Eleventh Air Force on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Eleventh Air Force (11 AF) is a Numbered Air Force of the
 Military aircraft began flying in Alaska in 1920 when the Black Wolf Squadron, or The Alaska Flying Expedition, made The New York to Nome Flight. Capt. St. Clair Streett commanded 7 men in 4 DH-4s as they took off from
Military aircraft began flying in Alaska in 1920 when the Black Wolf Squadron, or The Alaska Flying Expedition, made The New York to Nome Flight. Capt. St. Clair Streett commanded 7 men in 4 DH-4s as they took off from


 Early in 1940, the question of air defense of the Alaska Territory came into the limelight when President Roosevelt pointed out in his message to Congress requesting funds for fortification of
Early in 1940, the question of air defense of the Alaska Territory came into the limelight when President Roosevelt pointed out in his message to Congress requesting funds for fortification of  Administratively speaking, the Eleventh Air Force also was born in that winter of 1941–1942. First conceived as the Air Force, Alaskan Defense Command, it emerged as an integral unit as the Alaskan Air Force on 15 January 1942, and was redesignated the Eleventh Air Force on 5 February. In May 1942, a field headquarters was established at
Administratively speaking, the Eleventh Air Force also was born in that winter of 1941–1942. First conceived as the Air Force, Alaskan Defense Command, it emerged as an integral unit as the Alaskan Air Force on 15 January 1942, and was redesignated the Eleventh Air Force on 5 February. In May 1942, a field headquarters was established at
 In mid-1942 the
In mid-1942 the
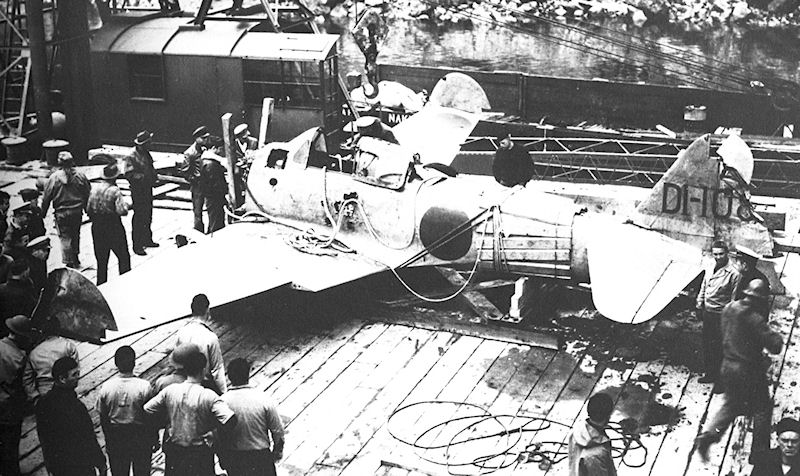 The first aerial bombing of the American continent during World War II took place on 3 and 4 June 1942, when two Japanese raids were made on the Dutch Harbor in the city of Unalaska, Alaska. While the first did little damage, the second destroyed the base's oil storage tanks, part of the hospital, and damaged a beached barracks ship. Although American pilots had finally located the Japanese carriers, attempts to destroy them proved fruitless. As bad weather again set in, all contact with the enemy fleet was lost.
In all, the Japanese raid claimed 43 U.S. lives, of which 33 were soldiers. Another 64 Americans were wounded. Eleven U.S. planes were downed, while the Japanese lost ten aircraft. During the two-day fight, Naval Task Force 8 had remained south of Kodiak Island, taking no part in the action. On 5 June, it received a report of enemy warships in the Bering Sea heading south toward Unalaska Island, which was interpreted to be a landing force intent upon seizing Dutch Harbor. While Task Force 8 entered the Bering Sea, Hosogaya's fleet moved south to join Yamamoto, who had just suffered the loss of his four large carriers at the
The first aerial bombing of the American continent during World War II took place on 3 and 4 June 1942, when two Japanese raids were made on the Dutch Harbor in the city of Unalaska, Alaska. While the first did little damage, the second destroyed the base's oil storage tanks, part of the hospital, and damaged a beached barracks ship. Although American pilots had finally located the Japanese carriers, attempts to destroy them proved fruitless. As bad weather again set in, all contact with the enemy fleet was lost.
In all, the Japanese raid claimed 43 U.S. lives, of which 33 were soldiers. Another 64 Americans were wounded. Eleven U.S. planes were downed, while the Japanese lost ten aircraft. During the two-day fight, Naval Task Force 8 had remained south of Kodiak Island, taking no part in the action. On 5 June, it received a report of enemy warships in the Bering Sea heading south toward Unalaska Island, which was interpreted to be a landing force intent upon seizing Dutch Harbor. While Task Force 8 entered the Bering Sea, Hosogaya's fleet moved south to join Yamamoto, who had just suffered the loss of his four large carriers at the



 On 30 August 1942, in the face of a howling gale, American Army troops went ashore on
On 30 August 1942, in the face of a howling gale, American Army troops went ashore on

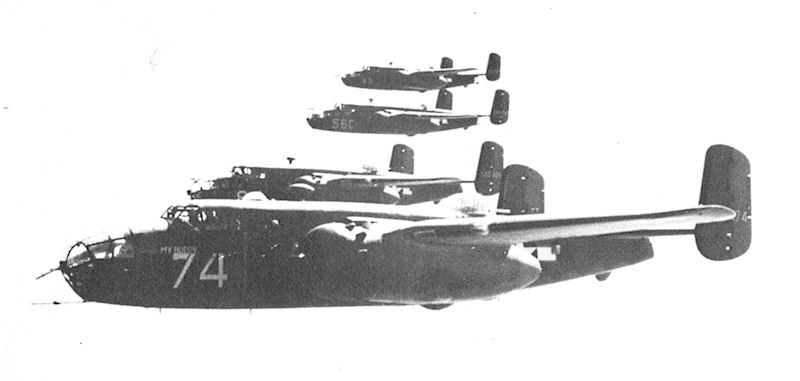 More than a month before the unopposed landing on Kiska, the Eleventh Air Force began a new phase of operations against the Japanese. On 10 July 1943, six Eleventh Air Force B-25 Mitchells made the long flight to Paramushiru Island in the
More than a month before the unopposed landing on Kiska, the Eleventh Air Force began a new phase of operations against the Japanese. On 10 July 1943, six Eleventh Air Force B-25 Mitchells made the long flight to Paramushiru Island in the

 1944 also saw a drastic reduction in the personnel of the Eleventh Air Force. Fort Glenn AAF and Fort Randall AAF were reduced to the status of gasoline stations for the Aleutian air transport routes, and were manned by small housekeeping units; Annette Island Landing Field and Yakutat Landing Field assigned as sub bases to Elmendorf Field. The
1944 also saw a drastic reduction in the personnel of the Eleventh Air Force. Fort Glenn AAF and Fort Randall AAF were reduced to the status of gasoline stations for the Aleutian air transport routes, and were manned by small housekeeping units; Annette Island Landing Field and Yakutat Landing Field assigned as sub bases to Elmendorf Field. The


 With the activation of the
With the activation of the


 The responsibilities for aerospace warning and aerospace control for North America are assigned to NORAD through the binational NORAD agreement. The Alaskan NORAD Region (ANR) is one of three NORAD regions responsible for the execution of the aerospace warning and aerospace control missions. ANR conducts these missions 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Eleventh Air Force is the United States Air Force component of ANR. Coordinating with the Canadian Forces Air Command, Both 11th AF and the Canadian Forces provide active duty forces to the 611th Air and Space Operations Center. The 176th Air Control Squadron, an Alaska Air National Guard unit, provides manning for the Alaskan Air Defense Sector to maintain continuous surveillance of Alaskan airspace with Alaskan Radar System long and short-range radars.
The appearance of a strategic cruise missile threat once again prompted a buildup of air defense capabilities. The Alaska NORAD Region Air Operations Center (AK RAOC), operated by U.S. and Canadian personnel, became operational in 1983 at Elmendorf AFB. It receives and analyses surveillance radar data from the sites in the Alaska Radar System (ARS) to determine range, direction altitude speed and whether or not the objects are friendly or hostile.
The Alaska RAOC enjoins state-of-the-art air defense systems and cutting-edge computer technology to significantly increase surveillance and identification capabilities, and better protect the nation's airways from intrusion and attack. It is fully integrated with the Boeing E-3 Sentry Airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system. The Battle Control System-Fixed (BCS-F) fuses data from airborne, ground and naval elements and civil air traffic sensors into an integrated air defence and sovereignty picture. This allows commanders to monitor the airspace above, beyond and within U.S. and Canadian borders, providing a major component for homeland defense. It also incorporates a newly developed situational awareness system that gives ANR unprecedented tools and technology to assist state and local responders in dealing with natural disasters.
