Egyptian–Ottoman War (1831–1833) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The First Egyptian–Ottoman War or First Syrian War (1831–1833) was a military conflict between the
 In 1825, the Sultan again called on Muhammad Ali to suppress a local uprising, this time a nationalist revolution by Greek Christians. He was promised rule over Crete, Cyprus, and the Morea (the modern Peloponnese) for his services. His son, Ibrahim Pasha, won quick victories at the head of a conscript army and controlled nearly the entire Peloponnesian peninsula within 10 months of his arrival in February 1825.David Howarth. (1976). ''The Greek Adventure: Lord Byron and other eccentrics in the War of Independence''. New York: Atheneum, 1976. The Greeks continued guerrilla operations however, and by September 1827 public opinion in
In 1825, the Sultan again called on Muhammad Ali to suppress a local uprising, this time a nationalist revolution by Greek Christians. He was promised rule over Crete, Cyprus, and the Morea (the modern Peloponnese) for his services. His son, Ibrahim Pasha, won quick victories at the head of a conscript army and controlled nearly the entire Peloponnesian peninsula within 10 months of his arrival in February 1825.David Howarth. (1976). ''The Greek Adventure: Lord Byron and other eccentrics in the War of Independence''. New York: Atheneum, 1976. The Greeks continued guerrilla operations however, and by September 1827 public opinion in
PDF The Sultan organized a new army of 80,000 men under Reşid Mehmed Pasha, Reshid Mehmed Pasha, the Grand Vizier, in a last-ditch attempt to block Ibrahim's advance towards the capital. While Ibrahim commanded a force of 50,000 men, most of them were spread out along his supply lines from Cairo, and he had only 15,000 in Konya. Nevertheless, when the armies met on December 21, Ibrahim's forces won in a rout, capturing the Grand Vizier after he became lost in fog attempting to rally the collapsing left flank of his forces. The Egyptians suffered only 792 casualties, compared to the Ottoman army's 3,000 dead, and they captured 46 of the 100 guns with which the army had left Istanbul. The stunning victory at Konya would be the final and most impressive victory of the Egyptian campaign against the Sublime Porte, and would represent the high point of Muhammad Ali's power in the region.
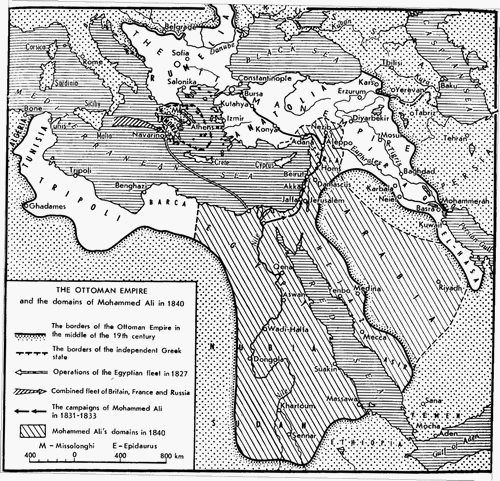 With no military forces between the Egyptian army and Istanbul, the Ottomans suffered a humiliating defeat by the hands of the Egyptians. Egypt had conquered almost all of Turkey besides the city of Istanbul where severe winter weather forced him to make camp at Konya long enough for the Sublime Porte to conclude an alliance with Russia, and for Russian forces to arrive in Anatolia, blocking his route to the capital. The arrival of a European power would prove to be too great a challenge for Ibrahim's army to overcome. Wary of Russia’s expanding influence in the Ottoman Empire and its potential to upset the balance of power, French and British pressure forced Muhammad Ali and Ibrahim to agree to the
With no military forces between the Egyptian army and Istanbul, the Ottomans suffered a humiliating defeat by the hands of the Egyptians. Egypt had conquered almost all of Turkey besides the city of Istanbul where severe winter weather forced him to make camp at Konya long enough for the Sublime Porte to conclude an alliance with Russia, and for Russian forces to arrive in Anatolia, blocking his route to the capital. The arrival of a European power would prove to be too great a challenge for Ibrahim's army to overcome. Wary of Russia’s expanding influence in the Ottoman Empire and its potential to upset the balance of power, French and British pressure forced Muhammad Ali and Ibrahim to agree to the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
brought about by Muhammad Ali Pasha's demand to the Sublime Porte for control of Greater Syria, as reward for aiding the Sultan during the Greek War of Independence. As a result, Egyptian forces temporarily gained control of Syria, advancing as far north as Kütahya.
