Environmental Impacts Of Lithium-ion Batteries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
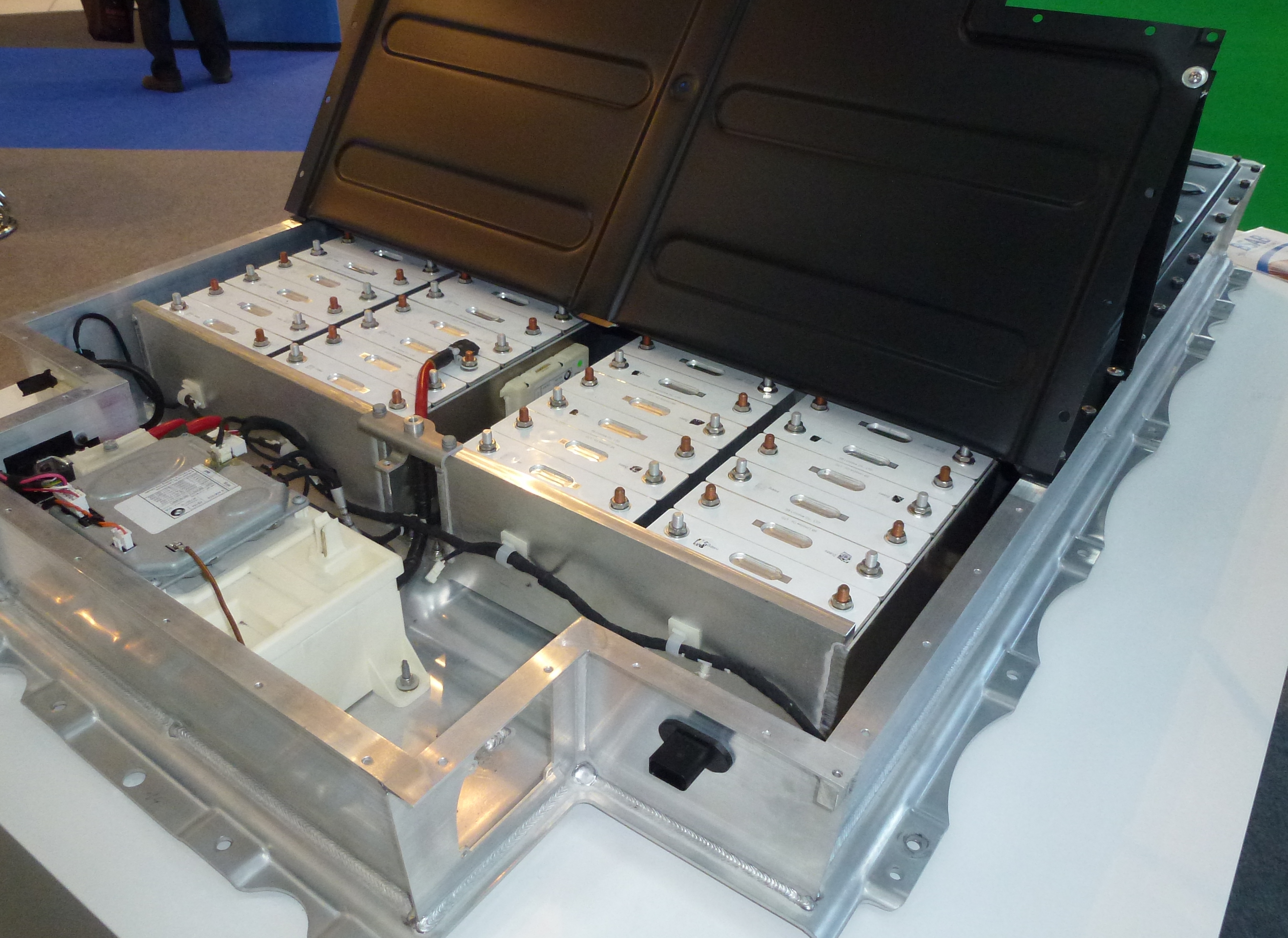



Lithium batteries
Lithium battery may refer to:
* Lithium metal battery, a non-rechargeable battery with lithium as an anode
** Rechargeable lithium metal battery, a rechargeable counterpart to the lithium metal battery
* Lithium-ion battery, a rechargeable batte ...
