East Asian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include


 Chinese civilization existed for about 1500 years before other East Asian civilizations emerged into history, Imperial China would exert much of its cultural, economic, technological, and political muscle onto its neighbours. Succeeding Chinese dynasties exerted enormous influence across East Asia culturally, economically, politically and militarily for over two millennia. The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's history for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural influence over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.
Chinese civilization existed for about 1500 years before other East Asian civilizations emerged into history, Imperial China would exert much of its cultural, economic, technological, and political muscle onto its neighbours. Succeeding Chinese dynasties exerted enormous influence across East Asia culturally, economically, politically and militarily for over two millennia. The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's history for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural influence over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.
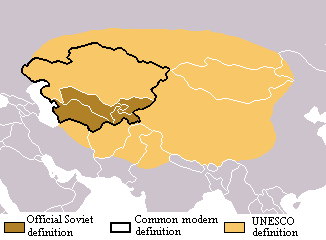 In common usage, the term "East Asia" typically refers to a region including Greater China,
In common usage, the term "East Asia" typically refers to a region including Greater China,
" ''

 The
The

* Japan switched the date to the Gregorian calendar after the Meiji Restoration.
* Not always on that Gregorian date, sometimes April 4.
File:Tokyo Station City (234809375).jpeg, Tokyo is the capital of Japan and the largest city in the world, both in metropolitan population and economy.
File:Namdaemun-ro, Seoul.jpg, Seoul is the capital of South Korea, leading global technology hub.
File:Lujiazui 2016.jpg, Shanghai is the largest city in China.
File:Parkview Green and CBD skyline (20210927131419).jpg, Beijing is the capital of the People's Republic of China.
File:Osaka Umeda Sky Building Panoramablick 05.jpg, Osaka is the second largest metropolitan area in Japan.
File:Guangzhou skyline.jpg, Guangzhou is one of the most important cities in southern China. It has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road and continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub today.
File:Nagoya Night View.jpg, Nagoya is the third largest metropolitan area in Japan. Nagoya is famous as the location of Lexus headquarters.
File:Kyoto, Japan (Unsplash UIN-pFfJ7c).jpg, Kyoto was the imperial capital of Japan for eleven centuries.
File:UB downtown.jpg, Ulaanbaatar is the capital of Mongolia with a population of 1 million as of 2008.
File:Hong Kong Night view from Victoria Peak.jpg, Hong Kong is one of the global financial centres and is known as a cosmopolitan metropolis.
File:Pyongyang City - Ryugyong Hotel in Background (13913572409).jpg, Pyongyang is the capital of North Korea, and is a metropolis on the Korean Peninsula.
File:Xian city wall 2.JPG, Xi'an or Chang'an is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China, having held the position under several of the most important dynasties. It has a significant cultural influence in East Asia.
