Eye Drops on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Eye drops or eyedrops are liquid drops applied directly to the surface of the eye usually in small amounts such as a single drop or a few drops. Eye drops usually contain saline to match the
Eye drops or eyedrops are liquid drops applied directly to the surface of the eye usually in small amounts such as a single drop or a few drops. Eye drops usually contain saline to match the
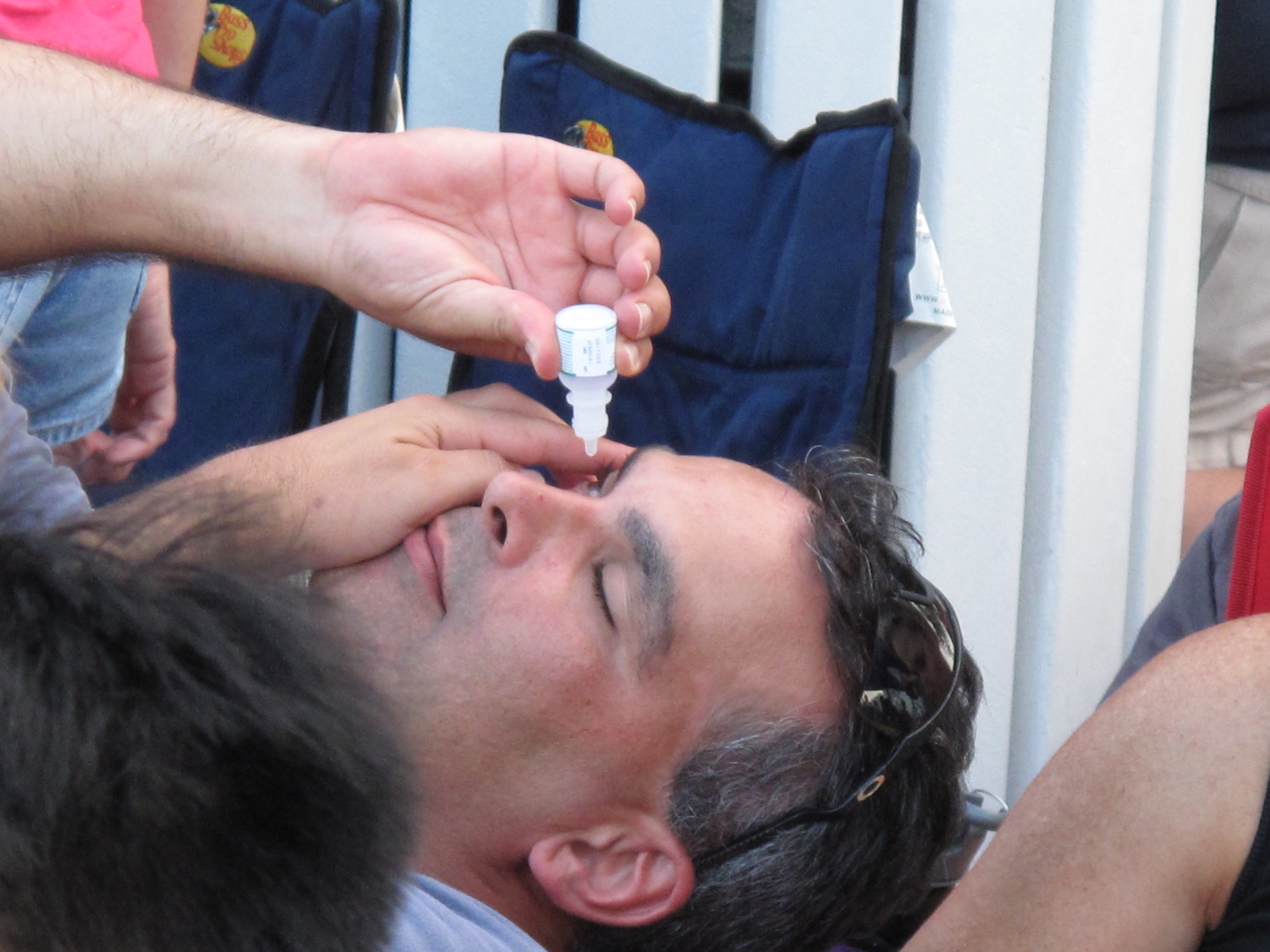 Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent
Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent

 Eye drops or eyedrops are liquid drops applied directly to the surface of the eye usually in small amounts such as a single drop or a few drops. Eye drops usually contain saline to match the
Eye drops or eyedrops are liquid drops applied directly to the surface of the eye usually in small amounts such as a single drop or a few drops. Eye drops usually contain saline to match the salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
of the eye. Drops containing only saline and sometimes a lubricant are often used as artificial tears
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of ...
to treat dry eyes
Dry eye syndrome (DES), also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), is the condition of having dry eyes. Other associated symptoms include irritation, redness, discharge, and easily fatigued eyes. Blurred vision may also occur. Symptoms rang ...
or simple eye irritation such as itching or redness. Eye drops may also contain one or more medications to treat a wide variety of eye diseases
This is a partial list of human eye diseases and disorders.