The ARS consists of minimally attended
The responsibilities for aerospace warning and aerospace control for North America are assigned to NORAD through the binational NORAD agreement. The Alaskan NORAD Region (ANR) is one of three NORAD regions responsible for the execution of the aerospace warning and aerospace control missions. ANR conducts these missions 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Eleventh Air Force is the United States Air Force component of ANR. Coordinating with the Canadian Forces Air Command, Both 11th AF and the Canadian Forces provide active duty forces to the 611th Air and Space Operations Center. The 176th Air Control Squadron, an Alaska Air National Guard unit, provides manning for the Alaskan Air Defense Sector to maintain continuous surveillance of Alaskan airspace with Alaskan Radar System long and short-range radars.
The appearance of a strategic cruise missile threat once again prompted a buildup of air defense capabilities. The Alaska NORAD Region Air Operations Center (AK RAOC), operated by U.S. and Canadian personnel, became operational in 1983 at Elmendorf AFB. It receives and analyses surveillance radar data from the sites in the Alaska Radar System (ARS) to determine range, direction altitude speed and whether or not the objects are friendly or hostile.
The Alaska RAOC enjoins state-of-the-art air defense systems and cutting-edge computer technology to significantly increase surveillance and identification capabilities, and better protect the nation's airways from intrusion and attack. It is fully integrated with the Boeing E-3 Sentry Airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system. The Battle Control System-Fixed (BCS-F) fuses data from airborne, ground and naval elements and civil air traffic sensors into an integrated air defence and sovereignty picture. This allows commanders to monitor the airspace above, beyond and within U.S. and Canadian borders, providing a major component for homeland defense. It also incorporates a newly developed situational awareness system that gives ANR unprecedented tools and technology to assist state and local responders in dealing with natural disasters.
The ARS consists of minimally attended
The 3rd Wing is stationed at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson, Anchorage, Alaska. Its mission is to support and defend U.S. interests in the Asia-Pacific region and around the world by providing units that are ready for worldwide air power projection and a base that is capable of meeting PACOM's theater staging and throughput requirements. *
The 354th Fighter Wing is stationed at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska. The wing's mission is to train and provide
Located at
Located at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson, the center consists of five squadrons and two numbered flights that develop plans, procedures and directives for the employment of Alaskan combat and support forces assigned to the 11th Air Force, PACAF and NORAD. *
The 611th Air Support Group at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson consists of two squadrons that provides surveillance radars, Arctic infrastructure including airfields, communications and worldwide ready EAF warriors for homeland defense, decisive force projection, and aerospace command and control in Alaska. * Missile Defense Flight or Command Representative for Missile Defense
Serves as the focal point for all issues related to Ground-based Midcourse Defense in Alaska, in support of Alaska Command, Alaska NORAD Region, and 11 AF. * 11th Air Force/Alaska NORAD Region (ANR) Logistics Flight
Provides a core group of logisticians to support Air Force and NORAD air operations throughout the theater, including manning the ANR Battlestaff and establishing logistics readiness centers when necessary.
The 168th Air Refueling Wing is stationed at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska, and flies the Boeing KC-135R Stratotanker. The 168th also has taken over the missile defense mission at
The 176th Wing operates from Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson. The 176th is a multifaceted organization consisting of an airlift squadron, a complete pararescue package, as well as the 176th Air Control Squadron, which supports the Alaska NORAD Region with continuous operations and maintenance.
Eleventh Air Force Factsheet
11th Air Force, Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson, Alaska
Alaskan Command, Elmendorf AFB, Alaska
3d Wing, Elmendorf AFB, Alaska
354th Fighter Wing, Eielson AFB, Alaska
353d Combat Training Squadron Factsheet, Eielson AFB
168th Air Refueling Wing, Eielson AFB, Alaska
176th Wing, Kulis ANGB, Alaska
Photos from 11th Air Force, Alexai Point Army Airfield, Attu Island, 1944
{{USAAF 11th Air Force World War II 11 11 Military units and formations established in 1942 Military units and formations in Alaska Aleutian Islands campaign
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
Pacific Air Forces
Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force and is also the air component command of the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). PACAF is headquartered at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam (f ...
(PACAF). It is headquartered at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson, Alaska.This unit is not related to the Eleventh Air Force headquartered in Pennsylvania described below.
11 AF plans, conducts, controls and coordinates air operations in accordance with the tasks assigned by the commander, Pacific Air Forces
Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force and is also the air component command of the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). PACAF is headquartered at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam (f ...
, and is the force provider for Alaskan Command
The Alaskan Command (ALCOM) is a joint subordinate unified command of the United States Northern Command, responsible for operations in and around the State of Alaska. Alaskan Command is charged with maintaining air sovereignty, deploying force ...
, the Alaska North American Aerospace Defense Command Region and other unified commanders. The Commander, Eleventh Air Force, also serves as Commander, Alaskan Command
The Alaskan Command (ALCOM) is a joint subordinate unified command of the United States Northern Command, responsible for operations in and around the State of Alaska. Alaskan Command is charged with maintaining air sovereignty, deploying force ...
, and as commander of the Alaskan North American Aerospace Defense Command Region. The NORAD mission is accomplished largely through the PACAF Regional Support Center (PRSC), the 611th Air and Space Operations Center, and units of the Alaska Air National Guard (AK ANG). Together, they carry out air surveillance, and command and control forces that provide tactical warning and attack assessment in defense of Alaska.
Established on 28 December 1941 as the Alaskan Air Force at Elmendorf Field Elmendorf may refer to:
People with the surname
*Dave Elmendorf, former NFL player
* Douglas Elmendorf, 2009-2015 director of the Congressional Budget Office
*Lucas Conrad Elmendorf, a United States Representative from New York
*Steven Elmendorf, l ...
, Alaska Territory
The Territory of Alaska or Alaska Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from August 24, 1912, until Alaska was granted statehood on January 3, 1959. The territory was previously Russian America, 1784–1867; th ...
. it was initially part of the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
. It provided air defense of Alaska during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and fought in the Aleutian Islands Campaign. It was re-designated as the Alaskan Air Command in late 1945, and became responsible for the air defense of Alaska. With the collapse of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, it was transferred to the control of PACAF in 1990 and reduced to the status of a Numbered Air Force.
History
 Military aircraft began flying in Alaska in 1920 when the Black Wolf Squadron, or The Alaska Flying Expedition, made The New York to Nome Flight. Capt. St. Clair Streett commanded 7 men in 4 DH-4s as they took off from
Military aircraft began flying in Alaska in 1920 when the Black Wolf Squadron, or The Alaska Flying Expedition, made The New York to Nome Flight. Capt. St. Clair Streett commanded 7 men in 4 DH-4s as they took off from Mitchel Field
Mitchell may refer to:
People
*Mitchell (surname)
*Mitchell (given name)
Places Australia
* Mitchell, Australian Capital Territory, a light-industrial estate
* Mitchell, New South Wales, a suburb of Bathurst
* Mitchell, Northern Territory ...
on 17 July 1920. Each plane had a black profile of a Wolf's head painted on their sides. The trip organizer, Billy Mitchell wanted to establish an airway to Alaska and Asia. The 9349 mile round trip route included flying west to North Dakota, then north through Saskatchewan, Alberta, British Columbia, the Yukon, and onwards to Fairbanks on 19 Aug. and finally Nome on the 23rd. They started their return trip on the 31st, landing Mitchel Field on 20 Oct. 1920 after 112 flying hours.
In 1924, the around the world flight by the Army using Douglas "World Cruiser"s also transited though Alaska. However, the first permanently based military aircraft began to deploy to Alaska during the last half of 1940 after the breakout of World War II in Europe and tensions began to deteriorate with Japan. To coordinate air activities there, the Alaskan Defense Command established the Air Field Forces, Alaskan Defense Command on 29 May 1941.
Origins

 Early in 1940, the question of air defense of the Alaska Territory came into the limelight when President Roosevelt pointed out in his message to Congress requesting funds for fortification of
Early in 1940, the question of air defense of the Alaska Territory came into the limelight when President Roosevelt pointed out in his message to Congress requesting funds for fortification of Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
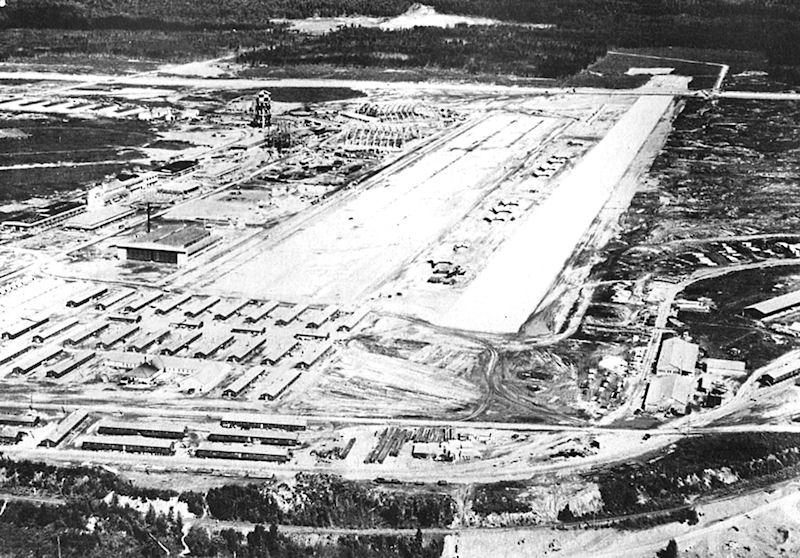
and Wake Islands and other strategic points in the Pacific that airfields were needed in Alaska. The original request for $12,000,000 to be appropriated for the construction of Alaskan defenses was cut to $600,000, but still was sufficient to begin the construction of an air base at Anchorage, Alaska. Thus was begun the construction of Elmendorf Field, primary fourth-echelon base for all future Eleventh Air Force operations. Construction of the airfield began on 8 June when 25 locally hired men began clearing brush, the Army intending it to be a permanent airfield.
