European Badgers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The European badger (''Meles meles''), also known as the Eurasian badger, is a badger species in the family Mustelidae native to almost all of Europe. It is classified as least concern on the IUCN Red List as it has a wide range and a large stable population size, and is thought to be increasing in some regions. Several subspecies are recognized with the
 European badger skulls are quite massive, heavy and elongated. Their
European badger skulls are quite massive, heavy and elongated. Their
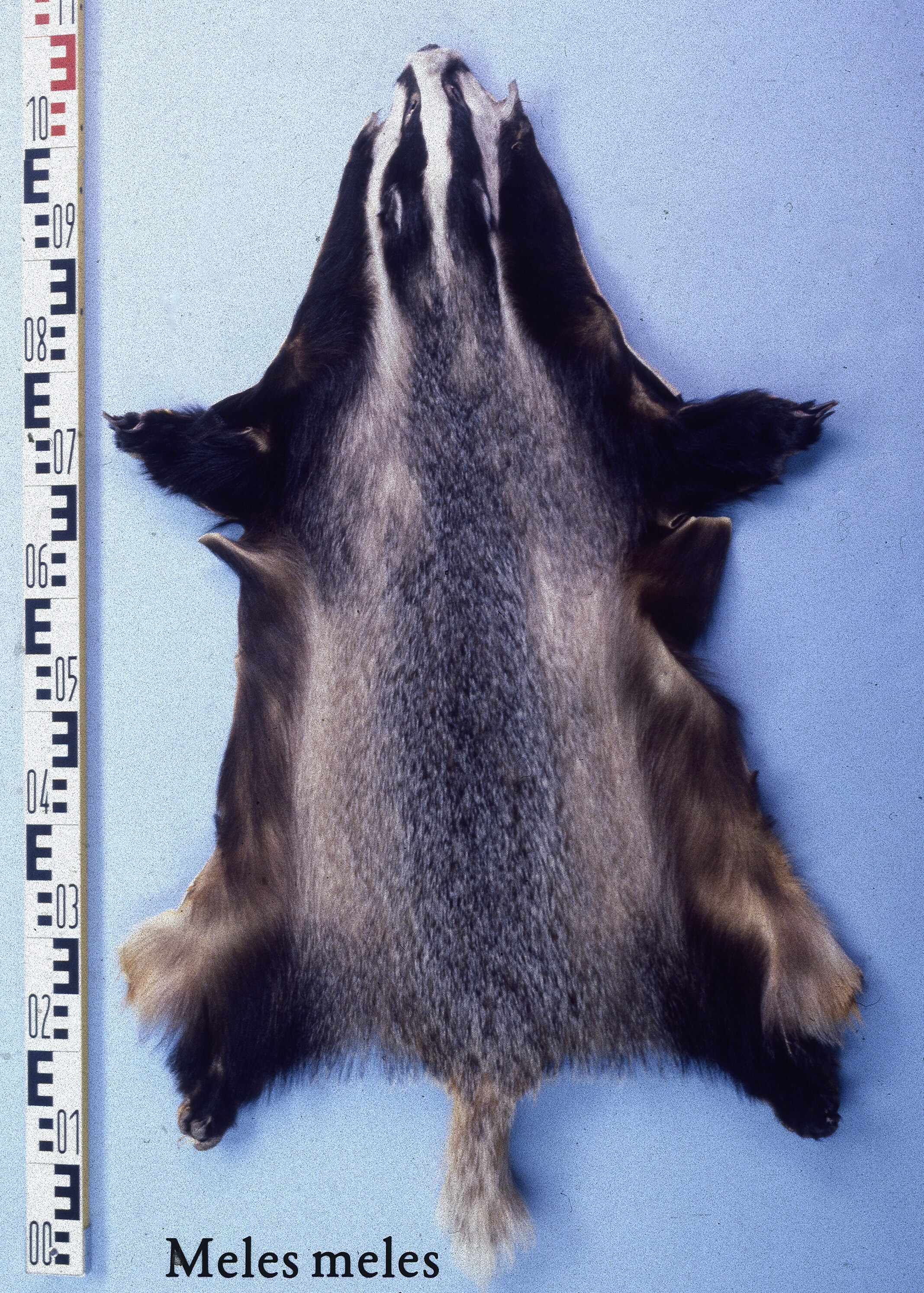
 In winter, the fur on the back and flanks is long and coarse, consisting of bristly guard hairs with a sparse, soft undercoat. The belly fur consists of short, sparse hairs, with skin being visible in the inguinal region. Guard hair length on the middle of the back is in winter. Prior to the winter, the throat, lower neck, chest and legs are black. The belly is of a lighter, brownish tint, while the inguinal region is brownish-grey. The general colour of the back and sides is light silvery-grey, with straw-coloured highlights on the sides. The tail has long and coarse hairs, and is generally the same colour as the back. Two black bands pass along the head, starting from the upper lip and passing upwards to the whole base of the ears. The bands sometimes extend along the neck and merge with the colour of the upper body. The front parts of the bands are , and widen to in the ear region. A wide, white band extends from the nose tip through the forehead and crown. White markings occur on the lower part of the head, and extend backwards to a great part of the neck's length. The summer fur is much coarser, shorter and sparser, and is deeper in colour, with the black tones becoming brownish, sometimes with yellowish tinges. Partial melanism in badgers is known, and albinos and leucists are not uncommon. Albino badgers can be pure white or yellowish with pink eyes, while leucistic ones are the same but with normal eyes instead.
In winter, the fur on the back and flanks is long and coarse, consisting of bristly guard hairs with a sparse, soft undercoat. The belly fur consists of short, sparse hairs, with skin being visible in the inguinal region. Guard hair length on the middle of the back is in winter. Prior to the winter, the throat, lower neck, chest and legs are black. The belly is of a lighter, brownish tint, while the inguinal region is brownish-grey. The general colour of the back and sides is light silvery-grey, with straw-coloured highlights on the sides. The tail has long and coarse hairs, and is generally the same colour as the back. Two black bands pass along the head, starting from the upper lip and passing upwards to the whole base of the ears. The bands sometimes extend along the neck and merge with the colour of the upper body. The front parts of the bands are , and widen to in the ear region. A wide, white band extends from the nose tip through the forehead and crown. White markings occur on the lower part of the head, and extend backwards to a great part of the neck's length. The summer fur is much coarser, shorter and sparser, and is deeper in colour, with the black tones becoming brownish, sometimes with yellowish tinges. Partial melanism in badgers is known, and albinos and leucists are not uncommon. Albino badgers can be pure white or yellowish with pink eyes, while leucistic ones are the same but with normal eyes instead.

 European badgers are the most social of badgers, forming groups of six adults on average, though larger associations of up to 23 individuals have been recorded. Group size may be related to habitat composition. Under optimal conditions, badger territories can be as small as , but may be as large as in marginal areas. Badger territories can be identified by the presence of communal latrines and well-worn paths. It is mainly males that are involved in territorial aggression. A hierarchical social system is thought to exist among badgers and large powerful boars seem to assert dominance over smaller males. Large boars sometimes intrude into neighboring territories during the main mating season in early spring.
Sparring and more vicious fights generally result from territorial defense in the breeding season. However, in general, animals within and outside a group show considerable tolerance of each other. Boars tend to mark their territories more actively than sows, with their territorial activity increasing during the mating season in early spring. Badgers
European badgers are the most social of badgers, forming groups of six adults on average, though larger associations of up to 23 individuals have been recorded. Group size may be related to habitat composition. Under optimal conditions, badger territories can be as small as , but may be as large as in marginal areas. Badger territories can be identified by the presence of communal latrines and well-worn paths. It is mainly males that are involved in territorial aggression. A hierarchical social system is thought to exist among badgers and large powerful boars seem to assert dominance over smaller males. Large boars sometimes intrude into neighboring territories during the main mating season in early spring.