The World Health Organization publishes a classification of known diseases and injuries, the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, or ICD-10. ...
. Depending on the condition being treated, they may contain steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
, antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides re ...
s, sympathomimetic
Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. Examples of sympathomimetic effects include increases in hea ...
s, beta receptor blockers, parasympathomimetic
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because ace ...
s, parasympatholytic A parasympatholytic agent is a substance or activity that reduces the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system. (The parasympathetic nervous system is often colloquially described as the "Feed and Breed" or "Rest and Digest" portion of the a ...
s, prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
s, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s (NSAIDs), antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s, antifungals
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as crypto ...
, or topical anesthetic A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Top ...
s.
Eye drops have less of a risk of side effects than do oral medicines, and such risk can be minimized by occluding the lacrimal punctum
The lacrimal punctum (plural ''puncta'') or lacrimal point, is a minute opening on the summits of the lacrimal papillae, seen on the margins of the eyelids at the lateral extremity of the lacrimal lake. There are two lacrimal puncta in the medial ( ...
(i.e. pressing on the inner corner of the eye) for a short while after instilling drops.
Prior to the development of single-use pre-loaded sterile plastic applicators, eye drops were administered using an eye dropper
An eye dropper, also called Pasteur pipette or simply dropper, is a device used to transfer small quantities of liquids. They are used in the laboratory and also to dispense small amounts of liquid medicines. A very common use was to dispense e ...
, a glass pipette with a rubber bulb.
Shelf life
Although most bottles of eye drops contain preservatives to inhibit contamination once opened, these will not prevent contamination indefinitely. Ophthalmologists recommend keeping bottles for no longer than three months after opening. Eye drops that contain no preservatives are usually packaged in single-use tubes. Dispensers typically oversize the drops; the human eye can only handle about 25 microlitres.Types and uses
Different pharmacological classes of eye drops can be recognized by patients by their different colored tops. For instance, the tops to dilating drops are a different color than anti-allergy drops.Dry eyes
Eyes drops sometimes do not have medications in them and are only lubricating and tear-replacing solutions. There is a wide variety ofartificial tear
Artificial tears are lubricating eye drops used to relieve dryness and irritation of the ocular surface.
Dry eye syndrome (keratoconjunctivitis sicca) is a common ocular surface disorder and is characterized by disruption of the tear film and inc ...
eye drops that provide different surface healing strategies. One can find bicarbonate ions, hypotonicity
In chemical biology, tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially-permeable cell membrane. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane ...
, high viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
gels and ointments, and non-preserved types. They all act differently and therefore, one may have to try different artificial tears to find the one that works the best.
Steroid and antibiotic eye drops
Steroid and antibiotic eye drops are used to treat eyeinfections
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmiss ...
. They also have prophylactic
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
properties and are used to prevent infections after eye surgeries. They should be used for the entire time prescribed without interruptions. The infection may relapse if the use of the medication is stopped.
Pink eye
Antibiotic eye drops are prescribed when infectionconjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the conjunctiva, outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may ...
is caused by bacteria but not when it is caused by a virus. In the case of allergic conjunctivitis, artificial tears can help dilute irritating allergens present in the tear film.
Allergies
Some eye drops may containhistamine antagonists
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides re ...
or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
(NSAIDs), which suppress the optical mast cell responses to allergens including (but not limited to) aerosolized dust particles.
Glaucoma
Eye drops used in managingglaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye rem ...
help the eye's fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear ...
to drain better and decrease the amount of fluid made by the eye which decreases eye pressure. They are classified by their active ingredient and they include: prostaglandin analogs, beta blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart ...
, alpha agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, ...
. There are also combination drugs available for those patients who require more than one type of medication.
Mydriatic eye drops
These make the eye'spupil
The pupil is a black hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black ...
widen to maximum, to let an optometrist
Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive primary eye care.
