Ethiopian–Egyptian War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ethiopian–Egyptian War was a war between the
p.14
/ref> The result of the war had a defining impact on the trajectories of both African states. Prior to the conflict, Egypt had been in regional and, relative, international ascendancy, with aspirations of achieving geopolitical parity with the Great Powers of Europe. The defeat shattered these aspirations, and, combined with a disastrous economic situation in Egypt itself, contributed to the eventual deposition of Isma'il and subjugation of Egypt by the Great Powers, thereby leading to the very outcome which Isma'il's hopes for a pan-Nile Valley empire were meant to avoid. Conversely, Ethiopia maintained its independence, and, hardened by war, was well prepared for its own defense during the imminent Scramble for Africa. The collapse of Egypt's African empire was seized upon by European empires, of whom Italy replaced Egypt in Eritrea, setting the stage for an eventual confrontation between Italy and Ethiopia in the
A Confederate Soldier in Egypt
* Moslem Egypt and Christian Abyssinia: William Dye (Eyewitness account from another General
* ttps://www.jstor.org/stable/718057?seq=1#metadata_info_tab_contents 'Egypt's Invasion of Ethiopia' ''African Affairs'' (1959), Czeslow Jesman {{DEFAULTSORT:Ethiopian-Egyptian War Military history of Egypt Military history of Ethiopia Wars involving Egypt Wars involving Ethiopia 1874 in Africa 1875 in Africa 1876 in Africa Egypt–Ethiopia relations Conflicts in 1874 Conflicts in 1875 Conflicts in 1876
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historical ...
and the Khedivate of Egypt
The Khedivate of Egypt ( or , ; ota, خدیویت مصر ') was an autonomous tributary state of the Ottoman Empire, established and ruled by the Muhammad Ali Dynasty following the defeat and expulsion of Napoleon Bonaparte's forces which br ...
, a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire, from 1874 to 1876. It remains the only war between Egypt and Ethiopia in modern times. The conflict resulted in an unequivocal Ethiopian victory that guaranteed continued independence of Ethiopia in the years immediately preceding the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonization of most of Africa by seven Western European powers during a short period known as New Imperialism ( ...
. Conversely, for Egypt the war was a costly failure, severely blunting the regional aspirations of Egypt as an African empire, and laying the foundations for the beginning of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
's 'veiled protectorate' over Egypt less than a decade later.
Background
Whilst nominally a vassal state of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
had acted as a virtually independent state since Muhammad Ali's seizure of power in 1805, eventually establishing an empire to its south in Sudan. Muhammad Ali's grandson, Isma'il Pasha
Isma'il Pasha ( ar, إسماعيل باشا ; 12 January 1830 – 2 March 1895), was the Khedive of Egypt and conqueror of Sudan from 1863 to 1879, when he was removed at the behest of Great Britain. Sharing the ambitious outlook of his gran ...
, became Khedive
Khedive (, ota, خدیو, hıdiv; ar, خديوي, khudaywī) was an honorific title of Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.Adam Mestyan" ...
in 1863, and sought to expand this burgeoning empire further southwards.
After annexing Darfur in 1875, he turned his attention to Ethiopia. It was Isma'il's intention that Egypt forge a contiguous African empire that would both rival the empires of Europe, and allow Egypt to escape the territorial ambitions of those same European great powers. In addition to expanding into modern-day Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Repub ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Re ...
, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
, and Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The south ...
, he wished to absorb within his empire the entirety of the Nile Valley
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ri ...
, including Ethiopia, the source of the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile (; ) is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the water ...
. Whilst Ethiopia's history mirrored that of Egypt in many respects, with both having ancient, continuous civilizations home to both Muslims and Orthodox Christians, the rapid modernization of Egypt under Muhammad Ali, and Isma'il's own enormous modernizing projects, convinced the Khedive that war with Ethiopia would result in certain Egyptian victory. Amongst Egypt's army were many European and American officers, whose training and experience further strengthened Isma'il's confidence.