The first "troops" of the Alaskan Air Force advance echelon to arrive in Alaska included a six-year-old Martin B-10 on 12 August 1940. On 12 December the Army designated the base Fort Richardson and flying field Elmendorf Field. The post was named for Brig Gen Wilds P. Richardson, former head of the Alaska Road Commission; the airfield and flying facilities were named Elmendorf Field in honor of Captain Hugh M. Elmendorf, killed in 1933 while flight testing an experimental fighter near Wright Field
Wilbur Wright Field was a military installation and an airfield used as a World War I pilot, mechanic, and armorer training facility and, under different designations, conducted United States Army Air Corps and Air Forces flight testing. Lo ...
, Ohio.
The first Air Corps unit to be assigned to Alaska was the 18th Pursuit Squadron
The 18th Aggressor Squadron (18 AGRS) is a subordinate unit of the 354th Fighter Wing based at Eielson Air Force Base in Alaska, and flies the Block 30 General Dynamics F-16C/D aircraft.
Mission
The 18th Aggressor Squadron prepares combat Ai ...
, which transferred to Elmendorf from Hamilton Army Airfield, California on 21 February 1941 with Curtiss P-40 Warhawks. The 23d Air Base Group was assigned shortly afterwards to provide base support. The 36th Bombardment Squadron arrived less than a month later from Lowry Field, Colorado, equipped with Douglas B-18 Bolo medium bombers.
A major problem was the training of personnel and the preparing of equipment for operation in the cold Alaskan climate. Mechanical things showed unusual behavior at 40 degrees below zero. Oil became almost solid, metal and rubber brittle and fractured easily. At the same time, Texas-trained pilots had to learn to fly in a country where sudden fogs could close out airports in less than 10 minutes and high-velocity "williwaws" could tear the wings off combat planes.
The first months activities of the new command were spent in reconnaissance for a rim of defense bases. The hub of this defense "wheel" was to be at Elmendorf Field near Anchorage. In the meantime, plans for the establishment of bases were moving slowly. Certain planned fields had to be constructed in summer, because the severe Alaskan frost in winter made construction impossible, but equipment for the construction of fields north of Nome and around Anchorage failed to arrive, and construction was postponed until the following summer. Construction had been completed, however, on two important coastal fields in southeastern Alaska, Annette Army Airfield at Annette Island
Annette Island or ''Taak'w Aan'' (Tlingit) is an island in the Gravina Islands of the Alexander Archipelago of the Pacific Ocean on the southeastern coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is at . It is about long and about wide. The land are ...
and Yakutat Army Airfield at Yakutat, and the first direct all-weather air route to Alaska from Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region o ...
was open.
An extremely fortunate accident took place in October 1941, which possibly changed the whole course of World War II in Alaska. Equipment for the construction of a CAA-DLA (Civil Aeronautics Authority-Defense Land Appropriation) airfield at McGrath, on the mainland, arrived too late to begin construction of the field, since the ground already had become frozen, and General Buckner requested and received permission to divert the equipment and men to Cold Bay on the Alaskan Peninsula and Otter Point on Umnak Island, to build two airfields for the defense of the Naval Base at Dutch Harbor
Dutch Harbor is a harbor on Amaknak Island in Unalaska, Alaska. It was the location of the Battle of Dutch Harbor in June 1942, and was one of the few sites in the United States to be subjected to aerial bombardment by a foreign power during ...
. To conceal their purpose, both fields were organized as ostensible business enterprises concerned with fishing and canning. The two cover names were: "Blair Packing Company" and "Saxton & Company", whose peculiar canning equipment consisted of bulldozers, power shovels and similar construction equipment. The top holding-company for these enterprises was the "Consolidated Packing Company" of Anchorage, known in military circles as the Alaskan Defense Command. Security was complete. Japanese intelligence never learned of the existence of these airfields and the Japanese tactical decisions were based on the assumption that their attack on Dutch Harbor would not be opposed by land-based aircraft.
All through the winter of 1941–1942, men worked at the construction of these two air bases, and by spring, two 5,000-foot airstrips were completed, one at Cold Bay (Fort Randall Army Airfield
Thornbrough Air Force Base is a former facility of the United States Air Force in Cold Bay, Alaska. Following its closure, it was redeveloped into Cold Bay Airport.
History
The airport was constructed during World War II as Fort Randall Army Air ...
), the other at Otter Point on Umnak (Fort Glenn Army Airfield
Cape Air Force Base also known as Fort Glenn Army Air Base, is a site significant for its role in World War II fighting, operating alongside Naval Air Facility Otter Point.
It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places and declare ...
). Another vital factor in the construction of the Umnak field was the use of perforated steel matting. No other medium could have been used to build that runway in the time required, since Umnak has no natural construction material. The matting was laid over a graded gash in the tundra and set the pattern for the construction of future Aleutian runways.
 Administratively speaking, the Eleventh Air Force also was born in that winter of 1941–1942. First conceived as the Air Force, Alaskan Defense Command, it emerged as an integral unit as the Alaskan Air Force on 15 January 1942, and was redesignated the Eleventh Air Force on 5 February. In May 1942, a field headquarters was established at
Administratively speaking, the Eleventh Air Force also was born in that winter of 1941–1942. First conceived as the Air Force, Alaskan Defense Command, it emerged as an integral unit as the Alaskan Air Force on 15 January 1942, and was redesignated the Eleventh Air Force on 5 February. In May 1942, a field headquarters was established at Fort Morrow Army Airfield
Fort Morrow Army Airfield is a former United States Army airfield and radar station located six nautical miles (7 mi, 11 km) northeast of the central business district of Port Heiden, in the Lake and Peninsula Borough of the U.S. ...
, Port Heiden, Alaska, and planes of the 73d Bombardment Squadron
: ''See 73d Bombardment Squadron (World War II) for the United States Army Air Forces World War II squadron''
The 73d Bombardment Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 4241st Strategic Wing, based ...
were deployed at Fort Randall Army Airfield, Cold Bay and the 21st Bombardment Squadron
021 is:
* in Brazil, the telephone area code for the city of Rio de Janeiro and surrounding cities ( Greater Rio de Janeiro)
* in China, the telephone area code for the city of Shanghai.
* in Indonesia, the area code for the city of Jakarta and s ...
at Fort Glenn Army Airfield, Umnak.
Ladd Field near Fairbanks became a secondary major air base in Alaska. It was named after Major Arthur K. Ladd, killed in a flying accident near Dale, South Carolina on 13 December 1935. Unlike Elmendorf, Ladd Field came the jurisdiction of Ferrying Command, which was a part of the Lend-Lease Program. Through Lend-Lease, the United States transferred nearly 8,000 aircraft to the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
though Ladd Field during the course of World War II. The aircraft were flown into Ladd from Great Falls Airfield, Montana by American civilian aircrews; Soviet crews then flew the planes west through Nome ( Marks Field) and on to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
. The pilots leaving Great Falls flew along a route of small airfields that became known as the Northwest Staging Route. One of those airfields, Big Delta Army Airfield, southeast of Fairbanks, became Fort Greely.
Aleutian Campaign 1942
 In mid-1942 the
In mid-1942 the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
laid plans to attack Alaska in conjunction with an attack on Midway Island in the central Pacific. The Japanese Northern Area Fleet's attacks on Dutch Harbor
Dutch Harbor is a harbor on Amaknak Island in Unalaska, Alaska. It was the location of the Battle of Dutch Harbor in June 1942, and was one of the few sites in the United States to be subjected to aerial bombardment by a foreign power during ...
and Adak Island
Adak Island ( ale, Adaax, russian: Адак) or Father Island is an island near the western extent of the Andreanof Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in Alaska. Alaska's southernmost town, Adak, is located on the island. The island has a l ...
resulted in the Aleutian Islands Campaign. But because United States Naval intelligence had broken the Japanese naval cypher code, Admiral Nimitz, Commander-in-Chief Pacific Ocean Areas in Hawaii, learned of Japanese plans by 21 May 1942. As of 1 June 1942, United States military strength in Alaska stood at 45,000 men. On that day the XI Intercepter Command, activated earlier, in March, was redesignated the XI Fighter Command
The XI Fighter Command was a command of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to Eleventh Air Force, stationed at Adak Army Airfield, Alaska.
