Extrasolar system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A planetary system is a set of
A planetary system is a set of
 ''
''
 Planetary systems come from
Planetary systems come from
Rosalba Perna, Paul Duffell, Matteo Cantiello, Andrew MacFadyen, (Submitted on December 17, 2013)
 As stars evolve and turn into red giants, asymptotic giant branch stars, and
As stars evolve and turn into red giants, asymptotic giant branch stars, and
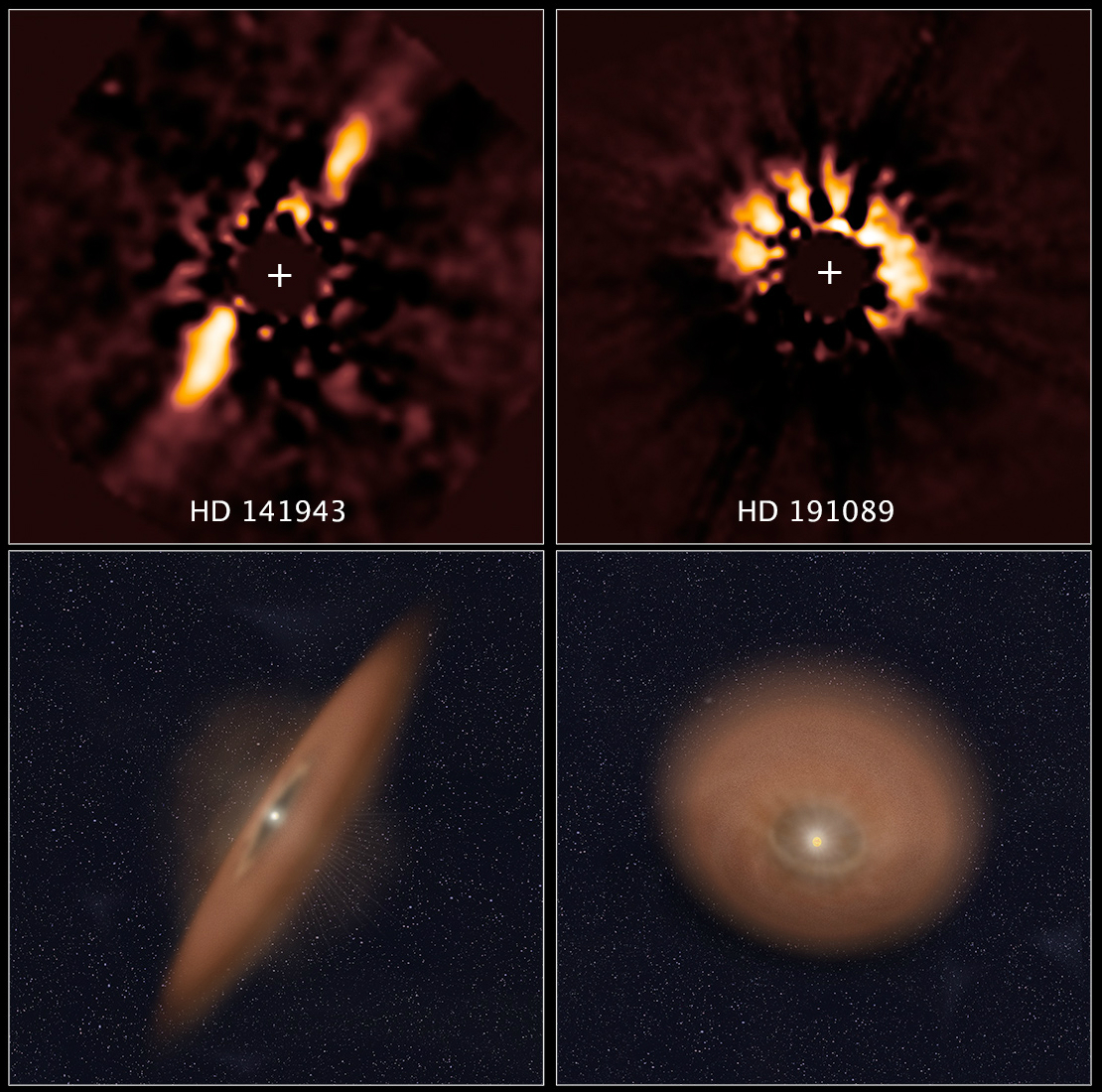 After planets, circumstellar disks are one of the most commonly-observed properties of planetary systems, particularly of young stars. The Solar System possesses at least four major circumstellar disks (the
After planets, circumstellar disks are one of the most commonly-observed properties of planetary systems, particularly of young stars. The Solar System possesses at least four major circumstellar disks (the
On The Relative Sizes of Planets Within Kepler Multiple Candidate Systems
David R. Ciardi et al. December 9, 2012
The Kepler Dichotomy among the M Dwarfs: Half of Systems Contain Five or More Coplanar Planets
Sarah Ballard, John Asher Johnson, October 15, 2014
Exoplanet Predictions Based on the Generalised Titius-Bode Relation
Timothy Bovaird, Charles H. Lineweaver, August 1, 2013
The Solar System and the Exoplanet Orbital Eccentricity - Multiplicity Relation
Mary Anne Limbach, Edwin L. Turner, April 9, 2014
The period ratio distribution of Kepler's candidate multiplanet systems
Jason H. Steffen, Jason A. Hwang, September 11, 2014
Are Planetary Systems Filled to Capacity? A Study Based on Kepler Results
Julia Fang, Jean-Luc Margot, February 28, 2013
Hagai B. Perets, M. B. N. Kouwenhoven, 2012
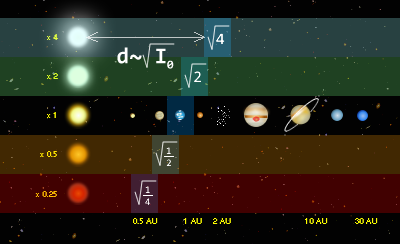 The habitable zone around a star is the region where the temperature range allows for liquid water to exist on a planet; that is, not too close to the star for the water to evaporate and not too far away from the star for the water to freeze. The heat produced by stars varies depending on the size and age of the star; this means the habitable zone will also vary accordingly. Also, the atmospheric conditions on the planet influence the planet's ability to retain heat so that the location of the habitable zone is also specific to each type of planet.
Habitable zones have usually been defined in terms of surface temperature; however, over half of Earth's biomass is from subsurface microbes, and temperature increases as depth underground increases, so the subsurface can be conducive for life when the surface is frozen; if this is considered, the habitable zone extends much further from the star.
Studies in 2013 indicated an estimated frequency of 22±8% of Sun-likeFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "Sun-like" means
