EIDAS on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 eIDAS (electronic IDentification, Authentication and trust Services) is an EU regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Single Market. It was established in EU Regulation 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and repeals 1999/93/EC from 13 December 1999.
It entered into force on 17 September 2014 and applies from 1 July 2016 except for certain articles, which are listed in its Article 52. All organizations delivering public digital services in an EU member state must recognize electronic identification from all EU member states from September 29, 2018.
eIDAS (electronic IDentification, Authentication and trust Services) is an EU regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Single Market. It was established in EU Regulation 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and repeals 1999/93/EC from 13 December 1999.
It entered into force on 17 September 2014 and applies from 1 July 2016 except for certain articles, which are listed in its Article 52. All organizations delivering public digital services in an EU member state must recognize electronic identification from all EU member states from September 29, 2018.
Hur skapar du en koppling mellan svenska och utländska eID:n?
(in Swedish. Title translation: How to connect Swedish and foreign eID?)

 eIDAS (electronic IDentification, Authentication and trust Services) is an EU regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Single Market. It was established in EU Regulation 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and repeals 1999/93/EC from 13 December 1999.
It entered into force on 17 September 2014 and applies from 1 July 2016 except for certain articles, which are listed in its Article 52. All organizations delivering public digital services in an EU member state must recognize electronic identification from all EU member states from September 29, 2018.
eIDAS (electronic IDentification, Authentication and trust Services) is an EU regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Single Market. It was established in EU Regulation 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and repeals 1999/93/EC from 13 December 1999.
It entered into force on 17 September 2014 and applies from 1 July 2016 except for certain articles, which are listed in its Article 52. All organizations delivering public digital services in an EU member state must recognize electronic identification from all EU member states from September 29, 2018.
Description
eIDAS oversees electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Union's internal market. It regulateselectronic signature
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as ...
s, electronic transactions, involved bodies, and their embedding processes to provide a safe way for users to conduct business online like electronic funds transfer
Electronic funds transfer (EFT) is the electronic transfer of money from one bank account to another, either within a single financial institution or across multiple institutions, via computer-based systems, without the direct intervention of b ...
or transactions with public services
A public service is any service intended to address specific needs pertaining to the aggregate members of a community. Public services are available to people within a government jurisdiction as provided directly through public sector agencies ...
. Both the signatory and the recipient can have more convenience and security" \n\n\nsecurity.txt is a proposed standard for websites' security information that is meant to allow security researchers to easily report security vulnerabilities. The standard prescribes a text file called \"security.txt\" in the well known locat ...
. Instead of relying on traditional methods, such as mail or facsimile
A facsimile (from Latin ''fac simile'', "to make alike") is a copy or reproduction of an old book, manuscript, map, art print, or other item of historical value that is as true to the original source as possible. It differs from other forms of ...
, or appearing in person to submit paper-based documents, they may now perform transactions across borders, like "1-Click
1-Click, also called one-click or one-click buying, is the technique of allowing customers to make purchases with the payment information needed to complete the purchase having been entered by the user previously. More particularly, it allows an o ...
" technology.
eIDAS has created standards for which electronic signatures, qualified digital certificate In the context of Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 ( eIDAS), a qualified digital certificate is a public key certificate issued by a trust service provider which has government-issued qualifications. The certificate is designed to ensure the authenticity ...
s, electronic seals, timestamp
A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. Timestamps do not have to be based on some absolut ...
s, and other proof for authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicatin ...
mechanisms enable electronic transactions, with the same legal standing as transactions that are performed on paper.
The regulation came into effect in July 2015, as a means to facilitate secure and seamless electronic transactions within the European Union. Member states are required to recognise electronic signatures that meet the standards of eIDAS.
Vision
eIDAS is a result of the European Commission's focus on Europe's Digital Agenda. With the Commission's oversight, eIDAS was implemented to spur digital growth within the EU. The intent of eIDAS is to drive innovation. By adhering to the guidelines set for technology under eIDAS, organisations are pushed towards using higher levels ofinformation security
Information security, sometimes shortened to InfoSec, is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks. It is part of Risk management information systems, information risk management. It typically involves preventing or re ...
and innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed enti ...
. Additionally, eIDAS focuses on the following:
*''Interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader defi ...
