Executive Branch of the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the
 The full name of the republic is "United States of America". No other name appears in the Constitution, and this is the name that appears on money, in treaties, and in legal cases to which it is a party (e.g. '' Charles T. Schenck v. United States''). The terms "Government of the United States of America" or "United States Government" are often used in official documents to represent the federal government as distinct from the states collectively. In casual conversation or writing, the term "Federal Government" is often used, and the term "National Government" is sometimes used. The terms "Federal" and "National" in government agency or program names generally indicate affiliation with the federal government (e.g.
The full name of the republic is "United States of America". No other name appears in the Constitution, and this is the name that appears on money, in treaties, and in legal cases to which it is a party (e.g. '' Charles T. Schenck v. United States''). The terms "Government of the United States of America" or "United States Government" are often used in official documents to represent the federal government as distinct from the states collectively. In casual conversation or writing, the term "Federal Government" is often used, and the term "National Government" is sometimes used. The terms "Federal" and "National" in government agency or program names generally indicate affiliation with the federal government (e.g.
 The United States Congress, under Article I of the Constitution, is the legislative branch of the federal government. It is
The United States Congress, under Article I of the Constitution, is the legislative branch of the federal government. It is
 The House currently consists of 435 voting members, each of whom represents a congressional district. The number of representatives each state has in the House is based on each state's population as determined in the most recent United States Census. All 435 representatives serve a two-year term. Each state receives a minimum of one representative in the House. In order to be elected as a representative, an individual must be at least 25 years of age, must have been a U.S. citizen for at least seven years, and must live in the state that they represent. There is no limit on the number of terms a representative may serve. In addition to the 435 voting members, there are 6 non-voting members, consisting of 5 delegates and one resident commissioner. There is one delegate each from the District of Columbia, Guam, the Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and the resident commissioner from Puerto Rico.
The House currently consists of 435 voting members, each of whom represents a congressional district. The number of representatives each state has in the House is based on each state's population as determined in the most recent United States Census. All 435 representatives serve a two-year term. Each state receives a minimum of one representative in the House. In order to be elected as a representative, an individual must be at least 25 years of age, must have been a U.S. citizen for at least seven years, and must live in the state that they represent. There is no limit on the number of terms a representative may serve. In addition to the 435 voting members, there are 6 non-voting members, consisting of 5 delegates and one resident commissioner. There is one delegate each from the District of Columbia, Guam, the Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and the resident commissioner from Puerto Rico.
 The Constitution grants numerous powers to Congress. Enumerated in Article I, Section 8, these include the powers to levy and collect taxes; to coin money and regulate its value; provide for punishment for counterfeiting; establish post offices and roads, issue patents, create federal courts inferior to the
The Constitution grants numerous powers to Congress. Enumerated in Article I, Section 8, these include the powers to levy and collect taxes; to coin money and regulate its value; provide for punishment for counterfeiting; establish post offices and roads, issue patents, create federal courts inferior to the

Article II, Section 3: Common Interpretation
, National Constitution Center (2021). Many presidential actions are undertaken via executive orders, presidential proclamations, and presidential memoranda. The president is the commander-in-chief of the
 The president may be
The president may be
 The vice president is the second-highest official in rank of the federal government. The vice president's duties and powers are established in the legislative branch of the federal government under Article 1, Section 3, Clauses 4 and 5 as the