The command controlled fighter units in Alaska during the World War II Aleutian Island ...
. However, Eleventh Air Force operational strength was small. It consisted of 10 B-17 Flying Fortress heavy bombers and 34 B-18 Bolo medium bombers at Elmendorf Airfield, and 95 P-40 Warhawk fighters divided between Fort Randall AAF at Cold Bay and Fort Glenn AAF on Umnak.
When the first inklings of a possible Japanese attack on the Aleutian Islands were known, the Eleventh Air Force was ordered to send out reconnaissance aircraft to locate the Japanese fleet reported heading toward Dutch Harbor and attack it with bombers, concentrating on sinking Hosogaya's two aircraft carriers. Once the enemy planes were removed, Task Force 8/ North Pacific Force of the Navy, under Rear-Admiral Robert A. Theobald, would engage the enemy fleet and destroy it. On the afternoon of 2 June a naval patrol plane spotted the approaching Japanese fleet, reporting its location as 800 miles southwest of Dutch Harbor. Eleventh Air Force was placed on full alert. Shortly thereafter bad weather set in, and no further sightings of the fleet were made that day.
Attack on Dutch Harbor
 The first aerial bombing of the American continent during World War II took place on 3 and 4 June 1942, when two Japanese raids were made on the Dutch Harbor in the city of Unalaska, Alaska. While the first did little damage, the second destroyed the base's oil storage tanks, part of the hospital, and damaged a beached barracks ship. Although American pilots had finally located the Japanese carriers, attempts to destroy them proved fruitless. As bad weather again set in, all contact with the enemy fleet was lost.
In all, the Japanese raid claimed 43 U.S. lives, of which 33 were soldiers. Another 64 Americans were wounded. Eleven U.S. planes were downed, while the Japanese lost ten aircraft. During the two-day fight, Naval Task Force 8 had remained south of Kodiak Island, taking no part in the action. On 5 June, it received a report of enemy warships in the Bering Sea heading south toward Unalaska Island, which was interpreted to be a landing force intent upon seizing Dutch Harbor. While Task Force 8 entered the Bering Sea, Hosogaya's fleet moved south to join Yamamoto, who had just suffered the loss of his four large carriers at the
The first aerial bombing of the American continent during World War II took place on 3 and 4 June 1942, when two Japanese raids were made on the Dutch Harbor in the city of Unalaska, Alaska. While the first did little damage, the second destroyed the base's oil storage tanks, part of the hospital, and damaged a beached barracks ship. Although American pilots had finally located the Japanese carriers, attempts to destroy them proved fruitless. As bad weather again set in, all contact with the enemy fleet was lost.
In all, the Japanese raid claimed 43 U.S. lives, of which 33 were soldiers. Another 64 Americans were wounded. Eleven U.S. planes were downed, while the Japanese lost ten aircraft. During the two-day fight, Naval Task Force 8 had remained south of Kodiak Island, taking no part in the action. On 5 June, it received a report of enemy warships in the Bering Sea heading south toward Unalaska Island, which was interpreted to be a landing force intent upon seizing Dutch Harbor. While Task Force 8 entered the Bering Sea, Hosogaya's fleet moved south to join Yamamoto, who had just suffered the loss of his four large carriers at the Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea. The U.S. Navy under ...
.
Possible attack at Nome
By mid-June the Joint Chiefs of Staff theorized that the attack on the Aleutian Islands and the occupation of its westernmost islands might be part of a holding action designed to screen a northward thrust by Japanese forces intoSiberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
's maritime provinces and the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and w ...
. As a result of their concern about a possible Japanese attack upon the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
that might also include the occupation of St. Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea and of nearby Nome and its adjacent airfields on the Alaskan mainland.
Supporting the possibility of an invasion of the Alaskan mainland were reports of a Japanese fleet operating in the Bering Sea. Three separate sightings placed an enemy fleet somewhere between the Pribilof and St. Lawrence Islands, suggesting that either an enemy raid on or an outright invasion of the Alaskan mainland was imminent, with Nome the likely objective. As a result, within thirty-six hours, Eleventh Air Force using commandeered civilian aircraft flew nearly 2,300 troops to Nome, along with artillery and antiaircraft guns and several tons of other equipment and supplies. Consolidated B-24 Liberator bombers of the 404th Bombardment Squadron were sent to the Air Transport Command
Air Transport Command (ATC) was a United States Air Force unit that was created during World War II as the strategic airlift component of the United States Army Air Forces.
It had two main missions, the first being the delivery of supplies ...
Marks Army Airfield with a mission to locate and attack the Japanese Fleet.
Not until late July when United States intelligence reported with some certainty the departure of Hosogaya's fleet from the Bering Sea did the threat of invasion of the Alaskan mainland decline, allowing for the redeployment of many of the troops hastily assembled at Nome.
United States response



 On 30 August 1942, in the face of a howling gale, American Army troops went ashore on
On 30 August 1942, in the face of a howling gale, American Army troops went ashore on Adak Island
Adak Island ( ale, Adaax, russian: Адак) or Father Island is an island near the western extent of the Andreanof Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in Alaska. Alaska's southernmost town, Adak, is located on the island. The island has a l ...
, some 250 miles east of Kiska. Adak affords a good fleet anchorage, a sheltered harbor and as was revealed later, a superlative site for quick construction of an airfield. The 807th Army Aviation Engineering Battalion set to work constructing a dike and draining the tidal flat between Kuluk Bay and the Sweeper Cove areas to create an airfield. Only ten days later engineers built a runway, and on 10 September the first aircraft, a B-18, landed at " Longview Army Airfield". Three days later there were 15 B-24s, a B-17, 15 P-38s and 16 P-39s on the island. On 12 September, the first air attack from Adak, consisting of 12 B-24s, 14 P-38s and 14 P-39s, was launched under the command of Major John S. Chennault of the 343d Fighter Group. The attack was launched against Japanese positions on Kiska. The airfield on Adak was renamed " Davis Army Airfield" in honor of Colonel Everett S. Davis, the first Commander, Eleventh Air Force, killed in an aircraft accident on 28 November 1942.
Throughout the winter of 1942–1943, the Eleventh Air Force bombed Kiska and Attu whenever possible, although the flyers were extremely handicapped by the almost constant fog which covered the island. At the same time, the bases to the east of Adak were consolidated and built up. In October, the Field Headquarters of the Eleventh Air Force was closed at Kodiak and moved to Davis AAF.
On 11 January 1943, American Army troops went ashore on the unoccupied Amchitka
Amchitka (; ale, Amchixtax̂; russian: Амчитка) is a volcanic, tectonically unstable and uninhabited
island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Ref ...
Island, barely 75 statute miles from Kiska, and a month later, on 16 February, the first aircraft, a P-38 and a P-40, landed on Amchitka Army Airfield
Amchitka (; ale, Amchixtax̂; russian: Амчитка) is a volcanic, tectonically unstable and uninhabited
island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Ref ...
, a quickly-built airstrip. The first mission against Kiska was flown on 18 February.
By March, both medium and heavy bombers could make the short hop from Amchitka to Kiska and on good days, rare enough, crews flew as many as four and occasionally six sorties per day. It was said that the Japanese needed no air warning system on Kiska, because they could hear the Eleventh Air Force bombers warming up on Amchitka, and knew from the sound of the engines when the raids were taking off.
Throughout this period, the striking power of the Eleventh Air Force included only three squadrons of medium bombers, three squadrons of heavies and four squadrons of fighters. An additional squadron of P-39 Airacobras operated in the Aleutian theater for a short while, but their light landing gear was unsatisfactory for use on the rough fields and they were returned to the States.
Tactically, the Eleventh Air Force was operating under the jurisdiction of the Navy, since Alaska was still in the situation of a "fleet-opposed invasion". The air arm, designated Task Force "X", was commanded by General Butler, and included the Air Striking Group (Eleventh Air Force) and the Air Search Group (Naval Fleet Air Wing Four). Overall command was vested in Vice Admiral Thomas Kinkaid
Thomas Cassin Kinkaid (3 April 1888 – 17 November 1972) was an admiral in the United States Navy, known for his service during World War II. He built a reputation as a "fighting admiral" in the aircraft carrier battles of 1942 and commanded ...
, Commander, North Pacific Force, abbreviated to ComNorPacFor or ComNorPac.
