FIBA Basketball World Championship on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The FIBA Basketball World Cup, also known as the FIBA World Cup of Basketball or simply the FIBA World Cup, between 1950 and 2010 known as the FIBA World Championship, is an international
 The FIBA Basketball World Cup was conceived at a meeting of the FIBA World Congress at the
The FIBA Basketball World Cup was conceived at a meeting of the FIBA World Congress at the
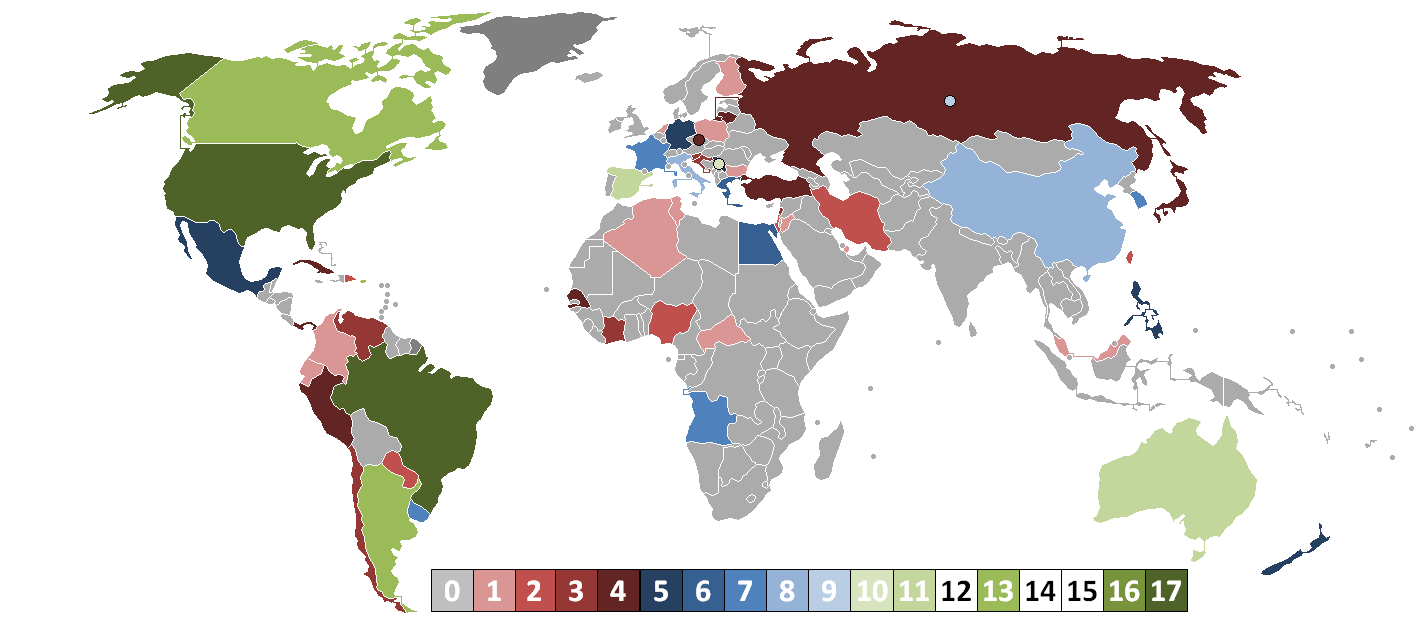 The Basketball World Cup has used various forms of qualification throughfive tournaments were held in South America and participation was dominated by teams from the Americas. At the first tournament, FIBA intended for the three Olympic medalists to compete, plus the host Argentina and two teams each from Europe, Asia, and South America. However, no Asian team was willing to travel to the event, so six of the ten teams were from the Americas (all three Olympic medalists were from the Americas, plus the zone received two continental berths and an Asia's berth). The former European powerhouse
The Basketball World Cup has used various forms of qualification throughfive tournaments were held in South America and participation was dominated by teams from the Americas. At the first tournament, FIBA intended for the three Olympic medalists to compete, plus the host Argentina and two teams each from Europe, Asia, and South America. However, no Asian team was willing to travel to the event, so six of the ten teams were from the Americas (all three Olympic medalists were from the Americas, plus the zone received two continental berths and an Asia's berth). The former European powerhouse
If the teams should be tied at the end of the preliminary round, the ties are broken by the following criteria in order: #Game results between tied teams #
 Since
Since
basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the International Basketball Federation
The International Basketball Federation (FIBA ; French: ) is an association of national organizations which governs the sport of basketball worldwide. Originally known as the (hence FIBA), in 1989 it dropped the word ''amateur'' from its nam ...