The vice president is the second-highest official in rank of the federal government. The vice president's duties and powers are established in the legislative branch of the federal government under Article 1, Section 3, Clauses 4 and 5 as the
 Article III section I of the Constitution establishes the
Article III section I of the Constitution establishes the
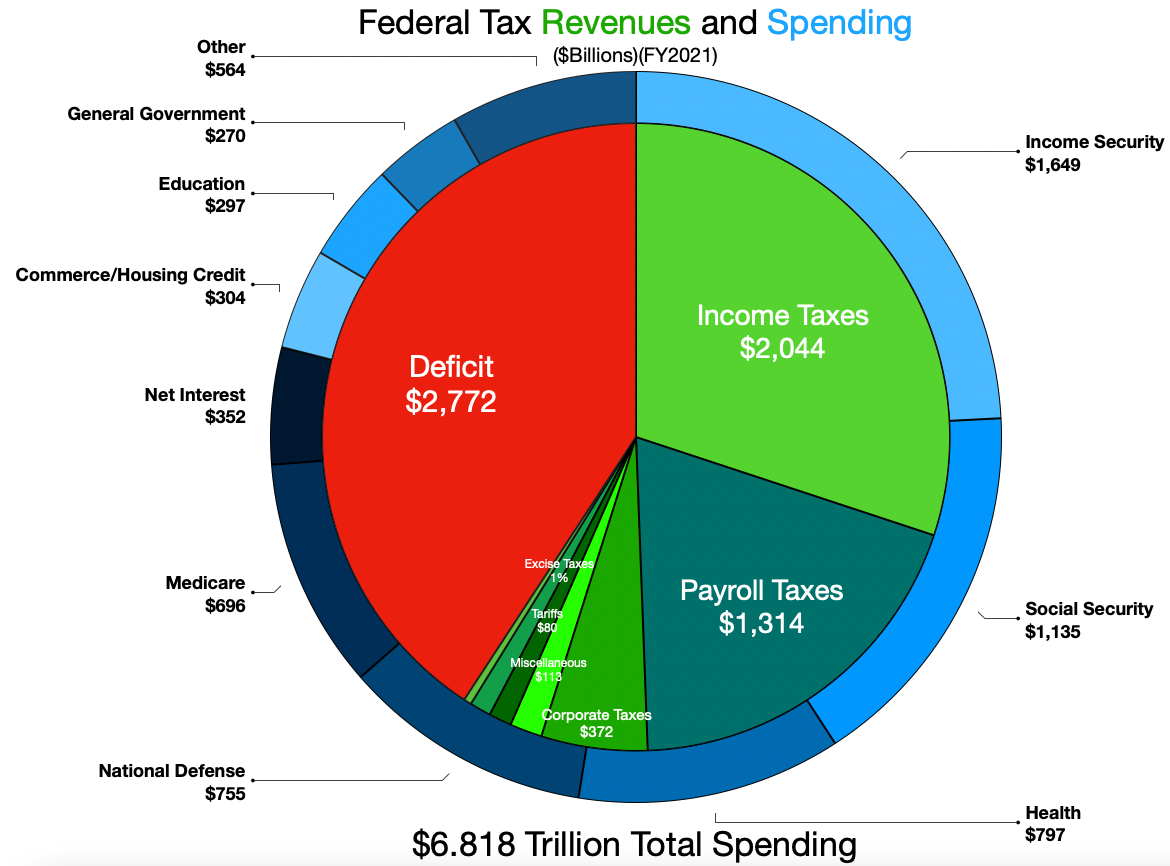
 The budget document often begins with the president's proposal to Congress recommending funding levels for the next fiscal year, beginning October 1 and ending on September 30 of the year following. The fiscal year refers to the year in which it ends.
For fiscal year (FY) 2018, the federal government spent $4.11 trillion. Spending equalled 20.3% of gross domestic product (GDP), equal to the 50-year average. The deficit equalled $779 billion, 3.8 percent of GDP. Tax revenue amounted to $3.33 trillion, with receipt categories including individual income taxes ($1,684B or 51%), Social Security/Social Insurance taxes ($1,171B or 35%), and corporate taxes ($205B or 6%).
The budget document often begins with the president's proposal to Congress recommending funding levels for the next fiscal year, beginning October 1 and ending on September 30 of the year following. The fiscal year refers to the year in which it ends.
For fiscal year (FY) 2018, the federal government spent $4.11 trillion. Spending equalled 20.3% of gross domestic product (GDP), equal to the 50-year average. The deficit equalled $779 billion, 3.8 percent of GDP. Tax revenue amounted to $3.33 trillion, with receipt categories including individual income taxes ($1,684B or 51%), Social Security/Social Insurance taxes ($1,171B or 35%), and corporate taxes ($205B or 6%).
Puerto Rico pays taxes. The US is obligated to help it just as much as Texas and Florida.
, ''Vox'' (October 4, 2017).David L. Brumbaugh
U.S. Federal Taxes in Puerto Rico
, Congressional Research Service (October 30, 2000). and do not pay most federal
 State governments have the greatest influence over most Americans' daily lives. The
State governments have the greatest influence over most Americans' daily lives. The
online
4 *
national government A national government is the government of a nation.
National government or
National Government may also refer to:
* Central government in a unitary state, or a country that does not give significant power to regional divisions
* Federal governme ...
of the United States, a federal republic
A federal republic is a federation of states with a republican form of government. At its core, the literal meaning of the word republic when used to reference a form of government means: "a country that is governed by elected representatives ...
located primarily in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, composed of 50 states, a city within a federal district (the city of Washington in the District of Columbia, where most of the federal government is based), five major self-governing territories and several island possessions. The federal government, sometimes simply referred to as Washington, is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the president and the federal courts
Federal court may refer to:
United States
* Federal judiciary of the United States
** United States district court, a particular federal court
Elsewhere
* Federal Court of Australia
* Federal courts of Brazil
* Federal Court (Canada)
* Federal co ...
, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of Congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
.
Naming
Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Park Service). Because the seat of government
The seat of government is (as defined by ''Brewer's Politics'') "the building, complex of buildings or the city from which a government exercises its authority".
In most countries, the nation’s capital is also seat of its government, thus that ...
is in Washington, D.C., "Washington" is commonly used as a metonym
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name' ...
for the federal government.
History
The United States government is based on the principles offederalism
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments (Province, provincial, State (sub-national), state, Canton (administrative division), can ...
and republicanism, in which power is shared between the national government and state governments. The interpretation and execution of these principles, including what powers the federal government should have and how those powers can be exercised, have been debated ever since the adoption of the Constitution. Some make a case for expansive federal powers while others argue for a more limited role for the central government in relation to individuals, the states, or other recognized entities.