Meanwhile, King Yohannes IV
''girmāwī''His Imperial Majesty, spoken= am , ጃንሆይ ''djānhoi''Your Imperial Majesty(lit. "O steemedroyal"), alternative= am , ጌቶቹ ''getochu''Our Lord (familiar)(lit. "Our master" (pl.)) yohanes
Yohannes IV ( Tigrinya: ዮሓ� ...
became the King of kings of Ethiopia in 1872 after defeating Tekle Giyorgis II
Tekle Giyorgis II ( Ge’ez: ተክለ ጊዮርጊስ, born Wagshum Gobeze (Amharic: ዋግሹም ጎበዜ), died 1873) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1868 to 1871.
Genealogy
Emperor Tekle Giorgis II based his claim to the Imperial throne on a ...
in battle. He worked on modernizing his army, some of whom were trained by the British adventurer John Kirkham.
The Battle of Gundet
The Egyptians under Arakil Bey and Danish Colonel Adolph Ahrendrup invaded from their coastal possessions in Massawa, in what is now Eritrea. Following some skirmishes, the armies of Yohannes and Isma'il met at Gundet on the morning of 16 November 1875. Not only were the Egyptians vastly outnumbered, they were also taken completely by surprise as they were marching through a narrow mountain pass. The mass of Ethiopian warriors sallied forth from their hiding places up the slope and swiftly charged down upon the shocked Egyptian columns, nullifying the latter's advantage in firepower and causing many of the unenthusiastic fellahin soldiers to rout. This encounter ended in the complete annihilation of the Egyptian expeditionary force led by Colonel Arrendrup and in the death of its commander. Arrendrup's expedition was hopelessly inadequate for the tasks he set out to do. It amounted to scarcely more than some 4,000 troops and had no cavalry. Its leaders were, apart from the already mentioned Danish artilleryman and Major Dennison, an American, Major Durholtz, a Swiss, late of the Papal army, and Major Rushdi Bey, a Turk. Arakal Bey, the young nephew of Nubar Pasha (the Christian Armenian Premier of the Khedive) joined the expedition and was killed in battle. About 2,000 Egyptians perished with him and his two six gun batteries and six rocket-stands fell into the hands of the enemy. The Egyptians withdrew to Massawa on the coast and then to Keren, garrisoned since 1872 by some 1,200 Egyptians. ButIsma'il Pasha
Isma'il Pasha ( ar, إسماعيل باشا ; 12 January 1830 – 2 March 1895), was the Khedive of Egypt and conqueror of Sudan from 1863 to 1879, when he was removed at the behest of Great Britain. Sharing the ambitious outlook of his gran ...