(FIBA), the sport's global governing body. It is considered the flagship event of FIBA.
The tournament structure is similar, but not identical, to that of the FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
; both of these international competitions were played in the same year from 1970 through 2014. A parallel event for women's teams, now known as the FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup
The FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup, also known as the Basketball World Cup for Women or simply the FIBA Women's World Cup, is an international basketball tournament for women's national teams held quadrennially. It was created by the Internat ...
, is also held quadrennially. From 1986 through 2014, the men's and women's championships were held in the same year, though in different countries. The current format of the tournament involves 32 teams competing for the title at venues within the host nation. The winning team receives the Naismith Trophy
The Naismith Trophy is a trophy awarded to the men's champion of the FIBA Basketball World Cup, and is named in honor of basketball's inventor, James Naismith. The trophy was first awarded to the winner of the 1967 FIBA World Championship. The ...
, first awarded in 1967
Events
January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 5
** Spain and Romania sign an agreement in Paris, establishing full consular and ...
. The current champions are Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, who defeated Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
in the final of the 2019 tournament.
Following the 2014 FIBA championships for men and women, the men's World Cup was scheduled on a new four-year cycle to avoid conflict with the FIFA World Cup. The men's World Cup was held in 2019, in the year following the FIFA World Cup. The women's championship, which was renamed from "FIBA World Championship for Women" to "FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup", after its 2014 edition, will remain on the previous four-year cycle, with championships in the same year as the FIFA World Cup.
The 1994 FIBA World Championship, which was held in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, was the first FIBA World Cup tournament in which currently active US NBA players, that had also already played in an official NBA regular season game, were allowed to participate. All FIBA World Championship/World Cup tournaments since then, are thus considered as fully professional
A professional is a member of a profession or any person who works in a specified professional activity. The term also describes the standards of education and training that prepare members of the profession with the particular knowledge and ski ...
level tournaments.
History
 The FIBA Basketball World Cup was conceived at a meeting of the FIBA World Congress at the
The FIBA Basketball World Cup was conceived at a meeting of the FIBA World Congress at the 1948 Summer Olympics
The 1948 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XIV Olympiad and also known as London 1948) were an international multi-sport event held from 29 July to 14 August 1948 in London, England, United Kingdom. Following a twelve-year hiatus ca ...
in London. Long-time FIBA Secretary-General Renato William Jones urged FIBA to adopt a World Championship, similar to the FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
, to be held in every four years between Olympiad
An olympiad ( el, Ὀλυμπιάς, ''Olympiás'') is a period of four years, particularly those associated with the ancient and modern Olympic Games.
Although the ancient Olympics were established during Greece's Archaic Era, it was not unti ...
s. The FIBA Congress, seeing how successful the 23-team Olympic tournament was that year, agreed to the proposal, beginning with a tournament in 1950
Events January
* January 1 – The International Police Association (IPA) – the largest police organization in the world – is formed.
* January 5 – Sverdlovsk plane crash: ''Aeroflot'' Lisunov Li-2 crashes in a snowstorm. All 19 ...
. Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
was selected as host, largely because it was the only country willing to take on the task. Argentina took advantage of the host selection, winning all their games en route to becoming the first FIBA World Champion.
The first five tournaments were held in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
, and teams from the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
dominated the tournament, winning eight of nine medals at the first three tournaments. By 1963
Events January
* January 1 – Bogle–Chandler case: Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation scientist Dr. Gilbert Bogle and Mrs. Margaret Chandler are found dead (presumed poisoned), in bushland near the Lane Co ...
, however, teams from Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
(the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
) and Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (a ...
(Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
), in particular – began to catch up to the teams from the American continents. Between 1963 and 1990, the tournament was dominated by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, and Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
who together accounted for every medal at the tournament.
The 1994 FIBA World Championship held in Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
marked the beginning of a new era, as currently active American NBA players participated in the tournament for the first time (prior to that only European and South American professionals were allowed to participate as they were still classified as amateurs), while the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
split into many new states. The United States dominated that year and won gold, while the former states of the USSR and Yugoslavia, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
and Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, won silver and bronze. The 1998 FIBA World Championship
The 1998 FIBA World Championship was the 13th FIBA World Championship, an international basketball tournament held by the International Basketball Federation and hosted in Greece from 29 July to 9 August 1998. The tournament was contested by 16 n ...
, held in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
(Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
and Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; el, Πειραιάς ; grc, Πειραιεύς ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens' city centre, along the east coast of the Saron ...