Sparring and more vicious fights generally result from territorial defense in the breeding season. However, in general, animals within and outside a group show considerable tolerance of each other. Boars tend to mark their territories more actively than sows, with their territorial activity increasing during the mating season in early spring. Badgers
 Like other badger species, European badgers are burrowing animals. However, the dens they construct (called setts) are the most complex, and are passed on from generation to generation. The number of exits in one sett can vary from a few to fifty. These setts can be vast, and can sometimes accommodate multiple families. When this happens, each family occupies its own passages and nesting chambers. Some setts may have exits which are only used in times of danger or play. A typical passage has a wide base and a height. Three sleeping chambers occur in a family unit, some of which are open at both ends. The nesting chamber is located from the opening, and is situated more than a underground, in some cases . Generally, the passages are long. The nesting chamber is on average , and are high.
Badgers dig and collect bedding throughout the year, particularly in autumn and spring. Sett maintenance is usually carried out by subordinate sows and dominant boars. The chambers are frequently lined with bedding, brought in on dry nights, which consists of grass, bracken,
Like other badger species, European badgers are burrowing animals. However, the dens they construct (called setts) are the most complex, and are passed on from generation to generation. The number of exits in one sett can vary from a few to fifty. These setts can be vast, and can sometimes accommodate multiple families. When this happens, each family occupies its own passages and nesting chambers. Some setts may have exits which are only used in times of danger or play. A typical passage has a wide base and a height. Three sleeping chambers occur in a family unit, some of which are open at both ends. The nesting chamber is located from the opening, and is situated more than a underground, in some cases . Generally, the passages are long. The nesting chamber is on average , and are high.
Badgers dig and collect bedding throughout the year, particularly in autumn and spring. Sett maintenance is usually carried out by subordinate sows and dominant boars. The chambers are frequently lined with bedding, brought in on dry nights, which consists of grass, bracken,
 Badgers prey on rabbits throughout the year, especially during times when their young are available. They catch young rabbits by locating their position in their nest by scent, then dig vertically downwards to them. In mountainous or hilly districts, where vegetable food is scarce, badgers rely on rabbits as a principal food source. Adult rabbits are usually avoided, unless they are wounded or caught in traps. They consume them by turning them inside out and eating the meat, leaving the inverted skin uneaten. Hedgehogs are eaten in a similar manner. In areas where badgers are common, hedgehogs are scarce. Some rogue badgers may kill lambs, though this is very rare; they may be erroneously implicated in lamb killings through the presence of discarded wool and bones near their setts, though foxes, which occasionally live alongside badgers, are often the culprits, as badgers do not transport food to their setts. They typically kill lambs by biting them behind the shoulder. Poultry and game birds are also taken only rarely. Some badgers may build their setts in close proximity to poultry or game farms without ever causing damage. In the rare instances in which badgers do kill reared birds, the killings usually occur in February–March, when food is scarce due to harsh weather and increases in badger populations. Badgers can easily breach bee hives with their jaws, and are mostly indifferent to bee stings, even when set upon by swarms.
Badgers prey on rabbits throughout the year, especially during times when their young are available. They catch young rabbits by locating their position in their nest by scent, then dig vertically downwards to them. In mountainous or hilly districts, where vegetable food is scarce, badgers rely on rabbits as a principal food source. Adult rabbits are usually avoided, unless they are wounded or caught in traps. They consume them by turning them inside out and eating the meat, leaving the inverted skin uneaten. Hedgehogs are eaten in a similar manner. In areas where badgers are common, hedgehogs are scarce. Some rogue badgers may kill lambs, though this is very rare; they may be erroneously implicated in lamb killings through the presence of discarded wool and bones near their setts, though foxes, which occasionally live alongside badgers, are often the culprits, as badgers do not transport food to their setts. They typically kill lambs by biting them behind the shoulder. Poultry and game birds are also taken only rarely. Some badgers may build their setts in close proximity to poultry or game farms without ever causing damage. In the rare instances in which badgers do kill reared birds, the killings usually occur in February–March, when food is scarce due to harsh weather and increases in badger populations. Badgers can easily breach bee hives with their jaws, and are mostly indifferent to bee stings, even when set upon by swarms.
 European badgers have few natural enemies. While normally docile, badgers can become extremely aggressive and ferocious when cornered, making it dangerous for predators to target them. Grey wolves (''Canis lupus''), Eurasian lynxes (''Lynx lynx'') and brown bears (''Ursus arctos''), Europe's three largest remaining land predators, and large domestic dogs (''C. familiaris'') can pose a threat to adult badgers, though deaths caused by them are quantitatively rare as these predators are often limited in population due to human persecution and usually prefer easier, larger prey like ungulates, while badgers may fight viciously if aware of a predator and cornered without an escape route.Sidorovich, V. E., Rotenko, I. I., & Krasko, D. A. (2011, March). ''Badger ''Meles meles'' spatial structure and diet in an area of low earthworm biomass and high predation risk''. In Annales Zoologici Fennici (Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 1–16). Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing.Butler, J. M., & Roper, T. J. (1995). ''Escape tactics and alarm responses in badgers Meles meles: a field experiment''. Ethology, 99(4), 313-322. They may live alongside
European badgers have few natural enemies. While normally docile, badgers can become extremely aggressive and ferocious when cornered, making it dangerous for predators to target them. Grey wolves (''Canis lupus''), Eurasian lynxes (''Lynx lynx'') and brown bears (''Ursus arctos''), Europe's three largest remaining land predators, and large domestic dogs (''C. familiaris'') can pose a threat to adult badgers, though deaths caused by them are quantitatively rare as these predators are often limited in population due to human persecution and usually prefer easier, larger prey like ungulates, while badgers may fight viciously if aware of a predator and cornered without an escape route.Sidorovich, V. E., Rotenko, I. I., & Krasko, D. A. (2011, March). ''Badger ''Meles meles'' spatial structure and diet in an area of low earthworm biomass and high predation risk''. In Annales Zoologici Fennici (Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 1–16). Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing.Butler, J. M., & Roper, T. J. (1995). ''Escape tactics and alarm responses in badgers Meles meles: a field experiment''. Ethology, 99(4), 313-322. They may live alongside
 Badgers play a part in European folklore and are featured in modern literature. In Irish mythology, badgers are portrayed as shape-shifters and kinsmen to Tadg, the king of Tara and foster father of Cormac mac Airt. In one story, Tadg berates his adopted son for having killed and prepared some badgers for dinner. In German folklore, the badger is portrayed as a cautious, peace-loving
Badgers play a part in European folklore and are featured in modern literature. In Irish mythology, badgers are portrayed as shape-shifters and kinsmen to Tadg, the king of Tara and foster father of Cormac mac Airt. In one story, Tadg berates his adopted son for having killed and prepared some badgers for dinner. In German folklore, the badger is portrayed as a cautious, peace-loving
 European badger appears on the coat of arms of the municipality of Luhanka in Central Finland, referring to the former importance of the
European badger appears on the coat of arms of the municipality of Luhanka in Central Finland, referring to the former importance of the
 European badgers are of little significance to hunting economies, though they may be actively hunted locally. Methods used for hunting badgers include catching them in jaw traps, ambushing them at their setts with guns, smoking them out of their earths and through the use of specially bred dogs such as Fox Terriers and
European badgers are of little significance to hunting economies, though they may be actively hunted locally. Methods used for hunting badgers include catching them in jaw traps, ambushing them at their setts with guns, smoking them out of their earths and through the use of specially bred dogs such as Fox Terriers and
 There are several accounts of European badgers being tamed. Tame badgers can be affectionate pets, and can be trained to come to their owners when their names are called. They are easily fed, as they are not fussy eaters, and will instinctively unearth rats, moles and young rabbits without training, though they do have a weakness for pork. Although there is one record of a tame badger befriending a fox, they generally do not tolerate the presence of cats and dogs, and will chase them.