Background
Muhammad Ali Pasha of Egypt is recorded as planning to extend his rule to the Ottoman Empire's Syrian provinces as early as 1812, secretly telling the British consul of his designs on the territory that year.E.R. Toledano. (2012). "Muhammad Ali Pasha." ''Encyclopedia of Islam, Second Edition''. This desire was left on hold, however, as he consolidated his rule over Egypt, modernizing its government administration, public services, and armed forces, and suppressing various rebellions, includingMamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
and Wahhabi uprisings—on behalf of Sultan Mahmud II.
 In 1825, the Sultan again called on Muhammad Ali to suppress a local uprising, this time a nationalist revolution by Greek Christians. He was promised rule over Crete, Cyprus, and the Morea (the modern Peloponnese) for his services. His son, Ibrahim Pasha, won quick victories at the head of a conscript army and controlled nearly the entire Peloponnesian peninsula within 10 months of his arrival in February 1825.David Howarth. (1976). ''The Greek Adventure: Lord Byron and other eccentrics in the War of Independence''. New York: Atheneum, 1976. The Greeks continued guerrilla operations however, and by September 1827 public opinion in
In 1825, the Sultan again called on Muhammad Ali to suppress a local uprising, this time a nationalist revolution by Greek Christians. He was promised rule over Crete, Cyprus, and the Morea (the modern Peloponnese) for his services. His son, Ibrahim Pasha, won quick victories at the head of a conscript army and controlled nearly the entire Peloponnesian peninsula within 10 months of his arrival in February 1825.David Howarth. (1976). ''The Greek Adventure: Lord Byron and other eccentrics in the War of Independence''. New York: Atheneum, 1976. The Greeks continued guerrilla operations however, and by September 1827 public opinion in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, Britain, and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
forced the great powers to intervene in favour of the Greeks. The joint British–Russian–French fleet destroyed Muhammad Ali's fleet that October at the Battle of Navarino, and Ibrahim’s forces were expelled from the Morea a year later following the arrival of a French expeditionary force and a settlement negotiated by the European powers.P. Kahle and P.M. Holt. (2012) “Ibrahim Pasha.” ''Encyclopedia of Islam, Second Edition''. Once Ibrahim and his forces returned from Greece, preparations to wrest control of Syria began in earnest.
Invasion of Syria
The governor of Acre, Abdullah Pasha ibn Ali was harboring fugitives of the Egyptian draft, and was said to have refused a request to contribute towards Muhammad Ali's war effort. With these insults as pretext, land and sea forces under the command of Ibrahim Pasha were sent north to besiege Acre in October 1831. The city fell to Ibrahim's army six months later in May 1832. After Acre he continued on to win control of Aleppo, Homs,Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
, Sidon, Tripoli, and Damascus;Trevor N. Dupuy. (1993). "The First Turko-Egyptian War." ''The Harper Encyclopedia of Military History''. HarperCollins Publishers, , p. 851 the armies sent by the Sultan and various local governors were unable to check Ibrahim's forces,Khaled Fahmy. ''All the Pasha's Men: Mehmed Ali, His Army and the Making of Modern Egypt''. Cairo: The American University in Cairo Press, 2002. notably at the Battle of Homs, considered to have decided the fate of Syria.
