-speed dive), making it the fastest bird in the world, as well as the fastest member of the animal kingdom. According to a ''National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
'' TV program, the highest measured speed of a peregrine falcon is . As is typical for bird-eating raptors, peregrine falcons are sexually dimorphic, with females being considerably larger than males.
The peregrine's breeding range includes land regions from the Arctic tundra to the tropics. It can be found nearly everywhere on Earth, except extreme polar region
The polar regions, also called the frigid geographical zone, zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North Pole, North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high l ...
s, very high mountains, and most tropical rainforests; the only major ice-free landmass from which it is entirely absent is New Zealand. This makes it the world's most widespread raptor, and one of the most widely found bird species. In fact, the only land-based bird species found over a larger geographic area is not always naturally occurring, but one widely introduced by humans, the rock pigeon, which in turn now supports many peregrine populations as a prey species. The peregrine is a highly successful example of urban wildlife in much of its range, taking advantage of tall buildings as nest sites and an abundance of prey such as pigeons and ducks. Both the English and scientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
s of this species mean "wandering falcon," referring to the migratory habits of many northern populations. Experts recognize 17 to 19 subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
, which vary in appearance and range; disagreement exists over whether the distinctive Barbary falcon is represented by two subspecies of ''Falco peregrinus,'' or is a separate species, ''F. pelegrinoides''. The two species' divergence is relatively recent, during the time of the last ice age, therefore the genetic differential between them (and also the difference in their appearance) is relatively tiny. They are only about 0.6–0.8% genetically differentiated.
Although its diet consists almost exclusively of medium-sized birds, the peregrine will sometimes hunt small mammals, small reptiles, or even insects. Reaching sexual maturity at one year, it mates for life and nests in a scrape, normally on cliff edges or, in recent times, on tall human-made structures. The peregrine falcon became an endangered species in many areas because of the widespread use of certain pesticides, especially DDT. Since the ban on DDT from the early 1970s, populations have recovered, supported by large-scale protection of nesting places and releases to the wild.
The peregrine falcon is a well-respected falconry
Falconry is the hunting of wild animals in their natural state and habitat by means of a trained bird of prey. Small animals are hunted; squirrels and rabbits often fall prey to these birds. Two traditional terms are used to describe a person ...
bird due to its strong hunting ability, high trainability, versatility, and availability via captive breeding
Captive breeding, also known as captive propagation, is the process of plants or animals in controlled environments, such as wildlife reserves, zoos, botanic gardens, and other conservation facilities. It is sometimes employed to help species that ...
. It is effective on most game bird species, from small to large. It has also been used as a religious, royal, or national symbol across multiple eras and areas of human civilization.
Description
plumage
Plumage ( "feather") is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, ...
but, as with many birds of prey, the peregrine falcon displays marked sexual dimorphism in size, with the female measuring up to 30% larger than the male. Males weigh and the noticeably larger females weigh . In most subspecies, males weigh less than and females weigh more than , and cases of females weighing about 50% more than their male breeding mates are not uncommon. The standard linear measurements of peregrines are: the wing chord measures , the tail measures and the tarsus measures .
The back and the long pointed wings of the adult are usually bluish black to slate grey with indistinct darker barring (see "Subspecies" below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
*Bottom (disambiguation)
Bottom may refer to:
Anatomy and sex
* Bottom (BDSM), the partner in a BDSM who takes the passive, receiving, or obedient role, to that of the top or ...
); the wingtips are black. The white to rusty underparts are barred with thin clean bands of dark brown or black. The tail, coloured like the back but with thin clean bars, is long, narrow, and rounded at the end with a black tip and a white band at the very end. The top of the head and a "moustache" along the cheeks are black, contrasting sharply with the pale sides of the neck and white throat. The cere is yellow, as are the feet, and the beak and claws are black. The upper beak is notched near the tip, an adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
which enables falcons to kill prey by severing the spinal column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordates ...
at the neck. An immature bird is much browner, with streaked, rather than barred, underparts, and has a pale bluish cere and orbital ring.
A study shows that their black malar stripe
The cheeks ( la, buccae) constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside ...
exists to reduce glare
Glare (derived from GLAss REinforced laminate ) is a fiber metal laminate (FML) composed of several very thin layers of metal (usually aluminum) interspersed with layers of S-2 glass-fiber ''pre-preg'', bonded together with a matrix such as epo ...
from solar radiation, allowing them to see better. Photos from The Macaulay Library and iNaturalist showed that the malar stripe is thicker where there is more solar radiation. That supports the solar glare hypothesis.
Taxonomy and systematics
 ''Falco peregrinus'' was first described under its current
''Falco peregrinus'' was first described under its current binomial name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
by English ornithologist Marmaduke Tunstall in his 1771 work ''Ornithologia Britannica''. The scientific name ''Falco peregrinus'' is a Medieval Latin phrase that was used by Albertus Magnus in 1225. The specific name is taken from the fact that juvenile birds were taken while journeying to their breeding location rather than from the nest, as falcon nests were difficult to get at. The Latin term for falcon, , is related to , meaning " sickle", in reference to the silhouette of the falcon's long, pointed wings in flight.
The peregrine falcon belongs to a genus whose lineage includes the hierofalcon
The hierofalcons are four closely related species of falcon which make up the subgenus ''Hierofalco'':
* Lanner falcon, ''Falco biarmicus''
* Laggar falcon, ''Falco jugger''
* Saker falcon, ''Falco cherrug''
* Gyrfalcon, ''Falco rusticolus''
Th ...
s and the prairie falcon (''F. mexicanus''). This lineage probably diverged from other falcons towards the end of the Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million ye ...
or in the Early Pliocene, about 5–8 million years ago (mya). As the peregrine-hierofalcon group includes both Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
and North American species, it is likely that the lineage originated in western Eurasia or Africa. Its relationship to other falcons is not clear, as the issue is complicated by widespread hybridization
Hybridization (or hybridisation) may refer to:
*Hybridization (biology), the process of combining different varieties of organisms to create a hybrid
*Orbital hybridization, in chemistry, the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals
*Nu ...
confounding mtDNA sequence analyses. For example, a genetic lineage of the saker falcon (''F. cherrug'') is known which originated from a male saker producing fertile young with a female peregrine ancestor, and the descendants further breeding with sakers.
