F-statistics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
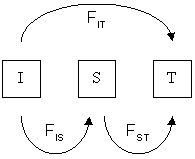 Consider a population that has a population structure of two levels; one from the individual (I) to the subpopulation (S) and one from the subpopulation to the total (T). Then the total , known here as , can be
Consider a population that has a population structure of two levels; one from the individual (I) to the subpopulation (S) and one from the subpopulation to the total (T). Then the total , known here as , can be
Shane's Simple Guide to F-Statistics
Analyzing the genetic structure of populations
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20160303172553/http://helix.mcmaster.ca/brent/node10.html IAM based F-statistics
F-statistics for Population Genetics Eco-Tool
Population Structure (slides)
{{DEFAULTSORT:F-Statistics Population genetics
population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and pop ...
, ''F''-statistics (also known as fixation indices) describe the statistically expected level of heterozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
in a population; more specifically the expected degree of (usually) a reduction in heterozygosity when compared to Hardy–Weinberg expectation.
''F''-statistics can also be thought of as a measure of the correlation between genes drawn at different levels of a (hierarchically) subdivided population. This correlation is influenced by several evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
ary processes, such as genetic drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance.
Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and there ...
, founder effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
, bottleneck
Bottleneck literally refers to the narrowed portion (neck) of a bottle near its opening, which limit the rate of outflow, and may describe any object of a similar shape. The literal neck of a bottle was originally used to play what is now known as ...
, genetic hitchhiking
Genetic may refer to:
*Genetics, in biology, the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms
**Genetic, used as an adjective, refers to genes
***Genetic disorder, any disorder caused by a genetic mutation, whether inherited or de nov ...
, meiotic drive
Meiotic drive is a type of intragenomic conflict, whereby one or more loci within a genome will effect a manipulation of the meiotic process in such a way as to favor the transmission of one or more alleles over another, regardless of its phenotyp ...
, mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
, gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent a ...
, inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders and o ...
, natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charle ...
, or the Wahlund effect
In population genetics, the Wahlund effect is a reduction of heterozygosity (that is when an organism has two different alleles at a locus) in a population caused by subpopulation structure. Namely, if two or more subpopulations are in a Hardy– ...
, but it was originally designed to measure the amount of allelic fixation owing to genetic drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance.
Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and there ...
.
The concept of ''F''-statistics was developed during the 1920s by the American geneticist Sewall Wright
Sewall Green Wright FRS(For) Honorary FRSE (December 21, 1889March 3, 1988) was an American geneticist known for his influential work on evolutionary theory and also for his work on path analysis. He was a founder of population genetics alongsi ...
, who was interested in inbreeding in cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
. However, because complete dominance
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
causes the phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
s of homozygote
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
dominants and heterozygotes to be the same, it was not until the advent of molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is a sub-field of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the ...
from the 1960s onwards that heterozygosity in populations could be measured.
''F'' can be used to define effective population size
The effective population size (''N'e'') is a number that, in some simplified scenarios, corresponds to the number of breeding individuals in the population. More generally, ''N'e'' is the number of individuals that an idealised population wo ...
.
Definitions and equations
The measures FIS, FST, and FIT are related to the amounts of heterozygosity at various levels of population structure. Together, they are called ''F''-statistics, and are derived from ''F'', theinbreeding coefficient
The coefficient of inbreeding of an individual is the probability that two alleles at any locus in an individual are identical by descent from the common ancestor(s) of the two parents.
The coefficient of inbreeding is: The probability that two ...
