Economy Of Barbados on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Since the island country's independence in 1966, the economy of Barbados has been transformed from a low-income economy dependent upon
Barbados Government website containing the text of the majority of the above tax treaties
The bilateral tax treaty negotiated with Canada in particular has been a political-football for the government of that country. The treaty was made to allow the profits for IBCs and
 About , or 37.2% of the total land area, are classified as arable. At one time, nearly all arable land was devoted to sugarcane, but the percentage devoted to ground crops for local consumption has been increasing. In 1999, 500,000 tons of sugarcane were produced, down from the annual average of 584,000 tons in 1989–91. In 2001, sugar exports amounted to US$22 million, or 8.4% of total exports. Major food crops ("
About , or 37.2% of the total land area, are classified as arable. At one time, nearly all arable land was devoted to sugarcane, but the percentage devoted to ground crops for local consumption has been increasing. In 1999, 500,000 tons of sugarcane were produced, down from the annual average of 584,000 tons in 1989–91. In 2001, sugar exports amounted to US$22 million, or 8.4% of total exports. Major food crops ("
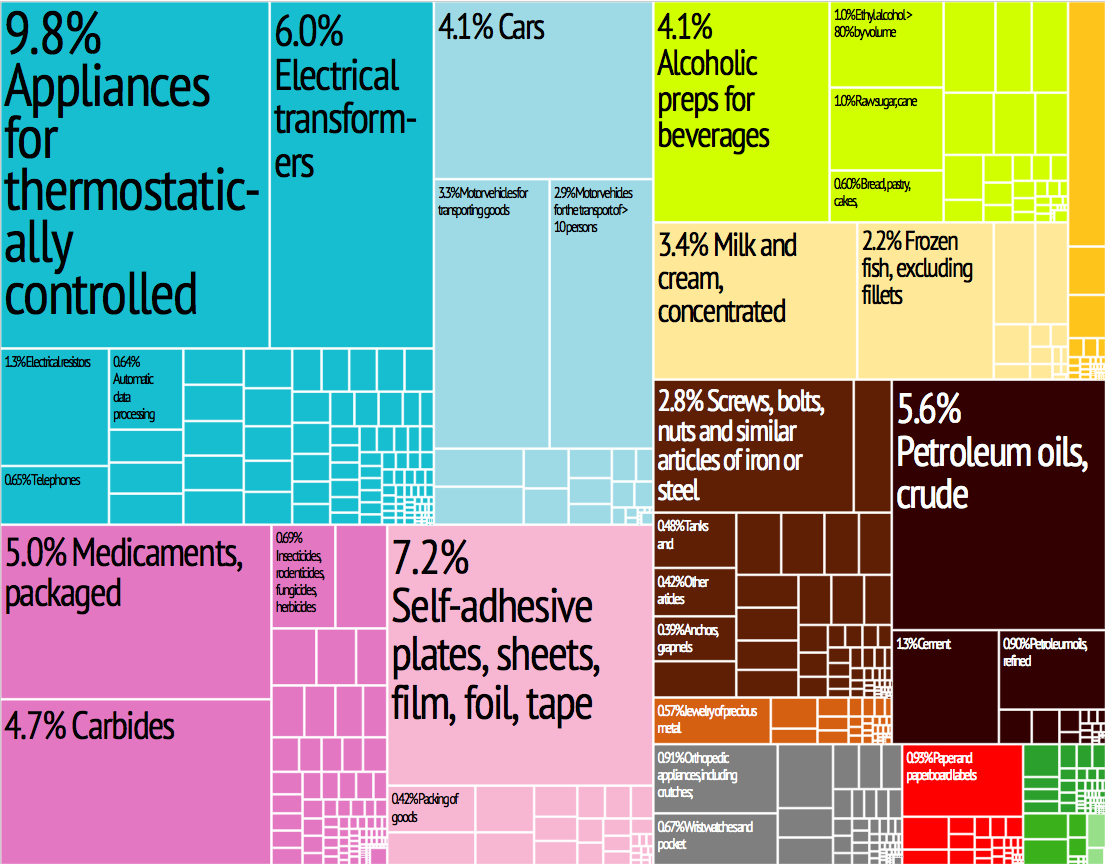 The manufacturing sector in Barbados has yet to recover from the recession of the late 1980s when many bankruptcies occurred and almost one-third of the workforce lost their jobs. Today, approximately 10,000 Barbadians work in manufacturing. The electronics sector in particular was badly hit when the U.S. semi-conductor company, Intel, closed its factory in 1986. Except for traditional manufacturing—such as sugar refining and rum distilling—Barbados's industrial activity is partly aimed at the local market, which produces goods such as tinned food, drinks, and cigarettes. Many industrial estates are located throughout the island. A cement factory is located in St. Lucy.
Export markets have been severely damaged by competition from cheaper Caribbean and Latin American countries. But domestic manufacturing also faces serious potential problems, as trade liberalisation means that the government can no longer protect national industries by imposing high tariffs on imported goods. Thus, Barbadian manufacturers must compete with other regional economies with lower wage costs and other overhead. The other significant industrial employer is the petroleum sector. Oil deposits are located in the southern parishes, but oil has not been produced in commercial quantities. The island's one small oil refinery closed in 1998 and moved refining to Trinidad and Tobago, where labour and other costs are cheaper.