There are several accounts of European badgers being tamed. Tame badgers can be affectionate pets, and can be trained to come to their owners when their names are called. They are easily fed, as they are not fussy eaters, and will instinctively unearth rats, moles and young rabbits without training, though they do have a weakness for pork. Although there is one record of a tame badger befriending a fox, they generally do not tolerate the presence of cats and dogs, and will chase them.
 Badger meat is eaten in some districts of the former Soviet Union, though in most cases it is discarded. Smoked hams made from badgers were once highly esteemed in England, Wales and Ireland.
Some badger products have been used for medical purposes; badger expert Ernest Neal, quoting from an 1810 edition of ''
Badger meat is eaten in some districts of the former Soviet Union, though in most cases it is discarded. Smoked hams made from badgers were once highly esteemed in England, Wales and Ireland.
Some badger products have been used for medical purposes; badger expert Ernest Neal, quoting from an 1810 edition of ''
ARKive
Photographs and video
The Badger Trust – representing over 80 British badger groups
Scottish Badgers
Steve Jackson's Badger Pages – Facts about and photos of the badgers of the world
Badgerland – The Definitive On-Line Guide to Badgers (Meles meles) in the UK
Badgerwatcher.com – A guide to watching badgers in the UK
Wildlife Online – Natural History of the European Badger
Lancashire Badger Group
Dublin and Wicklow Badger Group
Science & Nature: Animals
BBC.
Badgers in the Netherlands
Badgergroup Brabant Foundation.
The Census Foundation.
Waarneming.nl
Originally a Dutch site, but you can change language at the top of the page. Sightings, pictures and distribution maps of European badgers in the Netherlands.
Badgers in France
L'assiociation Meles.
A video of an adult european badger. This is a close up video showing their behavior
Video of a European Badger feeding on peanuts by its sett
Video of an evening's badger-watching in mid-Wales, U.K.
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070807063236/http://www.defra.gov.uk/animalh/tb/culling/index.htm The Randomised Badger Culling Trial
Godfray Report, ''Independent Scientific Review of the Randomised Badger Culling Trial and Associated Epidemiological Research'', March 2004. PDF format
National Farmers Union proposals to control badgers (would involve repeal of the 1992 act) July 2005
NFBG (now Badger Trust) response to the National Farmers Union proposals, August 2005
{{Taxonbar, from=Q27066 Mammals described in 1758 Badgers Mammals of Asia Mammals of Azerbaijan Mammals of Europe Mammals of the Middle East Fauna of Turkey Fauna of Syria Fauna of Lebanon Articles containing video clips Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Fauna of Albania
nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
(''M. m. meles'') predominating in most of Europe. In Europe, where no other badger species commonly occurs, it is generally just called the "badger".
The European badger is a powerfully built, black, white, brown, and grey animal with a small head, a stocky body, small, black eyes, and short tail. Its weight varies, being 7–13 kg (15–29 lb) in spring, but building up to 15–17 kg (33–37 lb) in autumn before the winter sleep
Winter rest (from the German term ''Winterruhe'') is a state of reduced activity of plants and warm-blooded animals living in extratropical regions of the world during the more hostile environmental conditions of winter. In this state, they save e ...
period. It is nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
and is a social, burrowing animal that sleeps during the day in one of several setts in its territorial range. These burrows have multiple chambers and entrances, and are extensive systems of underground passages of length. They house several badger families that use these setts for decades. Badgers are fussy over the cleanliness of their burrow, carrying in fresh bedding and removing soiled material, and they defecate in latrines strategically situated outside their setts or en route to other setts.
Although classified as a carnivore, the European badger feeds on a wide variety of plant and animal foods, feeding on earthworms, large insects, small mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
, cereals, and tubers. Litters of up to five cubs are produced in spring. The young are weaned a few months later, but usually remain within the family group. The European badger has been known to share its burrow with other species such as rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit speci ...
s, red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
es, and raccoon dogs, but it can be ferocious when provoked, a trait which has been exploited in the now-illegal blood sport of badger-baiting
Badger-baiting is a form of blood sport in which badgers are baited with dogs. A baiting session typically results in the death of the badger, and possibly serious injuries to the dogs.
Background
The badger is a usually quiet and docile creat ...
. Badgers can be carriers of bovine tuberculosis, which also affects cattle. In England, culling of badger populations is used to attempt to reduce the incidence of bovine tuberculosis in cattle, although the efficacy of this practice is highly disputed, and badger culls are widely considered cruel and inhumane.
Nomenclature
The source of the word "badger" is uncertain. The Oxford English Dictionary states it probably derives from "badge" + ''-ard'', referring to the white mark borne like a badge on its forehead, and may date to the early 16th century. TheFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
word ('digger') has also been suggested as a source. A male badger is a boar, a female is a sow, and a young badger is a cub. A badger's home is called a sett. Badger colonies are often called clans.
The far older name "brock" ( ang, brocc), ( sco, brock) is a Celtic loanword (cf. Gaelic and Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, from Proto-Celtic ) meaning 'grey'. The Proto-Germanic term was (cf. German , Dutch , Norwegian ; Early Modern English ''dasse''), probably from the PIE
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), brown sugar ( sugar pie), swe ...
root 'to construct', so the badger would have been named after its digging of setts (tunnels); the Germanic term became or , in Latin glosses, replacing ('marten
A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus ''Martes'' within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on t ...
' or 'badger'), and from these words the common Romance terms for the animal evolved ( Italian , French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
—now is more common—, Catalan , Spanish , Portuguese ) except Asturian .
Until the mid-18th century, European badgers were variously known in English as brock, pate, grey, and bawson. The name "bawson" is derived from "bawsened", which refers to something striped with white. "Pate" is a local name which was once popular in northern England. The name "badget" was once common, but restricted to Norfolk, while "earth dog" was used in southern Ireland. The badger is commonly referred to in Welsh as a ('earth pig').
Taxonomy
''Ursus meles'' was thescientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
used by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, who described the badger in his work ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
''.
Evolution
The species likely evolved from the Chinese ''Meles thorali'' of the early Pleistocene. The modern species originated during the early Middle Pleistocene, with fossil sites occurring inEpiscopia Episkopi ( el, Επισκοπή), or Latinised forms Episcopia or Piscopia, may refer to the following places:
;Cyprus:
* Episkopi Bay, on the southeast coast
* Episkopi, Limassol, a village on Episkopi Bay
* Episkopi Cantonment, a British militar ...
, Grombasek, Süssenborn, Hundsheim, Erpfingen, Koneprusy, Mosbach
Mosbach (; South Franconian: ''Mossbach'') is a town in the north of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is the seat of the Neckar-Odenwald district and has a population of approximately 25,000 distributed in six boroughs: Mosbach Town, Lohrbach, N ...
2, and Stránská Skála
Stránská skála is a hill and a national nature monument in Brno in the Czech Republic. It refers to a Mid-Pleistocene- Cromerian interglacial most important paleontological site in Central Europe.
Location
Stránská skála is situated in t ...
. A comparison between fossil and living specimens shows a marked progressive adaptation to omnivory, namely in the increase in the molars' surface areas and the modification of the carnassials. Occasionally, badger bones are discovered in earlier strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum ( : strata) is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as ei ...
, due to the burrowing habits of the species.
Subspecies
In the 19th and 20th centuries, several badger type specimens were described and proposed assubspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
. , eight subspecies were recognized as valid
Validity or Valid may refer to:
Science/mathematics/statistics:
* Validity (logic), a property of a logical argument
* Scientific:
** Internal validity, the validity of causal inferences within scientific studies, usually based on experiments
** ...
taxa, but four (''canescens'', ''arcalus'', ''rhodius'', ''severzovi'') are now considered to belong to a distinct species, the Caucasian badger (''M. canescens'').