are primary batteries that use lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ...
as an anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
. This type of battery is also referred to as a lithium-ion battery and is most commonly used for electric vehicles and electronics. The first type of lithium battery was created by the British chemist M. Stanley Whittingham
Michael Stanley Whittingham (born 22 December 1941) is a British-American chemist. He is currently a professor of chemistry and director of both the Institute for Materials Research and the Materials Science and Engineering program at Binghamton ...
in the early 1970s and used titanium and lithium as the electrodes. Unfortunately, applications for this battery were limited by the high prices of titanium and the unpleasant scent that the reaction produced. Today's lithium ion battery, modeled after the Whittingham attempt by Akira Yoshino
is a Japanese chemist. He is a fellow of Asahi Kasei Corporation and a professor at Meijo University in Nagoya. He created the first safe, production-viable lithium-ion battery which became used widely in cellular phones and notebook computer ...
, was first developed in 1985.
Environmental impact
While safe for landfills, the physical mining of lithium and the production of lithium-ion are both labor-intensive processes. Additionally, most batteries are not properly recycled.Extraction
The extraction process of lithium is very resource demanding and specifically uses a lot of water in the extraction process. It is estimated that 500,000 gallons of water is used to mine one metric ton of lithium. With the world's leading country in production of lithium being Chile, the lithium mines are in rural areas with an extremely diverse ecosystem. In Chile’s Salar de Atacama, one of the driest places on earth, about 65% of the water is used to mine lithium; leaving many of the local farmers and members of the community to find water elsewhere. Along with physical implications on the environment, working conditions can violate the standards of sustainable development goals. Additionally, it is common for locals to be in conflict with the surrounding lithium mines. There have been many accounts of dead animals and ruined farms in the surrounding areas of many of these mines. In Tagong, a small town in Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture China, there are records of dead fish and large animals floating down some of the rivers near the Tibetan mines. After further investigation, researchers found that this may have been caused by leakage of evaporation pools that sit for months and sometimes even years.Disposal
Lithium-ion batteries contain metals such as cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are toxic and can contaminate water supplies and ecosystems if they leach out of landfills. Additionally, fires in landfills or battery-recycling facilities have been attributed to inappropriate disposal of lithium-ion batteries. As a result, some jurisdictions require lithium-ion batteries to be recycled. In spite of the environmental cost of improper disposal of lithium-ion batteries, the rate of recycling is still relatively low, as recycling processes remain costly and immature.Finite resource
While lithium ion batteries can be used as a part of sustainable solution, shifting all fossil fuel-powered devices to lithium based batteries might not be the Earth's best option. There is no scarcity yet, but it is a natural resource that can be depleted. According to researchers at Volkswagen, there are about 14 million tons of lithium left, which corresponds to 165 times the production volume in 2018.Recycling
The EPA has guidelines regarding recycling lithium batteries in the U.S. There are different processes for single-use or rechargeable batteries, so it is advised that batteries of all sizes are brought to special recycling centers. This will allow a safer process of breaking down the individual metals that can be reclaimed for further use. There are currently three major methods used for the recycling of lithium-ion batteries, those being:Pyrometallurgical recovery
The processes within thepyrometallurgical
Pyrometallurgy is a branch of extractive metallurgy. It consists of the thermal treatment of minerals and metallurgical ores and concentrates to bring about physical and chemical transformations in the materials to enable recovery of valuable ...
recovery include pyrolysis, incineration, roasting, and smelting. Right now, most traditional industrial processes are not able to recover lithium. They main process is to extract other metals including cobalt, nickel, and copper. There is a very low recycling efficiency in materials and use of capital resources. There are high energy requirements along with gas treatment mechanisms that will produce a lower volume of gas byproducts.
