FHAD1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Forkhead-associated domain containing protein 1 (FHAD1) is a
 The FHAD 1 protein is 1412 aa long, weighs 16.2 kDa and has an
The FHAD 1 protein is 1412 aa long, weighs 16.2 kDa and has an

 FHAD1 has been predicted to be a
FHAD1 has been predicted to be a

 The rate of evolution of FHAD1 was compared with that of
The rate of evolution of FHAD1 was compared with that of
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
encoded by the FHAD1 gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
.
As the name suggests, it has a forkhead-associated domain and an extensive coiled coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins in which two to seven alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope. ( Dimers and trimers are the most common types.) They have been found in roughly 5-10% of proteins and have a ...
structure. It is predicted to have a function related to DNA transcription. It is localized to the nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
and has a nuclear localization signal
A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysin ...
.
Gene
Locus and Size
Inhuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s, the FHAD1 gene is located on chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
1 (1p36.21) and the genomic sequence is on the plus strand starting from 15236559 bp and ending at 15400283 bp. There are 3 main genes around FHAD1, out of which 2 encode proteins with known functions. Two genes, EFHD2 and Chymotrypsin-C (CTRC) lie downstream of FHAD1 on the plus strand. TMEM51 lies upstream of FHAD1.
FHAD1 is 163,682 bases long and contains 43 exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence ...
s.
Common Aliases
FHAD1 has 4aliases
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true meaning (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individual's ow ...
, Forkhead associated phosphopeptide binding domain 1, Forkhead-associated (FHA) phosphopeptide binding domain 1, FHA Domain-Containing Protein 1, and KIAA1937.
mRNA
ThemRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
transcript of FHAD1 5138 bp long. The gene has 30 isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have uniqu ...
based on NCBI gene data.
Protein
 The FHAD 1 protein is 1412 aa long, weighs 16.2 kDa and has an
The FHAD 1 protein is 1412 aa long, weighs 16.2 kDa and has an isoelectric point
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electric charge, electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I). Howe ...
of 6.52. It has 3 isoforms, namely 1, 3 and 4, but only isoform 1 is supported by experimental evidence. It consists of 1 glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ...
rich region and 1 proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
rich region.
Domains and Motifs
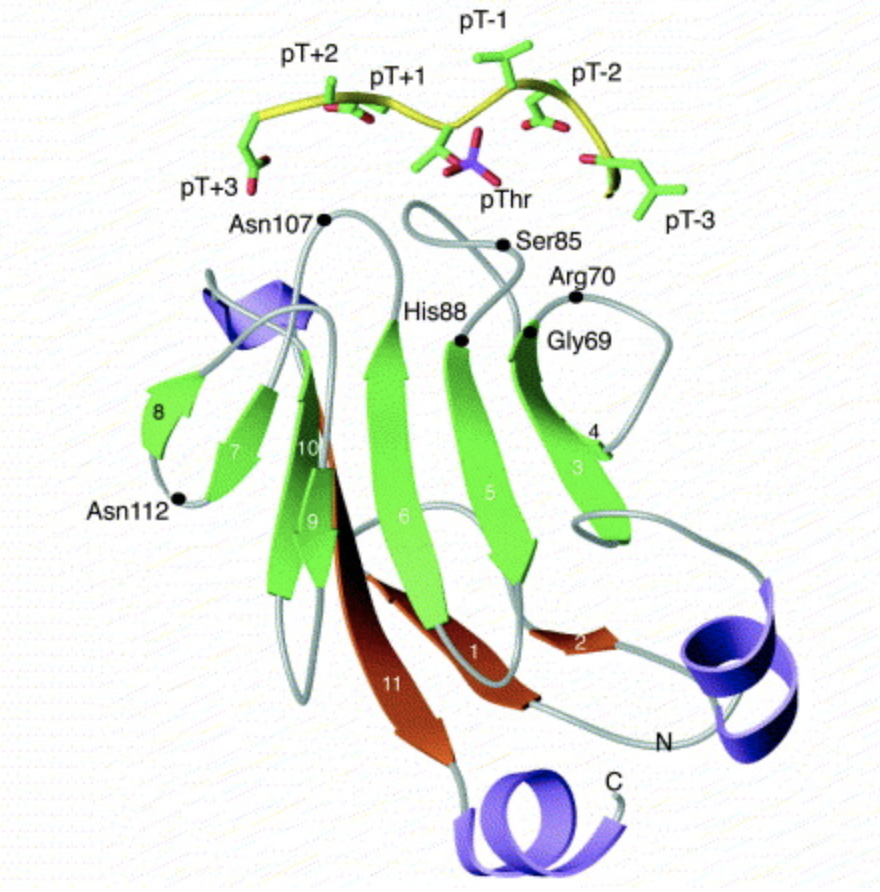
Forehead-associated domain
The FHA domain extends from 18 - 84 aa in the protein. It can recognize and bind tophosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
sites, specifically pSer, pThr and pTyr. The exact mechanism and function of this domain still being studied, but it is found in proteins performing many different functions, mainly DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
and transduction.