The habitable zone around a star is the region where the temperature range allows for liquid water to exist on a planet; that is, not too close to the star for the water to evaporate and not too far away from the star for the water to freeze. The heat produced by stars varies depending on the size and age of the star; this means the habitable zone will also vary accordingly. Also, the atmospheric conditions on the planet influence the planet's ability to retain heat so that the location of the habitable zone is also specific to each type of planet.
Habitable zones have usually been defined in terms of surface temperature; however, over half of Earth's biomass is from subsurface microbes, and temperature increases as depth underground increases, so the subsurface can be conducive for life when the surface is frozen; if this is considered, the habitable zone extends much further from the star.
Studies in 2013 indicated an estimated frequency of 22±8% of Sun-likeFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "Sun-like" means
 The
The
Guillem Anglada-Escudé, Pamela Arriagada, Mikko Tuomi, Mathias Zechmeister, James S. Jenkins, Aviv Ofir, Stefan Dreizler, Enrico Gerlach, Chris J. Marvin, Ansgar Reiners, Sandra V. Jeffers, R. Paul Butler, Steven S. Vogt, Pedro J. Amado, Cristina Rodríguez-López, Zaira M. Berdiñas, Julian Morin, Jeff D. Crane, Stephen A. Shectman, Ian B. Thompson, Mateo Díaz, Eugenio Rivera, Luis F. Sarmiento, Hugh R.A. Jones, (Submitted on June 3, 2014) Different types of galaxies have different histories of star formation and hence
 A planetary system is a set of
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stron ...
bound non- stellar objects in or out of orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
s constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consist of bodies such as dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the Sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to ...
s, asteroids, natural satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
s, meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
s, comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s, planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System a ...
s and circumstellar disk
A circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the ...
s. The Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
together with the planetary system revolving around it, including Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
, forms the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
. The term exoplanetary system is sometimes used in reference to other planetary systems.
Debris disks are also known to be common, though other objects are more difficult to observe.