Since the American Civil War, the powers of the federal government have generally expanded greatly, although there have been periods since that time of legislative branch dominance (e.g., the decades immediately following the Civil War) or when states' rights proponents have succeeded in limiting federal power through legislative action, executive prerogative or by a constitutional interpretation by the courts.
One of the theoretical pillars of the U.S. Constitution is the idea of " checks and balances" among the powers and responsibilities of the three branches of American government: the executive, the legislative, and the judiciary. For example, while the legislative branch ( Congress) has the power to create law, the executive branch under the president can veto any legislation—an act which, in turn, can be overridden by Congress. The president nominates judges to the nation's highest judiciary authority, the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
, but those nominees must be approved by Congress. The Supreme Court, in turn, can invalidate unconstitutional laws passed by the Congress. These and other examples are examined in more detail in the text below.
Legislative branch
bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
, comprising the House of Representatives and the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
.
Makeup of Congress
House of Representatives
 The House currently consists of 435 voting members, each of whom represents a congressional district. The number of representatives each state has in the House is based on each state's population as determined in the most recent United States Census. All 435 representatives serve a two-year term. Each state receives a minimum of one representative in the House. In order to be elected as a representative, an individual must be at least 25 years of age, must have been a U.S. citizen for at least seven years, and must live in the state that they represent. There is no limit on the number of terms a representative may serve. In addition to the 435 voting members, there are 6 non-voting members, consisting of 5 delegates and one resident commissioner. There is one delegate each from the District of Columbia, Guam, the Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and the resident commissioner from Puerto Rico.
The House currently consists of 435 voting members, each of whom represents a congressional district. The number of representatives each state has in the House is based on each state's population as determined in the most recent United States Census. All 435 representatives serve a two-year term. Each state receives a minimum of one representative in the House. In order to be elected as a representative, an individual must be at least 25 years of age, must have been a U.S. citizen for at least seven years, and must live in the state that they represent. There is no limit on the number of terms a representative may serve. In addition to the 435 voting members, there are 6 non-voting members, consisting of 5 delegates and one resident commissioner. There is one delegate each from the District of Columbia, Guam, the Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and the resident commissioner from Puerto Rico.
Senate
In contrast, the Senate is made up of two senators from each state, regardless of population. There are currently 100 senators (2 from each of the 50 states), who each serve six-year terms. Approximately one-third of the Senate stands for election every two years.Different powers
The House and Senate each have particular exclusive powers. For example, the Senate must approve (give " advice and consent" to) many important presidential appointments, including cabinet officers, federal judges (including nominees to the Supreme Court), department secretaries (heads of federal executive branch departments), U.S. military and naval officers, and ambassadors to foreign countries. All legislative bills for raising revenue must originate in the House of Representatives. The approval of both chambers is required to pass all legislation, which then may only become law by being signed by the president (or, if the presidentvetoes
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto pow ...
the bill, both houses of Congress then re-pass the bill, but by a two-thirds majority of each chamber, in which case the bill becomes law without the president's signature). The powers of Congress are limited to those enumerated in the Constitution; all other powers are reserved to the states and the people. The Constitution also includes the " Necessary and Proper Clause", which grants Congress the power to "make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers". Members of the House and Senate are elected by first-past-the-post voting in every state except Louisiana and Georgia, which have runoffs, and Maine and Alaska, which use ranked-choice voting.
Impeachment of federal officers
Congress has the power to remove the president, federal judges, and other federal officers from office. The House of Representatives and Senate have separate roles in this process. The House must first vote to "impeach" the official. Then, a trial is held in the Senate to decide whether the official should be removed from office. , three presidents have been impeached by the House of Representatives:Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency as he was vice president at the time of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a Dem ...
, Bill Clinton, and Donald Trump (twice). None of the three were removed from office following trial in the Senate.
Congressional procedures
Article I, Section 2, paragraph 2 of the U.S. Constitution gives each chamber the power to "determine the rules of its proceedings". From this provision were createdcongressional committees
A congressional committee is a legislative sub-organization in the United States Congress that handles a specific duty (rather than the general duties of Congress). Committee membership enables members to develop specialized knowledge of the ...
, which do the work of drafting legislation and conducting congressional investigations into national matters. The 108th Congress
The 108th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives from January 3, 2003 to January 3, 2005, during ...
(2003–2005) had 19 standing committees in the House and 17 in the Senate, plus 4 joint permanent committees with members from both houses overseeing the Library of Congress, printing, taxation, and the economy. In addition, each house may name special, or select, committees to study specific problems. Today, much of the congressional workload is borne by the subcommittees, of which there are around 150.
Powers of Congress
 The Constitution grants numerous powers to Congress. Enumerated in Article I, Section 8, these include the powers to levy and collect taxes; to coin money and regulate its value; provide for punishment for counterfeiting; establish post offices and roads, issue patents, create federal courts inferior to the
The Constitution grants numerous powers to Congress. Enumerated in Article I, Section 8, these include the powers to levy and collect taxes; to coin money and regulate its value; provide for punishment for counterfeiting; establish post offices and roads, issue patents, create federal courts inferior to the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
, combat piracies and felonies, declare war, raise and support armies, provide and maintain a navy, make rules for the regulation of land and naval forces, provide for, arm and discipline the militia, exercise exclusive legislation in the District of Columbia, regulate interstate commerce, and to make laws necessary to properly execute powers. Over the two centuries since the United States was formed, many disputes have arisen over the limits on the powers of the federal government. These disputes have often been the subject of lawsuits that have ultimately been decided by the United States Supreme Court.