Today, peregrines are regularly paired in captivity with other species such as the lanner falcon (''F. biarmicus'') to produce the " perilanner", a somewhat popular bird in falconry
Falconry is the hunting of wild animals in their natural state and habitat by means of a trained bird of prey. Small animals are hunted; squirrels and rabbits often fall prey to these birds. Two traditional terms are used to describe a person ...
as it combines the peregrine's hunting skill with the lanner's hardiness, or the gyrfalcon to produce large, strikingly coloured birds for the use of falconers. As can be seen, the peregrine is still genetically close to the hierofalcons, though their lineages diverged in the Late Pliocene (maybe some 2.5–2 mya in the Gelasian).
Subspecies
Numeroussubspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
of ''Falco peregrinus'' have been described, with 19 accepted by the 1994 ''Handbook of the Birds of the World
The ''Handbook of the Birds of the World'' (HBW) is a multi-volume series produced by the Spanish publishing house Lynx Edicions in partnership with BirdLife International. It is the first handbook to cover every known living species of bird. T ...
'', which considers the Barbary falcon of the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
and coastal North Africa to be two subspecies (''pelegrinoides'' and ''babylonicus'') of ''Falco peregrinus'', rather than a distinct species, ''F. pelegrinoides''. The following map shows the general ranges of these 19 subspecies.

 *', described by Bonaparte in 1838, is known as the American peregrine falcon or "duck hawk"; its scientific name means "duck peregrine falcon". At one time, it was partly included in ''leucogenys''. It is mainly found in the Rocky Mountains today. It was formerly common throughout North America between the tundra and northern Mexico, where current
*', described by Bonaparte in 1838, is known as the American peregrine falcon or "duck hawk"; its scientific name means "duck peregrine falcon". At one time, it was partly included in ''leucogenys''. It is mainly found in the Rocky Mountains today. It was formerly common throughout North America between the tundra and northern Mexico, where current reintroduction
Species reintroduction is the deliberate release of a species into the wild, from captivity or other areas where the organism is capable of survival. The goal of species reintroduction is to establish a healthy, genetically diverse, self-sustainin ...
efforts are seeking to restore the population. Most mature ''anatum'', except those that breed in more northern areas, winter in their breeding range. Most vagrant
Vagrancy is the condition of homelessness without regular employment or income. Vagrants (also known as bums, vagabonds, rogues, tramps or drifters) usually live in poverty and support themselves by begging, scavenging, petty theft, temporar ...
s that reach western Europe seem to belong to the more northern and strongly migratory '' tundrius'', only considered distinct since 1968. It is similar to the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
, but is slightly smaller; adults are somewhat paler and less patterned below, but juveniles are darker and more patterned below. Males weigh , while females weigh . It has become extinct in eastern North America and populations there are hybrids as a result of reintroductions of birds from elsewhere.
 *''Falco peregrinus babylonicus'', described by
*''Falco peregrinus babylonicus'', described by P.L. Sclater
Philip Lutley Sclater (4 November 1829 – 27 June 1913) was an English lawyer and zoologist. In zoology, he was an expert ornithologist, and identified the main zoogeographic regions of the world. He was Secretary of the Zoological Societ ...
in 1861, is found in eastern Iran along the Hindu Kush and the Tian Shan to the Mongolian Altai
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The m ...
ranges. A few birds winter in northern and northwestern India, mainly in dry semi-desert habitats. It is paler than ''pelegrinoides'' and somewhat similar to a small, pale lanner falcon (''Falco biarmicus''). Males weigh , while females weigh .
*', described by Sharpe in 1873, is also known as the Mediterranean peregrine falcon or the Maltese falcon. It includes ''caucasicus'' and most specimens of the proposed race ''punicus'', though others may be ''pelegrinoides'' ( Barbary falcons), or perhaps the rare hybrids between these two which might occur around Algeria. They occur from the Iberian Peninsula around the Mediterranean, except in arid regions, to the Caucasus. They are non-migratory. It is smaller than the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
and the underside usually has a rusty hue. Males weigh around , while females weigh up to .
*', described by John Latham in 1790, it was formerly called ''leucogenys'' and includes ''caeruleiceps''. It breeds in the Arctic tundra of Eurasia from Murmansk Oblast
Murmansk Oblast (russian: Му́рманская о́бласть, p=ˈmurmənskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, r=Murmanskaya oblast, ''Murmanskaya oblast''; Kildin Sami: Мурман е̄ммьне, ''Murman jemm'ne'') is a federal subject (an oblast) of ...
to roughly Yana and Indigirka Rivers, Siberia. It is completely migratory and travels south in winter as far as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
. It is often seen around wetland habitats. It is paler than the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
, especially on the crown. Males weigh , while females weigh .
*''Falco peregrinus cassini'', described by Sharpe in 1873, is also known as the austral peregrine falcon. It includes ''kreyenborgi'', the pallid falcon, a leucistic colour morph
Morph may refer to:
Biology
* Morph (zoology), a visual or behavioral difference between organisms of distinct populations in a species
* Muller's morphs, a classification scheme for genetic mutations
* "-morph", a suffix commonly used in tax ...
occurring in southernmost South America, which was long believed to be a distinct species. Its range includes South America from Ecuador through Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
, northern Argentina and Chile to Tierra del Fuego and the Falkland Islands. It is non-migratory. It is similar to the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
, but slightly smaller with a black ear region. The pallid falcon morph ''kreyenborgi'' is medium grey above, has little barring below and has a head pattern like the saker falcon (''Falco cherrug''), but the ear region is white.
*''Falco peregrinus ernesti'', described by Sharpe in 1894, is found from the Sunda Islands
The Sunda Islands ( id, Kepulauan Sunda) are a group of islands in the Malay Archipelago.Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Sunda Islands" . ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 26 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. They consist of the Greater Sunda ...
to the Philippines and south to eastern New Guinea and the nearby Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
. Its geographical separation from '' nesiotes'' requires confirmation. It is non-migratory. It differs from the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
in the very dark, dense barring on its underside and its black ear coverts.
*''Falco peregrinus furuitii'', described by Momiyama in 1927, is found on the Izu and Ogasawara Islands south of Honshū
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separa ...
, Japan. It is non-migratory. It is very rare and may only remain on a single island. It is a dark form, resembling '' pealei'' in colour, but darker, especially on the tail.
*''Falco peregrinus japonensis'', described by Gmelin Gmelin may refer to:
* Gmelin's test, a chemical test
* Gmelin database, a German handbook/encyclopedia of inorganic compounds initiated by Leopold Gmelin
People
* Carl Christian Gmelin (1762–1837), German botanist, author of ''Flora Badensis ...
in 1788, includes ''kleinschmidti'', ''pleskei'', and ''harterti'', and seems to refer to intergrades with '' calidus''. It is found from northeast Siberia to Kamchatka (though it is possibly replaced by ''pealei'' on the coast there) and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. Northern populations are migratory, while those of Japan are resident. It is similar to the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
, but the young are even darker than those of '' anatum''.