Of particular interest to astrobiology is the habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), or simply the habitable zone, is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure.J. F. Kast ...
of planetary systems where planets could have surface liquid water, and thus the capacity to support Earth-like life.
History
Heliocentrism
Historically, heliocentrism (the doctrine that the Sun is at the centre of the universe) was opposed togeocentrism
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, a ...
(placing Earth at the centre of the universe).
The notion of a heliocentric Solar System with the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
at its centre is possibly first suggested in the Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
literature of ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
, which often refer to the Sun as the "centre of spheres". Some interpret Aryabhatta
Aryabhata ( ISO: ) or Aryabhata I (476–550 CE) was an Indian mathematician and astronomer of the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. He flourished in the Gupta Era and produced works such as the ''Aryabhatiya'' (which ...
's writings in Āryabhaṭīya
''Aryabhatiya'' (IAST: ') or ''Aryabhatiyam'' ('), a Indian astronomy, Sanskrit astronomical treatise, is the ''Masterpiece, magnum opus'' and only known surviving work of the 5th century Indian mathematics, Indian mathematician Aryabhata. Philos ...
as implicitly heliocentric.
The idea was first proposed in Western philosophy
Western philosophy encompasses the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics. The word ' ...
and Greek astronomy
Greek astronomy is astronomy written in the Greek language in classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the Ancient Greek, Hellenistic, Greco-Roman, and Late Antiquity eras. It is not limited geographically to Greece or to e ...
as early as the 3rd century BC by Aristarchus of Samos, but received no support from most other ancient astronomers.
Discovery of the Solar System
 ''
''De revolutionibus orbium coelestium
''De revolutionibus orbium coelestium'' (English translation: ''On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres'') is the seminal work on the heliocentric theory of the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543) of the Polish Renaissance. The book, ...
'' by Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated ...
, published in 1543, presented the first mathematically predictive heliocentric model of a planetary system. 17th-century successors Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He wa ...
, Johannes Kepler, and Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the g ...
developed an understanding of physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
which led to the gradual acceptance of the idea that Earth moves around the Sun and that the planets are governed by the same physical laws that governed Earth.
Speculation on extrasolar planetary systems
In the 16th century the Italian philosopher Giordano Bruno, an early supporter of the Copernican theory that Earth and other planets orbit the Sun, put forward the view that the fixed stars are similar to the Sun and are likewise accompanied by planets. He was burned at the stake for his ideas by theRoman Inquisition
The Roman Inquisition, formally the Supreme Sacred Congregation of the Roman and Universal Inquisition, was a system of partisan tribunals developed by the Holy See of the Roman Catholic Church, during the second half of the 16th century, respons ...
.
In the 18th century the same possibility was mentioned by Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the g ...
in the " General Scholium" that concludes his '' Principia''. Making a comparison to the Sun's planets, he wrote "And if the fixed stars are the centres of similar systems, they will all be constructed according to a similar design and subject to the dominion of ''One''."
His theories gained traction through the 19th and 20th centuries despite a lack of supporting evidence. Long before their confirmation by astronomers, conjecture on the nature of planetary systems had been a focus of the search for extraterrestrial intelligence and has been a prevalent theme in fiction, particularly science fiction.
Detection of exoplanets
The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992, with the discovery of several terrestrial-mass planets orbiting the pulsarPSR B1257+12
PSR B1257+12, previously designated PSR 1257+12, alternatively designated PSR J1300+1240, is a millisecond pulsar located 2,300 light-years from the Sun in the constellation of Virgo, rotating at about 161 times per second (faster than ...
. The first confirmed detection of exoplanets of a main-sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar He ...
star was made in 1995, when a giant planet, 51 Pegasi b
51 Pegasi b, officially named Dimidium , and formerly unofficially dubbed Bellerophon , is an extrasolar planet approximately away in the constellation of Pegasus. It was the first exoplanet to be discovered orbiting a main-sequence star, th ...
, was found in a four-day orbit around the nearby G-type star
A G-type main-sequence star (Spectral type: G-V), also often, and imprecisely called a yellow dwarf, or G star, is a main-sequence star (luminosity class V) of spectral type G. Such a star has about 0.9 to 1.1 solar masses and an effective temp ...
51 Pegasi. The frequency of detections has increased since then, particularly through advancements in methods of detecting extrasolar planets
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty o ...
and dedicated planet finding programs such as the Kepler mission
The Kepler space telescope is a disused space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbi ...