Congressional oversight
Congressional oversight is intended to prevent waste and fraud, protectcivil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties may ...
and individual rights, ensure executive compliance with the law, gather information for making laws and educating the public, and evaluate executive performance.
It applies to cabinet departments, executive agencies, regulatory commissions, and the presidency.
Congress's oversight function takes many forms:
* Committee inquiries and hearings
* Formal consultations with and reports from the president
* Senate advice and consent for presidential nominations and for treaties
* House impeachment
Impeachment is the process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In ...
proceedings and subsequent Senate trials
* House and Senate proceedings under the 25th Amendment if the president becomes disabled or if the office of the vice president falls vacant
* Informal meetings between legislators and executive officials
* Congressional membership: each state is allocated a number of seats based on its representation (or ostensible representation, in the case of D.C.) in the House of Representatives. Each state is allocated two senators regardless of its population. , the District of Columbia elects a non-voting representative to the House of Representatives along with American Samoa, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Northern Mariana Islands.
Executive branch
President
Executive powers and duties
The executive branch is established in Article Two of the United States Constitution, which vests executive power in a president of the United States. Article II, Constitution of the United States of America The president is both the head of state (performing ceremonial functions) and the head of government (the chief executive). The Constitution directs the president to " take care that the laws be faithfully executed" and requires the president to swear or affirm to "preserve, protect and defend the Constitution of the United States." Legal scholars William P. Marshall and Saikrishna B. Prakash write of the Clause: "the President may neither breach federal law nor order their subordinates to do so, for defiance cannot be considered faithful execution. The Constitution also incorporates the English bars on dispensing or suspending the law, with some supposing that the Clause itself prohibits both."William P. Marshall & Saikrishna B. PrakashArticle II, Section 3: Common Interpretation
, National Constitution Center (2021). Many presidential actions are undertaken via executive orders, presidential proclamations, and presidential memoranda. The president is the commander-in-chief of the
armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
. Under the Reception Clause, the president is empowered to "receive Ambassadors and other public Ministers"; the president has broad authority to conduct foreign relations, is generally considered to have the sole power of diplomatic recognition, and is the United States' chief diplomat, although the Congress also has an important role in legislating on foreign affairs, and can, for example, "institute a trade embargo, declare war upon a foreign government that the President had recognized, or decline to appropriate funds for an embassy in that country." The president may also negotiate and sign treaties, but ratifying treaties requires the consent of two-thirds of the Senate.
Article II's Appointments Clause provides that the president "shall nominate, and by and with the Advice and Consent of the Senate, shall appoint Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, Judges of the supreme Court, and all other Officers of the United States" while providing that "Congress may by Law vest the Appointment of such inferior Officers, as they think proper, in the President alone, in the Courts of Law, or in the Heads of Departments." These appointments delegate "by legal authority a portion of the sovereign powers of the federal government."
The Constitution grants the president the "Power to grant Reprieves and Pardons for Offences against the United States, except in Cases of Impeachment"; this clemency power includes the power to issue absolute or conditional pardons, and to issue commute sentences, to remit fines, and to issue general amnesties. The presidential clemency power extends only to federal crimes, and not to state crimes.
The president has informal powers beyond their formal powers. For example, the president has major agenda-setting powers to influence lawmaking and policymaking, and typically has a major role as the leader of their political party.
Election, succession, and term limits
The president and vice president are normally elected as running mates by the Electoral College; each state has a number of electoral votes equal to the size of its Congressional delegation (''i.e.'', its number of Representatives in the House plus its two senators). (The District of Columbia has a number of electoral votes "equal to the whole number of Senators and Representatives in Congress to which the District would be entitled if it were a State, but in no event more than the least populous State"). A President may also be seated bysuccession
Succession is the act or process of following in order or sequence.
Governance and politics
*Order of succession, in politics, the ascension to power by one ruler, official, or monarch after the death, resignation, or removal from office of ...
. As originally drafted, there was no limit to the time a President could serve, however the Twenty-second Amendment, ratified in 1951, originally limits any president to serving two four-year terms (8 years); the amendment specifically "caps the service of a president at 10 years" by providing that "if a person succeeds to the office of president without election and serves less than two years, he may run for two full terms; otherwise, a person succeeding to office of president can serve no more than a single elected term." Amendment XXII to the United States Constitution
Veto power, impeachment, and other issues
Under the Presentment Clause of Article I, a bill that passes both chambers of Congress shall be presented to the president, who may sign the bill into law or veto the bill by returning it to the chamber where it originated. If the president neither signs nor vetoes a bill "within ten Days (Sundays excepted) after it shall have been presented to him" it becomes a law without the president's signature, "unless the Congress by their Adjournment prevent its Return in which Case it shall not be a Law" (called apocket veto
A pocket veto is a legislative maneuver that allows a president or other official with veto power to exercise that power over a bill by taking no action (keeping it in their pocket), thus effectively killing the bill without affirmatively vetoing i ...