File:Pass over Eastern Asia to Philippine Sea and Guam.ogv, Pass of the ISS over Mongolia, looking out west towards the Pacific Ocean, China, and Japan. As the video progresses, you can see major cities along the coast and the Japanese islands on the
online 3rd edition 1958
* Crofts, Alfred. ''A history of the Far East'' (1958
online free to borrow
* Dennett, Tyler. ''Americans in Eastern Asia'' (1922
online free
* Ebrey, Patricia Buckley, and Anne Walthall. ''East Asia: A cultural, social, and political history'' (Cengage Learning, 2013). * Embree, Ainslie T., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Asian history'' (1988)
vol. 1 onlinevol 2 onlinevol 3 onlinevol 4 online
* Fairbank, John K., Edwin Reischauer, and Albert M. Craig. ''East Asia: The great tradition'' and ''East Asia: The modern transformation'' (1960) online free to borrow
famous textbook. * Flynn, Matthew J. ''China Contested: Western Powers in East Asia'' (2006), for secondary schools * Gelber, Harry. ''The dragon and the foreign devils: China and the world, 1100 BC to the present'' (2011). * Green, Michael J. ''By more than providence: grand strategy and American power in the Asia Pacific since 1783'' (2017) a major scholarly surve
excerpt
* Hall, D.G.E. ''History of South East Asia'' (Macmillan International Higher Education, 1981). * Holcombe, Charles. ''A History of East Asia'' (2d ed. Cambridge UP, 2017)
excerpt
* Iriye, Akira. ''After Imperialism; The Search for a New Order in the Far East 1921–1931.'' (1965). * Jensen, Richard, Jon Davidann, and Yoneyuki Sugita, eds. ''Trans-Pacific Relations: America, Europe, and Asia in the Twentieth Century'' (Praeger, 2003), 304 p
online review
* Keay, John. ''Empire's End: A History of the Far East from High Colonialism to Hong Kong'' (Scribner, 1997)
online free to borrow
* Levinson, David, and Karen Christensen, eds. ''Encyclopedia of Modern Asia''. (6 vol. Charles Scribner's Sons, 2002). * Mackerras, Colin. ''Eastern Asia: an introductory history'' (Melbourne: Longman Cheshire, 1992). * Macnair, Harley F. & Donald Lach. ''Modern Far Eastern International Relations.'' (2nd ed 1955
1950 edition online free
780pp; focus on 1900–1950. * Miller, David Y. ''Modern East Asia: An Introductory History'' (Routledge, 2007) * Murphey, Rhoads. ''East Asia: A New History'' (1996) * Norman, Henry. ''The Peoples and Politics of the Far East: Travels and studies in the British, French, Spanish and Portuguese colonies, Siberia, China, Japan, Korea, Siam and Malaya'' (1904
online
* Paine, S. C. M. ''The Wars for Asia, 1911–1949'' (2014
excerpt
* Prescott, Anne. ''East Asia in the World: An Introduction'' (Routledge, 2015) * Ring, George C. ''Religions of the Far East: Their History to the Present Day'' (Kessinger Publishing, 2006). * Szpilman, Christopher W. A., Sven Saaler. "Japan and Asia" in ''Routledge Handbook of Modern Japanese History'' (2017
online
* Steiger, G. Nye. ''A history of the Far East'' (1936). * Vinacke, Harold M. ''A History of the Far East in Modern Times'' (1964
online free
* Vogel, Ezra. ''China and Japan: Facing History'' (2019
excerpt
* Woodcock, George. ''The British in the Far East'' (1969
online
High resolution map of East Asian region
{{Authority control Regions of Asia">East Asia"> Regions of Asia Regions of Eurasia">Regions_of_Asia.html" ;"title="East Asia"> Regions of Asia">East Asia"> Regions of Asia Regions of Eurasia Asia-Pacific Articles containing Mongolian script text Articles containing video clips