), lost some of its luster when the 1998–99 NBA lockout
The 1998–99 NBA lockout was the third lockout of four in the history of the National Basketball Association (NBA). It lasted from July 1, 1998, to January 20, 1999, and forced the 1998–99 regular season to be shortened to 50 games per team ...
prevented NBA players from participating. The new Yugoslavian team, now consisting of the former Yugoslav republics of Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
and Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
, won the gold medal over Russia, while the USA, with professional basketball players playing in Europe and two college players, finished third.
In 2002, other nations eventually caught up to the four powerhouse countries and their successor states. FR Yugoslavia
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, Cрбија и Црна Гора, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yug ...
, led by Peja Stojaković of the Sacramento Kings
The Sacramento Kings are an American professional basketball team based in Sacramento, California. The Kings compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Western Conference Pacific Division. The Kings are the oldest ...
and Dejan Bodiroga
Dejan Bodiroga ( sr-Cyrl, Дејан Бодирога; born 2 March 1973) is a Serbian basketball executive and former professional player who is the Chairman of the Euroleague Basketball.
During his playing career, he mainly played at the sm ...
of FC Barcelona
Futbol Club Barcelona (), commonly referred to as Barcelona and colloquially known as Barça (), is a professional football club based in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, that competes in La Liga, the top flight of Spanish football.
Found ...
won the final game against Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, while Dirk Nowitzki
Dirk Werner Nowitzki (, ; born June 19, 1978) is a German former professional basketball player who is a special advisor for the Dallas Mavericks of the National Basketball Association (NBA). Listed at , he is widely regarded as one of the gre ...
, who was the tournament's MVP, led Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
to the bronze, its first ever World Championship medal. Meanwhile, the United States team, this time made up of NBA players, struggled to a sixth-place finish. This new era of parity convinced FIBA to expand the tournament to 24 teams for the 2006, 2010, and 2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wat ...
editions of the tournament.
In 2006, emerging powerhouse Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
beat Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
in the first appearance in the final for both teams. Spain became only the seventh team (Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and FR Yugoslavia
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, Cрбија и Црна Гора, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yug ...
are counted separately in the FIBA records) to capture a World Championship gold. The USA, who lost to Greece in a semi-final, won against Argentina in the third-place match and claimed bronze.
In the 2010 FIBA World Championship
The 2010 FIBA World Championship was the 16th FIBA World Championship, the international basketball world championship contested by the men's national teams. The tournament ran from 28 August to 12 September 2010. It was co-organised by the Inte ...
final, the USA defeated Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
and won gold for the first time in 16 years, while Lithuania beat Serbia and won bronze. The United States became the third country to defend the championship, winning against Serbia at the 2014 edition of the tournament. France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
beat Lithuania in the bronze medal game.
After the 2014 edition, FIBA instituted significant changes to the World Cup. The final competition was expanded from 24 to 32 teams. Also, for the first time since 1967, the competition would no longer overlap with the FIFA World Cup. To accommodate this change, the 2014 FIBA World Cup was followed by a 2019 edition in China, and will be followed by a 2023 edition in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Japan, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
.
Qualification
 The Basketball World Cup has used various forms of qualification throughfive tournaments were held in South America and participation was dominated by teams from the Americas. At the first tournament, FIBA intended for the three Olympic medalists to compete, plus the host Argentina and two teams each from Europe, Asia, and South America. However, no Asian team was willing to travel to the event, so six of the ten teams were from the Americas (all three Olympic medalists were from the Americas, plus the zone received two continental berths and an Asia's berth). The former European powerhouse
The Basketball World Cup has used various forms of qualification throughfive tournaments were held in South America and participation was dominated by teams from the Americas. At the first tournament, FIBA intended for the three Olympic medalists to compete, plus the host Argentina and two teams each from Europe, Asia, and South America. However, no Asian team was willing to travel to the event, so six of the ten teams were from the Americas (all three Olympic medalists were from the Americas, plus the zone received two continental berths and an Asia's berth). The former European powerhouse Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, later made their first tournament appearance in 1959
Events January
* January 1 - Cuba: Fulgencio Batista flees Havana when the forces of Fidel Castro advance.
* January 2 - Lunar probe Luna 1 was the first man-made object to attain escape velocity from Earth. It reached the vicinity of E ...
, after missing the first two events.
In the tournament's early years, only Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
had established continental tournaments, so participation in the tournament was largely by invitation. Later, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
added a continental championship in 1960, followed by Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
in 1962, Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
in 1965, and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
in 1971, As a result of these changes, qualification became more formalized starting with the 1967 tournament. In that year, the Asian champion received an automatic berth in the tournament, joining the top European and South American teams. In 1970
Events
January
* January 1 – Unix time epoch reached at 00:00:00 UTC.