). A presidential veto may be overridden by a two-thirds vote in both houses of Congress vote to override the veto; this occurs relatively infrequently.
 The president may be
The president may be impeached
Impeachment is the process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In ...
by a majority in the House and removed from office by a two-thirds majority in the Senate for " treason, bribery
Bribery is the Offer and acceptance, offering, Gift, giving, Offer and acceptance, receiving, or Solicitation, soliciting of any item of value to influence the actions of an official, or other person, in charge of a public or legal duty. With reg ...
, or other high crimes and misdemeanors".
The president may not dissolve Congress, but has the power to adjourn Congress whenever the House and Senate cannot agree when to adjourn; no president has ever used this power. The president also has the constitutional power to, "on extraordinary Occasions, convene both Houses, or either of them"; this power has been used " to consider nominations, war, and emergency legislation." This Section invests the President with the discretion to convene Congress on "extraordinary occasions"; this special session power that has been used to call the chambers to consider urgent matters.
Vice president
president of the Senate
President of the Senate is a title often given to the presiding officer of a senate. It corresponds to the speaker in some other assemblies.
The senate president often ranks high in a jurisdiction's succession for its top executive office: for e ...
; this means that they are the designated presiding officer of the Senate. In that capacity, the vice president has the authority (''ex officio
An ''ex officio'' member is a member of a body (notably a board, committee, council) who is part of it by virtue of holding another office. The term '' ex officio'' is Latin, meaning literally 'from the office', and the sense intended is 'by right ...
'', for they are not an elected member of the Senate) to cast a tie-breaking vote. Pursuant to the Twelfth Amendment, the vice president presides over the joint session of Congress when it convenes to count the vote of the Electoral College. As first in the U.S. presidential line of succession, the vice president's duties and powers move to the executive branch when becoming president upon the death, resignation, or removal of the president, which has happened nine times in U.S. history. Lastly, in the case of a Twenty-fifth Amendment
The Twenty-fifth Amendment (Amendment XXV) to the United States Constitution deals with presidential succession and disability.
It clarifies that the vice president becomes president if the president dies, resigns, or is removed from office, a ...
succession event, the vice president would become acting president, assuming all of the powers and duties of president, except being designated as president. Accordingly, by circumstances, the Constitution designates the vice president as routinely in the legislative branch, or succeeding to the executive branch as president, or possibly being in both as acting president pursuant to the Twenty-fifth Amendment
The Twenty-fifth Amendment (Amendment XXV) to the United States Constitution deals with presidential succession and disability.
It clarifies that the vice president becomes president if the president dies, resigns, or is removed from office, a ...
. Because of circumstances, the overlapping nature of the duties and powers attributed to the office, the title of the office and other matters, such has generated a spirited scholarly dispute regarding attaching an exclusive branch designation to the office of vice president.
Cabinet, executive departments, and agencies
The daily enforcement and administration of federal laws is in the hands of the various federal executive departments, created by Congress to deal with specific areas of national and international affairs. The heads of the 15 departments, chosen by the president and approved with the "advice and consent" of the U.S. Senate, form a council of advisers generally known as the president's "Cabinet". Once confirmed, these "cabinet officers" serve at the pleasure of the president. In addition to departments, a number of staff organizations are grouped into the Executive Office of the President. These include the White House staff, theNational Security Council
A national security council (NSC) is usually an executive branch governmental body responsible for coordinating policy on national security issues and advising chief executives on matters related to national security. An NSC is often headed by a na ...
, the Office of Management and Budget, the Council of Economic Advisers
The Council of Economic Advisers (CEA) is a United States agency within the Executive Office of the President established in 1946, which advises the President of the United States on economic policy. The CEA provides much of the empirical resea ...
, the Council on Environmental Quality, the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative, the Office of National Drug Control Policy
The Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) is a component of the Executive Office of the President of the United States.
The Director of the ONDCP, colloquially known as the Drug Czar, heads the office. "Drug Czar" was a term first used ...
, and the Office of Science and Technology Policy
An office is a space where an organization's employees perform administrative work in order to support and realize objects and goals of the organization. The word "office" may also denote a position within an organization with specific dut ...
. The employees in these United States government agencies are called federal civil servants.
There are also independent agencies such as the United States Postal Service (USPS), the National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding th ...
(NASA), the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), the Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
(EPA), and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). In addition, there are government-owned corporations such as the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and the National Railroad Passenger Corporation.
Judicial branch
The Judiciary, under Article III of the Constitution, explains and applies the laws. This branch does this by hearing and eventually making decisions on various legal cases.Overview of the federal judiciary
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
and authorizes the United States Congress to establish inferior courts as their need shall arise. Section I also establishes a lifetime tenure for all federal judges and states that their compensation may not be diminished during their time in office. Article II section II establishes that all federal judges are to be appointed by the president and confirmed by the United States Senate.