*''Falco peregrinus macropus'', described by Swainson in 1837, is the Australian peregrine falcon. It is found in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
in all regions except the southwest. It is non-migratory. It is similar to '' brookei'' in appearance, but is slightly smaller and the ear region is entirely black. The feet are proportionally large.
*''Falco peregrinus madens'', described by Ripley
Ripley may refer to:
People and characters
* Ripley (name)
* ''Ripley'', the test mannequin aboard the first International Space Station space station Dragon 2 space test flight Crew Dragon Demo-1
* Ellen Ripley, a fictional character from the Ali ...
and Watson in 1963, is unusual in having some sexual dichromatism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
. If the Barbary falcon (see below) is considered a distinct species, it is sometimes placed therein. It is found in the Cape Verde Islands and is non-migratory; it is also endangered, with only six to eight pairs surviving. Males have a rufous wash on the crown, nape, ears and back; the underside is conspicuously washed pinkish-brown. Females are tinged rich brown overall, especially on the crown and nape.
 *''Falco peregrinus minor'', first described by Bonaparte in 1850. It was formerly often known as ''perconfusus''. It is sparsely and patchily distributed throughout much of
*''Falco peregrinus minor'', first described by Bonaparte in 1850. It was formerly often known as ''perconfusus''. It is sparsely and patchily distributed throughout much of sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
and widespread in Southern Africa. It apparently reaches north along the Atlantic coast as far as Morocco. It is non-migratory and dark-coloured. This is the smallest subspecies, with smaller males weighing as little as approximately .
*', described by Mayr in 1941, is found in Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
and probably also Vanuatu and New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
. It is non-migratory.
*', described by Ridgway in 1873, is Peale's falcon and includes ''rudolfi''. It is found in the Pacific Northwest of North America, northwards from Puget Sound along the British Columbia coast (including the Haida Gwaii), along the Gulf of Alaska and the Aleutian Islands to the far eastern Bering Sea
The Bering Sea (, ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Ameri ...
coast of Russia, and may also occur on the Kuril Islands and the coasts of Kamchatka. It is non-migratory. It is the largest subspecies and it looks like an oversized and darker '' tundrius'' or like a strongly barred and large '' anatum''. The bill is very wide. Juveniles occasionally have pale crowns. Males weigh , while females weigh .
*'' Falco peregrinus pelegrinoides'', first described by Temminck in 1829, is found in the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
through North Africa and the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
to Mesopotamia. It is most similar to '' brookei'', but is markedly paler above, with a rusty neck, and is a light buff with reduced barring below. It is smaller than the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
; females weigh around .
*''Falco peregrinus peregrinator
The shaheen falcon (''Falco peregrinus peregrinator'') is a non-migratory subspecies of the peregrine falcon found mainly in the Indian subcontinent. It has also been described as a migratory subspecies. Describes subspecies ''peregrinator'' "f ...
'', described by Sundevall
Carl Jakob Sundevall (22 October 1801, Högestad – 2 February 1875) was a Swedish zoologist.
Sundevall studied at Lund University, where he became a Ph.D. in 1823. After traveling to East Asia, he studied medicine, graduating as Doctor of Med ...
in 1837, is known as the Indian peregrine falcon, black shaheen, Indian shaheen or shaheen falcon. It was formerly sometimes known as ''Falco atriceps'' or ''Falco shaheen''. Its range includes South Asia from across the Indian subcontinent to Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
and southeastern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. In India, the shaheen falcon is reported from all states except Uttar Pradesh, mainly from rocky and hilly regions. The shaheen falcon is also reported from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. It has a clutch size of 3 to 4 eggs, with the chicks fledging time of 48 days with an average nesting success of 1.32 chicks per nest. In India, apart from nesting on cliffs, it has also been recorded as nesting on man-made structures such as buildings and cellphone transmission towers. A population estimate of 40 breeding pairs in Sri Lanka was made in 1996. It is non-migratory and is small and dark, with rufous underparts. In Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
this species is found to favour the higher hills, while the migrant '' calidus'' is more often seen along the coast.
*', the nominate (first-named) subspecies, described by Tunstall in 1771, breeds over much of temperate Eurasia between the tundra in the north and the Pyrenees, Mediterranean region and Alpide belt in the south. It is mainly non-migratory in Europe, but migratory in Scandinavia and Asia. Males weigh , while females weigh . It includes ''brevirostris'', ''germanicus'', ''rhenanus'' and ''riphaeus''.
*''Falco peregrinus radama'', described by Hartlaub
Karel Johan Gustav Hartlaub (8 November 1814 – 29 November 1900) was a German physician and ornithologist.
Hartlaub was born in Bremen, and studied at Bonn and Berlin before graduating in medicine at Göttingen. In 1840, he began to study and ...
in 1861, is found in Madagascar and the Comoros
The Comoros,, ' officially the Union of the Comoros,; ar, الاتحاد القمري ' is an independent country made up of three islands in southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. It ...
. It is non-migratory.
*''Falco peregrinus submelanogenys'', described by Mathews in 1912, is the Southwest Australian peregrine falcon. It is found in southwestern Australia and is non-migratory.
*', described by C.M. White in 1968, was at one time included in ''leucogenys''. It is found in the Arctic tundra of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
to Greenland, and migrates to wintering grounds in Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and South America. Most vagrant
Vagrancy is the condition of homelessness without regular employment or income. Vagrants (also known as bums, vagabonds, rogues, tramps or drifters) usually live in poverty and support themselves by begging, scavenging, petty theft, temporar ...
s that reach western Europe belong to this subspecies, which was previously considered synonymous with '' anatum''. It is the New World equivalent to '' calidus''. It is smaller and paler than ''anatum''; most have a conspicuous white forehead and white in ear region, but the crown and "moustache" are very dark, unlike in ''calidus''. Juveniles are browner and less grey than in ''calidus'' and paler, sometimes almost sandy, than in ''anatum''. Males weigh , while females weigh . Despite its current recognition as a valid subspecies, a population genetic study of both pre-decline (i.e., museum) and recovered contemporary populations failed to distinguish genetically the ''anatum'' and ''tundrius'' subspecies.