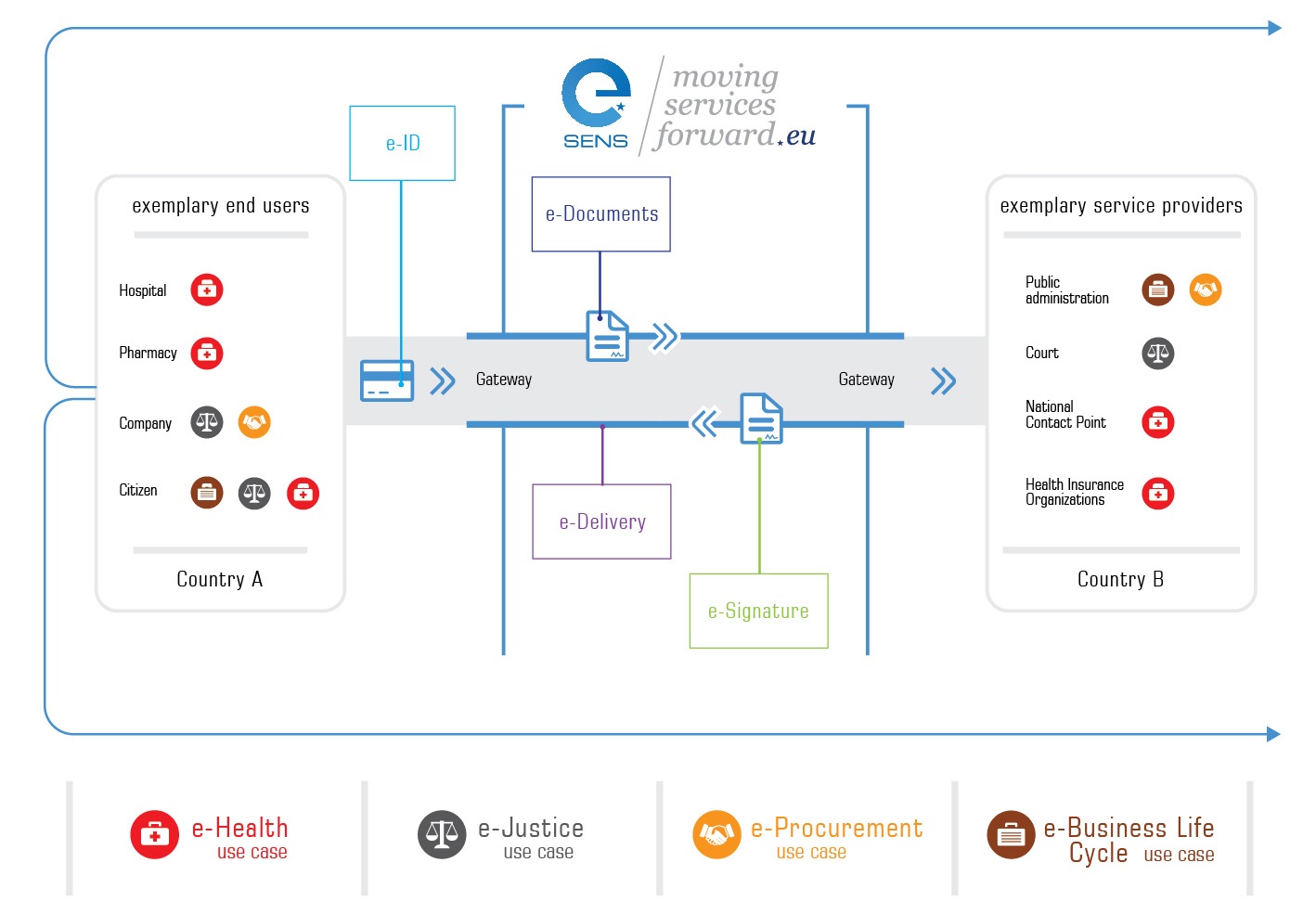
'': Member states are required to create a common framework that will recognize eIDs from other member states and ensure its authenticity and security. That makes it easy for users to conduct business across borders.
*'' Transparency'': eIDAS provides a clear and accessible list of trusted services that may be used within the centralised signing framework. That allows security stakeholders the ability to engage in dialogue about the best technologies and tools for securing digital signatures.
Regulated aspects in electronic transactions
The Regulation provides the regulatory environment for the following important aspects related to electronic transactions: *Digital identity
A digital identity is information used by computer systems to represent an external agent – a person, organization, application, or device. Digital identities allow access to services provided with computers to be automated and make it possibl ...
: a European-wide framework for digital authentication of citizens, with legal validity. Nine principles of EU digital identity have been defined: user choice, privacy, Interoperability and security, trust, convenience, user consent and control proportionality, counterpart knowledge and global scalability.
*'' Advanced electronic signature'': An electronic signature is considered advanced if it meets certain requirements:
**It provides unique identifying information that links it to its signatory.
**The signatory has sole control of the data used to create the electronic signature.
**It must be capable of identifying if the data accompanying the message has been tampered with after being signed. If the signed data has changed, the signature is marked invalid.
**There is a certificate for electronic signature, electronic proof that confirms the identity of the signatory and links the electronic signature validation data to that person.