.
Origin and evolution
 Planetary systems come from
Planetary systems come from protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, be ...
s that form around stars as part of the process of star formation.
During formation of a system, much material is gravitationally-scattered into distant orbits, and some planets are ejected completely from the system, becoming rogue planet
A rogue planet (also termed a free-floating planet (FFP), interstellar, nomad, orphan, starless, unbound or wandering planet) is an interstellar object of planetary-mass, therefore smaller than fusors (stars and brown dwarfs) and without a h ...
s.
Evolved systems
High-mass stars
Planets orbiting pulsars have been discovered. Pulsars are the remnants of the supernova explosions of high-mass stars, but a planetary system that existed before the supernova would likely be mostly destroyed. Planets would either evaporate, be pushed off of their orbits by the masses of gas from the exploding star, or the sudden loss of most of the mass of the central star would see them escape the gravitational hold of the star, or in some cases the supernova wouldkick
A kick is a physical Strike (attack), strike using the leg, in unison usually with an area of the knee or lower using the foot, heel, tibia (shin), ball of the foot, blade of the foot, toes or knee (the latter is also known as a knee (strike), ...
the pulsar itself out of the system at high velocity so any planets that had survived the explosion would be left behind as free-floating objects. Planets found around pulsars may have formed as a result of pre-existing stellar companions that were almost entirely evaporated by the supernova blast, leaving behind planet-sized bodies. Alternatively, planets may form in an accretion disk of fallback matter surrounding a pulsar. Fallback disks of matter that failed to escape orbit during a supernova may also form planets around black holes.The fate of fallback matter around newly born compact objectsRosalba Perna, Paul Duffell, Matteo Cantiello, Andrew MacFadyen, (Submitted on December 17, 2013)
Lower-mass stars
 As stars evolve and turn into red giants, asymptotic giant branch stars, and
As stars evolve and turn into red giants, asymptotic giant branch stars, and planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
e they engulf the inner planets, evaporating or partially evaporating them depending on how massive they are. As the star loses mass, planets that are not engulfed move further out from the star.
If an evolved star is in a binary or multiple system, then the mass it loses can transfer to another star, forming new protoplanetary disks and second- and third-generation planets which may differ in composition from the original planets, which may also be affected by the mass transfer.
System architectures
The Solar System consists of an inner region of small rocky planets and outer region of largegas giants
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Gas giants are also called failed stars because they contain the same basic elements as a star. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" ...
. However, other planetary systems can have quite different architectures. Studies suggest that architectures of planetary systems are dependent on the conditions of their initial formation. Many systems with a hot Jupiter
Hot Jupiters (sometimes called hot Saturns) are a class of gas giant exoplanets that are inferred to be physically similar to Jupiter but that have very short orbital periods (). The close proximity to their stars and high surface-atmosphere tem ...
gas giant very close to the star have been found. Theories, such as planetary migration
Planetary migration occurs when a planet or other body in orbit around a star interacts with a disk of gas or planetesimals, resulting in the alteration of its orbital parameters, especially its semi-major axis. Planetary migration is the most li ...
or scattering, have been proposed for the formation of large planets close to their parent stars.
At present, few systems have been found to be analogous to the Solar System with terrestrial planets close to the parent star. More commonly, systems consisting of multiple Super-Earth
A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively.
The term "super-Earth" refers only to ...
s have been detected.
Components
Planets and stars
Most known exoplanets orbit stars roughly similar to theSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
: that is, main-sequence stars of spectral categories F, G, or K. One reason is that planet-search programs have tended to concentrate on such stars. In addition, statistical analyses indicate that lower-mass stars ( red dwarfs, of spectral category M) are less likely to have planets massive enough to be detected by the radial-velocity method. Nevertheless, several tens of planets around red dwarfs have been discovered by the Kepler spacecraft by the transit method
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty o ...
, which can detect smaller planets.
Circumstellar disks and dust structures
 After planets, circumstellar disks are one of the most commonly-observed properties of planetary systems, particularly of young stars. The Solar System possesses at least four major circumstellar disks (the
After planets, circumstellar disks are one of the most commonly-observed properties of planetary systems, particularly of young stars. The Solar System possesses at least four major circumstellar disks (the asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, c ...
, Kuiper belt, scattered disc
The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small solar system bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc obje ...