* January 5 – The 7.1 Tonghai earthquake shakes Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). Between 10,000 and ...
, the African and Oceanian champion each received a berth, while the Centrobasket champion and runner-up were each invited. For most of these years, the tournament host, defending World Champion, and top Olympic basketball tournament finishers also qualified for the event.
From 1970 through the 2014 World Cup, qualification continued to be based on the continental competitions and the Olympic tournament. The only major change came in the 1990 FIBA World Championship, when the tournament started taking qualifiers from the newly redesigned FIBA Americas Championship
The FIBA AmeriCup (previously known as the FIBA Americas Championship) is the Americas Basketball Championship that takes place every four years between national teams of the Western Hemisphere continents.
Since FIBA organised the entire West ...
rather than from North, Central, and South America individually. After the tournament expanded to 24 teams in 2006, the tournament allocated qualification as follows:
* FIBA EuroBasket
EuroBasket, also commonly referred to as the European Basketball Championship, is the main international basketball competition that is contested quadrennially, by the senior men's national teams that are governed by FIBA Europe, which is the E ...
(Europe) – 6 berths
* FIBA AfroBasket (Africa) – 3 berths
* FIBA Asia Cup (Asia) – 3 berths
* FIBA AmeriCup
The FIBA AmeriCup (previously known as the FIBA Americas Championship) is the Americas Basketball Championship that takes place every four years between national teams of the Western Hemisphere continents.
Since FIBA organised the entire West ...
(Americas) – 5 berths
* FIBA Oceania Championship
FIBA Oceania Championship was the Oceania basketball championships that took place every two years between national teams of the continent. Through the 2015 edition, the Oceania Championship was also a qualifying tournament for the Basketball ...
(Oceania) – 2 berths
* Defending Olympic Champion – 1 berth, removed from the zone of the Olympic champion
* Host team – 1 berth
* FIBA-selected wild cards
''Wild Cards'' is a series of science fiction superhero shared universe anthologies, mosaic novels, and solo novels. They are written by a collection of more than forty authors (referred to as the "Wild Cards Trust") and are edited by George ...
– 4 berths
Each of the five continental championships also served as qualification for the Olympics, so all were held every two years. The year immediately preceding the World Championship was used to determine the berths at the tournament. For example, all of the berths at the 2010 FIBA World Championship
The 2010 FIBA World Championship was the 16th FIBA World Championship, the international basketball world championship contested by the men's national teams. The tournament ran from 28 August to 12 September 2010. It was co-organised by the Inte ...
were determined by continental championships held in 2009. After the first 20 teams qualified, FIBA then selected four wild card teams, based on sporting, economic, and governance criteria, as well as a required registration fee from each team to be considered by the FIBA board. Of the four wild cards, only three could come from one continental zone. In each of the two tournaments that the wild card system was in place, FIBA selected the maximum three European teams to compete in the event.
FIBA instituted major changes to its competition calendar and the qualifying process for both the World Cup and Olympics in 2017.
First, the continental championships are now held once every four years, specifically in years that immediately follow the Summer Olympics. The continental championships no longer play a role in qualifying for either the World Cup or Olympics.
The 2019 World Cup qualifying process, which began in 2017, is the first under a new format. Qualifying takes place over a two-year cycle, involving six windows of play. Qualifying zones mirror the FIBA continental zones, except that FIBA Asia and FIBA Oceania are now combined into a single Asia-Pacific qualifying zone. In each qualifying zone, nations are divided into Division A and Division B, with promotion and relegation
In sports leagues, promotion and relegation is a process where teams are transferred between multiple divisions based on their performance for the completed season. Leagues that use promotion and relegation systems are often called open leagues ...
between the two. FIBA did not initially reveal full details of the new process, but announced that at least in opening phases, it would feature groups of three or four teams, playing home-and-away within the group. Below is the list of distribution of berths according to each FIBA qualifying zone.
* FIBA Europe – 12 berths
* FIBA Americas
FIBA Americas ( es, Confederación Panamericana de Baloncesto, french: FIBA Amériques) is a zone within FIBA (International Basketball Federation). It is one of FIBA's five continental confederations. FIBA Americas is responsible for the organiz ...
– 7 berths
* FIBA Africa
FIBA Africa is a zone within the FIBA basketball association which contains all 54 national African FIBA federations. It was founded in 1961. FIBA Africa maintains offices in Cairo and in Abidjan.
Members
FIBA World Rankings Overview
...
– 5 berths
* Asia-Pacific (FIBA Asia
FIBA Asia is a zone within the International Basketball Federation (FIBA) which contains all 44 Asian FIBA federations.