Barbary falcon
The Barbary falcon is a subspecies of the peregrine falcon that inhabits parts of North Africa; namely, from the Canary Islands to the Arabian Peninsula. There is discussion concerning the taxonomic status of the bird, with some considering it a subspecies of the peregrine falcon and others considering it a full species with two subspecies (White et al. 2013). Compared to the other peregrine falcon subspecies, Barbary falcons sport a slimmer body and a distinct plumage color pattern. Despite numbers and range of these birds throughout the Canary Islands generally increasing, they are considered endangered, with human interference through falconry and shooting threatening their well-being. Falconry can further complicate the speciation and genetics of these Canary Islands falcons, as the practice promotes genetic mixing between individuals from outside the islands with those originating from the islands. Population density of the Barbary falcons on Tenerife, the biggest of the seven major Canary Islands, was found to be 1.27 pairs/100 km², with the mean distance between pairs being 5869 ± 3338 m. The falcons were only observed near large and natural cliffs with a mean altitude of 697.6 m. Falcons show an affinity for tall cliffs away from human-mediated establishments and presence. Barbary falcons have a red neck patch, but otherwise differ in appearance from the peregrine falcon proper merely according to Gloger's rule, relating pigmentation to environmental humidity. The Barbary falcon has a peculiar way of flying, beating only the outer part of its wings like fulmars sometimes do; this also occurs in the peregrine falcon, but less often and far less pronounced. The Barbary falcon's shoulder andpelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
bones are stout by comparison with the peregrine falcon and its feet are smaller. Barbary falcons breed at different times of year than neighboring peregrine falcon subspecies, but they are capable of interbreeding. There is a 0.6–0.7% genetic distance in the peregrine falcon-Barbary falcon ("peregrinoid") complex.
Ecology and behaviour

 The peregrine falcon lives mostly along mountain ranges, river valleys, coastlines, and increasingly in cities. In mild-winter regions, it is usually a permanent resident, and some individuals, especially adult males, will remain on the breeding territory. Only populations that breed in Arctic climates typically migrate great distances during the northern winter.
The peregrine falcon reaches faster speeds than any other animal on the planet when performing the stoop, which involves soaring to a great height and then diving steeply at speeds of over , hitting one wing of its prey so as not to harm itself on impact. The air pressure from such a dive could possibly damage a bird's
The peregrine falcon lives mostly along mountain ranges, river valleys, coastlines, and increasingly in cities. In mild-winter regions, it is usually a permanent resident, and some individuals, especially adult males, will remain on the breeding territory. Only populations that breed in Arctic climates typically migrate great distances during the northern winter.
The peregrine falcon reaches faster speeds than any other animal on the planet when performing the stoop, which involves soaring to a great height and then diving steeply at speeds of over , hitting one wing of its prey so as not to harm itself on impact. The air pressure from such a dive could possibly damage a bird's lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s, but small bony tubercles on a falcon's nostrils are theorized to guide the powerful airflow away from the nostrils, enabling the bird to breathe more easily while diving by reducing the change in air pressure. To protect their eyes, the falcons use their nictitating membrane
The nictitating membrane (from Latin '' nictare'', to blink) is a transparent or translucent third eyelid present in some animals that can be drawn across the eye from the medial canthus to protect and moisten it while maintaining vision. All ...
s (third eyelids) to spread tears and clear debris from their eyes while maintaining vision. The distinctive malar stripe or 'moustache', a dark area of feathers below the eyes, is thought to reduce solar glare and improve contrast sensitivity when targeting fast moving prey in bright light condition; the malar stripe has been found to be wider and more pronounced in regions of the world with greater solar radiation supporting this solar glare hypothesis. Peregrine falcons have a flicker fusion frequency of 129 Hz (cycles per second), very fast for a bird of its size, and much faster than mammals. A study testing the flight physics of an "ideal falcon" found a theoretical speed limit at for low-altitude flight and for high-altitude flight. In 2005, Ken Franklin recorded a falcon stooping at a top speed of .
The life span of peregrine falcons in the wild is up to 19 years 9 months. Mortality in the first year is 59–70%, declining to 25–32% annually in adults. Apart from such anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human im ...
threats as collision with human-made objects, the peregrine may be killed by larger hawk
Hawks are bird of prey, birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. Th ...
s and owls.
The peregrine falcon is host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
* Michel Host ...
to a range of parasites and pathogens. It is a vector for Avipoxvirus, Newcastle disease virus Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area in Australia, named after Newcastle ...
, Falconid herpesvirus 1 (and possibly other Herpesviridae), and some mycoses and bacterial infections. Endoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has c ...
s include '' Plasmodium relictum'' (usually not causing malaria in the peregrine falcon), Strigeidae trematodes, '' Serratospiculum amaculata'' (nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
), and tapeworms. Known peregrine falcon ectoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s are chewing lice, ''Ceratophyllus garei
''Ceratophyllus garei'', the duck flea, is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Rothschild
Rothschild () is a name derived from the German ''zum rothen Schild'' (with the old spelling "th"), meaning "with the re ...
'' (a flea), and Hippoboscidae flies (''Icosta nigra
''Icosta'' are genus of biting flies in the family of louse flies, Hippoboscidae. There are 52 known species, making it the largest Hippoboscid genus. All species are parasites of birds.
Distribution
Worldwide, excluding Antarctica.
Systematics ...
'', ''Ornithoctona erythrocephala
''Ornithoctona'' are genus of biting flies in the family of louse flies, Hippoboscidae. There are 12 known species. All species are parasites of birds.
Distribution
''Ornithoctona'' are found worldwide with the exception of Antarctica.
Systemati ...
'').
In the Arctic Peregrine falcons chasing away small rodent predators from their nesting territory and Rough-legged Hawks (''Buteo lagopus'') could use these hot spots as a nesting territory.