Recapture of Attu and Kiska
On 1 April, a plan to by-pass Kiska and capture Attu was presented to the Joint Chiefs of Staff, was approved, and on 11 May, American troops went ashore on Attu. In a short and fierce battle, the Japanese garrison was wiped out, and on 29 May, the island was declared secure. The first plane, a hospital C-47, landed on a newly completed runway atAlexai Point Army Airfield
Alexai Point Army Airfield is an abandoned World War II airfield with two runways laid across Alexai Point on Attu Island, Alaska. The remains of the Seabee built airbase are located about 4 miles east of the closed Casco Cove Coast Guard Statio ...
, Attu, on 7 June. The operation against Attu also included the occupation of the Semichi Islands
The Semichi Islands (Samiyan in Aleut; russian: Семичи) are a cluster of small islands in the Near Islands group of the Aleutian Islands, Alaska. They are located southeast of Attu Island and northeast of Agattu Island, near . Named islands ...
, an archipelago of three tiny bits of land some 35 miles east of Attu. The flattest of these, Shemya, was to be the site of the most important American air base for future operations. Barely four miles long and only two miles wide, Shemya Army Airfield
Eareckson Air Station , formerly Shemya Air Force Base, is a United States Air Force military airport located on the island of Shemya, in the Alaskan Aleutian Islands.
The airport was closed as an active Air Force Station on 1 July 1994. Howe ...
became, literally, a stationary aircraft carrier. These islands were taken without opposition, on 29 May.
With Kiska cut off by the occupation of Attu, the Japanese made plans to evacuate the Aleutian Islands. Numerous sorties were made by the Japanese Fifth Fleet, based at Paramushiru, but finally on 28 July, under cover of a thick fog, destroyers were able to enter Kiska Harbor and remove all occupation troops. When American troops went ashore on 15 August, the island was deserted, ending the Aleutian Campaign.
Six million pounds of bombs had been dropped on Kiska and Attu in Eleventh Air Force operations. The Japanese had been prevented from building an air field and from bringing in reinforcements. 'Rufe' seaplane fighters were shot out of the air as soon as they came up to give combat. Air Force fighters and bombers had played an instrumental part in driving Japanese out of the Aleutian Islands. Illustrative of the challenges omnipresent in Alaska, only 35 aircraft were lost in combat compared to 150 operational accidents. It was the highest American combat-to-accidental loss ratio for any theater in World War II. Weather was the prime culprit. The Eleventh Air Force accounted for approximately 60 Japanese aircraft, one destroyer, one submarine and seven transport ships destroyed by air operations.
With the Aleutian Campaign completed, the Eleventh Air Force had the following units reassigned to other combat areas between 20 August and 1 September: the 21st Bombardment Squadron
021 is:
* in Brazil, the telephone area code for the city of Rio de Janeiro and surrounding cities ( Greater Rio de Janeiro)
* in China, the telephone area code for the city of Shanghai.
* in Indonesia, the area code for the city of Jakarta and s ...
(Heavy), 36th Bombardment Squadron (Heavy), 73d Bombardment Squadron
: ''See 73d Bombardment Squadron (World War II) for the United States Army Air Forces World War II squadron''
The 73d Bombardment Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 4241st Strategic Wing, based ...
(Medium), 406th Bombardment Squadron (Medium) and the 407th Bombardment Squadron
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smallest ...
(Dive Bomber).
Operations against Japan

 More than a month before the unopposed landing on Kiska, the Eleventh Air Force began a new phase of operations against the Japanese. On 10 July 1943, six Eleventh Air Force B-25 Mitchells made the long flight to Paramushiru Island in the
More than a month before the unopposed landing on Kiska, the Eleventh Air Force began a new phase of operations against the Japanese. On 10 July 1943, six Eleventh Air Force B-25 Mitchells made the long flight to Paramushiru Island in the Kuriles
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in th ...
and made the first direct attack on the Japanese home islands since the famous Doolittle raid in April 1942. From Alexai Point AAF on Attu, eight Mitchells of the 77th Bomb Squadron. (28th BG) struck Paramushiro bases principally. All returned safely.
A week later, B-24 Liberator heavy bombers from Attu bombed the Kuriles and secured pictures of the Japanese installations, the first pictures taken of northern Japan home-island defenses. The next Kurile raid, carried out on 11 August, was a diversionary raid prior to the landings on Kiska. On this mission, the first plane was lost over the Kuriles and Lieutenant James C. Pottenger and his crew made a forced landing in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
.
These operations led to a joint mission on 11 September 1943, when Eleventh Air Force dispatched eight B-24 Liberators and 12 B-25
The North American B-25 Mitchell is an American medium bomber that was introduced in 1941 and named in honor of Major General William "Billy" Mitchell, a pioneer of U.S. military aviation. Used by many Allied air forces, the B-25 served in ...
s. However the Japanese were alert and reinforced their defenses. 74 crew members in three B-24s and seven B-25 failed to return. Twenty two men were killed in action, one taken prisoner and 51 interned in Kamchatka, Russia. It had proven that the Kurile Islands could be attacked, but new methods had to be devised as the raid lost Eleventh Air Force over half its offensive striking power. No more combat missions were flown in 1943.
Several changes took place following the occupation of Kiska. The Eleventh Air Force became a component of Task Force "Y", still under Navy jurisdiction. Vice Admiral Frank Jack Fletcher was named ComNorPac and Major General Davenport Johnson
Davenport Johnson (28 March 1890 – 21 October 1963) was a United States Army Air Forces major general. During World War II, he commanded the Eleventh Air Force in Alaska from November 1943 to November 1945.
Early life and education
Born in Tyl ...
relieved General Butler as commander of the Eleventh Air Force. One of General Johnson's first acts was the establishment of the Eleventh Air Force Instrument flying school and the promotion of an intensive training program in navigation and instrument flying, as well as the accelerated development of radio and navigation aids in the Aleutian Islands. Because of the tremendous advances brought about by intensive instrument training and the increased aids to navigation and radio, planes that used to be grounded by weather, were now flying regular schedules. Troop Carrier Command
The I Troop Carrier Command is a disbanded United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with Continental Air Forces, at Stout Field, Indiana, where it was disbanded in November 1945, and its resources transferred to IX Troop Carrier Co ...
and Air Transport Command planes were operating in the Aleutian Islands with airline regularity.
In November 1943 a second airfield, Casco Cove Army Airfield
Casco Cove Coast Guard Station was a military facility and private use airfield on Attu Island, one of the Aleutian Islands in the U.S. state of Alaska. Owned by the United States Coast Guard, Casco Cove CGS is located west of Anchorage, Alaska ...
was constructed on Attu for long-range bombing operations.
Eleventh Air Force carried out another bombing mission against northern Kurils on 5 February 1944, when it attacked with six B-24s from the 404th Bomb Sqdn. (28th BG) and 16 P-38s from the 54th Fighter Sqdn. (343d FG). March 1944 saw Eleventh Air Force bombers over the Kuriles on daylight armed reconnaissance missions. Not many, but a sufficient number to convince the Japanese that there were aircraft in the Aleutian Islands and that the Kuriles were in constant danger of air attack. During the crucial period, while other United States forces were advancing in the South Pacific, the Japanese were forced to keep much-needed aircraft, in the Kuriles and Hokkaido
is Japan, Japan's Japanese archipelago, second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost Prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own List of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; th ...
as defense against possible attack from the North.
Operations against Northern Japan became the new mission of the Eleventh Air Force, and it was being successfully carried out. Except for July 1944, when the weather was especially bad, each month of 1944 showed a steady increase in operations against the Kuriles. Each month's record showed planes turned back short of their targets, weather again protecting the Japanese. Often, too, B-24 Liberator bomb loads were dropped through the undercast by aid of the newly installed radar bombing equipment, a far cry from the timed runs made on the Kiska main camp area using the Kiska volcano as an initial point when the target was closed in. The record month, June 1945, for the Eleventh Air Force showed a record number of tons of bombs dropped.
The B-25 Mitchell medium bombers, too, were playing their part in operations against the Kuriles. They had been kept on shipping alert since the abortive 11 September raid, but in May, two planes on a gasoline consumption test west of Attu, discovered and sank two armed Japanese trawlers. From that time on, the Mitchells, made sweeps against shipping when weather permitted, and by fall were bombing land targets in the Kuriles.
Air Transport Command operations
Although Eleventh Air Force was engaged in combat during the Aleutian Campaign, the command also supported the Lend-Lease transport of aircraft though Alaska to theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
by Air Transport Command beginning in September 1942. Lend-Lease aircraft were ferried from Great Falls Army Air Base, Montana to Ladd Field by the 7th Ferrying Group (Later Alaskan Wing), ATC. The United States manufactured aircraft were turned over to Red Air Force pilots at Ladd Field, and from there the Soviet pilots would fly to Marks Army Airfield, near Nome as a final refueling and maintenance stop on-route to Uel'kal', Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
. From Siberia, the aircraft were flown westward across the Soviet Union (Uelkal-Krasnoyarsk route) to the combat areas in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
for use against Nazi forces. Eleventh Air Force aircraft were also ferried up the NWSR, with the aircraft being flown to Elmendorf from RCAF Station Whitehorse
{{Location map, Canada, label=RCAF Station Whitehorse
, marksize=6, mark=Red_pog.svg
, lat_dir=N, lat_deg=60, lat_min=42, lat_sec=34
, lon_dir=W, lon_deg=135, lon_min=04, lon_sec=32
, position=width=300, float=right
, caption=Location of RCAF Stati ...