Member associations
Tournaments Organized by FIBA Asia National teams
* FIBA Asia Cup – since 2017, also inclu ...
and FIBA Oceania
The International Basketball Federation (FIBA ; French: ) is an association of national organizations which governs the sport of basketball worldwide. Originally known as the (hence FIBA), in 1989 it dropped the word ''amateur'' from its nam ...
) – 7 berths
* Host team – 1 berth / 2 berths in 2023
Events
Predicted and scheduled events
* January 1
** In the United States, books, films, and other works published in 1927 will enter the public domain, assuming there are no changes made to copyright law.
** Croatia will adopt the eu ...
Tournament format
The Basketball World Cup has existed in several different formats throughout the years, as it has expanded and contracted between 10 and 24 teams. The first tournament, in1950
Events January
* January 1 – The International Police Association (IPA) – the largest police organization in the world – is formed.
* January 5 – Sverdlovsk plane crash: ''Aeroflot'' Lisunov Li-2 crashes in a snowstorm. All 19 ...
, began with a ten-team double-elimination tournament
A double-elimination tournament is a type of elimination tournament competition in which a participant ceases to be eligible to win the tournament's championship upon having lost ''two'' games or matches. It stands in contrast to a single-elimina ...
, followed by a six-team round robin
Round-robin may refer to:
Computing
* Round-robin DNS, a technique for dealing with redundant Internet Protocol service hosts
* Round-robin networks, communications networks made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology
* Round-robin schedu ...
round to determine the champion. Between 1954 and 1974, each tournament started with a group stage preliminary round; the top teams in each preliminary round group then moved on to a final round robin group to determine the champion. In 1978, FIBA added a gold medal game between the top two finishers in the final group and a bronze medal game between the third and fourth place teams. In each year between 1959 and 1982, the host team received a bye into the final group. Of the seven host teams in this era, only three won medals, despite the head start. As a result, FIBA made the host team compete in the preliminary round starting in 1986
The year 1986 was designated as the International Year of Peace by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
**Aruba gains increased autonomy from the Netherlands by separating from the Netherlands Antilles.
**Spain and Portugal enter ...
.
In 1986, the tournament briefly expanded to 24 teams. Four groups of six teams each competed in the preliminary round group stage. The top three teams in each group then competed in the second group stage, followed by a four-team knockout tournament between the top two finishers in each group. The championship contracted back down to 16 teams for the 1990 tournament. The three tournaments between 1990 and 1998, each had two group stages followed by a four-team knockout tournament to determine the medalists. The 2002 tournament expanded the knockout round to eight teams.
In 2006, FIBA made the decision to expand back to 24 teams and introduced the format that was in place through 2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wat ...
. Under that format, the teams were divided into four preliminary round groups of six teams each.
In 2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
, the final tournament will expand to 32 teams.If the teams should be tied at the end of the preliminary round, the ties are broken by the following criteria in order: #Game results between tied teams #
Goal average
A goal is an idea of the future or desired result that a person or a group of people envision, plan and commit to achieve. People endeavour to reach goals within a finite time by setting deadlines.
A goal is roughly similar to a purpose or ai ...
between games of the tied teams
#Goal average for all games of the tied teams
#Drawing of lots
The top two teams in each group then advance to a sixteen-team single-elimination knockout round. It begins with the eighth finals, where the top teams in each group play the fourth-placed teams in another group and the second and third-placed teams in each group face off. This is followed by the quarterfinals, semi-finals, and final. The semi-final losers play in the bronze medal game, while the quarterfinal losers play in a consolation bracket to determine fifth through eighth places.
Naismith Trophy
1967
Events
January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 5
** Spain and Romania sign an agreement in Paris, establishing full consular and ...
, the champion of each tournament has been awarded the Naismith Trophy
The Naismith Trophy is a trophy awarded to the men's champion of the FIBA Basketball World Cup, and is named in honor of basketball's inventor, James Naismith. The trophy was first awarded to the winner of the 1967 FIBA World Championship. The ...
, named in honor of basketball's inventor, James Naismith
James Naismith (; November 6, 1861November 28, 1939) was a Canadian-American physical educator, physician, Christian chaplain, and sports coach, best known as the inventor of the game of basketball. After moving to the United States, he wrote ...
. A trophy had been planned since the first World Championship in 1950, but did not come to fruition until FIBA finally commissioned a trophy in 1965, after receiving a US$1,000 donation. The original trophy was used from 1967 through 1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nelson ...