Smc region
FHAD1 contains one Smc (Structural maintenance of chromosomes) region from 275 - 1401 aa. This region encodes Smc proteins that are involved in cell cycle control, cell division and chromosome separation.TMPIT-like protein, pfam07851
This region extends from 394 - 494 aa in FHAD1. The proteins encoded by the TMPIT proteins are predicted to betransmembrane protein
A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently un ...
s. However, there is lack of literature to support this.
DUF342
This domain extends from 694 - 777 aa in FHAD1. It encodes a protein from a family ofbacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
l proteins with no known function.

Structure
FHAD1 contains the forkhead-associated domain that consists ofbeta sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a gene ...
s. Based on structure prediction software, the rest of the protein consists of alpha helices
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix).
The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of l ...
and random coils. Overall, FHAD1 has a coiled coil structure as shown in the figure.
Post-translational modifications
FHAD1 is predicted to undergo multiple different types of post-translational modifications based on prediction software. *Glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not ...
: There were 101 possible glycosylation sites on FHAD1 and consisted mainly of amino acids involved in O-linked glycosyaltion.
* Phosphorylation: The protein was predicted to have a large number of phosphorylation sites, at least more than 100.
* Glycation
Glycation (non-enzymatic glycosylation) is the covalent bond, covalent attachment of a sugar to a protein, lipid or nucleic acid molecule. Typical sugars that participate in glycation are glucose, fructose, and their derivatives. Glycation is th ...
: Multiple lysine residues of FHAD1 were predicted for glycation of their ε amino groups.
* SUMOylation
In molecular biology, SUMO (Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier) proteins are a family of small proteins that are covalently attached to and detached from other proteins in cells to modify their function. This process is called SUMOylation (pronounced ...
: 4 SUMOylation consensus sequences and 3 interaction sites were predicted on FHAD1.
* O-GlcNAc
''O''-GlcNAc (short for ''O''-linked GlcNAc or ''O''-linked β-''N''-acetylglucosamine) is a reversible Enzyme, enzymatic post-translational modification that is found on serine and threonine residues of Cell nucleus, nucleoCytoplasm, cytoplasmi ...
sites: 6 sites for O-GlcNAc glycosylation were predicted on FHAD1. Research has shown that this specific type of glycosylation is most abundant in nucleocytoplasmic proteins.
Subcellular localization
 FHAD1 has been predicted to be a
FHAD1 has been predicted to be a nuclear protein
A nuclear protein is a protein found in the cell nucleus. Proteins are transported inside the nucleus with the help of Nuclear Pore Complex, the nuclear pore complex, which acts a barrier between cytoplasm and nuclear membrane. The import and expor ...
with 94.1% reliability. It also contains possible nuclear localization signal sequences between 1100 - 1107 aa. Two pat4 and one pat7 sequences were predicted. Pat4 and pat7 are consensus sequences consisting of clusters of lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
or arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
residues.
Expression
In humans, FHAD1 is expressed intestis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
, fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the Ovary, ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproduct ...
and uterine
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more fertilized eggs until bir ...
tissues in female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and ...
s, nasopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
and bronchi
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
of lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s based on studies found on the Human Protein Atlas. NCBI's EST Profile also showed that FHAD1 is highly expressed in the testis, with some expression in the trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
and esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
. In mice
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, the gene was also expressed in the testis, along with the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
, lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
and brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
.
Regulation of expression
FHAD1 has a promoter that extends from 15246234 – 15247380 bp and is 1147 bp long. It includes an initial part of the5' UTR
The 5′ untranslated region (also known as 5′ UTR, leader sequence, transcript leader, or leader RNA) is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly Upstream and downstream (DNA), upstream from the initiation codon. This region is im ...
of FHAD1. Some transcription factors predicted to bind to this promoter are:
* MAX binding protein - This protein is likely a transcriptional repressor
In molecular genetics, a repressor is a DNA- or RNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator or associated silencers. A DNA-binding repressor blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the ...
from the E-box