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
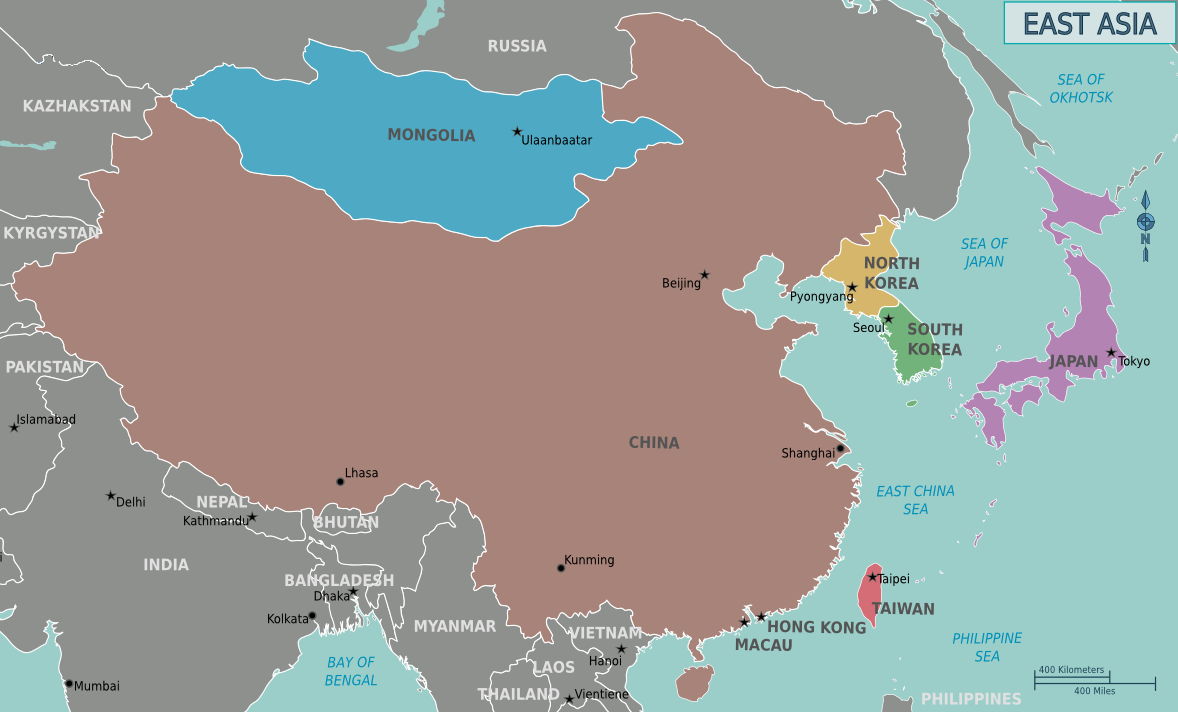
, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognised by at least one other East Asian state due to severe ongoing political tensions in the region, specifically the division of Korea and the political status of Taiwan
The controversy surrounding the political status of Taiwan or the Taiwan issue is a result of World War II, the second phase of the Chinese Civil War (1945–1949), and the Cold War.
The basic issue hinges on who the islands of Taiwan, Peng ...
. Hong Kong and Macau, two small coastal quasi-dependent territories located in the south of China, are officially highly autonomous but are under Chinese sovereignty. Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, Taiwan, South Korea, Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau are among the world's largest and most prosperous economies. East Asia borders Siberia and the Russian Far East to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean and to the southeast is Micronesia (a Pacific Ocean island group, classified as part of Oceania).
East Asia, especially Chinese civilization, is regarded as one of the earliest cradles of civilization. Other ancient civilizations in East Asia that still exist as independent countries in the present day include the Japanese, Korean and Mongolian civilizations. Various other civilizations existed as independent polities in East Asia in the past but have since been absorbed into neighbouring civilizations in the present day, such as Tibet, Baiyue, Manchuria, Ryukyu (Okinawa) and Ainu
Ainu or Aynu may refer to:
*Ainu people, an East Asian ethnic group of Japan and the Russian Far East
*Ainu languages, a family of languages
**Ainu language of Hokkaido
**Kuril Ainu language, extinct language of the Kuril Islands
**Sakhalin Ainu la ...
among many others. Taiwan has a relatively young history in the region after the prehistoric era; originally, it was a major site of Austronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, M ...
civilization prior to colonisation by European colonial powers and China from the 17th century onward. For thousands of years, China was the leading civilization in the region, exerting influence on its neighbours. Historically, societies in East Asia have fallen within the Chinese sphere of influence, and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. The Chinese calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar (also known as the Agricultural Calendar ��曆; 农历; ''Nónglì''; 'farming calendar' Former Calendar ��曆; 旧历; ''Jiùlì'' Traditional Calendar ��曆; 老历; ''Lǎolì'', is a lunisolar calendar ...
serves as the root from which many other East Asian calendars are derived. Major religions in East Asia include Buddhism (mostly Mahayana), Confucianism and Neo-Confucianism, Taoism, Ancestral worship, and Chinese folk religion in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, Shinto in Japan, and Christianity, and Musok in Korea. Tengerism and Tibetan Buddhism are prevalent among Mongols and Tibetans while other religions such as Shamanism
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world through Altered state of consciousness, altered states of consciousness, such as tranc ...
