External intercostals on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The external intercostal muscles, or external intercostals (Intercostales externi) are eleven in number on both sides.
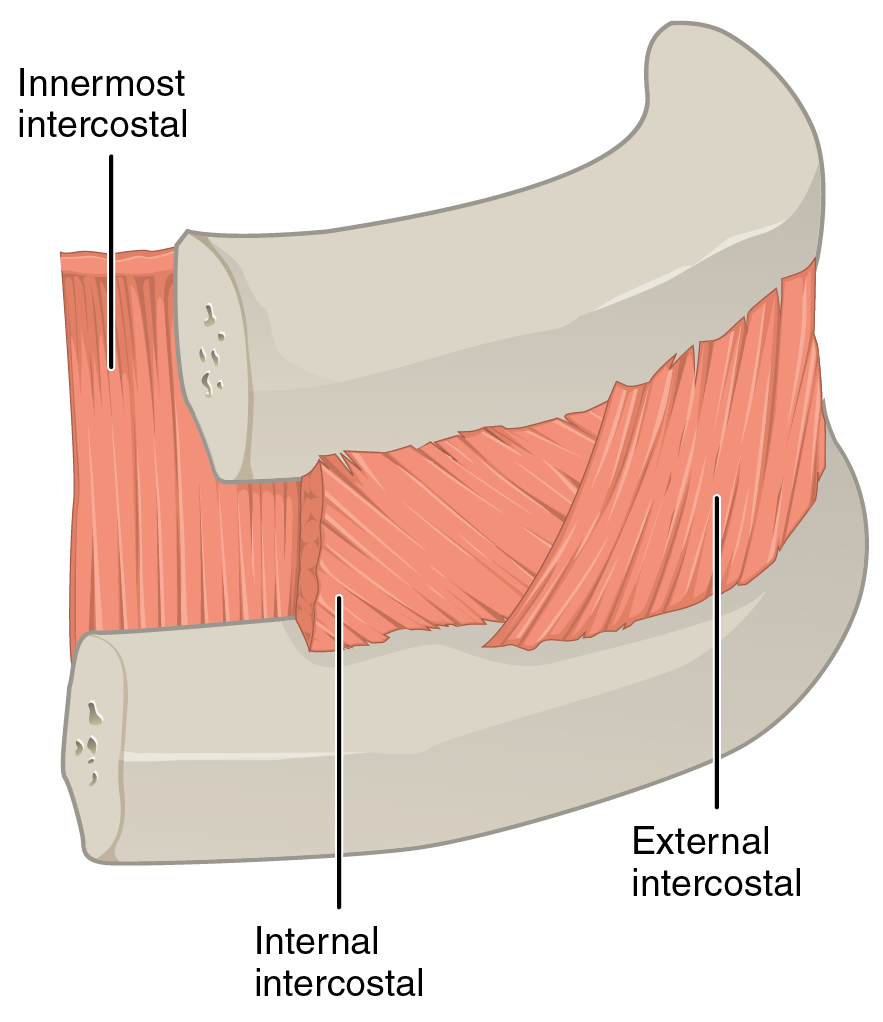 The muscles extend from the tubercles of the
The muscles extend from the tubercles of the
File:External intercostal muscles animation.gif, Position of the external intercostal muscles (shown in red). Animation.
File:Gray395.png, Deep muscles of the chest and front of the arm, with the boundaries of the
Structure
 The muscles extend from the tubercles of the
The muscles extend from the tubercles of the ribs
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi- ...
behind, to the cartilages of the ribs in front, where they end in thin membranes, the external intercostal membrane
Unlike the other two intercostal muscles, the external intercostal muscle does not retain its muscular character all the way to the sternum, and so the tissue in this location is called the external intercostal membrane.
The fibers of the external ...
s, which are continued forward to the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sh ...
.
These muscles work in unison when inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
occurs. The internal intercostal muscle
The internal intercostal muscles (intercostales interni) are a group of skeletal muscles located between the ribs. They are eleven in number on either side. They commence anteriorly at the sternum, in the intercostal spaces between the cartilages ...
s relax while the external muscles contract causing the expansion of the chest cavity and an influx of air into the lungs.
Each arises from the lower border of a rib, and is inserted into the upper border of the rib below. In the two lower spaces they extend to the ends of the cartilages, and in the upper two or three spaces they do not quite reach the ends of the ribs.
They are thicker than the internal intercostals, and their fibers are directed obliquely downward and laterally on the back of the thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the cre ...
, and downward, forward, and medially on the front.
Variations
Continuation with theexternal oblique
The abdominal external oblique muscle (also external oblique muscle, or exterior oblique) is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.
Structure
The external oblique is situated on the lateral ...
or serratus anterior
The serratus anterior is a muscle that originates on the surface of the 1st to 8th ribs at the side of the chest and inserts along the entire anterior length of the medial border of the scapula. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula fo ...
: A supracostalis muscle, from the anterior end of the first rib down to the second, third or fourth ribs occasionally occurs.
Additional images
axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superior ...
. (Intercostalis externus labeled at bottom center.)
File:Gray122.png, A central rib of the left side. Inferior aspect.
File:Gray819.png, Diagram of the course and branches of a typical intercostal nerve.
See also
*Inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
References
Muscles of the torso {{muscle-stub