The Judiciary Act of 1789
The Judiciary Act of 1789 (ch. 20, ) was a United States federal statute enacted on September 24, 1789, during the first session of the First United States Congress. It established the federal judiciary of the United States. Article III, Secti ...
subdivided the nation jurisdictionally into judicial districts and created federal courts for each district. The three tiered structure of this act established the basic structure of the national judiciary: the Supreme Court, 13 courts of appeals, 94 district courts, and two courts of special jurisdiction. Congress retains the power to re-organize or even abolish federal courts lower than the Supreme Court.
The U.S. Supreme Court decides " cases and controversies"—matters pertaining to the federal government, disputes between states, and interpretation of the United States Constitution, and, in general, can declare legislation or executive action made at any level of the government as unconstitutional, nullifying the law and creating precedent for future law and decisions. The United States Constitution does not specifically mention the power of judicial review (the power to declare a law unconstitutional). The power of judicial review was asserted by Chief Justice Marshall in the landmark Supreme Court Case '' Marbury v. Madison'' (1803). There have been instances in the past where such declarations have been ignored by the other two branches. Below the U.S. Supreme Court are the United States Courts of Appeals, and below them in turn are the United States District Courts, which are the general trial courts for federal law, and for certain controversies between litigants who are not deemed citizens of the same state (" diversity jurisdiction").
There are three levels of federal courts with ''general jurisdiction'', meaning that these courts handle criminal cases and civil lawsuits between individuals. Other courts, such as the bankruptcy courts and the Tax Court Tax courts are courts of limited jurisdiction that deal with tax issues.
Notable examples include:
*United States Tax Court, a United States federal court
** List of Judges of the United States Tax Court
**Uniformity and jurisdiction in U.S. feder ...
, are specialized courts handling only certain kinds of cases (" subject matter jurisdiction"). The Bankruptcy Courts are "under" the supervision of the district courts, and, as such, are not considered part of the " Article III" judiciary. Also as such, their judges do not have lifetime tenure, nor are they Constitutionally exempt from diminution of their remuneration. The Tax Court is not an Article III court (but is, instead an "Article I Court").
The district courts are the trial courts wherein cases that are considered under the Judicial Code (Title 28, United States Code) consistent with the jurisdictional precepts of " federal question jurisdiction" and "diversity jurisdiction" and " pendent jurisdiction" can be filed and decided. The district courts can also hear cases under " removal jurisdiction", wherein a case brought in State court meets the requirements for diversity jurisdiction, and one party litigant chooses to "remove" the case from state court to federal court.
The United States Courts of Appeals are appellate courts that hear appeals of cases decided by the district courts, and some direct appeals from administrative agencies, and some interlocutory appeals. The U.S. Supreme Court hears appeals from the decisions of the courts of appeals or state supreme courts, and in addition has original jurisdiction over a few cases.
The judicial power extends to cases arising under the Constitution, an Act of Congress
An Act of Congress is a statute enacted by the United States Congress. Acts may apply only to individual entities (called Public and private bills, private laws), or to the general public (Public and private bills, public laws). For a Bill (law) ...
; a U.S. treaty; cases affecting ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sov ...
s, ministers and consuls of foreign countries in the U.S.; cases and controversies to which the federal government is a party; controversies between states (or their citizens) and foreign nations (or their citizens or subjects); and bankruptcy cases (collectively "federal-question jurisdiction"). The Eleventh Amendment removed from federal jurisdiction cases in which citizens of one state were the plaintiffs and the government of another state was the defendant. It did not disturb federal jurisdiction in cases in which a state government is a plaintiff and a citizen of another state the defendant.
The power of the federal courts extends both to civil actions for damages and other redress, and to criminal cases arising under federal law. The interplay of the Supremacy Clause and Article III has resulted in a complex set of relationships between state and federal courts. Federal courts can sometimes hear cases arising under state law pursuant to diversity jurisdiction, state courts can decide certain matters involving federal law, and a handful of federal claims are primarily reserved by federal statute to the state courts (for example, those arising from the Telephone Consumer Protection Act of 1991). Both court systems thus can be said to have exclusive jurisdiction in some areas and concurrent jurisdiction
Concurrent jurisdiction exists where two or more courts from different systems simultaneously have jurisdiction over a specific case. This situation leads to forum shopping, as parties will try to have their civil or criminal case heard in the c ...
in others.
The U.S. Constitution safeguards judicial independence by providing that federal judges shall hold office "during good behavior"; in practice, this usually means they serve until they die, retire, or resign. A judge who commits an offense while in office may be impeached
Impeachment is the process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In ...
in the same way as the president or other officials of the federal government. U.S. judges are appointed by the president, subject to confirmation by the Senate. Another Constitutional provision prohibits Congress from reducing the pay of any Article III judge (Congress is able to set a lower salary for all future judges that take office after the reduction, but may not decrease the rate of pay for judges already in office).