Feeding

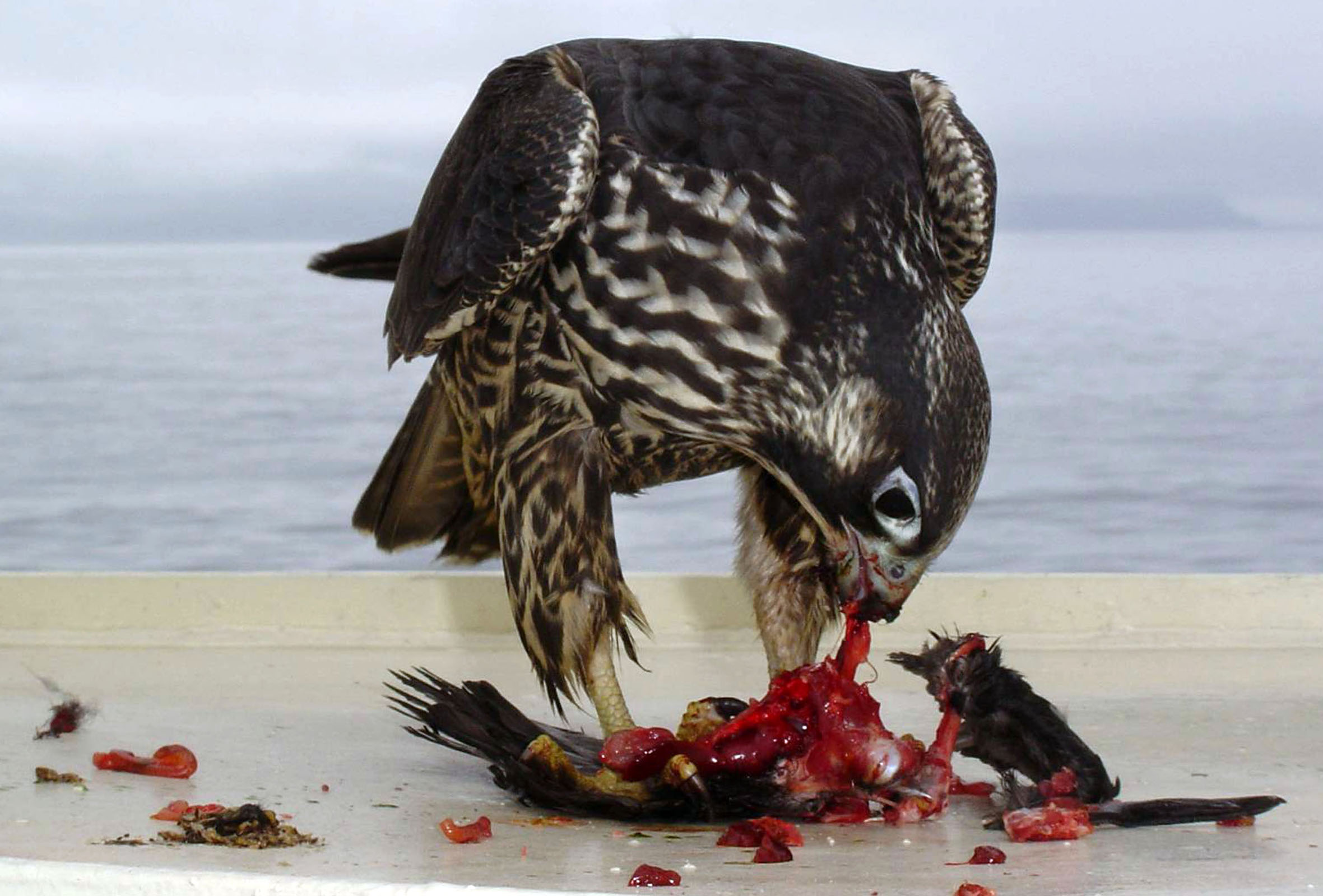
 The peregrine falcon feeds almost exclusively on medium-sized birds such as
The peregrine falcon feeds almost exclusively on medium-sized birds such as pigeons and doves
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily ...
, waterfowl, songbirds, and waders. This falcon tends to nest on tall buildings or bridges, and these urban dwelling birds subsist mostly on different pigeons. Worldwide, it is estimated that between 1,500 and 2,000 bird species (up to roughly a fifth of the world's bird species) are predated somewhere by these falcons. In North America, prey has varied in size from hummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the biological family Trochilidae. With about 361 species and 113 genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but the vast majority of the species are found in the tropics aro ...
s ('' Selasphorus'' and ''Archilochus
Archilochus (; grc-gre, Ἀρχίλοχος ''Arkhilokhos''; c. 680 – c. 645 BC) was a Greek lyric poet of the Archaic period from the island of Paros. He is celebrated for his versatile and innovative use of poetic meters, and is the ea ...
'' ssp.) to a sandhill crane (killed in Alaska by a peregrine in a stoop), although most prey taken by peregrines weigh from (small passerines) to (such as ducks and gulls). The peregrine falcon takes the most diverse range of bird species of any raptor in North America, with more than 300 species having fallen victim to the falcon, including nearly 100 shorebirds. Smaller hawk
Hawks are bird of prey, birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. Th ...
s and owls are regularly predated, mainly smaller falcons such as the American kestrel, merlin
Merlin ( cy, Myrddin, kw, Marzhin, br, Merzhin) is a mythical figure prominently featured in the legend of King Arthur and best known as a mage, with several other main roles. His usual depiction, based on an amalgamation of historic and le ...
and sharp-shinned hawks. In urban areas, the main component of the peregrine's diet is the rock or feral pigeon, which comprise 80% or more of the dietary intake for peregrines in some cities. Other common city birds are also taken regularly, including mourning doves, common wood pigeons, common swifts, northern flicker
The northern flicker or common flicker (''Colaptes auratus'') is a medium-sized bird of the woodpecker family. It is native to most of North America, parts of Central America, Cuba, and the Cayman Islands, and is one of the few woodpecker spec ...
s, common starling
The common starling or European starling (''Sturnus vulgaris''), also known simply as the starling in Great Britain and Ireland, is a medium-sized passerine bird in the starling family, Sturnidae. It is about long and has glossy black plumage ...
s, American robin
The American robin (''Turdus migratorius'') is a migratory bird of the true thrush genus and Turdidae, the wider thrush family. It is named after the European robin because of its reddish-orange breast, though the two species are not closel ...
s, common blackbird
The common blackbird (''Turdus merula'') is a species of true thrush. It is also called the Eurasian blackbird (especially in North America, to distinguish it from the unrelated New World blackbirds), or simply the blackbird where this does not ...
s, and corvids (such as magpie
Magpies are birds of the Corvidae family. Like other members of their family, they are widely considered to be intelligent creatures. The Eurasian magpie, for instance, is thought to rank among the world's most intelligent creatures, and is one ...
s or carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
, house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
, and American crows). Other than bats taken at night, the peregrine rarely hunts mammals, but will on occasion take small species such as rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
s, voles, hare
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores, and live solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are able to fend for themselves shortly after birth. The ge ...
s, shrews, mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
and squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squ ...
s. Coastal populations of the large subspecies ''pealei'' feed almost exclusively on seabirds. In the Brazilian mangrove swamp of Cubatão, a wintering falcon of the subspecies ''tundrius'' was observed while successfully hunting a juvenile scarlet ibis. Insects and reptiles make up a small proportion of the diet, which varies greatly depending on what prey is available.