, and Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
) and clearly-observable disks have been detected around nearby solar analogs including Epsilon Eridani
Epsilon Eridani ( Latinized from ε Eridani), formally named Ran, is a star in the southern constellation of Eridanus, at a declination of 9.46° south of the celestial equator. This allows it to be visible from most of Earth's surf ...
and Tau Ceti
Tau Ceti, Latinized from τ Ceti, is a single star in the constellation Cetus that is spectrally similar to the Sun, although it has only about 78% of the Sun's mass. At a distance of just under from the Solar System, it is a rela ...
. Based on observations of numerous similar disks, they are assumed to be quite common attributes of stars on the main sequence.
Interplanetary dust cloud
The interplanetary dust cloud, or zodiacal cloud (as the source of the zodiacal light), consists of cosmic dust (small particles floating in outer space) that pervades the space between planets within planetary systems, such as the Solar System ...
s have been studied in the Solar System and analogs are believed to be present in other planetary systems. Exozodiacal dust, an exoplanetary analog of zodiacal dust, the 1–100 micrometre-sized grains of amorphous carbon Amorphous carbon is free, reactive carbon that has no crystalline structure. Amorphous carbon materials may be stabilized by terminating dangling-π bonds with hydrogen. As with other amorphous solids, some short-range order can be observed. Amor ...
and silicate dust that fill the plane of the Solar System has been detected around the 51 Ophiuchi, Fomalhaut
Fomalhaut is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Piscis Austrinus, the "Southern Fish", and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Piscis Austrini, which is Latinized from � ...
, Tau Ceti
Tau Ceti, Latinized from τ Ceti, is a single star in the constellation Cetus that is spectrally similar to the Sun, although it has only about 78% of the Sun's mass. At a distance of just under from the Solar System, it is a rela ...
, and Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, a ...
systems.
Comets
there are 5,253 known Solar System comets and they are thought to be common components of planetary systems. The first exocomets were detected in 1987 around Beta Pictoris, a very youngA-type main-sequence star
An A-type main-sequence star (A V) or A dwarf star is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type A and luminosity class V (five). These stars have spectra defined by strong hydrogen Balmer absorption lines. They measure between ...
. There are now a total of 11 stars around which the presence of exocomets have been observed or suspected. All discovered exocometary systems ( Beta Pictoris, HR 10
HD 256 is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. It has a white hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 6.20. Based upon parallax measurements, the system is located at a d ...
, 51 Ophiuchi, HR 2174, 49 Ceti, 5 Vulpeculae, 2 Andromedae, HD 21620, HD 42111, HD 110411, and more recently HD 172555
HD 172555 is a white-hot A7V star located relatively close by, 95 light years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Pavo (constellation), Pavo. Spectrographic evidence indicates a relatively recent collision between two planet ...
) are around very young A-type stars.
Other components
Computer modelling of an impact in 2013 detected around the starNGC 2547
NGC 2547 is a southern open cluster in Vela, discovered by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1751 from South Africa. The star cluster is young with an age of 20-30 million years.
Observations with the Spitzer Space Telescope showed a shell around the ...
-ID8 by the Spitzer Space Telescope, and confirmed by ground observations, suggests the involvement of large asteroids or protoplanet
A protoplanet is a large planetary embryo that originated within a protoplanetary disc and has undergone internal melting to produce a differentiated interior. Protoplanets are thought to form out of kilometer-sized planetesimals that gravitation ...
s similar to the events believed to have led to the formation of terrestrial planets like the Earth.
Based on observations of the Solar System's large collection of natural satellites, they are believed common components of planetary systems; however, the existence of exomoons has, so far, not been confirmed. The star 1SWASP J140747.93-394542.6
1SWASP J140747.93−394542.6 (also known as 1SWASP J140747, J1407 and Mamajek's Object) is a star similar to the Sun in the constellation Centaurus at a distance of about 434 light-years from Earth. A relatively young star, its age is estimated t ...
, in the constellation Centaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. ...
, is a strong candidate for a natural satellite. Indications suggest that the confirmed extrasolar planet WASP-12b also has at least one satellite.