. An updated trophy was introduced for the 1998 FIBA World Championship
The 1998 FIBA World Championship was the 13th FIBA World Championship, an international basketball tournament held by the International Basketball Federation and hosted in Greece from 29 July to 9 August 1998. The tournament was contested by 16 n ...
and the original now sits at the Pedro Ferrándiz
Pedro Ferrándiz González (20 November 1928 – 7 July 2022) was a Spanish basketball coach. He is most famous for coaching Real Madrid basketball club in the 1960s and 1970s. The International Olympic Committee awarded him the Olympic Order ...
Foundation in Spain.
The second trophy is designed in an Egyptian-inspired lotus shape, upon which there are carved maps of the continents and precious stones symbolizing the five continents (FIBA Americas
FIBA Americas ( es, Confederación Panamericana de Baloncesto, french: FIBA Amériques) is a zone within FIBA (International Basketball Federation). It is one of FIBA's five continental confederations. FIBA Americas is responsible for the organiz ...
represents both North America and South America). Dr. Naismith's name is engraved on all four sides in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, and Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs (, ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt, used for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with some 1,000 distinct characters.There were about 1, ...
. The trophy stands 47 centimeters (18.5 inches) tall and weighs nine kilograms (twenty pounds).
The most recent Naismith Trophy design was revealed in the 2019 FIBA World Cup
The 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup was the 18th tournament of the FIBA Basketball World Cup for men's national basketball teams. The tournament was hosted in China and was rescheduled from 2018 to 2019, becoming the first since 1967 FIBA World Ch ...
Qualifiers Draw Ceremonies, last 7 May 2017. The trophy, which stands about 60 centimeters high (13 cm. higher than the 1998 version), is made almost entirely out of gold, and features the names of the previous world cup champions at the base. FIBA's original name (Federation Internationale de Basketball Amateur) is also engraved at the trophy's "hoop". The trophy was designed by Radiant Studios Ltd, and handcrafted by the silversmith Thomas Lyte
Thomas Lyte is an English luxury brand specialising in gold and silverware, sporting trophies and leather accessories.
The company has designed, made or restored many well known trophies and medals, such as the football’s FA Cup, golf’s Ryder ...
.
Summary
(OT): game decided after overtime.Medal table
In the most current medal table released by FIBA as seen on the FIBA archive website, the 2014 championship is taken into account, and the records of SFR Yugoslavia and FR Yugoslavia are combined under "Yugoslavia". Previously, FIBA had a medal table from 1950 to 2006, and another medal table that included results from 1950 to 2006, that separated the results of SFR Yugoslavia/FR Yugoslavia and Serbia and Montenegro respectively into "Yugoslavia" or "Serbia and Montenegro". The ranking of teams between the latter two medal tables are different, with the FIBA.com ranking by number of total medals, while the FIBA World Cup website's ranking is by number of gold medals. The number of medals won by the United States differs between the latter two medal tables, despite encompassing the same period. The latter two medal tables also do not include the results of the 2010 and 2014 championships. Finally, a FIBA.com PDF linked from the FIBA.com history section that documents the championships from 1950 to 2002 also has a medal table that included tournaments from 1950 to 1998, which also separated pre-breakup Yugoslavia, called as "Yusgoslavia" from the post-breakup Yugoslavia, called as "Serbia and Montenegro", and ranked the teams by the number of total medals. The FIBA archive also lists the achievements of each national team, separating it per IOC codes. The national team representing Serbia's first international tournament is listed as 2007, Serbia and Montenegro's tournament participation lasted from 2003 to 2006, and Yugoslavia's participation was from 1947 to 2002. Chinese Taipei was listed not to have participated in the World Cup, indeed its first participation in any FIBA tournament started in 1986; a team called "Taiwan" participated from 1960 to 1973, and a "Formosa" team joined from 1954 to 1959. Below is the FIBA table as seen from the FIBA archive website, updated with results since 1998. The records of SFR Yugoslavia and FR Yugoslavia (counted together as "Yugoslavia") are separated from records of Serbia and Serbia and Montenegro. In the case of the Soviet Union, their records also didn't carry over to Russia.Participating nations
Most successful players
Boldface denotes active basketball players and highest medal count among all players (including these who not included in these tables) per type.Multiple gold medalists
The table shows players who have won at least 2 gold medals at the World Cups.Multiple medalists
The table shows players who have won at least 4 medals in total at the World Cups.Other records and statistics
Eleven players – Ubiratan Pereira Maciel ("Bira"), Marcel de Souza, Marcelinho Machado, Anderson Varejao, Leandrinho Barbosa and Alex Garcia ofBrazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Phil Smyth of Australia, Daniel Santiago
Daniel Gregg Santiago (born June 24, 1976) is a Puerto Rican former professional basketball player. A center, he had a collegiate career in the NCAA and NAIA. His professional career saw him play in the NBA, the Baloncesto Superior Nacional of ...
and Jerome Mincy of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Eduardo Mingas of Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
and Luis Scola
Luis Alberto Scola Balvoa (born April 30, 1980) is an Argentine former professional basketball player and current executive who currently serves as the chief executive officer for the Italian Lega Basket Serie A (LBA) team Pallacanestro Varese. ...
of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
– have appeared in five tournaments.