The peregrine falcon hunts most often at dawn and dusk, when prey are most active, but also nocturnally in cities, particularly during migration periods when hunting at night may become prevalent. Nocturnal migrants taken by peregrines include species as diverse as yellow-billed cuckoo, black-necked grebe, virginia rail, and common quail. The peregrine requires open space in order to hunt, and therefore often hunts over open water, marshes, valleys, fields, and tundra, searching for prey either from a high perch or from the air. Large congregations of migrants, especially species that gather in the open like shorebirds, can be quite attractive to hunting peregrines. Once prey is spotted, it begins its stoop, folding back the tail and wings, with feet tucked. Prey is typically struck and captured in mid-air; the peregrine falcon strikes its prey with a clenched foot, stunning or killing it with the impact, then turns to catch it in mid-air. If its prey is too heavy to carry, a peregrine will drop it to the ground and eat it there. If they miss the initial strike, peregrines will chase their prey in a twisting flight. Although previously thought rare, several cases of peregrines contour-hunting, i.e. using natural contours to surprise and ambush prey on the ground, have been reported and even rare cases of prey being pursued on foot. In addition, peregrines have been documented preying on chicks in nests, from birds such as kittiwakes. Prey is plucked before consumption. A recent study showed the presence of peregrines benefits non-preferred species while at the same time causing a decline in its preferred prey. As of 2018, the fastest recorded falcon was at 242 mph (nearly 390 km/h). Researchers at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands and at Oxford University used 3D computer simulations in 2018 to show that the high speed allows peregrines to gain better maneuverability and precision in strikes."Falcon Attack: How Peregrine Falcons Maneuver At Nearly 225 MPH"Fiona McMillan, 13 April 2018, ''Forbes''
Reproduction

 The peregrine falcon nests in a scrape, normally on cliff edges. The female chooses a nest site, where she scrapes a shallow hollow in the loose soil, sand, gravel, or dead vegetation in which to lay eggs. No nest materials are added. Cliff nests are generally located under an overhang, on ledges with vegetation. South-facing sites are favoured. In some regions, as in parts of
The peregrine falcon nests in a scrape, normally on cliff edges. The female chooses a nest site, where she scrapes a shallow hollow in the loose soil, sand, gravel, or dead vegetation in which to lay eggs. No nest materials are added. Cliff nests are generally located under an overhang, on ledges with vegetation. South-facing sites are favoured. In some regions, as in parts of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and on the west coast of northern North America, large tree hollows are used for nesting. Before the demise of most European peregrines, a large population of peregrines in central and western Europe used the disused nests of other large birds. In remote, undisturbed areas such as the Arctic, steep slopes and even low rocks and mounds may be used as nest sites. In many parts of its range, peregrines now also nest regularly on tall buildings or bridges; these human-made structures used for breeding closely resemble the natural cliff ledges that the peregrine prefers for its nesting locations.
The pair defends the chosen nest site against other peregrines, and often against raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned t ...
s, heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychus ...
s, and gulls, and if ground-nesting, also such mammals as fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelv ...
es, wolverines, felids, bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
s, wolves, and mountain lions. Both nests and (less frequently) adults are predated by larger-bodied raptorial birds like eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
s, large owls
Owls are birds from the Order (biology), order Strigiformes (), which includes over 200 species of mostly Solitary animal, solitary and Nocturnal animal, nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vi ...
, or gyrfalcons. The most serious predators of peregrine nests in North America and Europe are the great horned owl and the Eurasian eagle owl. When reintroductions have been attempted for peregrines, the most serious impediments were these two species of owls routinely picking off nestlings, fledglings and adults by night. Peregrines defending their nests have managed to kill raptors as large as golden eagles and bald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche as ...
s (both of which they normally avoid as potential predators) that have come too close to the nest by ambushing them in a full stoop. In one instance, when a snowy owl killed a newly fledged peregrine, the larger owl was in turn killed by a stooping peregrine parent.
The date of egg-laying varies according to locality, but is generally from February to March in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, and from July to August in the Southern Hemisphere, although the Australian subspecies ''macropus'' may breed as late as November, and equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
ial populations may nest anytime between June and December. If the eggs are lost early in the nesting season, the female usually lays another clutch, although this is extremely rare in the Arctic due to the short summer season. Generally three to four eggs, but sometimes as few as one or as many as five, are laid in the scrape. The eggs are white to buff with red or brown markings. They are incubated for 29 to 33 days, mainly by the female, with the male also helping with the incubation of the eggs during the day, but only the female incubating them at night. The average number of young found in nests is 2.5, and the average number that fledge is about 1.5, due to the occasional production of infertile eggs and various natural losses of nestlings.
After hatching, the chicks (called "es") are covered with creamy-white down and have disproportionately large feet. The male (called the "") and the female (simply called the "falcon") both leave the nest to gather prey to feed the young. The hunting territory of the parents can extend a radius of from the nest site. Chicks fledge
Fledging is the stage in a flying animal's life between hatching or birth and becoming capable of flight.
This term is most frequently applied to birds, but is also used for bats. For altricial birds, those that spend more time in vulnerable c ...
42 to 46 days after hatching, and remain dependent on their parents for up to two months.
Relationship with humans
Use in falconry
 The peregrine falcon is a highly admired falconry bird, and has been used in
The peregrine falcon is a highly admired falconry bird, and has been used in falconry
Falconry is the hunting of wild animals in their natural state and habitat by means of a trained bird of prey. Small animals are hunted; squirrels and rabbits often fall prey to these birds. Two traditional terms are used to describe a person ...
for more than 3,000 years, beginning with nomads in central Asia. Its advantages in falconry include not only its athleticism and eagerness to hunt, but an equable disposition that leads to it being one of the easier falcons to train. The peregrine falcon has the additional advantage of a natural flight style of circling above the falconer ("waiting on") for game to be flushed, and then performing an effective and exciting high-speed diving stoop to take the quarry. The speed of the stoop not only allows the falcon to catch fast flying birds, it also enhances the falcon's ability to exert maneuvers to catch highly agile prey, and allows the falcon to deliver a knockout blow with a fist-like clenched talon against game that may be much larger than itself.