The manufacturing sector in Barbados has yet to recover from the recession of the late 1980s when many bankruptcies occurred and almost one-third of the workforce lost their jobs. Today, approximately 10,000 Barbadians work in manufacturing. The electronics sector in particular was badly hit when the U.S. semi-conductor company, Intel, closed its factory in 1986. Except for traditional manufacturing—such as sugar refining and rum distilling—Barbados's industrial activity is partly aimed at the local market, which produces goods such as tinned food, drinks, and cigarettes. Many industrial estates are located throughout the island. A cement factory is located in St. Lucy.
Export markets have been severely damaged by competition from cheaper Caribbean and Latin American countries. But domestic manufacturing also faces serious potential problems, as trade liberalisation means that the government can no longer protect national industries by imposing high tariffs on imported goods. Thus, Barbadian manufacturers must compete with other regional economies with lower wage costs and other overhead. The other significant industrial employer is the petroleum sector. Oil deposits are located in the southern parishes, but oil has not been produced in commercial quantities. The island's one small oil refinery closed in 1998 and moved refining to Trinidad and Tobago, where labour and other costs are cheaper.
 Barbados has numerous internationally known hotels. Time-shares are available, and many smaller local hotels and private villas that dot the island have space available if booked in advance. The southern and western coasts of Barbados are popular, with the calm light-blue Caribbean Sea and their white and pinkish sandy beaches. Along the island's east coast, which faces the Atlantic Ocean, there are tumbling waves that are perfect for light
Barbados has numerous internationally known hotels. Time-shares are available, and many smaller local hotels and private villas that dot the island have space available if booked in advance. The southern and western coasts of Barbados are popular, with the calm light-blue Caribbean Sea and their white and pinkish sandy beaches. Along the island's east coast, which faces the Atlantic Ocean, there are tumbling waves that are perfect for light
 Retailing is an important economic activity, especially in Bridgetown where there are large department stores and supermarkets. In the countryside, most stores are small and family-run. Some 18,000 people work in the retail sector.
Retailing is an important economic activity, especially in Bridgetown where there are large department stores and supermarkets. In the countryside, most stores are small and family-run. Some 18,000 people work in the retail sector.
The Commonwealth of Nations – Barbados economy
Totally Barbados – Economy
* – Barbados Private Sector Trade Team * * *
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Barbados
Barbados Eligible For Dividend Tax Benefits, Says IRS
nbsp;– Tax-News.com *Standard & Poor's review on B'dos Economy �
Positive points
nbsp;– 27 July 2006
WTO reports on trade policy of Barbados
nbsp;– 18 September 2008
WTO announces role for Barbados in Task Force
nbsp;– February, 09th, 2006
A summary of the Budget
nbsp;– The B'dos Annual budget for the year 2006–2007
Value Added Tax refunds total $44.2M
(US$22.1M)
Barbados 2005 economic performance to be reviewed
Barbados
Atlas MIT.edu {{DEFAULTSORT:Economy of Barbados
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
production into a high-income economy based on tourism and the offshore sector. Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estima ...
went into a deep recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
in the 1990s after 3 years of steady decline brought on by fundamental macroeconomic
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, an ...
imbalances. After a painful re-adjustment process, the economy began to grow again in 1993. Growth rates have averaged between 3%–5% since then. The country's three main economic drivers are: tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
, the international business
International business refers to the trade of goods, services, technology, capital and/or knowledge across national borders and at a global or transnational scale.
It involves cross-border transactions of goods and services between two or mor ...
sector, and foreign direct-investment. These are supported in part by Barbados operating as a service-driven economy and an international business centre.
By the end of 2012 the Barbados economy still exhibited signs of weakness. Their main export (12.53% a value of $96.5 million) is liquor, closely followed by frozen-fish (8%) and preserved-milk (6.23%) to Nigeria (a total of 41.38% at $319 million) with nearly three-quarters of the imports (61.05% at $3 billion in natural-rubber and cocoa-beans) originating from there. Although it is often quoted that Barbados' main produce is "sugar", there are only two working sugar factories remaining in the country (in the 19th century there were 10). At the end of 2013, Barbados' economy continued to exhibit signs of weakness. In June 2018 Barbados announced the default on its bonds, after revealing that its debt amounted to $7.5 billion (the fourth highest debt in debt-to-GDP ratio
In economics, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio between a country's government debt (measured in units of currency) and its gross domestic product (GDP) (measured in units of currency per year). While it is a "ratio", it is technically measured ...
in the world).
History
Pre-independence
Since the first settlement by the British in 1625, through history the economy of Barbados was primarily dependent on agriculture. It had been recorded that minus the marshes and gully regions, during the 1630s much of the desirable land had been deforested across the entire island. In the 1640s, Barbados shifted from small-scale mixed crop farming using indentured labor to large-scale sugar production, introduced by the Jewish community that immigrated to Barbados when exiled fromDutch Brazil
Dutch Brazil ( nl, Nederlands-Brazilië), also known as New Holland ( nl, Nieuw-Holland), was a colony of the Dutch Republic in the northeastern portion of modern-day Brazil, controlled from 1630 to 1654 during Dutch colonization of the Americ ...
. Land was divided into large estate-plantations, with a labor-force that was almost entirely made up of enslaved men and women.