In the Uni ...
have the best view inside the eyeball
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conve ...
behind the iris. Afterwards in sunny weather they can cause dazzling and photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of ...
until the effect of the mydriatic
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drugs.
Normally, as ...
has worn off.
In some countries including Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Tropicamide, a mydriatic eye drop, is used to some degree as an inexpensive recreational drug. Like other anticholinergics, when taken recreationally, tropicamide acts as a deliriant. When injected intravenously, as is most often the case, the tropicamide may cause problems such as slurred speech, unconsciousness, unresponsiveness, hallucinations, kidney pain, dysphoria, hyperthermia, tremors, suicidal tendency, convulsions, psychomotor agitation, tachycardia and headache.
Injectable medication
Syringe designed saline drops (e.g. Wallace Cameron Ultra Saline Minipod) are distributed in modernneedle-exchange programme
A needle and syringe programme (NSP), also known as needle exchange program (NEP), is a social service that allows injecting drug users (IDUs) to obtain clean and unused hypodermic needles and associated paraphernalia at little or no cost. It ...
s as they can be used efficiently either by injection or ophthalmic (if the drug is potent in small doses) route of administer which is compared to intravenous use; by demonstration, the elimination of latanoprost acid from plasma is rapid (half-life 17 minutes) after either ophthalmic or intravenous administration.
Side effects
 Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent
Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. Usually, causes of sore throat include
* viral infections
* group A streptococcal infection (GAS) bacterial infection
* pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat)
* tonsi ...
, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, easy bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
or bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clos ...
when using drops with chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, a ...
. Also, one should be aware of symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as: rash
A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cr ...
, itching
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasan ...
, swelling, dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a common medical c ...
, and trouble breathing. Long term steroid use can cause many adverse effects including steroid-induced glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye rem ...
and cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble w ...
.
Prostaglandin analogs may cause changes in iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
color and eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyel ...
skin, growth of eyelashes
An eyelash (also called lash) (Latin: ''Cilia'') is one of the hairs that grows at the edge of the eyelids. It grows in one layer on the edge of the upper and lower eyelids. Eyelashes protect the eye from debris, dust, and small particles and p ...
, stinging, blurred vision, eye redness, itching, and burning. Beta blockers' side effects include low blood pressure
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
, reduced pulse rate, fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
, shortness of breath, and in rare occasions, reduced libido
Libido (; colloquial: sex drive) is a person's overall sexual drive or desire for sexual activity. Libido is influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors. Biologically, the sex hormones and associated neurotransmitters that act up ...
and depression. Alpha agonists can cause burning or stinging, fatigue, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, drowsiness
Somnolence (alternatively sleepiness or drowsiness) is a state of strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods (compare hypersomnia). It has distinct meanings and causes. It can refer to the usual state preceding falling asleep ...
, dry mouth
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is often seen as a side eff ...
and nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes th ...
, and also they have a higher likelihood of allergic reaction. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may cause stinging, burning, and eye discomfort.
Lubricant eye drops may cause some side effects and one should consult a doctor if pain in the eye or changes in vision occur. Furthermore, when redness occurs but lasts more than 3 days, one should immediately consult a doctor.
See also
*Artificial tears
Artificial tears are lubricating eye drops used to relieve dryness and irritation of the ocular surface.
Dry eye syndrome (keratoconjunctivitis sicca) is a common ocular surface disorder and is characterized by disruption of the tear film and inc ...
* Carboxymethyl cellulose
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) or cellulose gum is a cellulose derivative with carboxymethyl groups (-CH2-COOH) bound to some of the hydroxyl groups of the glucopyranose monomers that make up the cellulose backbone. It is often used as its sodiu ...
* Mydriasis
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drugs.
Normally, as ...
* Refractive error
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the human eye, eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedne ...
* Tetrahydrozoline hydrochloride
Tetryzoline (also known as tetrahydrozoline) is a drug used in some over-the-counter eye drops and nasal sprays. Tetryzoline was patented in 1954, and came into medical use in 1959.
Side effects
Tetryzoline eye drops may cause blurred vision, ey ...
* Visine
Visine is a brand of eye drops produced by Johnson & Johnson. Johnson & Johnson acquired Visine, along with Pfizer's entire consumer healthcare portfolio, in December 2006. In some countries it is called Vispring.
Visine Original
The active i ...
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Eye Drop Dosage forms Drug delivery devices Ophthalmology drugs Ophthalmic drug administration