could not leave the matter there, it was absolutely essential to regain the lost prestige. At all costs, his European creditors had to be impressed, and he set out on mobilizing a larger force for a second expedition that would make amends for the devastating and humiliating loss he had suffered at the hands of the Ethiopians at Gundet.
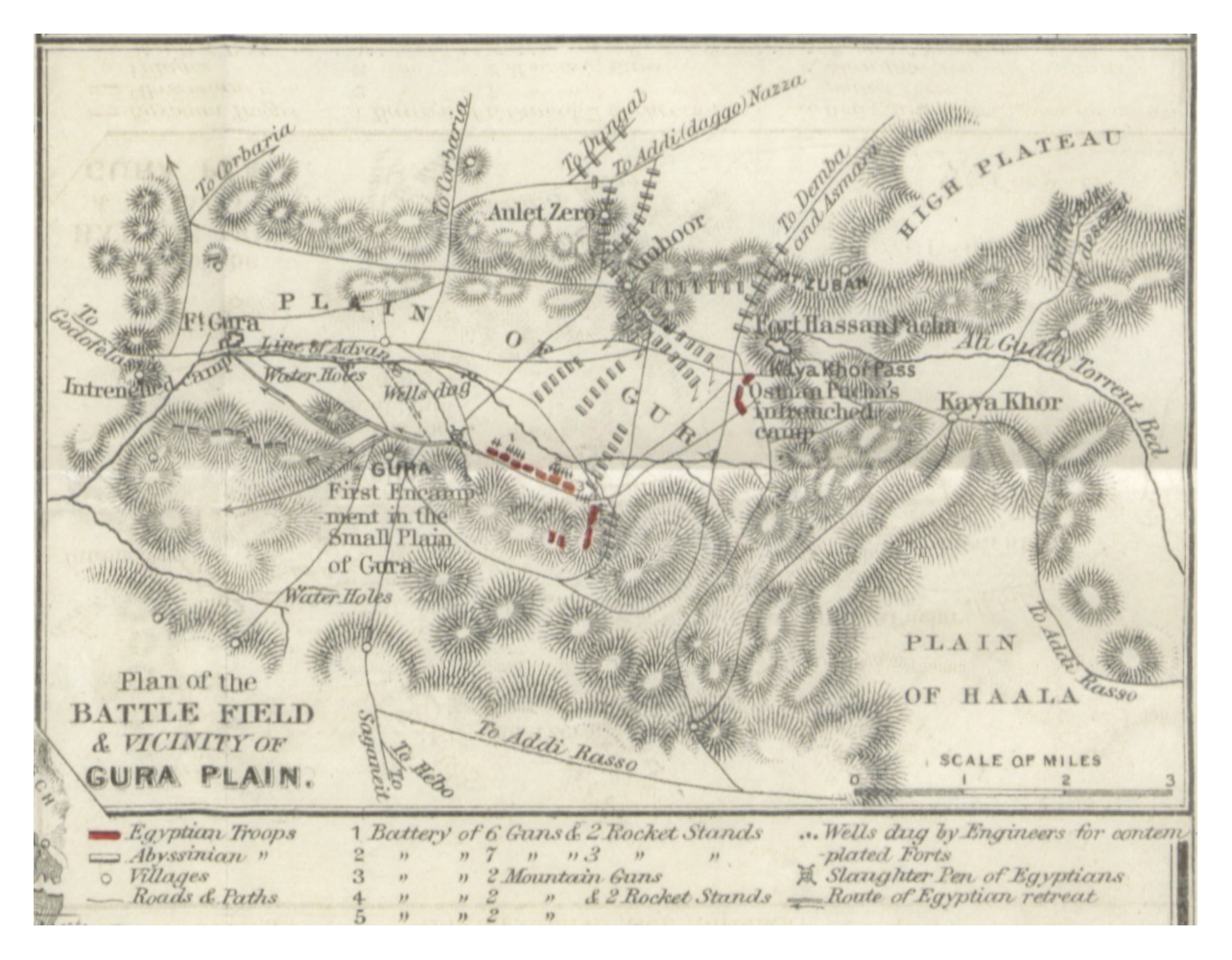
The Battle of Gura
Following the botched invasion, the Egyptians again attempted conquest of Ethiopia, this time with an army of about 13,000 men. The forces of Isma'il Pasha, now under Ratib Pasha, arrived atMassawa
Massawa ( ; ti, ምጽዋዕ, məṣṣəwaʿ; gez, ምጽዋ; ar, مصوع; it, Massaua; pt, Maçuá) is a port city in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea, located on the Red Sea at the northern end of the Gulf of Zula beside the Dahl ...
on 14 December 1875. By March, they had reached the plain of Gura and set up two forts, one in the Plains of Gura and the other at the Khaya Khor mountain pass a few kilometers away. Yohannes, had responded by issuing a call to arms to defend Christian Ethiopia against the Muslim invader. With the exception of Shewa
Shewa ( am, ሸዋ; , om, Shawaa), formerly romanized as Shua, Shoa, Showa, Shuwa (''Scioà'' in Italian), is a historical region of Ethiopia which was formerly an autonomous kingdom within the Ethiopian Empire. The modern Ethiopian capital Add ...
province, all of Ethiopia had responded. The Ethiopians, now with a force of some 50,000 (of whom only about 15,000 could fight at one time due to battlefield layout), engaged them on the 7 March 1875, and Ratib Pasha ordered just over 5,000 out of 7,500 men stationed at Fort Gura to leave the fort and engage the Ethiopians. This force was quickly surrounded by the Ethiopian advance guard, probably commanded by Ras Alula
Ras Alula Engida ( gez, ራስ አሉላ እንግዳ) (1827 – 15 February 1897; also known by his horse name Abba Nega and by Alula Qubi) was an Ethiopian general and politician who successfully led Abyssinian battles against Ottoman Egypt, ...
, and quickly broke. The Ethiopians then fell back, and, on the 10th of March, mounted a secondary attack on Fort Gura, which was repelled. The Ethiopian force dissolved the next day, and the devastated Egyptians soon withdrew.