. More than 8,000 airplanes were delivered over the route. Most were Bell Airacobras and Kingcobras, along with A-20s, B-25s and C-47s. ATC personnel were based at Edmonton as well as other Canadian bases.
A lesser-known part of the aircraft ferrying mission for ATC pilots was search and rescue for Ferrying Command pilots and crews who were forced down in the remote wilderness. The ATC Alaska Wing was equipped with a number of single-engine C-64 "Norseman" light transports, which were equipped alternatively with pontoons, skis and wheels, depending the season. The C-64s were used to resupply stations along the Canadian pipeline as well as for search and rescue work.
ATC also developed two transport routes to Alaska during the war to support Eleventh Air Force. The first was from McChord Field
McChord Field is a United States Air Force base in the northwest United States, in Pierce County, Washington. South of Tacoma, McChord Field is the home of the 62d Airlift Wing, Air Mobility Command, the field's primary mission being worldw ...
, near Seattle, Washington north along the British Columbia coastline to Annette Island, then to Yakutat and into Elmendorf AFB. The second was developed to support the Aleutian Campaign and was built as American forces moved westward along the island chain. It started in Anchorage and went through Nannek Airfield then to Point Heiden, Cold Bay and along the Aleutian Islands until reaching Shemya and Attu Islands in 1944. These transport routes ferried personnel, along with high-value equipment and supplies that could not be shipped by normal cargo sealift. This eventually extended to Hokkaido, Japan
is Japan, Japan's Japanese archipelago, second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost Prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own List of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; th ...
after the end of the war, the route becoming part of the Great Circle Route
Great-circle navigation or orthodromic navigation (related to orthodromic course; from the Greek ''ορθóς'', right angle, and ''δρóμος'', path) is the practice of navigating a vessel (a ship or aircraft) along a great circle. Such ro ...
from Japan to the United States. Much of the transport along the routes were an airline responsibility, with Northwest Airlines and Western Airlines operating the routes under contract.
Drawdown and redesignation, 1944–1945

 1944 also saw a drastic reduction in the personnel of the Eleventh Air Force. Fort Glenn AAF and Fort Randall AAF were reduced to the status of gasoline stations for the Aleutian air transport routes, and were manned by small housekeeping units; Annette Island Landing Field and Yakutat Landing Field assigned as sub bases to Elmendorf Field. The
1944 also saw a drastic reduction in the personnel of the Eleventh Air Force. Fort Glenn AAF and Fort Randall AAF were reduced to the status of gasoline stations for the Aleutian air transport routes, and were manned by small housekeeping units; Annette Island Landing Field and Yakutat Landing Field assigned as sub bases to Elmendorf Field. The XI Bomber Command
The XI Bomber Command was a formation of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to Eleventh Air Force, and its last station was Shemya Army Air Base, Alaska, where it was inactivated on 31 March 1944.
History
Eleventh Air Force orga ...
and XI Fighter Command
The XI Fighter Command was a command of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to Eleventh Air Force, stationed at Adak Army Airfield, Alaska.
The command controlled fighter units in Alaska during the World War II Aleutian Island ...
disbanded per General Order 9, Headquarters, Eleventh Air Force, 25 February 1944.
It took these actions due to the fact that only two bomber squadrons remained in the Eleventh Air Force and the need to reduce the number of personnel. The 28th Bombardment Group
Antigua and Barbuda (, ) is a sovereign country in the West Indies. It lies at the juncture of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the Leeward Islands part of the Lesser Antilles, at 17°N latitude. The country consists of two majo ...
on Shemya and the 343d Fighter Group at Alexai Point AAF, Attu, assumed the responsibilities of the two commands. The 404th Bombardment Squadron was responsible for conducting night reconnaissance missions over the Kuriles and flying a daily weather reconnaissance flights. The 77th Bombardment Squadron was held in readiness to repel a seaborne invasion and the fighter squadrons provided air defense. Air Corps supply and fourth echelon maintenance was carried on at the Alaska Air Depot at Elmendorf, and the normal paper-work, customarily handled by a Service command, devolved upon the Eleventh Air Force Headquarters.
Eleventh Air Force, sent between 24 August and 4 September 1945 two B-24 Liberators of the 28th BG flew reconnaissance overflights over the North Kuril Islands to take photos of the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
occupation in the area. Soviet fighters intercepted and forced them away a foretaste of the Cold war
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
that lay ahead.
Americans planners had briefly contemplated an invasion of northern Japan from the Aleutian Islands during fall of 1943, but rejected that idea as too risky and impractical. They considered the use of Boeing B-29
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 ...
Superfortresses, on Amchitka
Amchitka (; ale, Amchixtax̂; russian: Амчитка) is a volcanic, tectonically unstable and uninhabited
island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Ref ...
and Shemya Bases, but rejected that idea too. U.S. military maintained interest in these plans when they ordered the expansion of bases in the western Aleutian Islands, and major construction began on Shemya for a possible invasion of Japan via the Northern route in 1945.
The real nature of the Aleutian Islands the value of the Eleventh Air Force to America was known but not confirmed until 3 September 1945. On that day, a C-54 piloted by Major G. E. Cain, filed a flight plan at Atsugi Airdrome, near Tokyo, Honshū, Japan. Twelve hours later, he landed at Adak, refueled and took off for Seattle. He landed in Washington after 31 hours of flying time, with the first motion pictures of the Japanese surrender the previous day.
The Aleutian Islands, on the Great Circle route from North America to the Orient may not have fulfilled their hope of becoming the "Northern Highway to Victory," but they were established as an air transport route, vital during the early years of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
before long-distance air transports were developed.
With the end of the war, many of the small air bases in the Aleutian Islands closed permanently, and postwar emphasis turned to training. Air Transport Command transferred Ladd Field to the Eleventh Air Force on 1 November. On 15 December 1945, The Army reorganized its organization in Alaska. Eleventh Air Force, which was under the jurisdiction of the Army Western Defense Command, headquartered at the Presidio of San Francisco since its establishment in 1941, was transferred to the jurisdiction of the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
.
Under the USAAF, it was re-designated as Alaskan Air Command' on 18 December 1945, without any change in headquarters location. Alaskan Air Command was established at the same Major Command echelon as the other overseas combat commands, the United States Air Forces in Europe, Far East Air Forces and Caribbean Air Command, with its mission being the air defense of the Territory of Alaska.
Eleventh Air Force in Pennsylvania 1946–1948
Six months after Eleventh Air Force had been redesignated in Alaska, another headquarters, also named Eleventh Air Force, was established on 13 May 1946 and activated atOlmsted Field
Harrisburg Air National Guard Base is a United States Air Force base, located at Harrisburg International Airport, Pennsylvania. It is located west-southwest of Middletown, Pennsylvania.
The Pennsylvania Air National Guard facility is site ...
, Pennsylvania, on 13 June 1946. This new organization was assigned to Air Defense Command
Aerospace Defense Command was a major command of the United States Air Force, responsible for continental air defense. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was established in 1946, briefly inac ...
.
Major General Thomas J. Hanley, Jr. took command, and a cadre of enlisted personnel arrived at Olmsted on 19 June 1946. The headquarters was relocated to Harrisburg, Pennsylvania on 9 August 1946, base units were assigned and training commenced for reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US ...
and National Guard units in Indiana, Ohio and Pennsylvania. Training continued until the unit was inactivated on 1 July 1948. This organization was to have been activated on 1 July 1962 at Travis Air Force Base under Military Air Transport Service
The Military Air Transport Service (MATS) is an inactive United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense Unified Command. Activated on 1 June 1948, MATS was a consolidation of the United States Navy's Naval Air Transport Service (NA ...
, but that action was revoked three days before it became effective. This unit is not related to the current Eleventh Air Force.
Post-Cold War


 With the activation of the
With the activation of the Alaskan Command
The Alaskan Command (ALCOM) is a joint subordinate unified command of the United States Northern Command, responsible for operations in and around the State of Alaska. Alaskan Command is charged with maintaining air sovereignty, deploying force ...
in 1989, the next logical step was to place its air component (AAC) under the Pacific Air Forces
Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force and is also the air component command of the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). PACAF is headquartered at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam (f ...
. By reorganizing AAC into a Numbered Air Force (NAF), the Air Force was able to reduce its administrative manpower requirements during a period of massive Air Force strength reductions. On 9 August 1990, the Alaskan Air Command was redesignated the 11th Air Force once again and assigned as a NAF under United States Pacific Air Forces
Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force and is also the air component command of the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). PACAF is headquartered at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam (fo ...