Orbital configurations
Unlike the Solar System, which has orbits that are nearly circular, many of the known planetary systems display much higher orbital eccentricity. An example of such a system is 16 Cygni.Mutual inclination
The mutualinclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Eart ...
between two planets is the angle between their orbital plane
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) an ...
s. Many compact systems with multiple close-in planets interior to the equivalent orbit of Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
are expected to have very low mutual inclinations, so the system (at least the close-in part) would be even flatter than the Solar System. Captured planets could be captured into any arbitrary angle to the rest of the system. there are only a few systems where mutual inclinations have actually been measured One example is the Upsilon Andromedae
Upsilon Andromedae (υ Andromedae, abbreviated Upsilon And, υ And) is a binary star located 44 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Andromeda. The system consists of an F-type main-sequence star (designated υ Andromedae A, of ...
system: the planets c and d have a mutual inclination of about 30 degrees.
Orbital dynamics
Planetary systems can be categorized according to their orbital dynamics as resonant, non-resonant-interacting, hierarchical, or some combination of these. In resonant systems the orbital periods of the planets are in integer ratios. TheKepler-223
Kepler-223 (KOI-730, KIC 10227020) is a G5V star with an extrasolar planetary system discovered by the Kepler mission. Studies indicate that the Kepler-223 star system consists of 4 planets orbiting the star.
Planetary system
...
system contains four planets in an 8:6:4:3 orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relationsh ...
.
Giant planets are found in mean-motion resonances more often than smaller planets.
In interacting systems the planets orbits are close enough together that they perturb the orbital parameters. The Solar System could be described as weakly interacting. In strongly interacting systems Kepler's laws
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler between 1609 and 1619, describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. The laws modified the heliocentric theory of Nicolaus Copernicus, replacing its circular orbi ...
do not hold.
In hierarchical systems the planets are arranged so that the system can be gravitationally considered as a nested system of two-bodies, e.g. in a star with a close-in hot jupiter with another gas giant much further out, the star and hot jupiter form a pair that appears as a single object to another planet that is far enough out.
Other, as yet unobserved, orbital possibilities include: double planet
In astronomy, a double planet (also binary planet) is a binary satellite system where both objects are planets, or planetary-mass objects, that share an orbital axis external to both planetary bodies.
Although up to a third of the star syst ...
s; various co-orbital planets such as quasi-satellites, trojans and exchange orbits; and interlocking orbits maintained by precessing orbital planes.
Number of planets, relative parameters and spacings
On The Relative Sizes of Planets Within Kepler Multiple Candidate Systems
David R. Ciardi et al. December 9, 2012
The Kepler Dichotomy among the M Dwarfs: Half of Systems Contain Five or More Coplanar Planets
Sarah Ballard, John Asher Johnson, October 15, 2014
Exoplanet Predictions Based on the Generalised Titius-Bode Relation
Timothy Bovaird, Charles H. Lineweaver, August 1, 2013
The Solar System and the Exoplanet Orbital Eccentricity - Multiplicity Relation
Mary Anne Limbach, Edwin L. Turner, April 9, 2014
The period ratio distribution of Kepler's candidate multiplanet systems
Jason H. Steffen, Jason A. Hwang, September 11, 2014
Are Planetary Systems Filled to Capacity? A Study Based on Kepler Results
Julia Fang, Jean-Luc Margot, February 28, 2013
Planet capture
Free-floating planets in open clusters have similar velocities to the stars and so can be recaptured. They are typically captured into wide orbits between 100 and 105 AU. The capture efficiency decreases with increasing cluster size, and for a given cluster size it increases with the host/primary mass. It is almost independent of the planetary mass. Single and multiple planets could be captured into arbitrary unaligned orbits, non-coplanar with each other or with the stellar host spin, or pre-existing planetary system. Some planet–host metallicity correlation may still exist due to the common origin of the stars from the same cluster. Planets would be unlikely to be captured aroundneutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
s because these are likely to be ejected from the cluster by a pulsar kick when they form. Planets could even be captured around other planets to form free-floating planet binaries. After the cluster has dispersed some of the captured planets with orbits larger than 106 AU would be slowly disrupted by the galactic tide
A galactic tide is a tidal force experienced by objects subject to the gravitational field of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Particular areas of interest concerning galactic tides include galactic collisions, the disruption of dwarf or satelli ...
and likely become free-floating again through encounters with other field stars or giant molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
s.On the origin of planets at very wide orbits from the recapture of free-floating planetsHagai B. Perets, M. B. N. Kouwenhoven, 2012
Zones
Habitable zone
 The habitable zone around a star is the region where the temperature range allows for liquid water to exist on a planet; that is, not too close to the star for the water to evaporate and not too far away from the star for the water to freeze. The heat produced by stars varies depending on the size and age of the star; this means the habitable zone will also vary accordingly. Also, the atmospheric conditions on the planet influence the planet's ability to retain heat so that the location of the habitable zone is also specific to each type of planet.