**Advanced electronic signatures can be technically implemented, following the XAdES, PAdES, CAdES or ASiC Baseline Profile (Associated Signature Containers
Associated Signature Containers (ASiC) specifies the use of container structures to bind together one or more signed objects with either advanced electronic signatures or timestamp tokens into one single digital container.
Regulatory context
U ...
) standard for digital signatures, specified by the ETSI
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the field of information and communications. ETSI supports the development and testing of global technical standard ...
.
*''Qualified electronic signature A qualified electronic signature is an electronic signature that is compliant with EU Regulation No 910/2014 ( eIDAS Regulation) for electronic transactions within the internal European market. It enables to verify the authorship of a declaration ...
'', an advanced electronic signature that is created by a qualified electronic signature creation device based on a qualified certificate for electronic signatures.
*''Qualified digital certificate In the context of Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 ( eIDAS), a qualified digital certificate is a public key certificate issued by a trust service provider which has government-issued qualifications. The certificate is designed to ensure the authenticity ...
for electronic signature'', a certificate that attests to a qualified electronic signature's authenticity that has been issued by a qualified trust service provider.
*'' Qualified website authentication certificate'', a qualified digital certificate under the trust services defined in the eIDAS Regulation.
*''Trust service A trust service provider (TSP) is a person or legal entity providing and preserving digital certificates to create and validate electronic signatures and to authenticate their signatories as well as websites in general. Trust service providers are ...
'', an electronic service that creates, validates, and verifies electronic signatures
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as ...
, time stamps, seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
, and certificates. Also, a trust service may provide website authentication and preservation of created electronic signatures, certificates, and seals. It is handled by a trust service provider A trust service provider (TSP) is a person or legal entity providing and preserving digital certificates to create and validate electronic signatures and to authenticate their signatories as well as websites in general. Trust service providers are q ...
.
Evolution and legal implications
The eIDAS Regulation evolved from Directive 1999/93/EC, which set a goal that EU member states were expected to achieve in regards to electronic signing. Smaller European countries were among the first to start adopting digital signatures and identification, for example the first Estonian digital signature was given in 2002 and the first Latvian digital signature was given in 2006. Their experience has been used to develop a now EU-wideregulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. ...
, that became binding as law throughout the EU since the first of July, 2016. Directive 1999/93/EC made EU member states
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
responsible for creating laws that would allow them to meet the goal of creating an electronic signing system within the EU. The directive also allowed each member state to interpret the law and impose restrictions, thus preventing real interoperability, and leading toward a fragmented scenario. In contrast with the 1999 directive, eIDAS ensures mutual recognition of the eID for authentication among member states, thus achieving the goal of the Digital Single Market
On 6 May 2015, the European Commission, led at the time by Jean-Claude Juncker, communicated the Digital Single Market strategy which intends to remove virtual borders, boost digital connectivity, and make it easier for consumers to access cross ...
.
eIDAS provides a tiered approach of legal value. It requires that no electronic signature can be denied legal effect or admissibility in court solely for not being an advanced or qualified electronic signature. Qualified electronic signatures must be given the same legal effect as handwritten signatures.
For electronic seals (legal entities' version of signatures), probative value
Relevance, in the common law of evidence, is the tendency of a given item of evidence to prove or disprove one of the legal elements of the case, or to have probative value to make one of the elements of the case likelier or not. Probative is a te ...
is explicitly addressed, as seals should enjoy the presumption of integrity and the correctness of the origin of the attached data.
In June 2021, the Commission proposed an amendment and published a recommendation.
Identity number
Database information has to be linked to some kind of identity number. To certify that a person has the right to access some personal information involves several steps. *Connecting a person to a number, which can be done through methods developed in one country, such as digital certificates. *Connecting a number to specific information, done in databases. *For eIDAS it is needed to connect the number used by a country having information, to the number used by the country issuing the digital certificates. eIDAS has as minimum identity concept, the name and birth date. But in order to access more sensitive information, some kind of certification is needed that identity numbers issued by two countries refer to the same person.(in Swedish. Title translation: How to connect Swedish and foreign eID?)
Vulnerabilities
On October, 2019, two security flaws in ''eIDAS-Node'' (a sample implementation of the eID eIDAS Profile provided by the European Commission ) were discovered by security researchers; both vulnerabilities were patched for version 2.3.1 of eIDAS-Node.European Self-Sovereign Identity Framework
The European Union started creating an eIDAS compatible European Self-Sovereign Identity Framework (ESSIF).See also
* PAdES *Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; encompassing two-factor authentication, or 2FA, along with similar terms) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting ...
* Single Digital Gateway
References
External links
* {{cite web, url=https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2014.257.01.0073.01.ENG, title=REGULATION (EU) No 910/2014 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the internal market and repealing Directive 1999/93/EC - The text of the eIDAS EU regulation. Authentication methods Computer law Cryptography standards European Union regulations Information technology organizations based in Europe Signature