European involvement
Several foreigners were involved in the war. These include aBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English ...
adventurer John Kirkham on the Ethiopian side, and the Dane Adolph Arendrup
Adolf (also spelt Adolph or Adolphe, Adolfo and when Latinisation (literature), Latinised Adolphus) is a given name used in German language, German-speaking countries, Scandinavia, the Netherlands and Flanders, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, L ...
( da) as well as Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
*Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internati ...
explorer Werner Munzinger on the Egyptian side. Munzinger led one of the Egyptian attacks against Ethiopia, marching inland from Tadjoura
Tadjoura ( aa, Tagórri; ar, تاجوراء ''Tağūrah''; so, Tajuura) is one of the oldest towns in Djibouti and the capital of the Tadjourah Region. The town evolved into an early Islamic center with the arrival of Muslims shortly after th ...
, but his troops were overwhelmed by the army of Muhammad ibn Hanfadhe, Sultan of Aussa, and he was killed in battle.Edward Ullendorff, ''The Ethiopians: An Introduction to Country and People'', second edition (London: Oxford University Press, 1965), p. 90. .
American involvement
Several ex- Confederate officers and Union officers who had both previously fought in theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
participated in the conflict. The Egyptian Khedive
Khedive (, ota, خدیو, hıdiv; ar, خديوي, khudaywī) was an honorific title of Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.Adam Mestyan" ...
was introduced to the idea of hiring American officers to reorganize his army when he met Thaddeus Mott, an ex-Union artillery officer and adventurer, in the sultan’s court in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
in 1868. Mott regaled Ismail with testimonies about the advances the Americans had achieved in technology and tactics during the US Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states t ...
that he convinced the Khedive to hire American veterans to oversee the modernization of Egypt’s armed forces. In 1870, the first of these military overseers, ex-Confederate officers Henry Hopkins Sibley and William Wing Loring
William Wing Loring (December 4, 1818 – December 30, 1886) was an American soldier who served in the armies of the United States, the Confederacy, and Egypt.
Biography
Early life
William was born in Wilmington, North Carolina, to Reuben an ...
, arrived in Egypt. Loring was appointed by the Khedive as Inspector-General of the Egyptian army, and in 1875 was promoted to chief of staff to the commander-in-chief of the Egyptian military expedition in Ethiopia. Loring would take part in the Battle of Gura
The Battle of Gura was fought on 7–10 March 1876 between the Ethiopian Empire and the Khedivate of Egypt near the town of Gura in Eritrea. It was the second and decisive major battle of the Ethiopian–Egyptian War.
Background
The Egyptian ar ...
which ended in defeat. The Egyptians blamed the Americans for the disastrous war, and the Loring, Sibley and the other officers had to endure two years of endless frustration and humiliation in Cairo.
Aftermath
Following the war, Ethiopia and Egypt remained in a state of tension, which largely abated after the 1884Hewett Treaty
The Hewett Treaty, also called the Treaty of Adwa, was an agreement between Britain, Egypt and Ethiopia signed at Adwa on 3 June 1884. The treaty ended a long-simmering conflict between Egypt and Ethiopia, but indirectly started a new conflict betw ...
.
Ras Alula had shown himself to be a reliable general, and was promoted by Yohannes IV to the rank of ''Ras'', and appointed governor of the Mareb Malash.
The Egyptian defeat in the war had serious ramifications for Egypt. The war's costs added to the nation's massive financial debts, which, in 1879, were the cause of Isma'il's removal as Khedive at the insistence of Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
.
At the same time, many Egyptian soldiers who had served in the war became politicized by their experiences, posing a threat to the Egyptian monarchy itself. Among these disgruntled army officers was Colonel Ahmed Orabi
Ahmad ( ar, أحمد, ʾAḥmad) is an Arabic male given name common in most parts of the Muslim world. Other spellings of the name include Ahmed and Ahmet.
Etymology
The word derives from the root (ḥ-m-d), from the Arabic (), from the v ...
, who is said to have been "incensed at the way in which he warhad been mismanaged". Resentment over the defeat contributed to the general dissatisfaction with Tewfik Pasha
Mohamed Tewfik Pasha ( ar, محمد توفيق باشا ''Muḥammad Tawfīq Bāshā''; April 30 or 15 November 1852 – 7 January 1892), also known as Tawfiq of Egypt, was khedive of Egypt and the Sudan between 1879 and 1892 and the sixth rul ...