Brazilian legend Oscar Schmidt
Oscar Daniel Bezerra Schmidt (born February 16, 1958) is a retired Brazilian professional basketball player. He is also commonly known as Oscar Schmidt in Spain, where he played for Fórum Valladolid for the 1993–94 and 1994–95 seasons, ...
is the runaway all-time leading scorer, scoring 906 career points in four tournaments, between 1978 and 1990
File:1990 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1990 FIFA World Cup is played in Italy; The Human Genome Project is launched; Voyager I takes the famous Pale Blue Dot image- speaking on the fragility of humanity on Earth, astrophysicist ...
. Nikos Galis
Nikolaos Georgalis ( el, Νικόλαος Γεωργαλής; born July 23, 1957), commonly known as either Nikos Galis ( el, Νίκος Γκάλης), or Nick Galis, is a retired Greek professional basketball player. Galis, who during his playin ...
of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, is the all-time leading scorer, for a single tournament, averaging 33.7 points per game for the Greeks at the 1986 FIBA World Championship.
Serbian coach and former player Željko Obradović
Želimir "Željko" Obradović ( sr-cyr, Желимир "Жељко" Обрадовић, ; born 9 March 1960) is a Serbian professional basketball coach and former player who is currently the head coach for Partizan of the ABA League, the Basketba ...
is the only person who won the title, both as a coach and a player. He was a member of the Yugoslavia team that won the 1990 FIBA World Championship and coached the Yugoslavia team that won the 1998 FIBA World Championship
The 1998 FIBA World Championship was the 13th FIBA World Championship, an international basketball tournament held by the International Basketball Federation and hosted in Greece from 29 July to 9 August 1998. The tournament was contested by 16 n ...
.
Awards
FIBA names a Most Valuable Player for each tournament. Since the tournament opened to NBA players at the 1994 tournament for the first time, NBA players have won six of the seven MVP trophies awarded – Shaquille O'Neal for theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
in 1994, Germany's Dirk Nowitzki
Dirk Werner Nowitzki (, ; born June 19, 1978) is a German former professional basketball player who is a special advisor for the Dallas Mavericks of the National Basketball Association (NBA). Listed at , he is widely regarded as one of the gre ...
at the 2002 tournament, Spain's Pau Gasol
Pau Gasol Sáez (, ; born July 6, 1980) is a Spanish former professional basketball player. He was a six-time NBA All-Star and a four-time All-NBA team selection, twice on the second team and twice on the third team. Gasol won two NBA champion ...
at the 2006 tournament, Kevin Durant
Kevin Wayne Durant ( ; born September 29, 1988), also known by his initials KD, is an American professional basketball player for the Brooklyn Nets of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He played one season of college basketball for t ...
for the United States at the 2010 tournament, Kyrie Irving
Kyrie Andrew Irving (; lkt, Ȟéla, italic=no, ; born March 23, 1992) is an American professional basketball player for the Brooklyn Nets of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He was named the Rookie of the Year after being selected ...
for the United States at the 2014 tournament and Spain's Ricky Rubio at the 2019 tournament. The only exception was Dejan Bodiroga
Dejan Bodiroga ( sr-Cyrl, Дејан Бодирога; born 2 March 1973) is a Serbian basketball executive and former professional player who is the Chairman of the Euroleague Basketball.
During his playing career, he mainly played at the sm ...
of FR Yugoslavia
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, Cрбија и Црна Гора, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yug ...
, who was the MVP of the 1998 tournament, when the NBA players were not able to participate, due to the 1998–99 NBA lockout
The 1998–99 NBA lockout was the third lockout of four in the history of the National Basketball Association (NBA). It lasted from July 1, 1998, to January 20, 1999, and forced the 1998–99 regular season to be shortened to 50 games per team ...
.