The then-ongoing Tanzimat reforms of Mahmud II had experienced significant difficulties in adopting the innovative military methods of conscription and mass drill then being implemented in European armies, but Muhammad Ali had managed to adopt both. Ibrahim's overwhelming success cannot be attributed only to modern organization however. His officers had significantly more experience than their Ottoman counterparts, having borne the brunt of fighting in the Empire's two most recent major wars against the Wahhabi and Greek rebellions, and he attracted significant local support to his cause by calling his campaign one for "liberation from the Turkish yoke." With the provinces of Greater Syria under his control, the Egyptian army continued their campaign into Anatolia in late 1832.
Battle of Konya
On 21 November 1832, the Egyptian forces occupied the city ofKonya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
in central Turkey, within striking distance of the imperial capital of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
.Lt. Col. Osama Shams El-Din. "A Military History of Modern Egypt from the Ottoman Conquest to the Ramadan War." United States Army Command and General Staff College, 2007PDF The Sultan organized a new army of 80,000 men under Reşid Mehmed Pasha, Reshid Mehmed Pasha, the Grand Vizier, in a last-ditch attempt to block Ibrahim's advance towards the capital. While Ibrahim commanded a force of 50,000 men, most of them were spread out along his supply lines from Cairo, and he had only 15,000 in Konya. Nevertheless, when the armies met on December 21, Ibrahim's forces won in a rout, capturing the Grand Vizier after he became lost in fog attempting to rally the collapsing left flank of his forces. The Egyptians suffered only 792 casualties, compared to the Ottoman army's 3,000 dead, and they captured 46 of the 100 guns with which the army had left Istanbul. The stunning victory at Konya would be the final and most impressive victory of the Egyptian campaign against the Sublime Porte, and would represent the high point of Muhammad Ali's power in the region.
Aftermath
 With no military forces between the Egyptian army and Istanbul, the Ottomans suffered a humiliating defeat by the hands of the Egyptians. Egypt had conquered almost all of Turkey besides the city of Istanbul where severe winter weather forced him to make camp at Konya long enough for the Sublime Porte to conclude an alliance with Russia, and for Russian forces to arrive in Anatolia, blocking his route to the capital. The arrival of a European power would prove to be too great a challenge for Ibrahim's army to overcome. Wary of Russia’s expanding influence in the Ottoman Empire and its potential to upset the balance of power, French and British pressure forced Muhammad Ali and Ibrahim to agree to the
With no military forces between the Egyptian army and Istanbul, the Ottomans suffered a humiliating defeat by the hands of the Egyptians. Egypt had conquered almost all of Turkey besides the city of Istanbul where severe winter weather forced him to make camp at Konya long enough for the Sublime Porte to conclude an alliance with Russia, and for Russian forces to arrive in Anatolia, blocking his route to the capital. The arrival of a European power would prove to be too great a challenge for Ibrahim's army to overcome. Wary of Russia’s expanding influence in the Ottoman Empire and its potential to upset the balance of power, French and British pressure forced Muhammad Ali and Ibrahim to agree to the Convention of Kütahya
The Convention of Kütahya, also known as the Peace Agreement of Kütahya, ended the Egyptian–Ottoman War (1831–1833)
The First Egyptian–Ottoman War or First Syrian War (1831–1833) was a military conflict between the Ottoman Empir ...
. Under the settlement, the Syrian provinces were ceded to Egypt, and Ibrahim Pasha was made the governor-general of the region.
The treaty left Muhammad Ali a nominal vassal of the Sultan. Six years later, when Muhammad Ali moved to declare ''de jure'' independence, the Sultan declared him a traitor and sent an army to confront Ibrahim Pasha, launching the Second Egyptian–Ottoman War.
See also
* Treaty of Hünkâr İskelesiReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Egyptian-Ottoman War (1831-33) Wars involving the Ottoman Empire Conflicts in 1831 Conflicts in 1832 Conflicts in 1833 Wars of Muhammad Ali of Egypt 1831 in Ottoman Syria 1832 in Ottoman Syria 1833 in Ottoman Syria 1831 in Egypt 1832 in Egypt 1833 in Egypt