Description
European badgers are powerfully built animals with small heads, thick, short necks, stocky, wedge-shaped bodies and short tails. Their feet areplantigrade
151px, Portion of a human skeleton, showing plantigrade habit
In terrestrial animals, plantigrade locomotion means walking with the toes and metatarsals flat on the ground. It is one of three forms of locomotion adopted by terrestrial mammals. T ...
or semidigitigrade and short, with five toes on each foot. The limbs are short and massive, with naked lower surfaces on the feet. The claws are strong, elongated and have an obtuse end, which assists in digging. The claws are not retractable, and the hind claws wear with age. Old badgers sometimes have their hind claws almost completely worn away from constant use. Their snouts, which are used for digging and probing, are muscular and flexible. The eyes are small and the ears short and tipped with white. Whiskers are present on the snout and above the eyes.
Boars typically have broader heads, thicker necks and narrower tails than sows, which are sleeker, have narrower, less domed heads and fluffier tails. The guts of badgers are longer than those of red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
es, reflecting their omnivorous diet. The small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
has a mean length of and lacks a cecum. Both sexes have three pairs of nipples but these are more developed in females. European badgers cannot flex their backs as marten
A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus ''Martes'' within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on t ...
s, polecats and wolverines can, nor can they stand fully erect like honey badgers, though they can move quickly at full gallop.
Adults measure in shoulder height, in body length, in tail length, in hind foot length and in ear height. Males (or boars) slightly exceed females (or sows) in measurements, but can weigh considerably more. Their weights vary seasonally, growing from spring to autumn and reaching a peak just before the winter. During the summer, European badgers commonly weigh and in autumn.
The average weight of adults in the Białowieża Forest was in spring but up to in autumn, 46% higher than the spring low mass. In Woodchester Park
Woodchester Mansion is an unfinished, Gothic revival mansion house in Nympsfield, Gloucestershire, England. It is on the site of an earlier house known as Spring Park. The mansion is a Grade I listed building.
The mansion was abandoned by its ...
, England, adults in spring weighed on average and in fall average . In Doñana National Park, average weight of adult badgers is reported as , perhaps in accordance with Bergmann's rule
Bergmann's rule is an ecogeographical rule that states that within a broadly distributed taxonomic clade, populations and species of larger size are found in colder environments, while populations and species of smaller size are found in warmer ...
, that its size decreases in relatively warmer climates. Sows can attain a top autumn weight of around , while exceptionally large boars have been reported in autumn. The heaviest verified was , though unverified specimens have been reported to and even (if so, the heaviest weight for any terrestrial mustelid). If average weights are used, the European badger ranks as the second largest terrestrial mustelid, behind only the wolverine. Although their sense of smell
Smell may refer to;
* Odor, airborne molecules perceived as a scent or aroma
* Sense of smell, the scent also known scientifically as olfaction
* "Smells" (''Bottom''), an episode of ''Bottom''
* The Smell, a music venue in Los Angeles, Californ ...
is acute, their eyesight is monochromatic
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or color scheme, palette is composed of one color (or lightness, values of one color). Images using only Tint, shade and tone, shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or Black and wh ...
as has been shown by their lack of reaction to red lanterns. Only moving objects attract their attention. Their hearing is no better than that of humans.
 European badger skulls are quite massive, heavy and elongated. Their
European badger skulls are quite massive, heavy and elongated. Their braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
s are oval in outline, while the facial part of their skulls is elongated and narrow. Adults have prominent sagittal crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are exceptiona ...
s which can reach 15 mm tall in old males, and are more strongly developed than those of honey badgers. Aside from anchoring the jaw muscles, the thickness of the crests protect their skulls from hard blows. Similar to martens, the dentition of European badgers is well-suited for their omnivorous diets. Their incisors are small and chisel
A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge (such that wood chisels have lent part of their name to a particular grind) of blade on its end, for carving or cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal by hand, stru ...
-shaped, their canine teeth are prominent and their carnassials are not overly specialized. Their molars are flattened and adapted for grinding. Their jaws are powerful enough to crush most bones; a provoked badger was once reported as biting down on a man's wrist so severely that his hand had to be amputated. The dental formula is .
Scent glands are present below the base of the tail and on the anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
. The subcaudal gland secretes a musky-smelling, cream-coloured fatty substance, while the anal glands secrete a stronger-smelling, yellowish-brown fluid.
Fur
Erythristic
Erythrism or erythrochroism refers to an unusual reddish pigmentation of an animal's hair, skin, feathers, or eggshells.
Causes of erythrism include:
* Genetic mutations which cause an absence of a normal pigment and/or excessive production of o ...
badgers are more common than the former, being characterized by having a sandy-red colour on the usually black parts of the body. Yellow badgers are also known.
Distribution and habitat
The European badger is native to most of Europe. Its range includes Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Crete, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Kosovo, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and Ukraine. The distributional boundary between the ranges of European and Asian badgers is the Volga River, the European species being situated on the western bank. The boundary between the ranges of the European and Caucasian badgers is in the North Caucasus, but a clear boundary has not been defined, and they aresympatric
In biology, two related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter one another. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct species sh ...
in some regions, potentially forming a hybrid zone. They are common in European Russia
European Russia (russian: Европейская Россия, russian: европейская часть России, label=none) is the western and most populated part of Russia. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the cou ...
, with 30,000 individuals having been recorded there in 1990. They are abundant and increasing throughout their range, partly due to a reduction in rabies in Central Europe. In the UK, badgers experienced a 77% increase in numbers during the 1980s and 1990s. The badger population in Great Britain in 2012 is estimated to be 300,000.
The European badger is found in deciduous and mixed woodlands, clearings, spinneys, pastureland and scrub, including Mediterranean maquis shrubland
220px, Low maquis in Corsica
220px, High ''macchia'' in Sardinia
( , , ) or ( , ; often in Italian; hr, makija; ; ) is a shrubland biome in the Mediterranean region, typically consisting of densely growing evergreen shrubs.
Maquis is char ...
. It has adapted to life in suburban areas and urban parks, although not to the extent of red foxes. In mountainous areas it occurs up to an altitude of .
Behaviour and ecology
Social and territorial behaviour

groom
A bridegroom (often shortened to groom) is a man who is about to be married or who is newlywed.
When marrying, the bridegroom's future spouse (if female) is usually referred to as the bride. A bridegroom is typically attended by a best man an ...
each other very thoroughly with their claws and teeth. Grooming may have a social function. They are crepuscular
In zoology, a crepuscular animal is one that is active primarily during the twilight period, being matutinal, vespertine, or both. This is distinguished from diurnal and nocturnal behavior, where an animal is active during the hours of daylig ...
and nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
in habits. Aggression among badgers is largely associated with territorial defence and mating. When fighting, they bite each other on the neck and rump, while running and chasing each other and injuries incurred in such fights can be severe and sometimes fatal. When attacked by dogs or sexually excited, badgers may raise their tails and fluff up their fur.