Additionally the versatility of the species, with agility allowing capture of smaller birds and a strength and attacking style allowing capture of game much larger than themselves, combined with the wide size range of the many peregrine subspecies, means there is a subspecies suitable to almost any size and type of game bird. This size range, evolved to fit various environments and prey species, is from the larger females of the largest subspecies to the smaller males of the smallest subspecies, approximately five to one (approximately 1500 g to 300 g). The males of smaller and medium-sized subspecies, and the females of the smaller subspecies, excel in the taking of swift and agile small game birds such as dove, quail, and smaller ducks. The females of the larger subspecies are capable of taking large and powerful game birds such as the largest of duck species, pheasant, and grouse.
Peregrine falcons handled by falconers are also occasionally used to scare away birds at airports to reduce the risk of bird-plane strikes, improving air-traffic safety. They were also used to intercept homing pigeons during World War II.
Peregrine falcons have been successfully bred in captivity, both for falconry and for release into the wild. Until 2004 nearly all peregrines used for falconry in the US were captive-bred from the progeny of falcons taken before the US Endangered Species Act
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA or "The Act"; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of ec ...
was enacted and from those few infusions of wild genes available from Canada and special circumstances. Peregrine falcons were removed from the United States' endangered species list in 1999. The successful recovery program was aided by the effort and knowledge of falconers – in collaboration with The Peregrine Fund
The Peregrine Fund (named after the bird of prey of the same name the peregrine falcon) is a non-profit organization founded in 1970 that conserves threatened and endangered birds of prey worldwide. The successful recovery of the peregrine falco ...
and state and federal agencies – through a technique called hacking. Finally, after years of close work with the US Fish and Wildlife Service, a limited take of wild peregrines was allowed in 2004, the first wild peregrines taken specifically for falconry in over 30 years.
The development of captive breeding methods has led to peregrines being commercially available for falconry use, thus mostly eliminating the need to capture wild birds for support of falconry. The main reason for taking wild peregrines at this point is to maintain healthy genetic diversity in the breeding lines. Hybrids of peregrines and gyrfalcons are also available that can combine the best features of both species to create what many consider to be the ultimate falconry bird for the taking of larger game such as the sage-grouse
Sage-grouse are grouse belonging to the bird genus ''Centrocercus.'' The genus includes two species: the Gunnison grouse (''Centrocercus minimus'') and the greater sage-grouse (''Centrocercus urophasianus''). These birds are distributed through ...
. These hybrids combine the greater size, strength, and horizontal speed of the gyrfalcon with the natural propensity to stoop and greater warm weather tolerance of the peregrine.
Decline due to pesticides
The peregrine falcon became an endangered species over much of its range because of the use oforganochlorine pesticide
An organochloride, organochlorine compound, chlorocarbon, or chlorinated hydrocarbon is an organic compound containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted by chlor ...
s, especially DDT, during the 1950s, '60s, and '70s. Pesticide biomagnification caused organochlorine to build up in the falcons' fat tissues, reducing the amount of calcium in their eggshells. With thinner shells, fewer falcon eggs survived until hatching. In addition, the PCB concentrations found in these falcons is dependent upon the age of the falcon. While high levels are still found in young birds (only a few months old) and even higher concentrations are found in more mature falcons, further increasing in adult peregrine falcons. These pesticides caused falcon prey to also have thinner eggshells (one example of prey being the Black Petrels). In several parts of the world, such as the eastern United States and Belgium, this species became extirpated (locally extinct) as a result. An alternate point of view is that populations in the eastern North America had vanished due to hunting and egg collection. Following the ban of organochlorine pesticides, the reproductive success of Peregrines increased in Scotland in terms of territory occupancy and breeding success, although spatial variation in recovery rates indicate that in some areas Peregrines were also impacted by other factors such as persecution.
Recovery efforts
Peregrine falcon recovery teams breed the species in captivity. The chicks are usually fed through a chute or with a hand puppet mimicking a peregrine's head, so they cannot see toimprint
Imprint or imprinting may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Imprint'' (TV series), Canadian television series
* "Imprint" (''Masters of Horror''), episode of TV show ''Masters of Horror''
* ''Imprint'' (film), a 2007 independent drama/thriller film
...
on the human trainers. Then, when they are old enough, the rearing box is opened, allowing the bird to train its wings. As the fledgling gets stronger, feeding is reduced, forcing the bird to learn to hunt. This procedure is called hacking back to the wild. To release a captive-bred falcon, the bird is placed in a special cage at the top of a tower or cliff ledge for some days or so, allowing it to acclimate itself to its future environment.
Worldwide recovery efforts have been remarkably successful. The widespread restriction of DDT use eventually allowed released birds to breed successfully. The peregrine falcon was removed from the U.S. Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
list on 25 August 1999.
Some controversy has existed over the origins of captive breeding stock used by the Peregrine Fund
The Peregrine Fund (named after the bird of prey of the same name the peregrine falcon) is a non-profit organization founded in 1970 that conserves threatened and endangered birds of prey worldwide. The successful recovery of the peregrine falco ...
in the recovery of peregrine falcons throughout the contiguous United States. Several peregrine subspecies were included in the breeding stock, including birds of Eurasian origin. Due to the extirpation of the eastern population of ''Falco peregrinus anatum'', the near-extirpation of ''anatum'' in the Midwest and the limited gene pool within North American breeding stock, the inclusion of non-native subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
was justified to optimize the genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species, it ranges widely from the number of species to differences within species and can be attributed to the span of survival for a species. It is dis ...
found within the species as a whole.
During the 1970s, peregrine falcons in Finland experienced a population bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as specicide, widespread violen ...
as a result of large declines associated with bio-accumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated ...
of organochloride pesticides. However, the genetic diversity of peregrines in Finland is similar to other populations, indicating that high dispersal rates have maintained the genetic diversity of this species.
Since peregrine falcon eggs and chicks are still often targeted by illegal poachers, it is common practice not to publicize unprotected nest locations.
Current status
 Populations of the peregrine falcon have bounced back in most parts of the world. In the United Kingdom, there has been a recovery of populations since the crash of the 1960s. This has been greatly assisted by conservation and protection work led by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. The RSPB has estimated that there are 1,402 breeding pairs in the UK. In Canada, where peregrines were identified as endangered in 1978 (in the Yukon territory of northern Canada that year, only a single breeding pair was identified), the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada declared the species no longer at risk in December 2017.