Habitable zones have usually been defined in terms of surface temperature; however, over half of Earth's biomass is from subsurface microbes, and temperature increases as depth underground increases, so the subsurface can be conducive for life when the surface is frozen; if this is considered, the habitable zone extends much further from the star.
Studies in 2013 indicated an estimated frequency of 22±8% of Sun-likeFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "Sun-like" means
The habitable zone around a star is the region where the temperature range allows for liquid water to exist on a planet; that is, not too close to the star for the water to evaporate and not too far away from the star for the water to freeze. The heat produced by stars varies depending on the size and age of the star; this means the habitable zone will also vary accordingly. Also, the atmospheric conditions on the planet influence the planet's ability to retain heat so that the location of the habitable zone is also specific to each type of planet.
Habitable zones have usually been defined in terms of surface temperature; however, over half of Earth's biomass is from subsurface microbes, and temperature increases as depth underground increases, so the subsurface can be conducive for life when the surface is frozen; if this is considered, the habitable zone extends much further from the star.
Studies in 2013 indicated an estimated frequency of 22±8% of Sun-likeFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "Sun-like" means G-type star
A G-type main-sequence star (Spectral type: G-V), also often, and imprecisely called a yellow dwarf, or G star, is a main-sequence star (luminosity class V) of spectral type G. Such a star has about 0.9 to 1.1 solar masses and an effective temp ...
. Data for Sun-like stars were not available so this statistic is an extrapolation from data about K-type star
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
s stars having an Earth-sizedFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, Earth-sized means 1–2 Earth radii planet in the habitableFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "habitable zone" means the region with 0.25 to 4 times Earth's stellar flux (corresponding to 0.5–2 AU for the Sun). zone.
Venus zone
The Venus zone is the region around a star where aterrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
would have runaway greenhouse conditions like Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, but not so near the star that the atmosphere completely evaporates. As with the habitable zone, the location of the Venus zone depends on several factors, including the type of star and properties of the planets such as mass, rotation rate, and atmospheric clouds. Studies of the Kepler spacecraft data indicate that 32% of red dwarfs have potentially Venus-like planets based on planet size and distance from star, increasing to 45% for K-type and G-type stars.For the purpose of this, terrestrial-sized means 0.5–1.4 Earth radii, the "Venus zone" means the region with approximately 1 to 25 times Earth's stellar flux for M and K-type stars and approximately 1.1 to 25 times Earth's stellar flux for G-type stars. Several candidates have been identified, but spectroscopic follow-up studies of their atmospheres are required to determine whether they are like Venus.
Galactic distribution of planets
 The
The Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
is 100,000 light-years across, but 90% of planets with known distances are within about 2000 light years
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
of Earth, as of July 2014. One method that can detect planets much further away is microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects that range from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers ...
. The upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as Roman or the Roman Space Telescope, and formerly the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope or WFIRST) is a NASA infrared space telescope currently in development and scheduled to launch by Ma ...
could use microlensing to measure the relative frequency of planets in the galactic bulge
In astronomy, a galactic bulge (or simply bulge) is a tightly packed group of stars within a larger star formation. The term almost exclusively refers to the central group of stars found in most spiral galaxies (see galactic spheroid). Bulges ...
versus the galactic disk
A galactic disc (or galactic disk) is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies and lenticular galaxies. Galactic discs consist of a stellar component (composed of most of the galaxy's stars) and a gaseous component (mostly composed ...
. So far, the indications are that planets are more common in the disk than the bulge. Estimates of the distance of microlensing events is difficult: the first planet considered with high probability of being in the bulge is MOA-2011-BLG-293Lb at a distance of 7.7 kiloparsecs (about 25,000 light years).
''Population I'', or ''metal-rich stars'', are those young stars whose metallicity is highest. The high metallicity of population I stars makes them more likely to possess planetary systems than older populations, because planets form by the accretion of metals. The Sun is an example of a metal-rich star. These are common in the spiral arm
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
. Generally, the youngest stars, the extreme population I, are found farther in and intermediate population I stars are farther out, etc. The Sun is considered an intermediate population I star. Population I stars have regular elliptical orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. In a stricter sense, i ...
s around the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact ra ...