are widespread among the indigenous populations of northeastern China such as the Manchus. Major languages in East Asia include Mandarin Chinese, Japanese, and Korean. Major ethnic groups of East Asia include the Han (mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan), Yamato (Japan) and Koreans (North Korea, South Korea). Mongols, although not as populous as the previous three ethnic groups, constitute the majority of Mongolia's population. There are 76 officially-recognised minority
Minority may refer to:
Politics
* Minority government, formed when a political party does not have a majority of overall seats in parliament
* Minority leader, in American politics, the floor leader of the second largest caucus in a legislative b ...
or indigenous ethnic groups in East Asia; 55 native to mainland China (including Hui, Manchus, Chinese Mongols
Mongols in China or Mongolian Chinese () are ethnic Mongols who were integrated into the nation-building of the Republic of China (1912–1949) after the fall of Qing Empire (1636–1911). Those not integrated broke away in the Mongolian Revoluti ...
, Tibetans, Uyghurs and Zhuang in the frontier regions), 16 native to the island of Taiwan (collectively known as Taiwanese indigenous peoples), one native to the major Japanese island of Hokkaido (the Ainu
Ainu or Aynu may refer to:
*Ainu people, an East Asian ethnic group of Japan and the Russian Far East
*Ainu languages, a family of languages
**Ainu language of Hokkaido
**Kuril Ainu language, extinct language of the Kuril Islands
**Sakhalin Ainu la ...
) and four native to Mongolia ( Turkic peoples). Ryukyuan people are an unrecognised ethnic group indigenous to the Ryukyu Islands in southern Japan, which stretch from Kyushu Island
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
(Japan) to Taiwan. There are also several unrecognised indigenous ethnic groups in mainland China and Taiwan.
East Asian people comprise around billion people, making up about 38% of the population in Continental Asia and 20.5% of the global population. The region is home to major world metropolises such as Beijing, Hong Kong, Seoul, Shanghai, Taipei, and Tokyo. Although the coastal and riparian areas of the region form one of the world's most populated places, the population in Mongolia and Western China, both landlocked areas, is very sparsely distributed, with Mongolia having the lowest population density of a sovereign state. The overall population density of the region is , about three times the world average of .
History
China was the first region settled in East Asia and was undoubtedly the core of East Asian civilization from where other parts of East Asia were formed. The various other regions in East Asia were selective in the Chinese influences they adopted into their local customs. Historian Ping-ti Ho famously labeled Chinese civilization as the "Cradle of Eastern Civilization", in parallel with the " Cradle of Middle Eastern Civilization" along the Fertile Crescent encompassing Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt as well as the Cradle of Western Civilization encompassing Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome.
Warren I. Cohen Warren I. Cohen is an American historian specializing in the diplomatic history of the United States. He is Distinguished University Professor, Emeritus, at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County. Cohen formerly served as president of the Soci ...
. ''East Asia at the Center : Four Thousand Years of Engagement with the World.'' (New York: Columbia University Press, 2000. Imperial China's cultural preeminence not only led the country to become East Asia's first literate nation in the entire region, it also supplied Japan and Korea with Chinese loanwords and linguistic influences rooted in their writing systems.
Under Emperor Wu of Han
Emperor Wu of Han (156 – 29 March 87BC), formally enshrined as Emperor Wu the Filial (), born Liu Che (劉徹) and courtesy name Tong (通), was the seventh emperor of the Han dynasty of ancient China, ruling from 141 to 87 BC. His reign la ...
