Eighteen Kingdoms on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
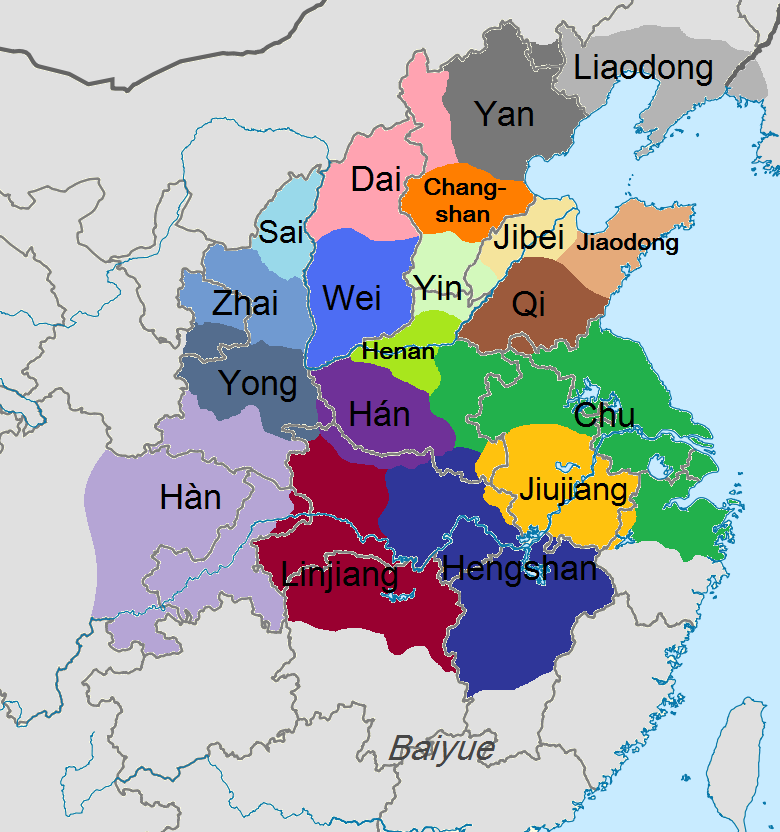 The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''
 The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''fengjian
''Fēngjiàn'' ( zh, c=封建, l=enfeoffment and establishment) was a political ideology and governance system in ancient China, whose social structure formed a decentralized system of confederation-like government based on the ruling class consis ...
'' states in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
created by military leader Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, –202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: 霸王, ''Bà Wáng'') of Western Chu during the Chu–Han Contention period (206–202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dynas ...
in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), ...
.林达礼,中华五千年大事记, 台南大孚书局, 1982, p. 56 The establishment and abolishment of the Eighteen Kingdoms marked the beginning and end of a turbulent interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
known as the Chu-Han Contention.
The details of the feudal division are as follows:
The Eighteen Kingdoms were short-lived: almost immediately rebellion broke out in Qi, after which Tian Rong conquered Jiaodong and Jibei, reuniting the old Qi state. Meanwhile, Xiang Yu had Emperor Yi of Chu and King Han Cheng
Han Cheng (died 206 BC), also known as Han Wang Cheng in some Chinese historical texts, was a ruler of the Kingdom of Hán () of the Eighteen Kingdoms during the Chu–Han Contention, an interregnum between the Qin and Han dynasties of China ...
of Hán killed. Thereafter, Liu Bang of Hàn conquered the lands of the Three Qins
The Three Qins () refer to three of the Eighteen Kingdoms, the short-lived power-sharing arrangement formed in 206 BC after the collapse of the Qin Dynasty. The three kingdoms were located in Guanzhong Plain (in present-day central Shaanxi), t ...
, thereby formally starting the Chu–Han Contention
The Chu–Han Contention ( zh, , lk=on) or Chu–Han War () was an interregnum period in ancient China between the fallen Qin dynasty and the subsequent Han dynasty. After the third and last Qin ruler, Ziying, unconditionally surrendered t ...
. Following many battles and changing alliances, Hàn defeated Chu and subdued all other kingdoms, where Liu Bang appointed vassal kings while making himself the first Emperor of the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
in 202 BCE.
See also
* ''Fengjian
''Fēngjiàn'' ( zh, c=封建, l=enfeoffment and establishment) was a political ideology and governance system in ancient China, whose social structure formed a decentralized system of confederation-like government based on the ruling class consis ...
''
* Ancient Chinese states
Ancient Chinese states () were typified by variously sized city-states and territories that existed in China prior to its unification by Qin Shi Huang in 221 BCE. In many cases these were vassal states and fiefs established in the '' fengjian'' s ...
* Kings of the Han dynasty
After Liu Bang defeated Xiang Yu and proclaimed himself emperor of the Han dynasty, he followed the practice of Xiang Yu and enfeoffed many generals, noblemen, and imperial relatives as kings (), the same title borne by the sovereigns of the Shan ...
Notes
References
{{Eighteen Kingdoms, state=collapsed Qin dynasty Han dynasty Dynasties in Chinese history Former countries in Chinese history