European badgers have an extensive vocal repertoire. When threatened, they emit deep growls and, when fighting, make low kekkering noises. They bark when surprised, whicker when playing or in distress, and emit a piercing scream when alarmed or frightened.König 1973, pp. 162–163
Denning behaviour

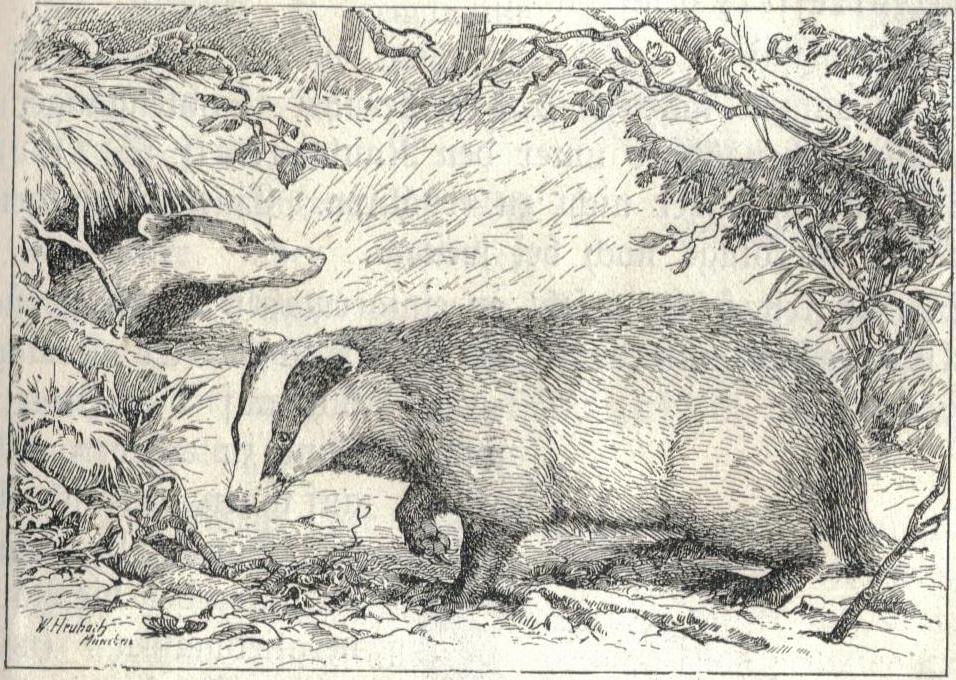
 Like other badger species, European badgers are burrowing animals. However, the dens they construct (called setts) are the most complex, and are passed on from generation to generation. The number of exits in one sett can vary from a few to fifty. These setts can be vast, and can sometimes accommodate multiple families. When this happens, each family occupies its own passages and nesting chambers. Some setts may have exits which are only used in times of danger or play. A typical passage has a wide base and a height. Three sleeping chambers occur in a family unit, some of which are open at both ends. The nesting chamber is located from the opening, and is situated more than a underground, in some cases . Generally, the passages are long. The nesting chamber is on average , and are high.
Badgers dig and collect bedding throughout the year, particularly in autumn and spring. Sett maintenance is usually carried out by subordinate sows and dominant boars. The chambers are frequently lined with bedding, brought in on dry nights, which consists of grass, bracken,
Like other badger species, European badgers are burrowing animals. However, the dens they construct (called setts) are the most complex, and are passed on from generation to generation. The number of exits in one sett can vary from a few to fifty. These setts can be vast, and can sometimes accommodate multiple families. When this happens, each family occupies its own passages and nesting chambers. Some setts may have exits which are only used in times of danger or play. A typical passage has a wide base and a height. Three sleeping chambers occur in a family unit, some of which are open at both ends. The nesting chamber is located from the opening, and is situated more than a underground, in some cases . Generally, the passages are long. The nesting chamber is on average , and are high.
Badgers dig and collect bedding throughout the year, particularly in autumn and spring. Sett maintenance is usually carried out by subordinate sows and dominant boars. The chambers are frequently lined with bedding, brought in on dry nights, which consists of grass, bracken, straw
Straw is an agricultural byproduct consisting of the dry stalks of cereal plants after the grain and chaff have been removed. It makes up about half of the yield of cereal crops such as barley, oats, rice, rye and wheat. It has a number ...
, leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
and moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
. Up to 30 bundles can be carried to the sett on a single night. European badgers are fastidiously clean animals which regularly clear out and discard old bedding. During the winter, they may take their bedding outside on sunny mornings and retrieve it later in the day. Spring cleaning
Spring cleaning is the practice of thoroughly cleaning a house in the springtime. The practice of spring cleaning is especially prevalent in climates with a cold winter. In many cultures, annual cleaning occurs at the end of the year, which may b ...
is connected with the birth of cubs, and may occur several times during the summer to prevent parasite levels building up.
If a badger dies within the sett, its conspecifics will seal off the chamber and dig a new one. Some badgers will drag their dead out of the sett and bury them outside. A sett is almost invariably located near a tree, which is used by badgers for stretching or claw scraping. Badgers defecate in latrines, which are located near the sett and at strategic locations on territorial boundaries or near places with abundant food supplies.
In extreme cases, when there is a lack of suitable burrowing grounds, badgers may move into haystacks in winter. They may share their setts with red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
es or European rabbits. The badgers may provide protection for the rabbits against other predators. The rabbits usually avoid predation by the badgers by inhabiting smaller, hard to reach chambers.
Reproduction and development
Estrus in European badgers lasts four to six days and may occur throughout the year, though there is a peak in spring. Sexual maturity in boars is usually attained at the age of twelve to fifteen months but this can range from nine months to two years. Males are normally fecund during January–May, withspermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubule ...
declining in summer. Sows usually begin ovulating in their second year, though some exceptionally begin at nine months. They can mate at any time of the year, though the main peak occurs in February–May, when mature sows are in postpartal estrus and young animals experience their first estrus. Matings occurring outside this period typically occur in sows which either failed to mate earlier in the year or matured slowly. Badgers are usually monogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a form of Dyad (sociology), dyadic Intimate relationship, relationship in which an individual has only one Significant other, partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time (Monogamy#Serial monogamy, ...
; boars typically mate with one female for life, whereas sows have been known to mate with more than one male. Mating lasts for fifteen to sixty minutes, though the pair may briefly copulate for a minute or two when the sow is not in estrus. A delay of two to nine months precedes the fertilized eggs implanting into the wall of the uterus, though matings in December can result in immediate implantation. Ordinarily, implantation happens in December, with a gestation period
In mammals, pregnancy is the period of reproduction during which a female carries one or more live offspring from implantation in the uterus through gestation. It begins when a fertilized zygote implants in the female's uterus, and ends once it ...
lasting seven weeks. Cubs are usually born in mid-January to mid-March within underground chambers containing bedding. In areas where the countryside is waterlogged, cubs may be born above ground in buildings. Typically, only dominant sows can breed, as they suppress the reproduction of subordinate females.
The average litter consists of one to five cubs. Although many cubs are sired by resident males, up to 54% can be fathered by boars from different colonies. Dominant sows may kill the cubs of subordinates. Cubs are born pink, with greyish, silvery fur and fused eyelids. Neonatal badgers are in body length on average and weigh , with cubs from large litters being smaller. By three to five days, their claws become pigmented, and individual dark hairs begin to appear. Their eyes open at four to five weeks and their milk teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 255 are the first set of teeth in th ...
erupt about the same time. They emerge from their setts at eight weeks of age, and begin to be weaned at twelve weeks, though they may still suckle until they are four to five months old. Subordinate females assist the mother in guarding, feeding and grooming the cubs. Cubs fully develop their adult coats at six to nine weeks. In areas with medium to high badger populations, dispersal from the natal group is uncommon, though badgers may temporarily visit other colonies. Badgers can live for up to about fifteen years in the wild.
Winter sleep
Badgers begin to prepare forwinter sleep
Winter rest (from the German term ''Winterruhe'') is a state of reduced activity of plants and warm-blooded animals living in extratropical regions of the world during the more hostile environmental conditions of winter. In this state, they save e ...
during late summer by accumulating fat reserves, which reach a peak in October. During this period, the sett is cleaned and the nesting chamber is filled with bedding. Upon retiring to sleep, badgers block their sett entrances with dry leaves and earth. They typically stop leaving their setts once snow has fallen. In Russia and the Nordic countries, European badgers retire for winter sleep from late October to mid-November and emerge from their setts in March and early April. In areas such as England and Transcaucasia, where winters are less harsh, badgers either forgo winter sleep entirely or spend long periods underground, emerging in mild spells.