, the Han dynasty made China the regional power in East Asia, projecting much of its imperial power on its neighbours. Han China hosted the largest unified population in East Asia, the most literate and urbanised as well as being the most economically developed, as well as the most technologically and culturally advanced civilization in the region at the time. Cultural and religious interaction between the Chinese and other regional East Asian dynasties and kingdoms occurred. China's impact and influence on Korea began with the Han dynasty's northeastern expansion in 108 BC when the Han Chinese conquered the northern part of the Korean peninsula and established a province called Lelang. Chinese influence would soon take root in Korea through the inclusion of the Chinese writing system, monetary system, rice culture, and Confucian political institutions. Jomon society in ancient Japan incorporated wet-rice cultivation and metallurgy through its contact with Korea. Starting from the fourth century AD, Japan incorporated the Chinese writing system which evolved into Kanji by the fifth century AD and has become a significant part of the Japanese writing system. Utilizing the Chinese writing system allowed the Japanese to conduct their daily activities, maintain historical records and give form to various ideas, thoughts, and philosophies. During the Tang dynasty, China exerted its greatest influence on East Asia as various aspects of Chinese culture spread to Japan and Korea. As full-fledged medieval East Asian states were established, Korea by the fourth century AD and Japan by the seventh century AD, Japan and Korea actively began to incorporate Chinese influences such as Confucianism, the use of written Han characters, Chinese style architecture, state institutions, political philosophies
Political philosophy or political theory is the philosophical study of government, addressing questions about the nature, scope, and legitimacy of public agents and institutions and the relationships between them. Its topics include politics, l ...
, religion, urban planning, and various scientific and technological methods into their culture and society through direct contacts with Tang China and succeeding Chinese dynasties. Drawing inspiration from the Tang political system, Prince Naka no oe launched the Taika Reform in 645 AD where he radically transformed Japan's political bureaucracy into a more centralised bureaucratic empire. The Japanese also adopted Mahayana Buddhism, Chinese style architecture, and the imperial court's rituals and ceremonies, including the orchestral music and state dances had Tang influences. Written Chinese gained prestige and aspects of Tang culture such as poetry, calligraphy
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "t ...
, and landscape painting became widespread. During the Nara period, Japan began to aggressively import Chinese culture and styles of government which included Confucian protocol that served as a foundation for Japanese culture as well as political and social philosophy. The Japanese also created laws adopted from the Chinese legal system that was used to govern in addition to the kimono, which was inspired from the Chinese robe (hanfu) during the eighth century AD. For many centuries, most notably from the 7th to the 14th centuries, China stood as East Asia's most advanced civilization and foremost military and economic power exerting its influence as the transmission of advanced Chinese cultural practices and ways of thinking greatly shaped the region up until the nineteenth century.
As East Asia's connections with Europe and the Western world strengthened during the late nineteenth century, China's power began to decline. By the mid-nineteenth century, the weakening Qing dynasty became fraught with political corruption, obstacles and stagnation that was incapable of rejuvenating itself as a world power in contrast to the industrializing Imperial European colonial powers and a rapidly modernizing Japan. The U.S. Commodore Matthew C. Perry would open Japan to Western ways, and the country would expand in earnest after the 1860s. Around the same time, Japan with its rush to modernity transformed itself from an isolated feudal samurai state into East Asia's first industrialised nation in the modern era. The modern and militarily powerful Japan would galvanise its position in the Orient as East Asia's greatest power with a global mission poised to advance to lead the entire world. By the early 1900s, the Japanese empire
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
succeeded in asserting itself as East Asia's most dominant power. With its newly found international status, Japan would begin to challenge the European colonial powers and inextricably took on a more active geopolitical position in East Asia and world affairs at large. Flexing its nascent political and military might, Japan soundly defeated the stagnant Qing dynasty during the First Sino-Japanese War as well as vanquishing imperial rival Russia in 1905; the first major military victory in the modern era of an East Asian power over a European one. Its hegemony was the heart of an empire that would include Taiwan and Korea. During World War II, Japanese expansionism with its imperialist aspirations through the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere would incorporate Korea, Taiwan, much of eastern China and Manchuria, Hong Kong, and Southeast Asia under its control establishing itself as a maritime colonial power in East Asia. After a century of exploitation by the European and Japanese colonialists, post-colonial East Asia saw the defeat and occupation of Japan
Japan was occupied and administered by the victorious Allies of World War II from the 1945 surrender of the Empire of Japan at the end of the war until the
Treaty of San Francisco took effect in 1952. The occupation, led by the United States wi ...