Relationships between state and federal courts
Separate from, but not entirely independent of, this federal court system are the court systems of each state, each dealing with, in addition to federal law when not deemed preempted, a state's own laws, and having its own court rules and procedures. Although state governments and the federal government are legally ''dual sovereigns'', the Supreme Court of the United States is in many cases the appellate court from the State Supreme Courts (e.g., absent the Court countenancing the applicability of the '' doctrine of adequate and independent State grounds''). The Supreme Courts of each state are by this doctrine the final authority on the interpretation of the applicable state's laws and Constitution. Many state constitution provisions are equal in breadth to those of the U.S. Constitution, but are considered "parallel" (thus, where, for example, the right to privacy pursuant to a state constitution is broader than the federal right to privacy, and the asserted ground is explicitly held to be "independent", the question can be finally decided in a State Supreme Court—the U.S. Supreme Court will decline to take jurisdiction). A State Supreme Court, other than of its own accord, is bound ''only'' by the U.S. Supreme Court's interpretation of federal law, but is ''not'' bound by interpretation of federal law by the federal court of appeals for the federal circuit in which the state is included, or even the federal district courts located in the state, a result of the ''dual sovereigns'' concept. Conversely, a federal district court hearing a matter involving only a question of state law (usually through diversity jurisdiction) must apply the substantive law of the state in which the court sits, a result of the application of the '' Erie Doctrine''; however, at the same time, the case is heard under theFederal Rules of Civil Procedure
The Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (officially abbreviated Fed. R. Civ. P.; colloquially FRCP) govern civil procedure in United States district courts. The FRCP are promulgated by the United States Supreme Court pursuant to the Rules Enabling ...
, the Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure and the Federal Rules of Evidence instead of state procedural rules (that is, the application of the ''Erie Doctrine'' only extends to a requirement that a federal court asserting diversity jurisdiction apply ''substantive'' state law, but not ''procedural'' state law, which may be different). Together, the laws of the federal and state governments form U.S. law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of Codification (law), codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the most important is the nation's Constitution of the United States, Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the ...
.
Budget

 The budget document often begins with the president's proposal to Congress recommending funding levels for the next fiscal year, beginning October 1 and ending on September 30 of the year following. The fiscal year refers to the year in which it ends.
For fiscal year (FY) 2018, the federal government spent $4.11 trillion. Spending equalled 20.3% of gross domestic product (GDP), equal to the 50-year average. The deficit equalled $779 billion, 3.8 percent of GDP. Tax revenue amounted to $3.33 trillion, with receipt categories including individual income taxes ($1,684B or 51%), Social Security/Social Insurance taxes ($1,171B or 35%), and corporate taxes ($205B or 6%).
The budget document often begins with the president's proposal to Congress recommending funding levels for the next fiscal year, beginning October 1 and ending on September 30 of the year following. The fiscal year refers to the year in which it ends.
For fiscal year (FY) 2018, the federal government spent $4.11 trillion. Spending equalled 20.3% of gross domestic product (GDP), equal to the 50-year average. The deficit equalled $779 billion, 3.8 percent of GDP. Tax revenue amounted to $3.33 trillion, with receipt categories including individual income taxes ($1,684B or 51%), Social Security/Social Insurance taxes ($1,171B or 35%), and corporate taxes ($205B or 6%).
Elections and voting

Suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in representative democracy, public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally i ...
, known as the ability to vote, has changed significantly over time. In the early years of the United States, voting was considered a matter for state governments, and was commonly restricted to white men who owned land. Direct elections were mostly held only for the U.S. House of Representatives and state legislatures, although what specific bodies were elected by the electorate varied from state to state. Under this original system, both senators representing each state in the U.S. Senate were chosen by a majority vote of the state legislature. Since the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, members of both houses of Congress have been directly elected. Today, U.S. citizens have almost universal suffrage under equal protection of the laws from the age of 18, regardless of race, gender, or wealth. The only significant exception to this is the disenfranchisement of convicted felons, and in some states former felons as well.
Under the U.S. Constitution, the representation of U.S. territories and the federal district of District of Columbia in Congress is limited
Limited may refer to:
Arts and media
*''Limited Inc'', a 1988 book by Jacques Derrida
*Limited series (comics), a comic book series with predetermined length
Businesses
*Limited Brands, an American company - owners of Victoria's Secret, Bath & Bo ...
: while residents of the District of Columbia are subject to federal laws and federal taxes, their only congressional representative is a non-voting delegate; however, they have participated in presidential elections since March 29, 1961.
Residents of Puerto Rico other than federal employees do not pay federal personal income taxes on income that has its source in Puerto Rico,Alexia Fernández CampbellPuerto Rico pays taxes. The US is obligated to help it just as much as Texas and Florida.
, ''Vox'' (October 4, 2017).David L. Brumbaugh
U.S. Federal Taxes in Puerto Rico
, Congressional Research Service (October 30, 2000). and do not pay most federal
excise tax
file:Lincoln Beer Stamp 1871.JPG, upright=1.2, 1871 U.S. Revenue stamp for 1/6 barrel of beer. Brewers would receive the stamp sheets, cut them into individual stamps, cancel them, and paste them over the Bunghole, bung of the beer barrel so when ...
es (for example, the federal gasoline tax); however, Puerto Ricans pay all other federal taxes, including the federal payroll taxes that fund Social Security and Medicare; the FUTA tax; and business, gift
A gift or a present is an item given to someone without the expectation of payment or anything in return. An item is not a gift if that item is already owned by the one to whom it is given. Although gift-giving might involve an expectation ...