, with a low relative velocity
The relative velocity \vec_ (also \vec_ or \vec_) is the velocity of an object or observer B in the rest frame of another object or observer A.
Classical mechanics
In one dimension (non-relativistic)
We begin with relative motion in the classi ...
.
''Population II'', or ''metal-poor stars'', are those with relatively low metallicity which can have hundreds (e.g. BD +17° 3248) or thousands (e.g. Sneden's Star) times less metallicity than the Sun. These objects formed during an earlier time of the universe. Intermediate population II stars are common in the bulge
__NOTOC__
Bulge may refer to:
Astronomy and geography
*Bulge (astronomy), a tightly packed group of stars at the center of a spiral galaxy
*Equatorial bulge, a bulge around the equator of a planet due to rotation
* Tharsis bulge, vast volcanic pl ...
near the center of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
, whereas Population II stars found in the galactic halo
A galactic halo is an extended, roughly spherical component of a galaxy which extends beyond the main, visible component. Several distinct components of galaxies comprise the halo:
* the stellar halo
* the galactic corona (hot gas, i.e. a plas ...
are older and thus more metal-poor. Globular clusters
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of membe ...
also contain high numbers of population II stars.
In 2014, the first planets around a halo star were announced around Kapteyn's star
Kapteyn's Star is a class M1 red subdwarf about 12.83 light-years from Earth in the southern constellation Pictor; it is the closest halo star to the Solar System. With a magnitude of nearly 9 it is visible through binoculars or a te ...
, the nearest halo star to Earth, around 13 light years away. However, later research suggests that Kapteyn b is just an artefact of stellar activity and that Kapteyn c needs more study to be confirmed. The metallicity of Kapteyn's star is estimated to be about 8 Metallicity of Kapteyn's star
Kapteyn's Star is a class M1 red subdwarf about 12.83 light-years from Earth in the southern constellation Pictor; it is the closest halo star to the Solar System. With a magnitude of nearly 9 it is visible through binoculars or a te ...
estimated at e/H −0.89. 10−0.89 ≈ 1/8 times less than the Sun.Two planets around Kapteyn's star : a cold and a temperate super-Earth orbiting the nearest halo red-dwarfGuillem Anglada-Escudé, Pamela Arriagada, Mikko Tuomi, Mathias Zechmeister, James S. Jenkins, Aviv Ofir, Stefan Dreizler, Enrico Gerlach, Chris J. Marvin, Ansgar Reiners, Sandra V. Jeffers, R. Paul Butler, Steven S. Vogt, Pedro J. Amado, Cristina Rodríguez-López, Zaira M. Berdiñas, Julian Morin, Jeff D. Crane, Stephen A. Shectman, Ian B. Thompson, Mateo Díaz, Eugenio Rivera, Luis F. Sarmiento, Hugh R.A. Jones, (Submitted on June 3, 2014) Different types of galaxies have different histories of star formation and hence
planet formation
The nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted model in the field of cosmogony to explain the formation and evolution of the Solar System (as well as other planetary systems). It suggests the Solar System is formed from gas and dust orbitin ...
. Planet formation is affected by the ages, metallicities, and orbits of stellar populations within a galaxy. Distribution of stellar populations within a galaxy varies between the different types of galaxies.
Stars in elliptical galaxies
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Real ...
are much older than stars in spiral galaxies
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''low-mass stars, with minimal star-formation activity.John, D, (2006), ''Astronomy'', , p. 224-225 The distribution of the different types of galaxies in the
universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
depends on their location within galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-lar ...
s, with elliptical galaxies found mostly close to their centers.
See also
*Protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, be ...
*List of exoplanets
These are lists of exoplanets. Most of these were discovered by the Kepler space telescope. There are an additional 2,054 potential exoplanets from Kepler's first mission yet to be confirmed, as well as 978 from its " Second Light" mission and ...
*List of multiplanetary systems
From the total of stars known to have exoplanets (as of ), there are a total of known multiplanetary systems, or stars with at least two confirmed planets, beyond the Solar System. This list includes systems with at least three confirmed planet ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * {{Authority control Concepts in astronomy