by the victorious Allies as well as the division of China and Korea during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. The Korean peninsula became independent but then it was divided into two rival states, while Taiwan became the main territory of de facto state Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
after the latter lost Mainland China to the People's Republic of China in the Chinese Civil War. During the latter half of the twentieth century, the region would see the post war economic miracle of Japan, which ushered in three decades of unprecedented growth, only to experience an economic slowdown during the 1990s, but nonetheless Japan continues to remain a global economic power. East Asia would also see the economic rise of Hong Kong, South Korea and Taiwan, and the integration of Mainland China into the global economy through its entry in the World Trade Organization while enhancing its emerging international status as a potential world power. Although there have been no wars in East Asia for decades, the stability of the region remains fragile because of North Korea's nuclear program.
Definitions and boundaries
 In common usage, the term "East Asia" typically refers to a region including Greater China,
In common usage, the term "East Asia" typically refers to a region including Greater China, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and Korea.
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and Korea represent the three core countries and civilizations of traditional East Asia - as they once shared a common written language, culture, as well as sharing Confucian philosophical tenets and the Confucian societal value system once instituted by Imperial China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
. Other usages define Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Japan, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan as countries that constitute East Asia based on their geographic proximity as well as historical and modern cultural and economic ties, particularly with Japan and Korea having strong cultural influences that originated from China. Some scholars include Vietnam as part of East Asia as it has been considered part of the greater Chinese sphere of influence. Mongolia is geographically north of Mainland China yet Confucianism and the Chinese writing system and culture had limited impact on Mongolian society. Thus, Mongolia is sometimes grouped with Central Asian countries such as Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan. Xinjiang ( East Turkestan) and Tibet are sometimes seen as part of Central Asia.
Broader and looser definitions by international organisations such as the World Bank refer to East Asia as the "three major Northeast Asian economies, i.e. Mainland China, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and South Korea", as well as Mongolia, North Korea, the Russian Far East and Siberia. The Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank
A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, mi ...
includes the Russia Far East, Mongolia, and Nepal.Northeast Asia" ''
Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank
A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, mi ...
''. Retrieved on August 10, 2009. The World Bank also acknowledges the roles of Chinese special administrative regions Hong Kong and Macau, as well as Taiwan, a country with limited recognition. The Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia defines the region as "China, Japan, the Koreas, Nepal, Mongolia, and eastern regions of the Russian Federation".

 The
The UNSD
The United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), formerly the United Nations Statistical Office, serves under the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) as the central mechanism within the Secretariat of the United Nations t ...
definition of East Asia is based on statistical convenience, but others commonly use the same definition of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan and Japan.
Certain Japanese islands are associated with Oceania due to non-continental geology, distance from mainland Asia or biogeographical similarities with Micronesia. Some groups, such as the World Health Organization, categorize China, Japan and Korea with Australia and the rest of Oceania. The World Health Organization label this region the "Western Pacific", with East Asia not being used in their concept of major world regions. Their definition of this region further includes Mongolia and the adjacent area of Cambodia, as well as the countries of the Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago (Indonesian/Malay: , tgl, Kapuluang Malay) is the archipelago between mainland Indochina and Australia. It has also been called the " Malay world," "Nusantara", "East Indies", Indo-Australian Archipelago, Spices Archipe ...
(excluding East Timor and Indonesia).