Diet
European badgers are among the least carnivorous members of theCarnivora
Carnivora is a Clade, monophyletic order of Placentalia, placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all felidae, cat-like and canidae, dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are f ...
; they are highly adaptable and opportunistic omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutr ...
s, whose diet encompasses a wide range of animals and plants. Earthworms are their most important food source, followed by large insects, carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
, cereals, fruit and small mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, including rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit speci ...
s, mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
s, voles, shrews, moles and hedgehogs. Insect prey includes chafers, dung
Dung most often refers to animal feces. Dung may also refer to:
Science and technology
* Dry animal dung fuel
* Manure
* Cow dung
* Coprolite, fossilized feces
* Dung beetle
Art
* Mundungus Fletcher or "Dung", a character in the Harry Potter n ...
and ground beetles, caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
s, leatherjackets, and the nests of wasps and bumblebees. They are able to destroy wasp nests, consuming the occupants, combs, and envelope, such as that of ''Vespula rufa
''Vespula rufa'', commonly known as the red wasp,Archer, M. E. (2001). Vespula rufa (Linnaeus,1758). Retrieved from: http://www.bwars.com/index.php?q=wasp/vespidae/vespinae/vespula-rufa is a social wasp species belonging to the genus ''Vespula''. ...
'' nests, since their thick skin and body hair protect the badgers from stings.Edwards, Robin. (1980). Social Wasps: Their Biology and Control. W. Sussex, Great Britain: Rentokil Limited. Cereal food includes wheat, oats, maize and occasionally barley. Fruits include windfall apples, pears, plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
s, blackberries, bilberries, raspberries, cherries
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The nam ...
, strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
, acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and borne ...
s, beechmast
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
, pignuts and wild arum corms.
Occasionally, they feed on medium to large birds, amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, fish, small reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s including tortoises and lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia alt ...
s, snails, slug
Slug, or land slug, is a common name for any apparently shell-less terrestrial gastropod mollusc. The word ''slug'' is also often used as part of the common name of any gastropod mollusc that has no shell, a very reduced shell, or only a smal ...
s, fungi, tubers and green food such as clover and grass, particularly in winter and during droughts. Badgers characteristically capture large numbers of one food type in each hunt. Generally, they do not eat more than of food per day, with young specimens yet to attain one year of age eating more than adults. An adult badger weighing eats a quantity of food equal to 3.4% of its body weight. Badgers typically eat prey on the spot, and rarely transport it to their setts. Surplus killing has been observed in chicken coops.
 Badgers prey on rabbits throughout the year, especially during times when their young are available. They catch young rabbits by locating their position in their nest by scent, then dig vertically downwards to them. In mountainous or hilly districts, where vegetable food is scarce, badgers rely on rabbits as a principal food source. Adult rabbits are usually avoided, unless they are wounded or caught in traps. They consume them by turning them inside out and eating the meat, leaving the inverted skin uneaten. Hedgehogs are eaten in a similar manner. In areas where badgers are common, hedgehogs are scarce. Some rogue badgers may kill lambs, though this is very rare; they may be erroneously implicated in lamb killings through the presence of discarded wool and bones near their setts, though foxes, which occasionally live alongside badgers, are often the culprits, as badgers do not transport food to their setts. They typically kill lambs by biting them behind the shoulder. Poultry and game birds are also taken only rarely. Some badgers may build their setts in close proximity to poultry or game farms without ever causing damage. In the rare instances in which badgers do kill reared birds, the killings usually occur in February–March, when food is scarce due to harsh weather and increases in badger populations. Badgers can easily breach bee hives with their jaws, and are mostly indifferent to bee stings, even when set upon by swarms.
Badgers prey on rabbits throughout the year, especially during times when their young are available. They catch young rabbits by locating their position in their nest by scent, then dig vertically downwards to them. In mountainous or hilly districts, where vegetable food is scarce, badgers rely on rabbits as a principal food source. Adult rabbits are usually avoided, unless they are wounded or caught in traps. They consume them by turning them inside out and eating the meat, leaving the inverted skin uneaten. Hedgehogs are eaten in a similar manner. In areas where badgers are common, hedgehogs are scarce. Some rogue badgers may kill lambs, though this is very rare; they may be erroneously implicated in lamb killings through the presence of discarded wool and bones near their setts, though foxes, which occasionally live alongside badgers, are often the culprits, as badgers do not transport food to their setts. They typically kill lambs by biting them behind the shoulder. Poultry and game birds are also taken only rarely. Some badgers may build their setts in close proximity to poultry or game farms without ever causing damage. In the rare instances in which badgers do kill reared birds, the killings usually occur in February–March, when food is scarce due to harsh weather and increases in badger populations. Badgers can easily breach bee hives with their jaws, and are mostly indifferent to bee stings, even when set upon by swarms.
Relationships with other non-human predators
 European badgers have few natural enemies. While normally docile, badgers can become extremely aggressive and ferocious when cornered, making it dangerous for predators to target them. Grey wolves (''Canis lupus''), Eurasian lynxes (''Lynx lynx'') and brown bears (''Ursus arctos''), Europe's three largest remaining land predators, and large domestic dogs (''C. familiaris'') can pose a threat to adult badgers, though deaths caused by them are quantitatively rare as these predators are often limited in population due to human persecution and usually prefer easier, larger prey like ungulates, while badgers may fight viciously if aware of a predator and cornered without an escape route.Sidorovich, V. E., Rotenko, I. I., & Krasko, D. A. (2011, March). ''Badger ''Meles meles'' spatial structure and diet in an area of low earthworm biomass and high predation risk''. In Annales Zoologici Fennici (Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 1–16). Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing.Butler, J. M., & Roper, T. J. (1995). ''Escape tactics and alarm responses in badgers Meles meles: a field experiment''. Ethology, 99(4), 313-322. They may live alongside
European badgers have few natural enemies. While normally docile, badgers can become extremely aggressive and ferocious when cornered, making it dangerous for predators to target them. Grey wolves (''Canis lupus''), Eurasian lynxes (''Lynx lynx'') and brown bears (''Ursus arctos''), Europe's three largest remaining land predators, and large domestic dogs (''C. familiaris'') can pose a threat to adult badgers, though deaths caused by them are quantitatively rare as these predators are often limited in population due to human persecution and usually prefer easier, larger prey like ungulates, while badgers may fight viciously if aware of a predator and cornered without an escape route.Sidorovich, V. E., Rotenko, I. I., & Krasko, D. A. (2011, March). ''Badger ''Meles meles'' spatial structure and diet in an area of low earthworm biomass and high predation risk''. In Annales Zoologici Fennici (Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 1–16). Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing.Butler, J. M., & Roper, T. J. (1995). ''Escape tactics and alarm responses in badgers Meles meles: a field experiment''. Ethology, 99(4), 313-322. They may live alongside red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
es (''Vulpes vulpes'') in isolated sections of large burrows. The two species possibly tolerate each other out of commensalism; foxes provide badgers with food scraps, while badgers maintain the shared burrow's cleanliness. However, cases are known of badgers driving vixens from their dens and destroying their litters without eating them. In turn, red foxes are known to have killed badger cubs in spring. Golden eagles (''Aquila chrysaetos'') are known predators of European badgers and attacks by them on badger cubs are not infrequent, including cases where they have been pulled out directly from below the legs of their mothers, and even adult badgers may be attacked by this eagle species when emerging weak and hungry from hibernation.Watson, J. (2010). ''The golden eagle''. Poyser Monographs; A&C Black. Eurasian eagle owls (''Bubo bubo'') may also take an occasional cub and other large raptors such as white-tailed eagles (''Haliaeetus albicilla'') and greater spotted eagle (''Clanga clanga'') are considered potential badger cub predators. Raccoon dogs may extensively use badger setts for shelter. There are many known cases of badgers and raccoon dogs wintering in the same hole, possibly because badgers enter hibernation two weeks earlier than the latter, and leave two weeks later. In exceptional cases, badger and raccoon dog cubs may coexist in the same burrow. Badgers may drive out or kill raccoon dogs if they overstay their welcome.