Sugar cane became the single best move for the Barbados economy at the time. Barbados soon had built so many windmills that the island had the second highest density of windmills per square mile in the world, after the Netherlands. For about the next 100 years Barbados remained the richest of all the European colonies in the Caribbean region due to sugar. The prosperity in the colony of Barbados remained regionally unmatched until sugar cane production caught up in geographically larger countries such as Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispa ...
and elsewhere. Despite being eclipsed by larger makers of sugar, Barbados continued to produce the crop well into the 20th century.
While the emancipation
Emancipation generally means to free a person from a previous restraint or legal disability. More broadly, it is also used for efforts to procure economic and social rights, political rights or equality, often for a specifically disenfranch ...
of African slaves in the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
in 1833,
nominally liberated the slaves, limited access to education and land kept the freed as a disenfranchised underclass. As such, emphasis began to be placed on increased labour rights as well as upward mobility and strong education to combat plantation living.
During the 1920s, politicians in Barbados started a push for more self-government. As the 1940s–1950s rolled around, Barbados moved towards developing political ties with neighbouring Caribbean islands. By 1958 the West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that ...
was proposed by the British government for Barbados and nine other Caribbean territories. The Federation was first led by the Premier of Barbados
This is a list of prime ministers of Barbados.
Premiers of Barbados (1953–1966)
Queen Elizabeth II in right of the United Kingdom (1953–66)
Prime Ministers of Barbados (1966–Present) Queen Elizabeth II in right of Barbados (1966–20 ...
, however the experiment ended by 1962. Later, Barbados tried to negotiate several other unions with other islands, yet it became likely that Barbados needed to move on. Subsequently, the island peacefully negotiated its independence with the British Government and the island became independent at midnight on November 30th, 1966.
Post-independence
After the country became independent of the United Kingdom on 30 November 1966 sugar cane still remained a chief money-maker for Barbados. The island's politicians tried to diversify the economy from just agriculture. During the 1950s–1960s visitors from both Canada and the United Kingdom started transforming tourism into a huge contributor for the Barbadian economy. The man-madeDeep Water Harbour
The Port of Bridgetown (officially the Deep Water Harbour), (UN/LOCODE: BB BGI, Port Callsign: 8PB) is a seaport in Bridgetown on the southwest coast of Barbados. Situated at the North-Western end of Carlisle Bay, the harbour handles all of th ...
port at Bridgetown
Bridgetown ( UN/LOCODE: BB BGI) is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The ...
had been completed in 1961, and thereafter the island could handle most modern oceangoing ships for shipping sugar or handling cargoes at the port facility.
As the 1970s progressed, global companies started to recognise Barbados for its highly educated population. In May 1972 Barbados formed its own Central Bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a centra ...
, breaking off from the East Caribbean Currency Authority (ECCA). By 1975 the Barbadian dollar was changed to a new fixed / constant rate of exchange rate with the US$ with the rate being changed to present day US$1 = BBD$1.98 (BBD$1.00 = ~US$0.50).
By the 1980s a growing manufacturing industry was seen as a considerable earner for the Barbados economy. With manufacturing then being led by companies such as Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 serie ...
and others, the Manufacturing industry contributed greatly to the economy during the 1980s and early 1990s.
In the early 1990s the country's economy was hit hard when real GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflo ...
declined by 5.1% per year between 1989 and 1992 partly due to the 1990 oil price spike. Barbados entered into an agreement with the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
financial assistance after a long and hard period of negotiations between the IMF, the government of Barbados, labour unions and employers. This led to a protocol on wages and prices in 1993. This helped prevent an inflationary spiral
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimize their holdings in that currency as t ...
and restored the island's international competitiveness thereby leading to a period of long-term economic growth of 2.7% between 1993 and 2000.
As one of the founding members, Barbados joined the World Trade Organization on 1 January 1995. Following the membership in the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Government of Barbados aggressively tried to make the Barbados economy fully WTO compliant. This led to collapse of much of the manufacturing industry of Barbados during the late 1990s in favour of many companies like Intel and others moving to lower cost Asian economies. During the late 1990s more companies started to become interested in Barbados' offshore sector, until it over took sugar as the new chief money maker. In 1999–2000 the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
(OECD) "blacklist" was circulated with Barbados listed in error. The negative fallout stymied new investment into Barbados' offshore sector Barbados for near two years as Barbados authorities acted swiftly successfully proving that Barbados' economy was regulated sufficiently to ward off financial criminal activity and that it was not a "tax haven" as charged, but instead a low-tax regime.
As the global recession hit in 2001, the offshore sector in Barbados slightly contracted further thereby making Tourism as the new chief money maker, after having earlier eclipsed manufacturing and sugar cane. The Government of Barbados further changed legislation to transform the Barbados economy into one which fosters investment. Leading to several new Hotel developments. The government continues to try maintaining constraint from personal involvement in the Hotel activity and instead seeks private investment into the Barbados economy for future growth.
Several large hotel projects like the Port Charles Marina project in Speightstown helped the tourism industry continue to expand in 1996–99, and more recently the new Hilton Hotel on Needhams Point, Saint Michael in 2005.