. The new organization was allotted the lineage of the previous Eleventh Air Force that had served in Alaska.
The early 1990s was a period of mission changes and force modernization. The 11th Air Force was reorganized as an objective Numbered Air Force during 1992–1993 and its headquarters reduced to only 100 authorizations. Its major units also changed. At Elmendorf AFB the 21st Tactical Fighter Wing was inactivated and was replaced by the 3rd Wing
The 3rd Wing is a unit of the United States Air Force, assigned to the Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) Eleventh Air Force. It is stationed at Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson, Alaska.
The Wing is the largest and principal unit within 11th Air Forc ...
transferred from Clark Air Base in December 1991 due to the destruction of Clark AB by the Mount Pinatubo eruption. The F-15E Strike Eagle-equipped 90th Fighter Squadron
The 90th Fighter Squadron is a squadron of the United States Air Force. It is assigned to the 3d Operations Group, 3d Wing, Elmendorf AFB, Alaska, Pacific Air Forces. The squadron is equipped with the F-22 Raptor fighter.
The 90 FS is one o ...
was added as were the 517th Airlift Squadron (C-130Hs and C-12Fs) and the 962d Airborne Air Control Squadron (E-3B).
There were also significant changes at Eielson AFB, when on 1 September 1992, Strategic Air Command inactivated the 6th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing, assigned there in 1967. The 343d Composite Wing
The 343d Wing is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with Pacific Air Forces at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska, where it was inactivated on 20 August 1993. The unit was formed at Eielson as the 343d Composite Wing a ...
became the host unit. The Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II assigned to the 18th Fighter Squadron were replaced with General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a success ...
s in 1992 and an OA-10A squadron was activated. Eielson AFB became home of the Exercise Cope Thunder
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic s ...
series, and the Alaskan range complex was greatly expanded and improved to accommodate not only Cope Thunder but other joint training requirements as well.
Finally, in keeping with Air Force Chief of Staff guidance to retain the most illustrious units, the 343rd Wing, a veteran of the Aleutian Campaign, was inactivated in August 1993. The 354th Fighter Wing
The 354th Fighter Wing is a United States Air Force wing that is part of Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). It is the host wing at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska, and is assigned to the Eleventh Air Force (11 AF).
The wing replaced the 343d Fighter ...
was activated in its place.
Other changes during the period included upgrading the 11th Tactical Air Control Group to the 11th Air Control Wing (11 ACW) at Eareckson AS in January 1992. During yet another reorganization, the wing was inactivated 1 July 1994 with the closure of the station. It was replaced by "..two groups organized under the 11 AF, the 611th Air Operations Group and 611th Air Logistics Group, later changed to the 611th Air Support Group
__NOTOC__
Year 611 ( DCXI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 611 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era b ...
."
Eleventh Air Force also accomplished the daunting drawdown of the forward operating bases at Galena Airport
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It c ...
, King Salmon Airport and Eareckson Air Force Station (Shemya Island), in a two-year period of time, 1993–1995, reflecting cost savings derived from the end of the Cold War. The stations remain in a standby status, their facilities being maintained by civilian contractors.
The mission of the Eleventh Air Force moved from statically defending Alaska against a bomber threat to committing its forces to worldwide deployment. The shift from a Major Command to an Objective Numbered Air Force was among the most drastic reorganizations undertaken anywhere in the Air Force.
Air Force personnel in Alaska were also fully integrated into the Air and Space Expeditionary Force deployment cycles, supporting operations as part of the Global War on Terrorism. In 2001–2002, the 18th Fighter Squadron deployed to Al Jaber, AB, Kuwait to take part in Operation Southern Watch, ENDURING FREEDOM, and ANACONDA; in 2004, The 355th Fighter Squadron deployed to Bagram AB, Afghanistan, as part of the War in Afghanistan.
The Secretary of Defense released the proposed 2005 Base Realignment And Closure recommendations and Eielson AFB was on the list. The original recommendations called for Eielson to be drawn down to a warm status...nearly to the point of closure. However, the final decision came later in the year and it called for the departure of all the A-10s. Shortly thereafter, the 18 FS learned that they would be converting to F-16 Aggressors over the next few years. In 2007, the last three A-10 aircraft departed Eielson
Alaskan NORAD Region
: ''see611th Air Support Group
__NOTOC__
Year 611 ( DCXI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 611 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era b ...
for a list of the AN/FPS-117
The AN/FPS-117 is an L-band active electronically scanned array (AESA) 3-dimensional air search radar first produced by GE Aerospace in 1980 and now part of Lockheed Martin. The system offers instrumented detection at ranges on the order of an ...
radar sites.''
: ''see North Warning System
The North Warning System (NWS) is a joint United States and Canadian early-warning radar system for the atmospheric air defense of North America. It provides surveillance of airspace from potential incursions or attacks from across North Americ ...
for the former DEW Line sites in Alaska''


 The responsibilities for aerospace warning and aerospace control for North America are assigned to NORAD through the binational NORAD agreement. The Alaskan NORAD Region (ANR) is one of three NORAD regions responsible for the execution of the aerospace warning and aerospace control missions. ANR conducts these missions 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Eleventh Air Force is the United States Air Force component of ANR. Coordinating with the Canadian Forces Air Command, Both 11th AF and the Canadian Forces provide active duty forces to the 611th Air and Space Operations Center. The 176th Air Control Squadron, an Alaska Air National Guard unit, provides manning for the Alaskan Air Defense Sector to maintain continuous surveillance of Alaskan airspace with Alaskan Radar System long and short-range radars.
The appearance of a strategic cruise missile threat once again prompted a buildup of air defense capabilities. The Alaska NORAD Region Air Operations Center (AK RAOC), operated by U.S. and Canadian personnel, became operational in 1983 at Elmendorf AFB. It receives and analyses surveillance radar data from the sites in the Alaska Radar System (ARS) to determine range, direction altitude speed and whether or not the objects are friendly or hostile.
The Alaska RAOC enjoins state-of-the-art air defense systems and cutting-edge computer technology to significantly increase surveillance and identification capabilities, and better protect the nation's airways from intrusion and attack. It is fully integrated with the Boeing E-3 Sentry Airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system. The Battle Control System-Fixed (BCS-F) fuses data from airborne, ground and naval elements and civil air traffic sensors into an integrated air defence and sovereignty picture. This allows commanders to monitor the airspace above, beyond and within U.S. and Canadian borders, providing a major component for homeland defense. It also incorporates a newly developed situational awareness system that gives ANR unprecedented tools and technology to assist state and local responders in dealing with natural disasters.
The ARS consists of minimally attended
The responsibilities for aerospace warning and aerospace control for North America are assigned to NORAD through the binational NORAD agreement. The Alaskan NORAD Region (ANR) is one of three NORAD regions responsible for the execution of the aerospace warning and aerospace control missions. ANR conducts these missions 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Eleventh Air Force is the United States Air Force component of ANR. Coordinating with the Canadian Forces Air Command, Both 11th AF and the Canadian Forces provide active duty forces to the 611th Air and Space Operations Center. The 176th Air Control Squadron, an Alaska Air National Guard unit, provides manning for the Alaskan Air Defense Sector to maintain continuous surveillance of Alaskan airspace with Alaskan Radar System long and short-range radars.
The appearance of a strategic cruise missile threat once again prompted a buildup of air defense capabilities. The Alaska NORAD Region Air Operations Center (AK RAOC), operated by U.S. and Canadian personnel, became operational in 1983 at Elmendorf AFB. It receives and analyses surveillance radar data from the sites in the Alaska Radar System (ARS) to determine range, direction altitude speed and whether or not the objects are friendly or hostile.
The Alaska RAOC enjoins state-of-the-art air defense systems and cutting-edge computer technology to significantly increase surveillance and identification capabilities, and better protect the nation's airways from intrusion and attack. It is fully integrated with the Boeing E-3 Sentry Airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system. The Battle Control System-Fixed (BCS-F) fuses data from airborne, ground and naval elements and civil air traffic sensors into an integrated air defence and sovereignty picture. This allows commanders to monitor the airspace above, beyond and within U.S. and Canadian borders, providing a major component for homeland defense. It also incorporates a newly developed situational awareness system that gives ANR unprecedented tools and technology to assist state and local responders in dealing with natural disasters.
The ARS consists of minimally attended AN/FPS-117
The AN/FPS-117 is an L-band active electronically scanned array (AESA) 3-dimensional air search radar first produced by GE Aerospace in 1980 and now part of Lockheed Martin. The system offers instrumented detection at ranges on the order of an ...
radar sites which were established between 1984 and 1985 at the former manned surveillance and Ground Control Intercept sites of Alaskan Air Command, first activated in the 1950s. Elements of the 1985 North American Air Defense Modernization program followed. Flexible and graduated alert concepts were introduced in the 1990s.