, and estate taxes. Puerto Rico is represented in the Congress by a nonvoting Resident Commissioner, a nonvoting delegate.
State, tribal, and local governments
 State governments have the greatest influence over most Americans' daily lives. The
State governments have the greatest influence over most Americans' daily lives. The Tenth Amendment
The Tenth Amendment (Amendment X) to the United States Constitution, a part of the Bill of Rights, was ratified on December 15, 1791. It expresses the principle of federalism, also known as states' rights, by stating that the federal governmen ...
prohibits the federal government from exercising any power not delegated to it by the Constitution; as a result, states handle the majority of issues most relevant to individuals within their jurisdiction. Because state governments are not authorized to print currency, they generally have to raise revenue through either taxes or bonds. As a result, state governments tend to impose severe budget cuts or raise taxes any time the economy is faltering.
Each state has its own written constitution, government and code of laws. The Constitution stipulates only that each state must have, "a Republican Government". Therefore, there are often great differences in law and procedure between individual states, concerning issues such as property, crime, health and education, amongst others. The highest elected official of each state is the Governor, with below him being the Lieutenant Governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
. Each state also has an elected state legislature
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United Sta ...
( bicameralism is a feature of every state except Nebraska), whose members represent the voters of the state. Each state maintains its own state court system. In some states, supreme and lower court justices are elected by the people; in others, they are appointed, as they are in the federal system.
As a result of the Supreme Court case ''Worcester v. Georgia
''Worcester v. Georgia'', 31 U.S. (6 Pet.) 515 (1832), was a landmark case in which the Supreme Court of the United States, United States Supreme Court Vacated judgment, vacated the conviction of Samuel Worcester and held that the Georgia criminal ...
'', American Indian tribes
In the United States, an American Indian tribe, Native American tribe, Alaska Native village, tribal nation, or similar concept is any extant or historical clan, tribe, band, nation, or other group or community of Native Americans in the Unit ...
are considered "domestic dependent nations" that operate as sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
governments subject to federal authority but, in some cases, outside of the jurisdiction of state governments. Hundreds of laws, executive orders and court cases have modified the governmental status of tribes vis-à-vis individual states, but the two have continued to be recognized as separate bodies. Tribal governments vary in robustness, from a simple council used to manage all aspects of tribal affairs, to large and complex bureaucracies with several branches of government. Tribes are currently encouraged to form their own governments, with power resting in elected tribal councils, elected tribal chairpersons, or religiously appointed leaders (as is the case with pueblos). Tribal citizenship and voting rights are typically restricted to individuals of native descent, but tribes are free to set whatever citizenship requirements they wish.
The institutions that are responsible for local government within states are typically counties, municipalities, and special-purpose districts, which make laws that affect their particular area. These laws concern issues such as traffic, the sale of alcohol and the keeping of animals. A county is an administrative or political subdivision of a state, while Louisiana and Alaska have county-equivalent subdivisions called parishes
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or m ...
and boroughs, respectively. The specific governmental powers of counties vary widely between the states, with those in Connecticut, Rhode Island, and some parts of Alaska and Massachusetts having little or no power, existing only as geographic distinctions. In other areas, county governments have more power, such as to collect taxes and maintain law enforcement agencies. Twenty states further divide their counties into civil townships. Population centers may be organized into incorporated municipalities of several types, including the city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, town, borough, and village. These municipal entities also vary from state to state, and typically subordinate to the government of a county or civil township. However, many rural and suburban regions are in unincorporated areas that have no municipal government below the county or civil township level. Certain cities have consolidated with their county government to form consolidated city-counties, or have been legally separated from counties altogether to form independent cities
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor states ...
. States may also create special-purpose districts that perform a single function or a set of related functions within an area inside one or more counties or municipalities, like school districts, water management districts, fire management districts, and library districts.
See also
President
* Executive Office * Line-item vetoCourts
* District courts *Federal courts
Federal court may refer to:
United States
* Federal judiciary of the United States
** United States district court, a particular federal court
Elsewhere
* Federal Court of Australia
* Federal courts of Brazil
* Federal Court (Canada)
* Federal co ...
* Federal judicial circuit
Law
* U.S. CodeAgencies
* Federal agenciesStates and territories
* Political divisions * U.S. territoryWorks and websites
*Business.gov
Business.gov is sponsored by the U.S. Small Business Administration to provide small business owners with access to federal, state and local government resources from a single access point.
History
Business.gov was launched in 1997 as the U.S. B ...
* Copyright status of work by the U.S. government
* USA.gov
Notes
References
Further reading
* Greenstein, Fred I. et al. ''Evolution of the modern presidency : a bibliographical survey'' (1977) bibliography and annotation of 2500 scholarly books and articlesonline
4 *
External links
* (Portal of the U.S. Federal government of the United States) {{Authority control Federalism in the United States 1789 establishments in the United States