Various firms from Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for ...
in New York provide routine economic analysis of the Barbadian economy. This has included such firms as Standard & Poor's
S&P Global Ratings (previously Standard & Poor's and informally known as S&P) is an American credit rating agency (CRA) and a division of S&P Global that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks, bonds, and commodities. S&P is con ...
and Moody's
Moody's Investors Service, often referred to as Moody's, is the bond credit rating business of Moody's Corporation, representing the company's traditional line of business and its historical name. Moody's Investors Service provides internationa ...
.
Data
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green.Current
As of 2008, Barbados has a GDP (PPP) of $5.466 billion, a GDP (official exchange rate) of $3.777 billion, a GDP real growth rate of 1.5%, and a per capita PPP of $19,300. The GDP is composed of the following sectors: agriculture 6%, industry 16%, and services 78% (2000 est.). As of 2001, it had a labor force of 128,500, of which 10% were in agriculture, 15% in industry, and 75% in services (1996 est.). The unemployment rate in 2003 was 10.7%, and the inflation rate in 2007 was 5.5%. The Barbadian government had estimated revenues of $847 million (including grants) in 2000, and expenditures of $886 million. The industrial production growth rate was -3.2%. Offshore finance and informatics are important foreign exchange earners, and there is also a light manufacturing sector. The government continues its efforts to reduce the unacceptably high unemployment rate, which it met in the 1990s, encourage direct foreign investment, and privatise remainingstate-owned enterprises
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn profit for the governme ...
.
The main factors responsible for the improvement in economic activity include an expansion in the number of tourist arrivals, an increase in manufacturing, and an increase in sugar production. Recently, offshore banking and financial services also have become an important source of foreign exchange and economic growth.
Economic growth has led to net increases in employment in the tourism sector, as well as in construction and other services sub-sectors of the economy. The public service remains Barbados' largest single employer. Total labour force has increased from 126,000 in 1993 to 140,000 persons in 2000, and unemployment has dropped significantly from over 20% in the early 1990s to 9.3% at the end of 2000.
The Barbados government encourages the development in: financial services, informatics, e-commerce, tourism, educational and health services, and cultural services for the future. In 2000 based on Barbados' level of growth – (at the time) Barbados was supposed to become the world's smallest developed country by 2008. This had then been restated as being achievable by around 2025.
In May 2018 The Prime Minister Mia Mottley
Mia Amor Mottley, (born 1 October 1965) is a Barbadian politician and attorney who has served as the eighth prime minister of Barbados since 2018 and as Leader of the Barbados Labour Party (BLP) since 2008. Mottley is the first woman to hold ...
disclosed previously uncovered financial obligations of the state. The Prime Minister said that the new government inherited 15 billion Barbados dollars of debt (about 7.5 billion US dollars). Disclosure of information about the current level of debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
has led to an increase in the debt-to-GDP ratio
In economics, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio between a country's government debt (measured in units of currency) and its gross domestic product (GDP) (measured in units of currency per year). While it is a "ratio", it is technically measured ...
from 137% to 175%. This is the fourth value in the world after Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, and Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
. Mia Mottley
Mia Amor Mottley, (born 1 October 1965) is a Barbadian politician and attorney who has served as the eighth prime minister of Barbados since 2018 and as Leader of the Barbados Labour Party (BLP) since 2008. Mottley is the first woman to hold ...
announced that new government had no other choice than to ask the IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glob ...
to facilitate debt restructuring
Debt restructuring is a process that allows a private or public company or a sovereign entity facing cash flow problems and financial distress to reduce and renegotiate its delinquent debts to improve or restore liquidity so that it can continu ...
. On 5 June 2018 Barbados didn't fulfill its obligation to pay the 26th coupon on Eurobonds maturing in 2035. According to Cbonds
Cbonds is a financial market data vendor covering global bonds, equities and ETFs. Cbonds core business is to provide the financial market data via website Cbonds.Com as well as API solutions and mobile application. Since 2018 the global headqu ...
, excluding the disclosure of the true level of debt, on 7 June 2018 the country had 47 debt issues in circulation totaling 4.425 billion US dollars.
Wages
Although Barbadians have been ranked as being on the high end of wages compared to those in the Americas, prices for food, goods and services are also extremely high. The only legislated minimum wage in Barbados is for shop assistants, where wages can be no less than BBD$5.00 (~ US$2.50) per hour. In October 2009, Dr. DeLisle Worrell, who later become the replacement governor of Barbados'Central Bank of Barbados
The Central Bank of Barbados (CBB) is the national monetary authority responsible for providing advice to the Government of Barbados on banking and other financial and monetary matters. The Central Bank of Barbados, was established by Act of par ...
and was executive director of the Centre for Money and Finance at the UWI Cave Hill Campus revealed that "the average Barbadian now earns between BBD$200 and BBD$499 per week...."
In 2010 Barbados' population was tabulated at some 281,968 with 80% at working age yet less than half (106,241 or 38%) were actually registered as employed.
Of these the overall estimates of his finds showed that:
*There was a roughly 4,400 (1.6%) workers who earned less than BBD$200 (US$100) per week.
*There were 32,800 (12%) workers who earned between BBD$200 (US$100) and BBD$499 (US$249.50) a week.
*About 19,100 (7%) workers who earned from BBD$500 (US$250) to BBD$999(US$449.50),
*3,700 (1.3%) workers who earned between BBD$1000 (US$500) and BBD$1300(US$650), and
*4,100 (1.5%) who earned more than BBD$1300 (US$650) a week.