Hydrometallurgical metals reclamation
Hydrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy, the obtaining of metals from their ores. Hydrometallurgy involve the use of aqueous solutions for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual m ...
is the application of aqueous solution to recover metal from ores. It is commonly used for copper recovery. This method has been used for other metals to help eliminate the problem of sulfur dioxide byproducts that more conventional smelting causes.
Direct recycling
While recycling is an option, it still generally remains being more expensive than mining the ores themselves. With the rising demand for lithium-ion batteries the need for a more efficient recycling program is detrimental with many companies racing to find the most efficient method. One of the most pressing issues is when the batteries are manufactured, recycling is not considered a design priority.Application
There are many uses for lithium-ion batteries since they are light, rechargeable and are compact. They mostly used in electric vehicles and hand held electronics, but they are also increasingly used in military andaerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astrona ...
applications.
Electric vehicles
The primary industry and source of the lithium-ion battery is electric vehicles (EV). Electric vehicles have seen a massive increase in sales in recent years with over 90% of all global car markets having EV incentives in place as of 2019. With this increase in sales of EVs and the continued sales of them we can see a significant improvement to environmental impacts from the reduction offossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
dependencies. There has been recent studies that explore different uses for recycled lithium ion batteries specifically from electric vehicles. Specifically the secondary use of lithium ion batteries recycled from electric vehicles for secondary use in power load peak shaving in China has been proven to be effective for grid companies. With the environmental threats that are posed by spent lithium-ion batteries paired with the future supply risks of battery components for electric vehicles, remanufacturing of lithium batteries must be considered. Based on the EverBatt model, a test was conducted in China which concluded that remanufacturing of lithium-ion batteries will only be cost effective when the purchase price of spent batteries remains low. Recycling will also have significant benefits to environmental impacts. In terms of greenhouse gas reduction we see a 6.62% reduction in total GHG emissions with the use of remanufacturing.{{Cite journal, last1=Xiong, first1=Siqin, last2=Ji, first2=Junping, last3=Ma, first3=Xiaoming, date=February 2020, title=Environmental and economic evaluation of remanufacturing lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles, url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.11.013, journal=Waste Management, volume=102, pages=579–586, doi=10.1016/j.wasman.2019.11.013, pmid=31770692, s2cid=208321682 , issn=0956-053X
See also
* Aluminum-ion battery *Battery recycling
Battery recycling is a recycling activity that aims to reduce the number of batteries being disposed as municipal solid waste. Batteries contain a number of heavy metals and toxic chemicals and disposing of them by the same process as regular ...
* Glass battery
The glass battery is a type of solid-state battery. It uses a glass electrolyte and lithium or sodium metal electrodes. The battery was invented by John B. Goodenough, inventor of the lithium cobalt oxide and lithium iron phosphate electrode m ...
* Lithium battery
Lithium battery may refer to:
* Lithium metal battery, a non-rechargeable battery with lithium as an anode
** Rechargeable lithium metal battery, a rechargeable counterpart to the lithium metal battery
* Lithium-ion battery, a rechargeable batte ...
* Lithium-sulfur battery
* Sodium-ion battery
The sodium-ion battery (NIB or SIB) is a type of rechargeable battery that uses sodium ions (Na+) as its Electric charge, charge carriers. Its Lithium-ion battery#Electrochemistry, working principle and Lithium-ion battery#Design, cell constructio ...
* Potassium-ion battery
A potassium-ion battery or K-ion battery (abbreviated as KIB) is a type of battery and analogue to lithium-ion batteries, using potassium ions for charge transfer instead of lithium ions. It was invented by the Iranian/American chemist Ali Eftekhar ...
* Environmental impact of Electric Cars
* Pyrometallurgical
Pyrometallurgy is a branch of extractive metallurgy. It consists of the thermal treatment of minerals and metallurgical ores and concentrates to bring about physical and chemical transformations in the materials to enable recovery of valuable ...
* Hydrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy, the obtaining of metals from their ores. Hydrometallurgy involve the use of aqueous solutions for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual m ...
References