. In a simple two-allele system with inbreeding, the genotypic frequencies are:
:
The value for is found by solving the equation for using heterozygotes in the above inbred population. This becomes one minus the observed frequency of heterozygotes in a population divided by the expected frequency of heterozygotes at Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium:
:
where the expected frequency at Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium is given by
:
where and are the allele frequencies
Allele frequency, or gene frequency, is the relative frequency of an allele (variant of a gene) at a particular locus in a population, expressed as a fraction or percentage. Specifically, it is the fraction of all chromosomes in the population that ...
of and , respectively. It is also the probability that at any locus
Locus (plural loci) is Latin for "place". It may refer to:
Entertainment
* Locus (comics), a Marvel Comics mutant villainess, a member of the Mutant Liberation Front
* ''Locus'' (magazine), science fiction and fantasy magazine
** ''Locus Award' ...
, two alleles from a random individual of the population are identical by descent
A DNA segment is identical by state (IBS) in two or more individuals if they have identical nucleotide sequences in this segment. An IBS segment is identical by descent (IBD) in two or more individuals if they have inherited it from a common an ...
.
For example, consider the data from E.B. Ford
Edmund Brisco "Henry" Ford (23 April 1901 – 2 January 1988) was a British ecological geneticist. He was a leader among those British biologists who investigated the role of natural selection in nature. As a schoolboy Ford became interested i ...
(1971) on a single population of the scarlet tiger moth
The scarlet tiger moth (''Callimorpha dominula'', formerly ''Panaxia dominula'') is a colorful moth belonging to the tiger moth subfamily, Arctiinae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae ...
:
From this, the allele frequencies
Allele frequency, or gene frequency, is the relative frequency of an allele (variant of a gene) at a particular locus in a population, expressed as a fraction or percentage. Specifically, it is the fraction of all chromosomes in the population that ...
can be calculated, and the expectation of derived :
:
:
:
The different F-statistics look at different levels of population structure. FIT is the inbreeding coefficient of an individual (I) relative to the total (T) population, as above; FIS is the inbreeding coefficient of an individual (I) relative to the subpopulation (S), using the above for subpopulations and averaging them; and FST is the effect of subpopulations (S) compared to the total population (T), and is calculated by solving the equation:
:
as shown in the next section.
Partition due to population structure
 Consider a population that has a population structure of two levels; one from the individual (I) to the subpopulation (S) and one from the subpopulation to the total (T). Then the total , known here as , can be
Consider a population that has a population structure of two levels; one from the individual (I) to the subpopulation (S) and one from the subpopulation to the total (T). Then the total , known here as , can be partition
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of a ...
ed into and :
:
This may be further partitioned for population substructure, and it expands according to the rules of binomial expansion
In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial into a sum involving terms of the form , where the ...
, so that for ''I'' partitions:
:
Fixation index
A reformulation of the definition of would be the ratio of the average number of differences between pairs of chromosomes sampled within diploid individuals with the average number obtained when sampling chromosomes randomly from the population (excluding the grouping per individual). One can modify this definition and consider a grouping per sub-population instead of per individual. Population geneticists have used that idea to measure the degree of structure in a population. Unfortunately, there is a large number of definitions for , causing some confusion in the scientific literature. A common definition is the following: : where the variance of is computed across sub-populations and is the expected frequency of heterozygotes.Fixation index in human populations
It is well established that the genetic diversity among human populations is low, although the distribution of the genetic diversity was only roughly estimated. Early studies argued that 85–90% of the genetic variation is found within individuals residing in the same populations within continents (intra-continental populations) and only an additional 10–15% is found between populations of different continents (continental populations). Later studies based on hundreds of thousands single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) suggested that the genetic diversity between continental populations is even smaller and accounts for 3 to 7% A later study based on three million SNPs found that 12% of the genetic variation is found between continental populations and only 1% within them. Most of these studies have used the ''F''''ST'' statistics or closely related statistics.See also
*Malecot's method of coancestry
Malecot's coancestry coefficient, f, refers to an indirect measure of genetic similarity of two individuals which was initially devised by the French mathematician Gustave Malécot.
f is defined as the probability that any two alleles, sampled ...
*Heterozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
References
External links
Shane's Simple Guide to F-Statistics
Analyzing the genetic structure of populations
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20160303172553/http://helix.mcmaster.ca/brent/node10.html IAM based F-statistics
F-statistics for Population Genetics Eco-Tool
Population Structure (slides)
{{DEFAULTSORT:F-Statistics Population genetics