Taxation
General
In 1997 Barbados implemented a general taxation that covers most items. Known as theValue-Added Tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the en ...
("VAT") it covers almost all items at a 17.5% tax rate and an 8.75% for hotel accommodations. Exported goods and services, prescription drugs and a few other specific items are zero rated under the legislation. The VAT replaced several other taxes such as: the Consumption Tax, Surcharge, Excise Tax and an Environmental Levy. People operating under Barbados' VAT regime must be registered for VAT and from 1 December 2010, the threshold for VAT registration has been BBD$80,000 (previously BBD$60,000).
The island continues to wean off of taxes outside of the VAT system. In 2002 the Barbados government increased the level of people in Barbados who are exempt from having to pay taxes on their homes. This has steadily grown with the island heading for a possible rate of 0% taxation in all other areas.
The government has also toyed with the idea of making retirement savings as tax exempt, to encourage Barbadians to spend less on goods and to encourage Barbadians to save more income as they once used to.
Building and land owners are liable to land tax on the market value of their property at rates currently ranging from 0.1 per cent (for valuations from BBD$150,000) to 0.75 per cent (BBD$1,000,000) on all properties (revalued on a three-year basis) and there are approximately 115,000 parcels listed. Exemptions include crown land; University of the West Indies; religious and benevolent organizations (of which there are many thousands); cemeteries; etc.
Personal income tax was lowered from 20% to 17.5% in 2012 and applied on income of less than BBD$30,000 with a rate of 35% apply on income over BBD$30,000 and individuals who are both resident and domiciled in Barbados are taxed on their worldwide income. Generally, persons paying salaries or wages or other emoluments must withhold tax from remuneration paid to employees (PAYE). Every individual between the ages of 16 and 65, who is employed in Barbados must be insured under the National Insurance and Social Security Act and contributions are determined as a percentage of insurable earnings up to a maximum of $4,090 per month or $944 per week up to 13.5% (6.5% from employee and 6.5% from employer).
A new tax, called the Municipal Solid Waste Tax, was introduced and took effective in 2014.
Tax on Income, Profits and Capital Gains include: Income Tax, Corporate Tax, Withholding Tax, and Insurance Premium Tax.
Tax on Goods and Services include: Consumption Tax, Excise Taxes, Value Added Tax, Hotel & Restaurant Tax, Other Taxes on Goods and Services (includes Licenses, Motor Vehicle Tax, and Selective Taxes on Services).
Corporation tax rates charge 'Regular' companies 25% and 'Small' companies 15%. Employers must remit tax withheld from employees' emoluments to the Department of Inland Revenue by the 15th day of the next month after they deducted the tax.
Stamp duty tax is still levied on sale of shares of companies listed on the Barbados Stock Exchange; on sale of real estate, leases and shares in public companies; and on mortgages.
Bilateral treaties
Barbados has several bilateral tax treaties, mostly aimed at removing double taxation on companies that operate in the Barbados economy. Since Barbados is at times considered an expensive place to conduct business, the treaties are mainly a measure to provide some savings to international businesses that operate in Barbados. Countries that Barbados has taxation agreements with include: *Austria, *Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kal ...
,
*Canada,
*China,
* CARICOM,
*Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
,
*Finland,
*Luxembourg
*Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
,
*Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
,
*Mexico,
*Netherlands
*Norway,
*Panama,
*Seychelles,
*Spain,
*Sweden,
*Switzerland,
*the United Kingdom,
*the United States and
*Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
.
''Source:'Barbados Government website containing the text of the majority of the above tax treaties
The bilateral tax treaty negotiated with Canada in particular has been a political-football for the government of that country. The treaty was made to allow the profits for IBCs and
offshore bank
An offshore bank is a bank regulated under international banking license (often called offshore license), which usually prohibits the bank from establishing any business activities in the jurisdiction of establishment. Due to less regulation and ...
ing companies to be repatriated to Canada tax-free after paying taxes in Barbados. The aim was mainly for companies like the Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce
The Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (CIBC; french: Banque canadienne impériale de commerce) is a Canadian multinational banking and financial services corporation headquartered at CIBC Square in the Financial District of Toronto, Ontario. ...
(CIBC), Royal Bank of Canada
Royal Bank of Canada (RBC; french: Banque royale du Canada) is a Canadian multinational financial services company and the largest bank in Canada by market capitalization. The bank serves over 17 million clients and has more than 89,000 ...
(RBC), and Scotiabank
The Bank of Nova Scotia (french: link=no, Banque de Nouvelle-Écosse), operating as Scotiabank (french: link=no, Banque Scotia), is a Canadian multinational banking and financial services company headquartered in Toronto, Ontario. One of Canada ...
, which (along with Barclays of the United Kingdom), when-combined control a healthy majority of Barbados' local Commercial Banking sector. In essence the treaty makes the economy of Barbados almost an unofficial part of the Canadian economy and it was aimed at allowing Canadian companies to extract profits back to Canada more easily.