Diseases and parasites
Bovine tuberculosis (bovine TB) caused by '' Mycobacterium bovis'' is a major mortality factor in badgers, though infected badgers can live and successfully breed for years before succumbing. The disease was first observed in badgers in 1951 in Switzerland where they were believed to have contracted it fromchamois
The chamois (''Rupicapra rupicapra'') or Alpine chamois is a species of goat-antelope native to mountains in Europe, from west to east, including the Alps, the Dinarides, the Tatra and the Carpathian Mountains, the Balkan Mountains, the Ril ...
(''Rupicapra rupicapra'') or roe deer (''Capreolus capreolus''). It was detected in the United Kingdom in 1971 where it was linked to an outbreak of bovine TB in cows. The evidence appears to indicate that the badger is the primary reservoir of infection for cattle in the southwest of England, Wales and Ireland. Since then there has been considerable controversy as to whether culling badgers will effectively reduce or eliminate bovine TB in cattle.
Badgers are vulnerable to the mustelid herpesvirus-1, as well as rabies and canine distemper, though the latter two are absent in Great Britain. Other diseases found in European badgers include arteriosclerosis, pneumonia, pleurisy, nephritis
Nephritis is inflammation of the kidneys and may involve the glomeruli, tubules, or interstitial tissue surrounding the glomeruli and tubules. It is one of several different types of nephropathy.
Types
* Glomerulonephritis is inflammation of th ...
, enteritis, polyarthritis and lymphosarcoma.
Internal parasites of badgers include trematodes, nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
s and several species of tapeworm. Ectoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s carried by them include the fleas ''Paraceras melis
''Paraceras melis'', the badger flea, is an external parasite of the European badger (''Meles meles''). It has also been found on the fox (''Vulpes vulpes''), the dog (''Canis familiaris''), the cat (''Felis catus''), the European polecat (''Must ...
'' (the badger flea), '' Chaetopsylla trichosa'' and '' Pulex irritans'' (the human flea), the lice
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result o ...
'' Trichodectes melis'' and the ticks '' Ixodes ricinus'', '' I. canisuga'', '' I. hexagonus'', '' I. reduvius'' and '' I. melicula''. They also suffer from mange. They spend much time grooming, individuals concentrating on their own ventral areas, alternating one side with the other, while social grooming occurs with one individual grooming another on its dorsal surface. Fleas tried to avoid the scratching, retreating rapidly downwards and backwards through the fur. This was in contrast to fleas away from their host, which ran upwards and jumped when disturbed. The grooming seems to disadvantage fleas rather than merely having a social function.
Conservation
The International Union for Conservation of Nature rates the European badger as being of least concern. This is because it is a relatively common species with a wide range and populations are generally stable. In Central Europe it has become more abundant in recent decades due to a reduction in the incidence of rabies. In other areas it has also fared well, with increases in numbers in Western Europe and the United Kingdom. However, in some areas of intensive agriculture it has reduced in numbers due to loss of habitat and in others it is hunted as a pest.Cultural significance
 Badgers play a part in European folklore and are featured in modern literature. In Irish mythology, badgers are portrayed as shape-shifters and kinsmen to Tadg, the king of Tara and foster father of Cormac mac Airt. In one story, Tadg berates his adopted son for having killed and prepared some badgers for dinner. In German folklore, the badger is portrayed as a cautious, peace-loving
Badgers play a part in European folklore and are featured in modern literature. In Irish mythology, badgers are portrayed as shape-shifters and kinsmen to Tadg, the king of Tara and foster father of Cormac mac Airt. In one story, Tadg berates his adopted son for having killed and prepared some badgers for dinner. In German folklore, the badger is portrayed as a cautious, peace-loving Philistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
, who loves more than anything his home, family and comfort, though he can become aggressive if surprised. He is a cousin of Reynard the Fox, whom he uselessly tries to convince to return to the path of righteousness.
In Kenneth Grahame's '' The Wind in the Willows'', Mr. Badger is depicted as a gruff, solitary figure who "simply hates society", yet is a good friend to Mole and Ratty. As a friend of Toad's now-deceased father, he is often firm and serious with Toad, but at the same time generally patient and well-meaning towards him. He can be seen as a wise hermit, a good leader and gentleman, embodying common sense. He is also brave and a skilled fighter, and helps rid Toad Hall of invaders from the wild wood.
The "Frances" series of children's books by Russell
Russell may refer to:
People
* Russell (given name)
* Russell (surname)
* Lady Russell (disambiguation)
* Lord Russell (disambiguation)
Places Australia
*Russell, Australian Capital Territory
*Russell Island, Queensland (disambiguation)
**Ru ...
and Lillian Hoban depicts an anthropomorphic
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology.
Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics t ...
badger family.
In T. H. White
Terence Hanbury "Tim" White (29 May 1906 – 17 January 1964) was an English writer best known for his Arthurian novels, published together in 1958 as ''The Once and Future King''. One of his most memorable is the first of the series, '' The Sw ...
's Arthurian series '' The Once and Future King'', the young King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a ...
is transformed into a badger by Merlin
Merlin ( cy, Myrddin, kw, Marzhin, br, Merzhin) is a mythical figure prominently featured in the legend of King Arthur and best known as a mage, with several other main roles. His usual depiction, based on an amalgamation of historic and le ...
as part of his education. He meets with an older badger who tells him "I can only teach you two things – to dig, and love your home."
A villainous badger named Tommy Brock appears in Beatrix Potter's 1912 book '' The Tale of Mr. Tod''. He is shown kidnapping the children of Benjamin Bunny and his wife Flopsy, and hiding them in an oven at the home of Mr. Tod the fox, whom he fights at the end of the book. The portrayal of the badger as a filthy animal which appropriates fox dens was criticized from a naturalistic viewpoint, though the inconsistencies are few and employed to create individual characters rather than evoke an archetypical fox and badger. A wise old badger named Trufflehunter
This is a list of characters in the series of fantasy novels by C. S. Lewis called ''The Chronicles of Narnia''. See also a list of portrayals.
A
*Ahoshta: a 60-year-old Tarkaan of Calormen who later becomes the Grand Vizier, chief adviser to ...
appears in C. S. Lewis' '' Prince Caspian'', where he aids Caspian X in his struggle against King Miraz.
A badger takes a prominent role in Colin Dann's '' The Animals of Farthing Wood'' series as second in command to Fox. The badger is also the house symbol for Hufflepuff in the ''Harry Potter
''Harry Potter'' is a series of seven fantasy literature, fantasy novels written by British author J. K. Rowling. The novels chronicle the lives of a young Magician (fantasy), wizard, Harry Potter (character), Harry Potter, and his friends ...
'' book series. The '' Redwall'' series also has the Badger Lords, who rule the extinct volcano fortress of Salamandastron and are renowned as fierce warriors. The children's television series '' Bodger & Badger'' was popular on CBBC during the 1990s and was set around the mishaps of a mashed potato-loving badger and his human companion.
An unnamed badger is part of Bosnian Serb writer Petar Kočić's satirical play ''Badger on Tribunal
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae (which also includes the otters, wolverines, martens, minks, polecats, weasels, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by ...
'' in which local farmer David Štrbac attempts to sue a badger for eating his crops. It is actually highly critical towards Austro-Hungarian rule in Bosnia and Herzegovina at the beginning of the 20th century. In honor of Kočić and his Badger, satirical theater in Banja Luka is named Jazavac (Badger).