An E-box (enhancer box) is a Response element, DNA response element found in some eukaryotes that acts as a protein-binding site and has been found to regulate gene expression in neurons, muscles, and other tissues. Its specific DNA sequence, CANNT ...
binding factors family
* TR4/TR2 - These proteins are part of a family of nuclear receptor
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These intracellular receptors work with other proteins to regulate the ex ...
s and bind to DR1 (direct repeat) elements of promoters. They act as anchors to recruit other corepressor
In genetics and molecular biology, a corepressor is a molecule that represses the expression of genes. In prokaryotes
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membra ...
s
* Kaiso
Kaiso is a type of music popular in Trinidad and Tobago, and other countries, especially of the Caribbean, such as Grenada, Belize, Barbados, St. Lucia, and Dominica, which originated in West Africa particularly among the Efik and Ibibio peopl ...
- This transcriptional regulator is encoded by the ZBTB33 gene and is involved in response to DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified ...
by interacting with p53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
* LYL1
Protein lyl-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LYL1'' gene.
Interactions
LYL1 has been shown to interact with TCF3
Transcription factor 3 (E2A immunoglobulin enhancer-binding factors E12/E47), also known as TCF3, is a protei ...
- E12 - This transcriptional factor is a dimer of two proteins, LYL1 and E12, where E12 is an E-box binding protein. LYL1 is also involved in some leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
s and is a possible oncogenic factor.
* Nur 77 - This protein is also known as NGFIB (Nerve growth factor IB) and belongs to a family of nuclear receptors. It is involved in apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
and cell growth
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
pathways.
In the 5' UTR and 3' UTR of FHAD1, multiple stem loops are predicted to form .
Function
FHAD1 can be involved in transcriptional regulation through interaction with other transcriptional regulators.Protein interactions
FHAD1 was found to be a binding partner forGTF2IRD1
General transcription factor II-I repeat domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GTF2IRD1'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene contains five GTF2I-like repeats and each repeat possesses a potential helix-lo ...
(GTF2I repeat domain containing protein 1) via a yeast 2 hybrid screen. GTF2I is a gene that encodes the general transcription factor II-1. This specific study showed that GTF2IRD1 is a nuclear protein that is involved transcriptional regulation through chromatin modification. The fact that it exists in the nucleus and was found in neuronal cells correlates with the localization and functional data for FHAD1. Additionally, FHAD1 and GTF2IRD1 interacted through RD2 (repeat domain 2) of GTF2IRD1. RD2 has shown some level of DNA binding activity.
FHAD1 was found to interact ( colocalization) with 14-3-3
14-3-3 proteins are a family of conserved regulatory molecules that are expressed in all eukaryotic cells. 14-3-3 proteins have the ability to bind a multitude of functionally diverse signaling proteins, including kinases, phosphatases, and tran ...
protein epsilon via cosedimentation. This protein binds to a number of binding partners, mostly by recognizing phosphothreonine or phosphoserine motifs.
Clinical Significance
FHAD1 showed differential expression in patients diagnosed withendometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which Tissue (biology), tissue similar to the endometrium, the lining of the uterus, grows in other places in the body, outside the uterus. It occurs in women and a limited number of other female mammals. Endomet ...
and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
.
Homology and Evolution
FHAD1 has no knownparalogs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speci ...
. It has orthologs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a spec ...
in the organisms in the following classes: Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
ia, Reptilia
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living spe ...
, Aves
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight ...
, Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class (biology), class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. The ...
, Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built ...
, Gastropoda
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and fro ...
and Lingulata
Lingulata is a class of brachiopods, among the oldest of all brachiopods having existed since the Cambrian period (). They are also among the most morphologically conservative of the brachiopods, having lasted from their earliest appearance to the ...
. There was significant conservation in the FHA domain in all the organisms in the table below.

 The rate of evolution of FHAD1 was compared with that of
The rate of evolution of FHAD1 was compared with that of fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (coagulation factor I) is a glycoprotein protein complex, complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted Enzyme, enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin ...
and cytochrome c and it showed that FHAD1 is a rapidly evolving gene.
References
{{reflist Proteins Genes on human chromosome 1