Primary industries
Agriculture
 About , or 37.2% of the total land area, are classified as arable. At one time, nearly all arable land was devoted to sugarcane, but the percentage devoted to ground crops for local consumption has been increasing. In 1999, 500,000 tons of sugarcane were produced, down from the annual average of 584,000 tons in 1989–91. In 2001, sugar exports amounted to US$22 million, or 8.4% of total exports. Major food crops ("
About , or 37.2% of the total land area, are classified as arable. At one time, nearly all arable land was devoted to sugarcane, but the percentage devoted to ground crops for local consumption has been increasing. In 1999, 500,000 tons of sugarcane were produced, down from the annual average of 584,000 tons in 1989–91. In 2001, sugar exports amounted to US$22 million, or 8.4% of total exports. Major food crops ("Ground provisions Ground provisions is the term used in West Indian nations to describe a number of traditional root vegetable staples such as yams, sweet potatoes, dasheen root (taro), eddos and cassava. They are often cooked and served as a side dish in local cui ...
") are yams, sweet potatoes, corn, eddoes, cassava, and several varieties of beans. Inadequate rainfall and lack of irrigation has prevented the development of other agricultural activity, although some vegetable farming takes place on a commercial scale. Some cotton is also grown in drier parts of the island, but until cotton can be picked by machine it is unlikely that output will rise to its former level.
Animal husbandry
Livestock rearing isn't a major occupation in Barbados, chiefly because good pasture has always been scarce & imported animal feed is expensive. The island must import large quantities of meat and dairy products. Most livestock is owned by individual households. Estimates for 1999 showed 23,000 head of cattle, 41,000 sheep, 33,000 hogs, 5,000 goats, and 4,000,000 chickens. Poultry production in 1999 included 9,000 tons of meat and 1,000 tons of hen eggs. Apart from self-sufficiency in milk and poultry, the limited agricultural sector means that Barbados imports large amounts of basic foods, including wheat and meat.Fishing
The fishing industry employs about 2,000 persons, and the fleet consists of more than 500 powered boats. The catch in 2000 was 3,100 metric tons. Flying fish, dolphin fish, tuna, turbot, kingfish, and swordfish are among the main species caught. A fisheries terminal complex opened at Oistins in 1983.Forestry
Fewer than of original forests have survived the 300 years of sugar cultivation. There are an estimated of forested land, covering about 12% of the total land area. Roundwood production in 2000 totalled 5,000 cu m (176,500 cu ft), and imports amounted to 3,000 cu m (106,000 cu ft). In 2000, Barbados imported $35.3 million in wood and forest products.Mining
Deposits of limestone and coral were quarried to meet local construction needs. Production of limestone in 2000 amounted to 1.5 million tons. Clays and shale, sand and gravel, and carbonaceous deposits provided limited yields. Hydraulic cement production totalled 267,659 tons in 2000, up from 106,515 in 1996. Oil production is also undertaken in Barbados, with much of the on-shore activity taking place in Woodbourne,Saint Philip Saint Philip, São Filipe, or San Felipe may refer to:
People
* Saint Philip the Apostle
* Saint Philip the Evangelist also known as Philip the Deacon
* Saint Philip Neri
* Saint Philip Benizi de Damiani also known as Saint Philip Benitius or Fili ...
.
Secondary industries
Manufacturing
 The manufacturing sector in Barbados has yet to recover from the recession of the late 1980s when many bankruptcies occurred and almost one-third of the workforce lost their jobs. Today, approximately 10,000 Barbadians work in manufacturing. The electronics sector in particular was badly hit when the U.S. semi-conductor company, Intel, closed its factory in 1986. Except for traditional manufacturing—such as sugar refining and rum distilling—Barbados's industrial activity is partly aimed at the local market, which produces goods such as tinned food, drinks, and cigarettes. Many industrial estates are located throughout the island. A cement factory is located in St. Lucy.
Export markets have been severely damaged by competition from cheaper Caribbean and Latin American countries. But domestic manufacturing also faces serious potential problems, as trade liberalisation means that the government can no longer protect national industries by imposing high tariffs on imported goods. Thus, Barbadian manufacturers must compete with other regional economies with lower wage costs and other overhead. The other significant industrial employer is the petroleum sector. Oil deposits are located in the southern parishes, but oil has not been produced in commercial quantities. The island's one small oil refinery closed in 1998 and moved refining to Trinidad and Tobago, where labour and other costs are cheaper.
The manufacturing sector in Barbados has yet to recover from the recession of the late 1980s when many bankruptcies occurred and almost one-third of the workforce lost their jobs. Today, approximately 10,000 Barbadians work in manufacturing. The electronics sector in particular was badly hit when the U.S. semi-conductor company, Intel, closed its factory in 1986. Except for traditional manufacturing—such as sugar refining and rum distilling—Barbados's industrial activity is partly aimed at the local market, which produces goods such as tinned food, drinks, and cigarettes. Many industrial estates are located throughout the island. A cement factory is located in St. Lucy.
Export markets have been severely damaged by competition from cheaper Caribbean and Latin American countries. But domestic manufacturing also faces serious potential problems, as trade liberalisation means that the government can no longer protect national industries by imposing high tariffs on imported goods. Thus, Barbadian manufacturers must compete with other regional economies with lower wage costs and other overhead. The other significant industrial employer is the petroleum sector. Oil deposits are located in the southern parishes, but oil has not been produced in commercial quantities. The island's one small oil refinery closed in 1998 and moved refining to Trinidad and Tobago, where labour and other costs are cheaper.