Heraldry
fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
in the locality. The badger is also the title animal of the Nurmijärvi municipality in Uusimaa, Finland, where it is a very common mammal.
Hunting
 European badgers are of little significance to hunting economies, though they may be actively hunted locally. Methods used for hunting badgers include catching them in jaw traps, ambushing them at their setts with guns, smoking them out of their earths and through the use of specially bred dogs such as Fox Terriers and
European badgers are of little significance to hunting economies, though they may be actively hunted locally. Methods used for hunting badgers include catching them in jaw traps, ambushing them at their setts with guns, smoking them out of their earths and through the use of specially bred dogs such as Fox Terriers and Dachshund
The dachshund ( or ; German: "badger dog"), also known as the wiener dog, badger dog, and sausage dog, is a short-legged, long-bodied, hound-type dog breed. The dog may be smooth-haired, wire-haired, or long-haired, and comes in a variety of c ...
s to dig them out. Badgers are, however, notoriously durable animals; their skins are thick, loose and covered in long hair which acts as protection, and their heavily ossified skulls allow them to shrug off most blunt trauma
Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical traumas, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue ...
s, as well as shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which usually discharges numerous small p ...
pellets.
Badger-baiting
Badger-baiting was once a popular blood sport, in which badgers were captured alive, placed in boxes, and attacked with dogs. In the UK, this was outlawed by the Cruelty to Animals Act of 1835 and again by the Protection of Animals Act of 1911. Moreover, the cruelty towards and killing of the badger constitute offences under the Protection of Badgers Act 1992, and further offences under this act are inevitably committed to facilitate badger-baiting (such as interfering with a sett, or the taking or the very possession of a badger for purposes other than nursing an injured animal to health). If convicted, badger-baiters may face a sentence of up to six months in jail, a fine of up to £5,000, and other punitive measures, such as community service or a ban from owning dogs.Culling
Many badgers in Europe were gassed during the 1960s and 1970s to control rabies. Until the 1980s, badger culling in the United Kingdom was undertaken in the form of gassing, to control the spread of bovine tuberculosis (bTB). Limited culling resumed in 1998 as part of a 10-year randomized trial cull which was considered byJohn Krebs
John Richard Krebs, Baron Krebs, Kt FRS (born 11 April 1945) is an English zoologist researching in the field of behavioural ecology of birds. He was the principal of Jesus College, Oxford, from 2005 until 2015."Elliott Coues Award, 1999: ...
and others to show that culling was ineffective. Some groups called for a selective cull, while others favoured a programme of vaccination, and vets support the cull on compassionate grounds as they say that the illness causes much suffering in badgers. In 2012, the government authorized a limited cull led by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
The Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for environmental protection, food production and standards, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in the United K ...
(Defra), however, this was later deferred with a wide range of reasons given. In August 2013, a full culling programme began where about 5,000 badgers were killed over six weeks in West Somerset and Gloucestershire by marksmen with high-velocity rifles using a mixture of controlled shooting and free shooting (some badgers were trapped in cages first). The cull caused many protests with emotional, economic and scientific reasons being cited. The badger is considered an iconic species of the British countryside, though is not endangered. It was claimed by shadow ministers that "The government's own figures show it will cost more than it saves...", and Lord Krebs, who led the Randomised Badger Culling Trial in the 1990s, said the two pilots "will not yield any useful information". A scientific study of culling from 2013 to 2017 has shown a reduction of 36–55% incidence of bovine tuberculosis in cattle.
Tameability

 There are several accounts of European badgers being tamed. Tame badgers can be affectionate pets, and can be trained to come to their owners when their names are called. They are easily fed, as they are not fussy eaters, and will instinctively unearth rats, moles and young rabbits without training, though they do have a weakness for pork. Although there is one record of a tame badger befriending a fox, they generally do not tolerate the presence of cats and dogs, and will chase them.
There are several accounts of European badgers being tamed. Tame badgers can be affectionate pets, and can be trained to come to their owners when their names are called. They are easily fed, as they are not fussy eaters, and will instinctively unearth rats, moles and young rabbits without training, though they do have a weakness for pork. Although there is one record of a tame badger befriending a fox, they generally do not tolerate the presence of cats and dogs, and will chase them.
Uses
 Badger meat is eaten in some districts of the former Soviet Union, though in most cases it is discarded. Smoked hams made from badgers were once highly esteemed in England, Wales and Ireland.
Some badger products have been used for medical purposes; badger expert Ernest Neal, quoting from an 1810 edition of ''
Badger meat is eaten in some districts of the former Soviet Union, though in most cases it is discarded. Smoked hams made from badgers were once highly esteemed in England, Wales and Ireland.
Some badger products have been used for medical purposes; badger expert Ernest Neal, quoting from an 1810 edition of ''The Sporting Magazine
''The Sporting Magazine'' (1793–1870) was the first English sporting periodical to devote itself to every type of sport.
Its subtitle was "Monthly Calendar of the Transactions of the Turf, the Chase and Every Other Diversion Interesting to the ...
'', wrote;
The flesh, blood and grease of the badger are very useful for oils, ointments, salves and powders, for shortness of breath, the cough of the lungs, for the stone, sprained sinews, collachs etc. The skin being well dressed is very warm and comfortable for ancient people who are troubled with paralytic disorders.The hair of the European badger has been used for centuries for making
sporran
The sporran (; Scottish Gaelic and Irish for " purse"), a traditional part of male Scottish Highland dress, is a pouch that performs the same function as pockets on the pocketless kilt. Made of leather or fur, the ornamentation of the sporran is ...
s and shaving brushes. Sporrans are traditionally worn as part of male Scottish highland dress. They form a bag or pocket made from a pelt and a badger or other animal's mask may be used as a flap. The pelt was also formerly used for pistol furniture
A pistol is a handgun, more specifically one with the chamber integral to its gun barrel, though in common usage the two terms are often used interchangeably. The English word was introduced in , when early handguns were produced in Europe, an ...
.
References
* * * * * * * * * *External links
ARKive
Photographs and video
The Badger Trust – representing over 80 British badger groups
Scottish Badgers
Steve Jackson's Badger Pages – Facts about and photos of the badgers of the world
Badgerland – The Definitive On-Line Guide to Badgers (Meles meles) in the UK
Badgerwatcher.com – A guide to watching badgers in the UK
Wildlife Online – Natural History of the European Badger
Lancashire Badger Group
Dublin and Wicklow Badger Group
Science & Nature: Animals
BBC.
Badgers in the Netherlands
Badgergroup Brabant Foundation.
The Census Foundation.
Waarneming.nl
Originally a Dutch site, but you can change language at the top of the page. Sightings, pictures and distribution maps of European badgers in the Netherlands.
Badgers in France
L'assiociation Meles.
A video of an adult european badger. This is a close up video showing their behavior
Video of a European Badger feeding on peanuts by its sett
Video of an evening's badger-watching in mid-Wales, U.K.
Badgers and TB in the UK
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070807063236/http://www.defra.gov.uk/animalh/tb/culling/index.htm The Randomised Badger Culling Trial
Godfray Report, ''Independent Scientific Review of the Randomised Badger Culling Trial and Associated Epidemiological Research'', March 2004. PDF format
National Farmers Union proposals to control badgers (would involve repeal of the 1992 act) July 2005
NFBG (now Badger Trust) response to the National Farmers Union proposals, August 2005
Claims of continued badger-hunting in the UK
* Allegations of lamping (among other practices) were made in the appendix to th{{Taxonbar, from=Q27066 Mammals described in 1758 Badgers Mammals of Asia Mammals of Azerbaijan Mammals of Europe Mammals of the Middle East Fauna of Turkey Fauna of Syria Fauna of Lebanon Articles containing video clips Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Fauna of Albania