The ANR provides an ongoing capability to detect, validate, and warn of any aircraft and/or cruise missile threat in its area of operations that could threaten North American security. By maintaining surveillance of Northwest Canadian and U.S. airspace, ANR is able to determine what goes on in and near North American airspace 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Aerospace control requires capabilities to intercept, shadow, escort, divert, direct landings, and if necessary, use force utilizing interceptors and other means up to and including the destruction of airborne objects.
Lineage
* Established as Air Force, Alaska Defense Command, 17 October 1941 :: General Order 51: HQ, Alaska Defense Command * Established as Alaskan Air Force* on 28 December 1941 :: War Department Letter: Activation of Air Corps Unit, AG 320.2 : Activated on 15 January 1942 :: General Order 3, HQ Alaskan Defense Command : Redesignated 11th Air Force on 5 February 1942 : Redesignated Eleventh Air Force on 18 September 1942 : Redesignated Alaskan Air Command on 18 December 1945 :: AssumedMajor Command Major Command or Major Commands are large formations of the United States Armed Forces. Historically, a Major Command is the highest level of command. Within the United States Army, the acronym MACOM is used for Major Command. Within the United Sta ...
Status 18 December 1945
: Redesignated Eleventh Air Force on 9 August 1990
:: Headquarters Pacific Air Forces Special Order GA-44, 1 August 1990
:: Became subordinate organization to Pacific Air Forces
Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force and is also the air component command of the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). PACAF is headquartered at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam (f ...
, 9 August 1990
* Under authority from Western Defense Command, the Alaska Defense Command replaced the Air Field Forces, Alaskan Defense Command, with the Air Force, Alaskan Defense Command, on 17 October 1941. Neither the Air Field Forces nor the Air Force, Alaskan Defense Command, were legitimate War Department establishments and must be classified in the same category as provisional units, although the term "provisional" was never used in connection with them.
The United States Department of War
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department (and occasionally War Office in the early years), was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army, ...
activated the Alaskan Air Force to manage the buildup of the Army Air Forces in Alaska and replacing the Air Force, Alaskan Defense Command.
Assignments
* Alaska Defense Command, 17 October 1941 * Western Defense Command, 15 December 1941 – 18 December 1945 *Pacific Air Forces
Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force and is also the air component command of the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). PACAF is headquartered at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam (f ...
, 9 August 1990 – present
Airbases
The formation's headquarters was located at Elmendorf Airfield, from 15 January 1942; then Davis Army Airfield, August 1943 – 18 December 1945, and, after being reformed as Eleventh Air Force, at Elmendorf Air Force Base from 9 August 1990 onwards.World War II airfields
Combat airfields
Support/Transferred airfields
Components
During World War II
Commands
*XI Bomber Command
The XI Bomber Command was a formation of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to Eleventh Air Force, and its last station was Shemya Army Air Base, Alaska, where it was inactivated on 31 March 1944.
History
Eleventh Air Force orga ...
:: Constituted 4 March 1943
:: Activated on 19 March 1943
:: Inactivated on 31 March 1944
: Longview Army Airfield, Adak, 19 March 1941
: Amchitka Army Airfield, 24 June 1943
: Davis Army Airfield, Adak, 4 September 1943
: Shemya Army Airfield, 3–31 March 1944
* XI Fighter Command
The XI Fighter Command was a command of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to Eleventh Air Force, stationed at Adak Army Airfield, Alaska.
The command controlled fighter units in Alaska during the World War II Aleutian Island ...
:: Constituted as XI Interceptor Command, 8 March 1942
:: Activated on 15 March 1942
:: Re-designated as XI Fighter Command, 1 May 1942
:: Inactivated on 31 March 1944
: Elmendorf Army Airfield, 15 March 1942
: Davis Army Airfield, Adak, 12 September 1943 – 31 March 1944
* XI Air Force Service Command: 11 August 1942 – 25 October 1944.
Groups
Squadrons
Twenty-first century
*3rd Wing
The 3rd Wing is a unit of the United States Air Force, assigned to the Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) Eleventh Air Force. It is stationed at Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson, Alaska.
The Wing is the largest and principal unit within 11th Air Forc ...
The 3rd Wing is stationed at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson, Anchorage, Alaska. Its mission is to support and defend U.S. interests in the Asia-Pacific region and around the world by providing units that are ready for worldwide air power projection and a base that is capable of meeting PACOM's theater staging and throughput requirements. *
354th Fighter Wing
The 354th Fighter Wing is a United States Air Force wing that is part of Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). It is the host wing at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska, and is assigned to the Eleventh Air Force (11 AF).
The wing replaced the 343d Fighter ...
The 354th Fighter Wing is stationed at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska. The wing's mission is to train and provide
General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a success ...
fighters and support forces to combatant commanders anytime, anyplace, in support of U.S. national security objectives. The wing also hosts Air Education and Training Command
Air Education and Training Command (AETC) is one of the nine Major Commands (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force (USAF), reporting to Headquarters, United States Air Force. It was established 1 July 1993, with the realignment of Air Training ...
's Arctic Survival School.
* 36th WingLocated at
Andersen Air Force Base
Andersen Air Force Base (Andersen AFB, AAFB) is a United States Air Force base located primarily within the village of Yigo in the United States territory of Guam. The host unit at Andersen AFB is the 36th Wing (36 WG), assigned to the Pacific ...
, Guam. The 36th Wing has three major missions: Operate Andersen AFB via its subordinate 36th Mission Support and 36th Medical Groups; Provide power projection through an attached, rotational bomber force via its subordinate 36th Operations and 36th Maintenance Groups; and provide rapid air base opening and initial air base operation ability via its subordinate 36th Contingency Response Group.
* 611th Air and Space Operations CenterLocated at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson, the center consists of five squadrons and two numbered flights that develop plans, procedures and directives for the employment of Alaskan combat and support forces assigned to the 11th Air Force, PACAF and NORAD. *
611th Air Support Group
__NOTOC__
Year 611 ( DCXI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 611 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era b ...
The 611th Air Support Group at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson consists of two squadrons that provides surveillance radars, Arctic infrastructure including airfields, communications and worldwide ready EAF warriors for homeland defense, decisive force projection, and aerospace command and control in Alaska. * Missile Defense Flight or Command Representative for Missile Defense
Serves as the focal point for all issues related to Ground-based Midcourse Defense in Alaska, in support of Alaska Command, Alaska NORAD Region, and 11 AF. * 11th Air Force/Alaska NORAD Region (ANR) Logistics Flight
Provides a core group of logisticians to support Air Force and NORAD air operations throughout the theater, including manning the ANR Battlestaff and establishing logistics readiness centers when necessary.
Alaska Air National Guard
If activated for federal service, the 11th Air Force gains two wings of the Alaska Air National Guard. *168th Air Refueling Wing
The 168th Wing (168 WG) is a unit of the Alaska Air National Guard, stationed at Eielson Air Force Base, Fairbanks, Alaska. Before it was redesignated in February 2016, it was known as the 168th Air Refueling Wing (168 ARW). If activated to ...
The 168th Air Refueling Wing is stationed at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska, and flies the Boeing KC-135R Stratotanker. The 168th also has taken over the missile defense mission at
Clear Air Force Station
Clear Space Force Station is a United States Space Force radar station for detecting incoming ICBMs and submarine-launched ballistic missiles to NORAD's command center and to provide Space Surveillance data to the United States Space Force. Cle ...
with their 213th Space Warning Squadron.
* 176th WingThe 176th Wing operates from Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson. The 176th is a multifaceted organization consisting of an airlift squadron, a complete pararescue package, as well as the 176th Air Control Squadron, which supports the Alaska NORAD Region with continuous operations and maintenance.
List of commanders
See also
* Joint Task Force-Alaska *Alaska World War II Army Airfields
During World War II, Alaska was a major United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) location for personnel, aircraft, and airfields to support Lend-Lease aid for the Soviet Union. In addition, it was in Alaska that the Empire of Japan bombed and seized ...
* Report from the Aleutians 1943 film by John Houston about the daily lives of the servicemen at Adak Airfield.
References
; Notes ; NotesBibliography
* Chloe, John Hale, (1984), Top Cover for America. the Air Force in Alaska. 1920–1983, Pictorial Histories Publishing Company, * * *External links
Eleventh Air Force Factsheet
11th Air Force, Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson, Alaska
Alaskan Command, Elmendorf AFB, Alaska
3d Wing, Elmendorf AFB, Alaska
354th Fighter Wing, Eielson AFB, Alaska
353d Combat Training Squadron Factsheet, Eielson AFB
168th Air Refueling Wing, Eielson AFB, Alaska
176th Wing, Kulis ANGB, Alaska
Photos from 11th Air Force, Alexai Point Army Airfield, Attu Island, 1944
{{USAAF 11th Air Force World War II 11 11 Military units and formations established in 1942 Military units and formations in Alaska Aleutian Islands campaign