Construction
A construction boom, linked to tourism and residential development, has assisted the recovery of a large cement plant in the north of the island that was closed for some years and reopened in 1997.Tertiary industries
Tourism
Tourism is Barbados's crucial economic activity and has been since the 1960s. At least 10 percent of the working population (some 13,000 people) are employed in this sector, which offers a range of tourist accommodations from luxury hotels to modest self-catering establishments. After the recession years, tourism picked up again in the mid-1990s, only to face another slowdown in 1999. This drop was in part due to increasing competition from other Caribbean countries such as the Dominican Republic, and in part to a reduction in visits from cruise ships as they shifted to non-Caribbean routes or shorter routes such as the Bahamas. Cruise ship visitors totalled 445,821 in 1999, a reduction from 517,888 in 1997, but stay-over visitors rose to 517,869 in 1999, setting a new record. Overall, the country witnessed over US$700 million in tourism receipts in 1999. A problem in Barbados is that tourist facilities are too densely concentrated on the south coast, which is highly urbanised, while the Atlantic coast—with a rugged shoreline and large waves—is not suitable for beach tourism. There are few large brand-name hotels, which makes marketing the island in the United States difficult. On the other hand, the absence of conglomerates and package tours results in more direct tourist spending among the general population. Barbados has numerous internationally known hotels. Time-shares are available, and many smaller local hotels and private villas that dot the island have space available if booked in advance. The southern and western coasts of Barbados are popular, with the calm light-blue Caribbean Sea and their white and pinkish sandy beaches. Along the island's east coast, which faces the Atlantic Ocean, there are tumbling waves that are perfect for light
Barbados has numerous internationally known hotels. Time-shares are available, and many smaller local hotels and private villas that dot the island have space available if booked in advance. The southern and western coasts of Barbados are popular, with the calm light-blue Caribbean Sea and their white and pinkish sandy beaches. Along the island's east coast, which faces the Atlantic Ocean, there are tumbling waves that are perfect for light surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitable ...
. Some areas remain risky to swimmers due to under-tow currents. The Crane beach was named one of the top 10 best beaches in the world.
Shopping
Shopping is an activity in which a customer browses the available goods or services presented by one or more retailers with the potential intent to purchase a suitable selection of them. A typology of shopper types has been developed by scho ...
districts are popular in Barbados, with ample duty-free shop
A duty-free shop (or store) is a retail outlet whose goods are exempt from the payment of certain local or national taxes and duties, on the requirement that the goods sold will be sold to travelers who will take them out of the country, w ...
ping. There is also a festive night-life in mainly tourist areas such as the Saint Lawrence Gap
Saint Lawrence Gap, Christ Church is one of the best-known neighbourhoods in the country of Barbados. Sometimes just called "the Gap", Saint Lawrence Gap is located on the southern coast of Barbados along the island's Highway 7. Found between O ...
. Other attractions include wildlife reserves (Graeme Hall Nature Sanctuary
Graeme Hall Nature Sanctuary occupies 42 per cent of the Ramsar wetland at Graeme Hall, in Christ Church, Barbados. It is owned by Peter Allard, a Canadian investor and philanthropist. In late 2011 he was named Queen's Counsel by the province o ...
), jewellery stores, scuba diving
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface air supply. The name "scuba", an acronym for " Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus", was coined by Chr ...
, helicopter rides, golf, festivals (the largest being the annual Crop Over
Crop Over is a traditional harvest festival which began in Barbados, having had its early beginnings on the sugar cane plantations during slavery.
History
The original crop-over tradition began in 1687 as a way to mark the end of the yearly harves ...
festival July/Aug), sightseeing, cave exploration ( Harrison's Cave), exotic drinks and fine clothes shopping
Shopping is an activity in which a customer browses the available goods or services presented by one or more retailers with the potential intent to purchase a suitable selection of them. A typology of shopper types has been developed by scho ...
.
Attractions, landmarks and points of interest
Tourism accounts for almost one half of the economy. Name / Parish Location:Informatics
Informatics employed almost 1,700 workers in 1999, about the same number as the sugar industry. The island has been involved in data processing since the 1980s and now specialises in operations such as database management and insurance claims processing. Costs in Barbados are higher than elsewhere in the Caribbean (although still only half of costs in the United States), but the island offers strong advantages such as a literate English-speaking workforce and location in the same time zone as the eastern United States. Despite these factors, employment has fallen in recent years, reflecting increasing mobility on the part of foreign companies, which frequently relocate to lower-cost areas.Financial services
The international business and financial services sector continues to be an important contributor to the economy of Barbados. During fiscal year 2010/2011 the sector contributed approximately BBD$186 million in corporate taxes – almost 60% of the total corporate tax intake. At the end of December 2010, there were 45 offshore banks, 242 captive insurance companies, 3,065 international business companies, and 408 international societies with restricted liability. The financial sector is also under threat of sanctions from the EU and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), both of which have expressed concerns about money laundering, tax evasion, and other financial improprieties in Caribbean offshore centres.Cruise industry
In 2006 the Central Bank governor of Barbados urged the Government to consider investing in a Barbadian cruise ship company. The government at that time did not invest in that opportunity but it is unknown if it will in futureRum
Barbados has three commercial rum distilleries:West Indies Rum Distillers Ltd
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
, Mount Gay Rum
Mount Gay Rum is produced by Mount Gay Distilleries Ltd. of Barbados, the easternmost island of the West Indies. The oldest surviving deed for the company is from 1703, making Mount Gay Rum the world's oldest commercial rum distillery. The curre ...
and Four Square
Four square is a team sport played among two teams with two players each on a square court divided into four quadrants: A, B, C, and D (usually numbers 3, 4, 2, and 1, respectively, depending on the court.) The square that a player gets to bef ...