, whom the Great Powers selected as Isma'il's successor, provoking the Orabi Revolt Orabi is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Ahmed ‘Urabi ("Orabi" in Egyptian Arabic; 1841–1911), Egyptian rebel and patriot
* Ibrahim Orabi (born 1912), Egyptian sport wrestler
* Mohamed Orabi (born 1951), Egyptian diplomat a ...
against the monarchy. The initial success of the revolt was met with alarm in Europe, and led ultimately to the United Kingdom dispatching its forces to occupy Egypt in support of Tewfik, thereby beginning the United Kingdom's occupation of Egypt.Wilfrid Scawen Blunt, ''Secret History of the English Occupation of Egypt'' (A.A. Knopf, 1922)p.14
/ref> The result of the war had a defining impact on the trajectories of both African states. Prior to the conflict, Egypt had been in regional and, relative, international ascendancy, with aspirations of achieving geopolitical parity with the Great Powers of Europe. The defeat shattered these aspirations, and, combined with a disastrous economic situation in Egypt itself, contributed to the eventual deposition of Isma'il and subjugation of Egypt by the Great Powers, thereby leading to the very outcome which Isma'il's hopes for a pan-Nile Valley empire were meant to avoid. Conversely, Ethiopia maintained its independence, and, hardened by war, was well prepared for its own defense during the imminent Scramble for Africa. The collapse of Egypt's African empire was seized upon by European empires, of whom Italy replaced Egypt in Eritrea, setting the stage for an eventual confrontation between Italy and Ethiopia in the
First Italo-Ethiopian War
The First Italo-Ethiopian War, lit. ''Abyssinian War'' was fought between Italy and Ethiopia from 1895 to 1896. It originated from the disputed Treaty of Wuchale, which the Italians claimed turned Ethiopia into an Italian protectorate. Full-s ...
1895. Ethiopia's triumph in that war would in turn contribute to Fascist Italy
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the ...
's desire to conquer Ethiopia in the 1930s.
See also
*British Expedition to Abyssinia
The British Expedition to Abyssinia was a rescue mission and punitive expedition carried out in 1868 by the armed forces of the British Empire against the Ethiopian Empire (also known at the time as Abyssinia). Emperor Tewodros II of Ethiopia, ...
* First Italo-Ethiopian War
The First Italo-Ethiopian War, lit. ''Abyssinian War'' was fought between Italy and Ethiopia from 1895 to 1896. It originated from the disputed Treaty of Wuchale, which the Italians claimed turned Ethiopia into an Italian protectorate. Full-s ...
* Battle of Adwa
The Battle of Adwa (; ti, ውግእ ዓድዋ; , also spelled ''Adowa'') was the climactic battle of the First Italo-Ethiopian War. The Ethiopian forces defeated the Italian invading force on Sunday 1 March 1896, near the town of Adwa. The d ...
* Second Italo-Ethiopian War
The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression which was fought between Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy and Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethio ...
* Military history of Ethiopia
*
The military history of Ethiopia dates back to the foundation of early Ethiopian Kingdoms in 980 BC. Ethiopia has been involved many of the major conflicts in the horn of Africa, and was one of the few native African nations which remained ind ...
* Battle of Gura
The Battle of Gura was fought on 7–10 March 1876 between the Ethiopian Empire and the Khedivate of Egypt near the town of Gura in Eritrea. It was the second and decisive major battle of the Ethiopian–Egyptian War.
Background
The Egyptian ar ...
References
Further reading
* A Confederate Soldier in Egypt: William Loring (Eyewitness account Egyptian General in the WarA Confederate Soldier in Egypt
* Moslem Egypt and Christian Abyssinia: William Dye (Eyewitness account from another General
* ttps://www.jstor.org/stable/718057?seq=1#metadata_info_tab_contents 'Egypt's Invasion of Ethiopia' ''African Affairs'' (1959), Czeslow Jesman {{DEFAULTSORT:Ethiopian-Egyptian War Military history of Egypt Military history of Ethiopia Wars involving Egypt Wars involving Ethiopia 1874 in Africa 1875 in Africa 1876 in Africa Egypt–Ethiopia relations Conflicts in 1874 Conflicts in 1875 Conflicts in 1876