Peregrines now breed in many mountainous and coastal areas, especially in the west and north, and nest in some urban areas, capitalising on the urban feral pigeon populations for food. In Southampton, a nest prevented restoration of mobile telephony services for several months, after Vodafone engineers despatched to repair a faulty
Populations of the peregrine falcon have bounced back in most parts of the world. In the United Kingdom, there has been a recovery of populations since the crash of the 1960s. This has been greatly assisted by conservation and protection work led by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. The RSPB has estimated that there are 1,402 breeding pairs in the UK. In Canada, where peregrines were identified as endangered in 1978 (in the Yukon territory of northern Canada that year, only a single breeding pair was identified), the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada declared the species no longer at risk in December 2017.
Peregrines now breed in many mountainous and coastal areas, especially in the west and north, and nest in some urban areas, capitalising on the urban feral pigeon populations for food. In Southampton, a nest prevented restoration of mobile telephony services for several months, after Vodafone engineers despatched to repair a faulty transmitter mast
Radio masts and towers are typically tall structures designed to support antennas for telecommunications and broadcasting, including television. There are two main types: guyed and self-supporting structures. They are among the tallest human-made ...
discovered a nest in the mast, and were prevented by the Wildlife and Countryside Act – on pain of a possible prison sentence – from proceeding with repairs until the chicks fledged. In many parts of the world peregrine falcons have adapted to urban habitats, nesting on cathedrals, skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
window ledges, tower blocks, and the towers of suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridg ...
s. Many of these nesting birds are encouraged, sometimes gathering media attention and often monitored by cameras.
Cultural significance
Due to its striking hunting technique, the peregrine has often been associated with aggression and martial prowess. The Ancient Egyptian solar deity Ra was often represented as a man with the head of a Peregrine Falcon adorned with the solar disk. Native Americans of theMississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
(c. 800–1500) used the peregrine, along with several other birds of prey, in imagery as a symbol of "aerial (celestial) power" and buried men of high status in costumes associating to the ferocity of raptorial birds. In the late Middle Ages, the Western European nobility that used peregrines for hunting, considered the bird associated with princes in formal hierarchies of birds of prey, just below the gyrfalcon associated with kings. It was considered "a royal bird, more armed by its courage than its claws". Terminology used by peregrine breeders also used the Old French term , "of noble birth; aristocratic", particularly with the peregrine.
The peregrine falcon is the national animal of the United Arab Emirates. Since 1927, the peregrine falcon has been the official mascot of Bowling Green State University in Bowling Green, Ohio. The 2007 U.S. Idaho state quarter features a peregrine falcon. The peregrine falcon has been designated the official city bird of Chicago.
''The Peregrine'', by J. A. Baker, is widely regarded as one of the best nature books in English written in the twentieth century. Admirers of the book include Robert Macfarlane, Mark Cocker
Mark Cocker (born 1959) is a British author and naturalist. He lives with his wife, Mary Muir, and two daughters in Claxton, Norfolk; the countryside around Claxton is a theme for two of his twelve books.
Cocker has written extensively for ...
, who regards the book as "one of the most outstanding books on nature in the twentieth century" and Werner Herzog, who called it "the one book I would ask you to read if you want to make films", and said elsewhere "it has prose of the calibre that we have not seen since Joseph Conrad
Joseph Conrad (born Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski, ; 3 December 1857 – 3 August 1924) was a Poles in the United Kingdom#19th century, Polish-British novelist and short story writer. He is regarded as one of the greatest writers in t ...
". In the book, Baker recounts, in diary form, his detailed observations of peregrines (and their interaction with other birds) near his home in Chelmsford, Essex, over a single winter from October to April.
An episode of the hour-long TV series ''Starman
''StarMan'' is a 1996 fantasy novel by Australian writer Sara Douglass. It follows the second book in the series, '' Enchanter'', with Axis marching north with his army to confront a formidable enemy.
Background
''StarMan'' was first published ...
'' in 1986 titled "Peregrine" was about an injured peregrine falcon and the endangered species program. It was filmed with the assistance of the University of California's peregrine falcon project in Santa Cruz. (Note: the episode was titled "The Falcon" during filming and retitled "Peregrine" before broadcast. An end credit gives thanks to Brian Walton and the Peregrine Fund Facility at UCSC.)
See also
*List of birds by flight speed
This is a list of the fastest flying birds in the world. A bird's velocity is necessarily variable; a hunting bird will reach much greater speeds while diving to catch prey than when flying horizontally. The bird that can achieve the greatest airs ...
* Perilanner, a hybrid of the peregrine falcon and the lanner falcon (''Falco biarmicus'')
* Perlin, a hybrid of the peregrine falcon and the merlin
Merlin ( cy, Myrddin, kw, Marzhin, br, Merzhin) is a mythical figure prominently featured in the legend of King Arthur and best known as a mage, with several other main roles. His usual depiction, based on an amalgamation of historic and le ...
(''Falco columbarius'')
Explanatory notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
; Conservation organizationsArctic Raptors – Ongoing research with raptors in the Canadian Arctic
Falcon Research Group
Peregrine Falcon Fund
The Canadian Peregrine Foundation
London Peregrine Partnership (UK)
; Video and other media of peregrines
* ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j3mTPEuFcWk A video of the falcon stooping at a top speed of
Derby Cathedral Peregrine Project, UK. Links to webcams and video sequences
Norwich Cathedral Peregrine Web Cam 2015, UK.
*
The Raptor Resource Project. Links to Peregrine Falcon webcams
Peregrines on Brussels Cathedral
* ttp://www.ntu.ac.uk/ecoweb/biodiversity/falcons/index.html Nottingham Trent University, where peregrines return to breed on the top of the Newton building every year. Includes images and webcam.
University of Massachusetts Amherst Live Falcon Cam at the top of the W.E.B. DuBois library, active each year from when the bonded pair of peregrine falcons brood eggs until the chicks are fledged.
Worcester Peregrine Falcon Project, UK. Includes feeds from 'Peregrines in Worcester' Facebook Fan page, YouTube & Flickr photo groups
Peregrine Falcon Banding
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 3 June 2010; 3-minute YouTube video clip
Throgs Neck Bridge Peregrine Banding 2011
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 27 May 2011; 10:54 YouTube video clip
Peregrine Falcon Banding 2012
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 4 June 2012; 2:40 YouTube video clip
Peregrine Falcon Banding 2016
Metropolitan Transportation Authority Bridges and Tunnels; 2 June 2016; 4:15 YouTube video clip {{DEFAULTSORT:Falcon, peregrine
Peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
Peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
Cosmopolitan birds
Birds of prey of Africa
Birds of Asia
Birds of Europe
Birds of North America
Birds of North Africa
Birds of South America
Diurnal raptors of Australia
Peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
Peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
Peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
Birds of the Dominican Republic