. Mount Gay Eclipse Silver is one of the most recent Rums created back in 2008. There is also St. Nicholas Abbey, a smaller boutique operation.
Retail
 Retailing is an important economic activity, especially in Bridgetown where there are large department stores and supermarkets. In the countryside, most stores are small and family-run. Some 18,000 people work in the retail sector.
Retailing is an important economic activity, especially in Bridgetown where there are large department stores and supermarkets. In the countryside, most stores are small and family-run. Some 18,000 people work in the retail sector.
See also
*Barbadian dollar
The dollar has been the currency of Barbados since 1935. Globally its currency has the ISO 4217 code ''BBD'', however, unofficially in Barbados the International vehicle registration code code BDS is also commonly used, a currency code that is o ...
* Barbados Stock Exchange
The Barbados Stock Exchange or BSE is Barbados' main stock exchange. Its headquarters are in the capital-city Bridgetown. The body was established in 1987 by the Parliament of Barbados as the Securities Exchange of Barbados (SEB), and remained ...
* Central Bank of Barbados
The Central Bank of Barbados (CBB) is the national monetary authority responsible for providing advice to the Government of Barbados on banking and other financial and monetary matters. The Central Bank of Barbados, was established by Act of par ...
* Central banks and currencies of the Caribbean This is a list of the central banks and currencies of the Caribbean.
There are a number of currencies serving multiple territories; the most widespread are the East Caribbean dollar (8 countries and territories), the United States dollar (5) and ...
* Economy of the Caribbean
* Telecommunications in Barbados
Communications in Barbados refers to the telephony, internet, postal, radio, and television systems of Barbados. Barbados has long been an informational and communications centre in the Caribbean region. Electricity coverage throughout Barbados ...
* List of Barbadian companies
Barbados is a sovereign island country in the Lesser Antilles, in the Caribbean. Despite being classified as an Atlantic island, Barbados is considered to be a part of the Caribbean, where it is ranked as a leading tourist destination. Forty perc ...
* List of countries by credit rating
* List of Commonwealth of Nations countries by GDP
List of Commonwealth of Nations countries by GDP may refer to:
* List of Commonwealth of Nations countries by GDP (nominal), a list using the current exchange rates for national currencies
* List of Commonwealth of Nations countries by GDP (PPP)
* List of countries by future gross government debt
This is a list of countries by estimated future gross central government debt based on data released in October 2020 by the International Monetary Fund, with figures in percentage of national GDP.
Projected debt estimates
See also
* List of ...
* List of countries by leading trade partners
For most economies in the world, their leading export and import trading partner in terms of value is either the European Union or China, and to a certain degree, the United States and Russia. Other countries like Brazil, India, South Africa, So ...
* List of countries by public debt
Below is a list of countries and territories by government debt , public debt (also called government debt or sovereign debt). ''Gross'' government debt is government financial liabilities that are debt instruments. A ''debt instrument'' is a f ...
* List of countries by tax revenue as percentage of GDP
This article lists countries alphabetically, with total tax revenue as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) for the listed countries. The tax percentage for each country listed in the source has been added to the chart.
Tax as ...
* List of countries by wealth per adult
This is a list of countries of the world by wealth per adult or household, from sources such as Credit Suisse's annual ''Global Wealth Databook'' See table 3-1 for all countries, on pages 119-122, for mean and median wealth, Gini coefficient, ...
* List of Latin American and Caribbean countries by GDP growth
This is a list of estimates of the real gross domestic product growth rate (not rebased GDP) in Latin American and the Caribbean nations for the latest years recorded in the CIA World Factbook. Nations are not included if their latest growth est ...
* List of Latin American and Caribbean countries by GDP (nominal)
This is a list of Latin American and Caribbean countries by gross domestic product (nominal) in USD according to the International Monetary Fund's estimates in the October 2018 World Economic Outlook database.
Cuba is not included in the list d ...
* List of Latin American and Caribbean countries by GDP (PPP)
References
Further reading
* *The Commonwealth of Nations – Barbados economy
Totally Barbados – Economy
* – Barbados Private Sector Trade Team * * *
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Barbados
External links
*Barbados Eligible For Dividend Tax Benefits, Says IRS
nbsp;– Tax-News.com *Standard & Poor's review on B'dos Economy �
Positive points
nbsp;– 27 July 2006
WTO reports on trade policy of Barbados
nbsp;– 18 September 2008
WTO announces role for Barbados in Task Force
nbsp;– February, 09th, 2006
A summary of the Budget
nbsp;– The B'dos Annual budget for the year 2006–2007
Value Added Tax refunds total $44.2M
(US$22.1M)
Barbados 2005 economic performance to be reviewed
Barbados
Atlas MIT.edu {{DEFAULTSORT:Economy of Barbados
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estima ...