Alternative definitions
In business and economics, "East Asia" is sometimes used to refer to the geographical area covering ten Southeast Asian countries in ASEAN, Greater China, Japan and Korea. However, in this context, the term "Far East" is used by the Europeans to cover ASEAN countries and the countries in East Asia. However, being a Eurocentric term, Far East describes the region's geographical position in relation to Europe rather than its location within Asia. Alternatively, the term " Asia Pacific Region" is often used in describing East Asia, Southeast Asia as well as Oceania. On rare occasion, the term is also sometimes taken to include India and other South Asian countries not within the bounds of the Pacific, although the termIndo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth.
In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
is more commonly used for such a definition.
Observers preferring a broader definition of "East Asia" often use the term Northeast Asia to refer to China, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan, with Southeast Asia covering the ten ASEAN countries. This usage, which is seen in economic and diplomatic discussions, is at odds with the historical meanings of both "East Asia" and "Northeast Asia". The Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank
A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, mi ...
of the United States defines Northeast Asia as Japan and Korea.
Economy
Territorial and regional data
Etymology
Demographics

Ethnic groups
* Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only.East Asian culture
Overview
The culture of East Asia has largely been influenced byChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, as it was the civilization that had the most dominant influence in the region throughout the ages that ultimately laid the foundation for East Asian civilization. The vast knowledge and ingenuity of Chinese civilization and the classics of Chinese literature and culture were seen as the foundations for a civilised life in East Asia. Imperial China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
served as a vehicle through which the adoption of Confucian ethical philosophy, Chinese calendar system, political and legal systems, architectural style, diet, terminology, institutions, religious beliefs, imperial examinations that emphasised a knowledge of Chinese classics, political philosophy and cultural value systems, as well as historically sharing a common writing system reflected in the histories of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
and Korea. The Imperial Chinese tributary system was the bedrock of network of trade and foreign relations between China and its East Asian tributaries, which helped to shape much of East Asian affairs during the ancient and medieval eras. Through the tributary system, the various dynasties of Imperial China facilitated frequent economic and cultural exchange that influenced the cultures of Japan and Korea and drew them into a Chinese international order. The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's foreign policy and trade for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural dominance over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular. The relationship between China and its cultural influence on East Asia has been compared to the historical influence of Greco-Roman civilization on Europe and the Western World.
Religions
Festivals
Collaboration
East Asian Youth Games
Formerly the East Asian Games, it is a multi-sport event organised by the East Asian Games Association (EAGA) and held every four years since2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
among athletes from East Asian countries and territories of the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), as well as the Pacific island of Guam, which is a member of the Oceania National Olympic Committees.
It is one of five Regional Games of the OCA. The others are the Central Asian Games, the Southeast Asian Games (SEA Games), the South Asian Games and the West Asian Games.
Free trade agreements
Military alliances
Major cities
Philippine Sea
The Philippine Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean east of the Philippine archipelago (hence the name), the largest in the world, occupying an estimated surface area of . The Philippine Sea Plate forms the floor of the sea. Its ...
. The island of Guam can be seen further down the pass into the Philippine Sea, and the pass ends just to the east of New Zealand. A lightning storm can be seen as light pulses near the end of the video.
File:Taipei skyline cityscape at night with full moon.jpg, alt=, With a population of 2.646 million, Taipei is the capital, financial centre of Taiwan and anchors a major high-tech industrial area in Taiwan.
See also
*China–Japan–South Korea trilateral summit
The China–Japan–South Korea trilateral summit is an annual summit meeting held between the China, People's Republic of China, Japan and South Korea, three major countries in East Asia and the World's 2nd, 3rd & 9th Largest Economies. The fi ...
* East Asia Summit
* East Asia–United States relations
East Asia–United States relations covers American relations with the region as a whole, as well as summaries of relations with China, Japan, Korea, Taiwan and smaller places. It includes diplomatic, military, economic, social and cultural ties. T ...
* East Asian Community The East Asian Community (EAC) is a proposed trade bloc for the East and Southeast Asian (ESEA) countries that may arise out of either ASEAN Plus Three or the East Asia Summit (EAS).
Economy
History
Prior to the EAS
The Association of Southe ...