Tournament growth
The2010 FIBA World Championship
The 2010 FIBA World Championship was the 16th FIBA World Championship, the international basketball world championship contested by the men's national teams. The tournament ran from 28 August to 12 September 2010. It was co-organised by the Inte ...
reached a global TV audience of 800 million people, across 171 countries, with the official website having 30 million views during the tournament. Both numbers broke the previous records set at the 2006 FIBA World Championship
The 2006 FIBA World Championship was the 15th FIBA World Championship, the international basketball world championship for men's national teams. The tournament was hosted by Japan and held from 19 August to 3 September 2006. It was co-organised by ...
and at the EuroBasket 2009
The 2009 FIBA European Championship, commonly called FIBA EuroBasket 2009, was the 36th FIBA EuroBasket regional basketball championship held by FIBA Europe. The tournament, which was hosted by Poland, began on 7 September and concluded with the ...
. Three of the games involving Lithuania were among the highest rated programs in that country. In China, 65 million watched the Chinese national team's game against Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, in the preliminary round. This was an improvement from the 2006 FIBA World Championship, which was held in Japan, and was shown in 150 countries. This meant that games aired in the morning in Europe and at night in the Americas; despite this, audiences broke records, with Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
's game against Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
achieving a 20% viewing share in Italy, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
's game against Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
netting a 33% share in Serbia, and a 600,000-audience in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
for the US national team's game against Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
at 1 am.
Before the 2010 FIBA World Championship started in Turkey, FIBA had already sold 350,000 tickets, for a revenue of between US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
8 to 10 million. The number of tickets sold was 10% higher than 2006, although the revenue was less than 2006's US$18 million, which was widely attributed to the strong Japanese yen. Meanwhile, FIBA got two-thirds of marketing rights revenue, of which one-third, or about US$8 million, went to the local organizers. FIBA had also successfully negotiated TV rights deals, which all went to FIBA, worth US$25 million, including a TV rights deal with ESPN
ESPN (originally an initialism for Entertainment and Sports Programming Network) is an American international basic cable sports channel owned by ESPN Inc., owned jointly by The Walt Disney Company (80%) and Hearst Communications (20%). Th ...
. In 2006, the Japanese organizers were targeting to sell 180,000 tickets, mostly to a Japanese audience; as for the overseas audience, the Japanese organizers didn't "expect them in great numbers". This was seen as a big improvement from the 2002 tournament, which was a financial loss for USA Basketball and Indianapolis, in which all games were held in one city. This led to the Japanese organizers to hold games throughout the country, instead of just in a single city.
At the most recent world championship, which was re-branded as the 2014 FIBA Basketball World Cup, in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, FIBA
The International Basketball Federation (FIBA ; French: ) is an association of national organizations which governs the sport of basketball worldwide. Originally known as the (hence FIBA), in 1989 it dropped the word ''amateur'' from its nam ...
reported impressive ratings from nations which were participating in the tournament during the first week of the group phase. Most games involving European teams had a market share of at least 20%, including a 40% market share in Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, for the Finnish national team's game against the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
. The TV ratings in the United States beat out the 2014 US Tennis Open, but some US sports media still described viewers in the US as not caring about the FIBA Basketball World Cup. In the Philippines, the entire tournament had an average reach of 67.8%.
See also
* Basketball at the Summer Olympic Games *FIBA Under-19 Basketball World Cup
The FIBA Under-19 Basketball World Cup (formerly FIBA Under-19 World Championship) is the under-19 men's world basketball championship organised by the International Basketball Federation (FIBA). From its inauguration in 1979, until 2007, it was ...
* FIBA Under-17 Basketball World Cup
* FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup
The FIBA Women's Basketball World Cup, also known as the Basketball World Cup for Women or simply the FIBA Women's World Cup, is an international basketball tournament for women's national teams held quadrennially. It was created by the Internat ...
* FIBA Under-19 Women's Basketball World Cup
The FIBA Under-19 Women's Basketball World Cup (formerly FIBA Under-19 World Championship for Women) is the women's international under-19 basketball championship organised by FIBA. From its inauguration in 1985, until 2005, it was held every fou ...
* FIBA Under-17 Women's Basketball World Cup
The FIBA Under-17 Women's Basketball World Cup (formerly FIBA Under-17 World Championship for Women) is the women's international under-17 Women's basketball, basketball championship organised by FIBA. The event started in July 2010, and is held ...
Notes
References
External links
* {{navboxes , titlestyle = background:black; color:#dbc068; border:1px solid #dbc068 , list = {{FIBA Basketball World Cup winners {{FIBA Basketball World Cup hosts {{FIBA Basketball World Cup host cities {{FIBA Basketball World Cup Final venues {{FIBA Basketball World Cup MVP Award {{FIBA Basketball World Cup top scorers {{FIBA navbox {{International basketball {{Main world championships {{Sports country lists {{Authority control * Recurring sporting events established in 1950 World championships in basketball Quadrennial sporting events