* East Asian languages
* East Asian studies
* East Asian cultural sphere
Notes
References
Further reading
* Church, Peter. ''A short history of South-East Asia'' (John Wiley & Sons, 2017). * Clyde, Paul H., and Burton F. Beers. ''The Far East: A History of Western Impacts and Eastern Responses, 1830–1975'' (1975)online 3rd edition 1958
* Crofts, Alfred. ''A history of the Far East'' (1958
online free to borrow
* Dennett, Tyler. ''Americans in Eastern Asia'' (1922
online free
* Ebrey, Patricia Buckley, and Anne Walthall. ''East Asia: A cultural, social, and political history'' (Cengage Learning, 2013). * Embree, Ainslie T., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Asian history'' (1988)
vol. 1 online
* Fairbank, John K., Edwin Reischauer, and Albert M. Craig. ''East Asia: The great tradition'' and ''East Asia: The modern transformation'' (1960) online free to borrow
famous textbook. * Flynn, Matthew J. ''China Contested: Western Powers in East Asia'' (2006), for secondary schools * Gelber, Harry. ''The dragon and the foreign devils: China and the world, 1100 BC to the present'' (2011). * Green, Michael J. ''By more than providence: grand strategy and American power in the Asia Pacific since 1783'' (2017) a major scholarly surve
excerpt
* Hall, D.G.E. ''History of South East Asia'' (Macmillan International Higher Education, 1981). * Holcombe, Charles. ''A History of East Asia'' (2d ed. Cambridge UP, 2017)
excerpt
* Iriye, Akira. ''After Imperialism; The Search for a New Order in the Far East 1921–1931.'' (1965). * Jensen, Richard, Jon Davidann, and Yoneyuki Sugita, eds. ''Trans-Pacific Relations: America, Europe, and Asia in the Twentieth Century'' (Praeger, 2003), 304 p
online review
* Keay, John. ''Empire's End: A History of the Far East from High Colonialism to Hong Kong'' (Scribner, 1997)
online free to borrow
* Levinson, David, and Karen Christensen, eds. ''Encyclopedia of Modern Asia''. (6 vol. Charles Scribner's Sons, 2002). * Mackerras, Colin. ''Eastern Asia: an introductory history'' (Melbourne: Longman Cheshire, 1992). * Macnair, Harley F. & Donald Lach. ''Modern Far Eastern International Relations.'' (2nd ed 1955
1950 edition online free
780pp; focus on 1900–1950. * Miller, David Y. ''Modern East Asia: An Introductory History'' (Routledge, 2007) * Murphey, Rhoads. ''East Asia: A New History'' (1996) * Norman, Henry. ''The Peoples and Politics of the Far East: Travels and studies in the British, French, Spanish and Portuguese colonies, Siberia, China, Japan, Korea, Siam and Malaya'' (1904
online
* Paine, S. C. M. ''The Wars for Asia, 1911–1949'' (2014
excerpt
* Prescott, Anne. ''East Asia in the World: An Introduction'' (Routledge, 2015) * Ring, George C. ''Religions of the Far East: Their History to the Present Day'' (Kessinger Publishing, 2006). * Szpilman, Christopher W. A., Sven Saaler. "Japan and Asia" in ''Routledge Handbook of Modern Japanese History'' (2017
online
* Steiger, G. Nye. ''A history of the Far East'' (1936). * Vinacke, Harold M. ''A History of the Far East in Modern Times'' (1964
online free
* Vogel, Ezra. ''China and Japan: Facing History'' (2019
excerpt
* Woodcock, George. ''The British in the Far East'' (1969
online
External links
High resolution map of East Asian region
{{Authority control Regions of Asia">East Asia"> Regions of Asia Regions of Eurasia">Regions_of_Asia.html" ;"title="East Asia"> Regions of Asia">East Asia"> Regions of Asia Regions of Eurasia Asia-Pacific Articles containing Mongolian script text Articles containing video clips